当前位置:网站首页>Understanding of out covariance, in inversion and invariance in kotlin
Understanding of out covariance, in inversion and invariance in kotlin
2022-07-07 08:14:00 【yu-Knight】
java in ? extends T amount to kotlin Medium out String yes CharSequence Subclasses of List<CharSequence> list = new ArrayList<CharSequence>(); List<? extends CharSequence> list2 = new ArrayList<String>(); // out T Generic concrete subclass objects can be assigned to the parent object at the generic declaration ------------------------------------------------------------- java in ? super T amount to kotlin Medium in List<? super String> list3 = new ArrayList<CharSequence>(); The parent object of the generic concrete , Cannot be assigned to Subclasses at the generic declaration
// producer out T Covariance [out T This generic type can be obtained Read So it is out]
interface Producer<out T> {
// out T Represents the whole production class This T Can only be read , Do not modify
// Cannot be modified ( Compile not pass )
// fun consumer(item: T)
// Can only be read
fun producer(): T
}
// consumer in T Inversion [in T This generic can only be modified to update So it is in]
interface Consumer<in T> {
// in T Represents the whole consumer category This T Can only be modified , Cannot read
// Can only be modified
fun consumer(item: T)
// Can't be read
// fun producer():T
}
// producers and consumers T By default , unchanged
interface ProducerAndConsumer<T> {
// Can be modified
fun consumer(item: T)
// Can be read
fun producer(): T
}
open class Animal // animal
open class Humanity : Animal() // human beings
open class Man : Humanity()// Man
open class WoMan : Humanity()// A woman
class ProducerClass1 : Producer<Animal> {
override fun producer(): Animal {
println(" producer Animal")
return Animal()
}
}
class ProducerClass2 : Producer<Humanity> {
override fun producer(): Humanity {
println(" producer Humanity")
return Humanity()
}
}
class ProducerClass3 : Producer<Man> {
override fun producer(): Man {
println(" producer Man")
return Man()
}
}
class ProducerClass4 : Producer<WoMan> {
override fun producer(): WoMan {
println(" producer WoMan")
return WoMan()
