当前位置:网站首页>Introduction of common API for socket programming and code implementation of socket, select, poll, epoll high concurrency server model
Introduction of common API for socket programming and code implementation of socket, select, poll, epoll high concurrency server model
2022-07-07 18:12:00 【cheems~】
socket Common use of programming api Introduction and socket、select、poll、epoll High concurrency server model code implementation
Preface
This article aims to learn socket The content of network programming ,epoll It's the top priority , Follow up articles are written reactor The model is based on epoll Above .
The knowledge points of this column are through Zero sound education Online learning , Make a summary and write an article , Yes c/c++linux Readers interested in the course , You can click on the link C/C++ Background advanced server course introduction Check the service of the course in detail .
socket Programming
socket Introduce
Traditional interprocess communication is provided by the kernel IPC The mechanism goes on , But it can only be limited to local communication , To communicate across machines , You must use network communication ( Essentially, with the help of the kernel - The kernel provides socket The mechanism of pseudo file realizes communication ---- It's actually using file descriptors ), This requires the kernel to provide users socket API function library .
Use socket Will create a socket pair, Here's the picture , One file descriptor operates on two buffers .
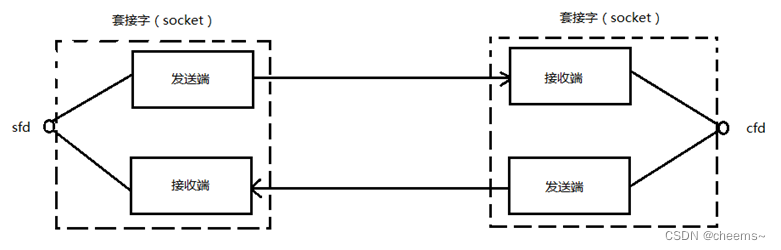
Use socket Of API Function to write server and client programs
Preliminary knowledge
Network byte order
Network byte order : The concept of big end and small end
- Big end : The low address stores the high data , The upper address stores the lower data
- The small end : Low order address stores low order data , The high-order address stores high-order data
Use occasions of big end and small end : In the network, we often need to consider the big end and the small end IP And port . The network transmission uses the big end , Computers use small terminals , So you need to convert the size end
below 4 The first function is the function that performs the size end conversion , Function name h Represents the host host, n The Internet network, s Express short, l Express long.
#include <arpa/inet.h>
uint32_t htonl(uint32_t hostlong);
uint16_t htons(uint16_t hostshort);
uint32_t ntohl(uint32_t netlong);
uint16_t ntohs(uint16_t netshort);
The above functions , If you don't need to convert originally, there will be no conversion inside the function .
IP Address translation function
IP Address translation function
int inet_pton(int af, const char *src, void *dst);
- p-> String form representing dotted decimal
- to-> To
- n-> Express network The Internet
Function description : Divide dots in string form into decimal IP Network converted to big end mode IP( plastic 4 Number of bytes )
Parameter description :
- af: AF_INET
- src: Dotted decimal in string form IP Address
- dst: The address of the converted variable
- for example
inet_pton(AF_INET, "127.0.0.1", &serv.sin_addr.s_addr);
It can also be calculated manually : Such as 192.168.232.145, First the 4 Positive numbers are converted into 16 Hexadecimal number ,
192—>0xC0 168—>0xA8 232—>0xE8 145—>0x91
Finally, it is stored in big end byte order : 0x91E8A8C0, This is 4 Integer value of bytes .