}
}
/******************************************************/
class ConsumerClass1:Consumer<Animal>{
override fun consumer(item: Animal) {
println(" consumer Animal")
}
}
class ConsumerClass2:Consumer<Humanity>{
override fun consumer(item: Humanity) {
println(" consumer Humanity")
}
}
class ConsumerClass3:Consumer<Man>{
override fun consumer(item: Man) {
println(" consumer Man")
}
}
class ConsumerClass4:Consumer<WoMan>{
override fun consumer(item: WoMan) {
println(" consumer WoMan")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val p1: Producer<Animal> = ProducerClass1()//ProducerClass1 It's delivery Animal
val p2: Producer<Animal> = ProducerClass2()//ProducerClass2 It was originally a transmission Humanity Yes out Modifiers can be turned into parent classes
val p3: Producer<Animal> = ProducerClass3()//ProducerClass3 It was originally a transmission Man Yes out Modifiers can be turned into parent classes
val p4: Producer<Animal> = ProducerClass4()//ProducerClass4 It was originally a transmission WoMan Yes out Modifiers can be turned into parent classes
// By default, generics are : Subclass objects of generics , Cannot assign to a generic parent object
// By default, generics are : Subclass objects in the specific place of the generic , Cannot assign to the parent object at the generic declaration
//out: Subclass objects of generics Can be assigned to generic parent objects
//out: Generic concrete subclass objects can be assigned to the parent object at the generic declaration
// Covariance : Parent class Generic declaration Office You can receive Subclass generic concrete object
/*********************************************/
val c1:Consumer<Man> = ConsumerClass1()//ConsumerClass Originally, it was Animal, Yes in Modification can be converted into subclasses
val c2:Consumer<WoMan> = ConsumerClass1()//ConsumerClass Originally, it was Animal, Yes in Modification can be converted into subclasses
// By default : The parent object of the generic concrete , Cannot be assigned to Subclasses at the generic declaration
//in: The parent class of the generic concrete , Is a subclass that can be assigned to a generic declaration