const char *inet_ntop(int af, const void *src, char *dst, socklen_t size);
Function description : The Internet IP Convert to dotted decimal in string form IP
Parameter description :
- af: AF_INET
- src: The shaping of the network IP Address
- dst: Converted IP Address , Generally, it is a string array
- size: dst The length of
Return value :
- success – Return execution dst The pointer to
- Failure – return NULL, And set up errno
for example : IP The address is 010aa8c0, Convert to dotted decimal format :
01---->1 0a---->10 a8---->168 c0---->192
Because from the network IP The address is high-end mode , So it should be : 192.168.10.1
struct sockaddr
socket Important structures used in programming :struct sockaddr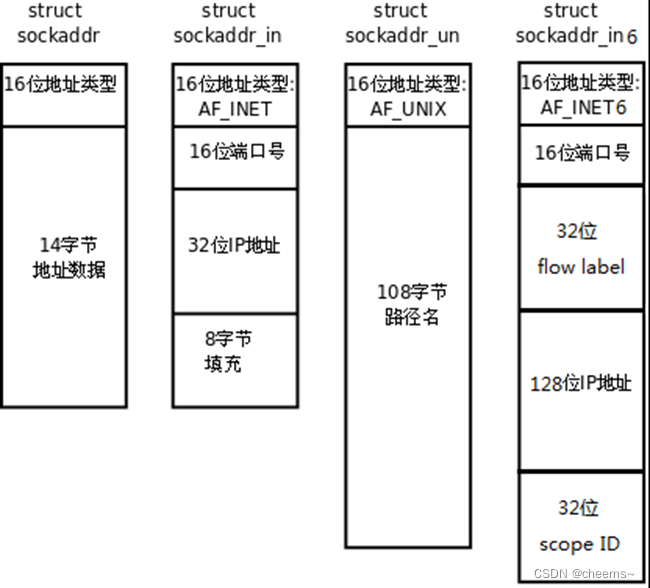
//struct sockaddr Structure description :
struct sockaddr {
sa_family_t sa_family;
char sa_data[14];
}
//struct sockaddr_in structure :
struct sockaddr_in {
sa_family_t sin_family; /* address family: AF_INET */
in_port_t sin_port; /* port in network byte order */
struct in_addr sin_addr; /* internet address */
};
/* Internet address. */
struct in_addr {
uint32_t s_addr; /* address in network byte order */
}; // Network byte order IP-- Big end model
adopt man 7 ip You can view the relevant instructions
The main API Function introduction
socket
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
Function description : establish socket
Parameter description :
- domain: Protocol version
- - AF_INET IPV4
- - AF_INET6 IPV6
- - AF_UNIX AF_LOCAL Local socket use
- type: Protocol type
- - SOCK_STREAM streaming , The default protocol is TCP agreement
- - SOCK_DGRAM The news , The default is UDP agreement
- protocal:
- - General filling 0, Indicates that the default protocol of the corresponding type is used .
- Return value :
- - success : Return a greater than 0 File descriptor for
- - Failure : return -1, And set up errno
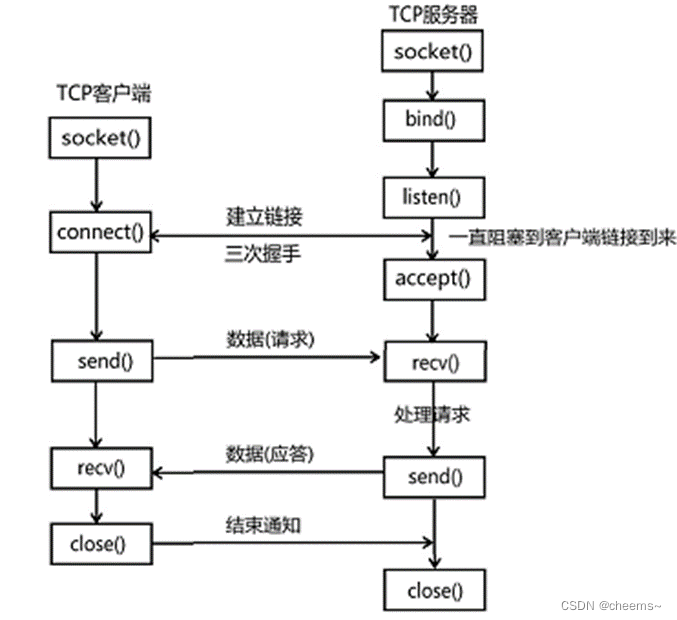
When calling socket After the function , Returns a file descriptor , The kernel will provide read and write buffers corresponding to the file descriptor , There are also two queues , They are the request connection queue and the connected queue ( Listen for file descriptors ,listenFd)
bind
int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
Function description : take socket File descriptors and IP,PORT binding
Parameter description :
- socket: call socket The file descriptor returned by the function
- addr: Local server IP Address and PORT,
struct sockaddr_in serv;
serv.sin_family = AF_INET;
serv.sin_port = htons(8888);
//serv.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
//INADDR_ANY: Indicates the use of any valid available IP
inet_pton(AF_INET, "127.0.0.1", &serv.sin_addr.s_addr);
- addrlen: addr Memory size occupied by variables
Return value :
- success : return 0
- Failure : return -1, And set up errno
listen
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);
Function description : Change the socket from active to passive
Parameter description :
- sockfd: call socket The file descriptor returned by the function
- backlog: stay linux In the system , Here represents the full connection queue ( Queue connected ) The number of . stay unix System type , Here represents the full connection queue ( Queue connected )+ Semi connected queues ( Request connection queue ) Total of
Return value :
- success : return 0
- Failure : return -1, And set up errno
accept
int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
Function description : Get a connection , If there is no connection at present, it will block waiting .