//---------------------------------------------//
// Covariance : out Parent class = Subclass
// Inversion : in Subclass = Parent class
}边栏推荐
- Recursive method to construct binary tree from preorder and inorder traversal sequence
- Openjudge noi 2.1 1752: chicken and rabbit in the same cage
- Niu Mei's mathematical problem --- combinatorial number
- 【數字IC驗證快速入門】15、SystemVerilog學習之基本語法2(操作符、類型轉換、循環、Task/Function...內含實踐練習)
- Summary of redis functions
- uniapp 移动端强制更新功能
- 使用 Nocalhost 开发 Rainbond 上的微服务应用
- 【无标题】
- buureservewp(2)
- 藏书馆App基于Rainbond实现云原生DevOps的实践
猜你喜欢
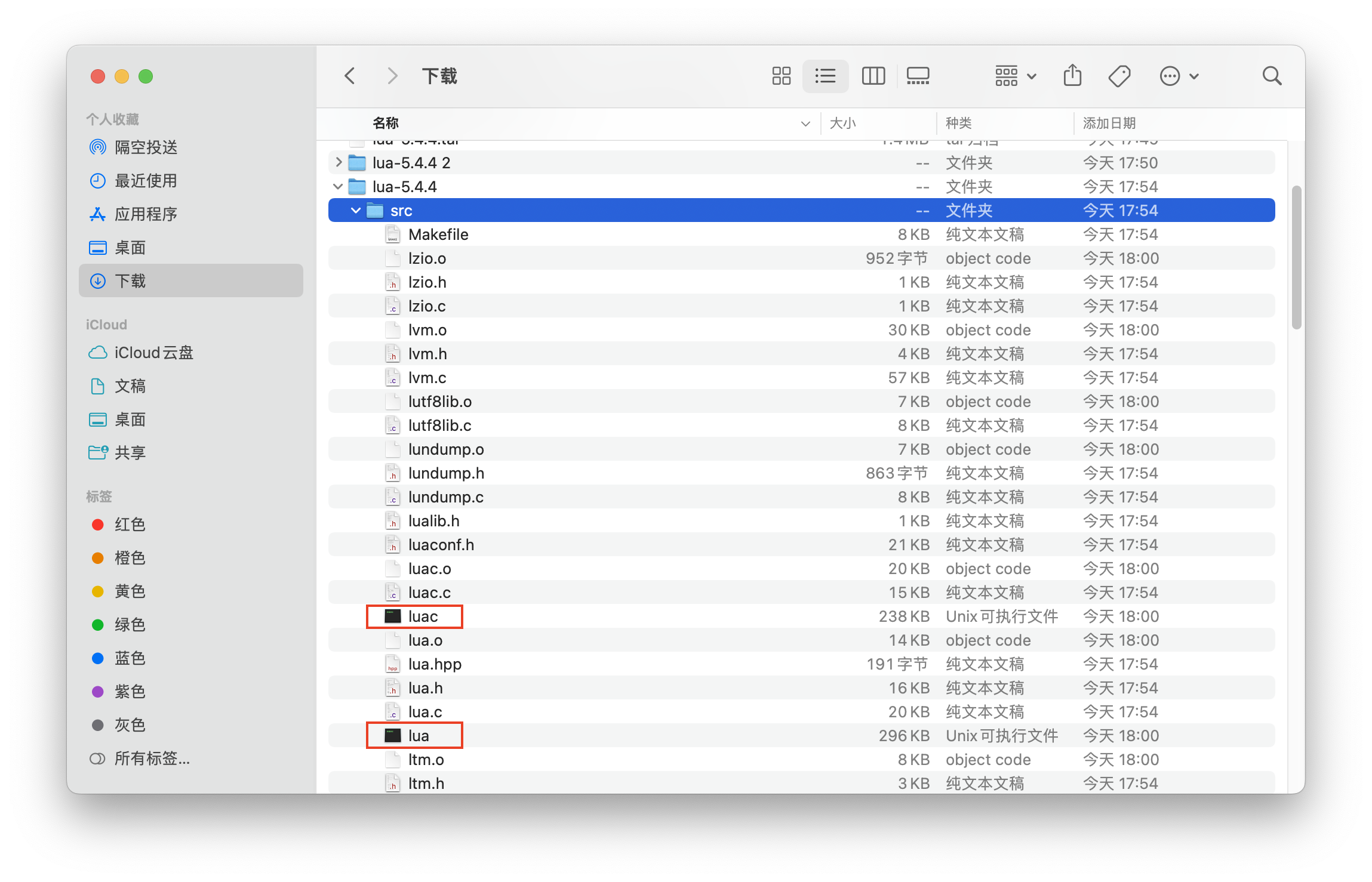
Lua 编程学习笔记

Fast parsing intranet penetration escorts the document encryption industry

CCTV is so warm-hearted that it teaches you to write HR's favorite resume hand in hand
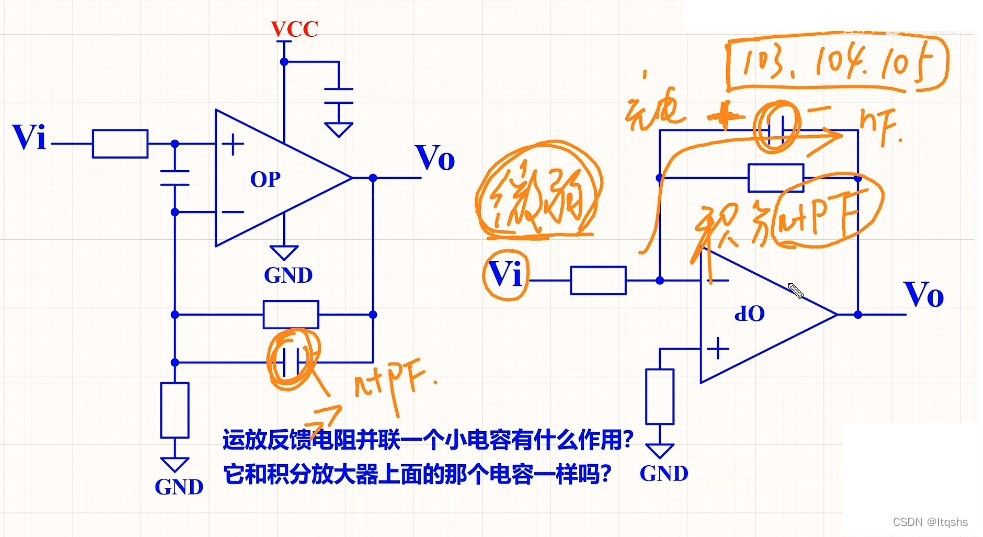
运放电路的反馈电阻上并联一个电容是什么作用
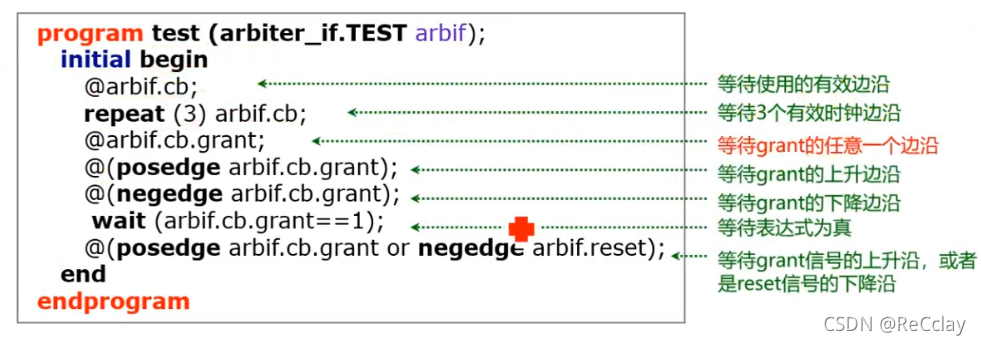
【数字IC验证快速入门】13、SystemVerilog interface 和 program 学习
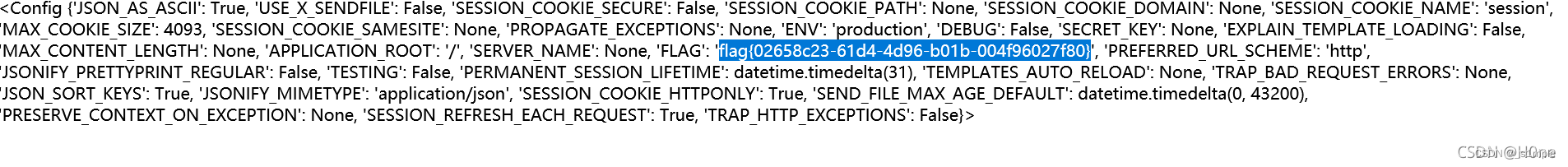
CTF-WEB shrine模板注入nmap的基本使用
Complex network modeling (I)

Don't stop chasing the wind and the moon. Spring mountain is at the end of Pingwu

解析机器人科技发展观对社会研究论
Network learning (II) -- Introduction to socket
随机推荐
【数字IC验证快速入门】10、Verilog RTL设计必会的FIFO
eBPF Cilium实战(1) - 基于团队的网络隔离
It's too true. There's a reason why I haven't been rich
【无标题】
The element with setfieldsvalue set is obtained as undefined with GetFieldValue
解析创新教育体系中的创客教育
Qinglong panel - today's headlines
[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 15. Basic syntax of SystemVerilog learning 2 (operators, type conversion, loops, task/function... Including practical exercises)
[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 11. Introduction to Verilog testbench (VTB)
It took "7" years to build the robot framework into a micro service
复杂网络建模(一)
【Go ~ 0到1 】 第七天 获取时间戳,时间比较,时间格式转换,Sleep与定时器
Interactive book delivery - signed version of Oracle DBA work notes
拓维信息使用 Rainbond 的云原生落地实践
Uniapp mobile terminal forced update function
LeetCode简单题之判断一个数的数字计数是否等于数位的值
Es FAQ summary
Game attack and defense world reverse
柯基数据通过Rainbond完成云原生改造,实现离线持续交付客户
Avatary's livedriver trial experience