Function parameter :
- sockfd: call socket The file descriptor returned by the function
- addr: Out parameter , Save the address information of the client
- addrlen: Incoming and outgoing parameters , addr The amount of memory space occupied by variables
Return value :
- success : Returns a new file descriptor , For communicating with clients
- Failure : return -1, And set up errno value .
accept Function is a blocking function , If there is no new connection request , It's blocking all the time .
Get a new connection from the connected queue , And get a new file descriptor , This file descriptor is used to communicate with the client . ( The kernel will be responsible for bringing the connections in the request queue to the connected queue )
connect
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
Function description : Connect to server
Function parameter :
- sockfd: call socket The file descriptor returned by the function
- addr: Address information of the server
- addrlen: addr Variable memory size
Return value :
- success : return 0
- Failure : return -1, And set up errno value
Read and send data
You can use write and read Function to read and write . Besides using read/write Function , You can also use recv and send function .
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
ssize_t recv(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len, int flags);
ssize_t send(int sockfd, const void *buf, size_t len, int flags);
// Corresponding recv and send These two functions flags Directly fill in 0 That's all right.
Be careful : If the write buffer is full , write It will also block , read When reading operations , If there is no data in the read buffer, it will cause blocking .
High concurrency server model -select
select Introduce
multiple IO technology : select, Listen for multiple file descriptors at the same time , Leave the monitored operations to the kernel to handle
int select(int nfds, fd_set * readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
data type fd_set:: File descriptor set —— The essence is bitmap
Function introduction : Delegate the kernel to monitor the read corresponding to the file descriptor , Write or the occurrence of error events
Parameter description :
- nfds: The largest file descriptor +1
- readfds: Read the set , Is an incoming and outgoing parameter
Pass in : It refers to telling the kernel which file descriptors need to be monitored
Efferent : It means that the kernel tells the application which file descriptors have changed
- writefds: Write file descriptor set ( Incoming and outgoing parameters , ditto )
- execptfds: Exception file descriptor collection ( Incoming and outgoing parameters , ditto )
- timeout:
NULL-- It means permanent blocking , Until something happens
0 -- Indicates no blocking , Go back to , Whether or not there is a monitored event
>0 -- Return to the specified event or when an event occurs
- Return value : The number of changed file descriptors is returned successfully . Failure to return -1, And set up errno value .
select-api
take fd from set Clear from set
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set);
Function description : Judge fd Is in collection
Return value : If fd stay set Collection , return 1, Otherwise return to 0
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set);
take fd Set to set Collection
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set);
initialization set aggregate
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set);
use select Function is actually entrusting the kernel to help us detect which file descriptors have readable data , Can write , Error occurred
int select(int nfds, fd_set * readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
select Advantages and disadvantages
select advantage :
- select Cross-platform support
select shortcoming :
- It's hard to code
- It will involve copying back and forth from the user area to the kernel area
- When the client has multiple connections , But a few active cases , select Low efficiency ( for example : As an extreme case , 3-1023 File descriptors are all open , But only 1023 Send data , select It's inefficient )
- The biggest support 1024 Client connection (select The biggest support 1024 Client connections do not have file descriptor tables, which can support at most 1024 Limited by file descriptors , But by the FD_SETSIZE=1024 The limit )
FD_SETSIZE=1024 fd_set Used this macro , Of course, you can modify the kernel , Then recompile the kernel , This is generally not recommended
select Code implementation
#include <errno.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/poll.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define MAX_LEN 4096
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int listenfd, connfd, n;
struct sockaddr_in svr_addr;
char buff[MAX_LEN];
if ((listenfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
printf("create socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
memset(&svr_addr, 0, sizeof(svr_addr));
svr_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
svr_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
svr_addr.sin_port = htons(8081);
if (bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &svr_addr, sizeof(svr_addr)) == -1) {
printf("bind socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
if (listen(listenfd, 10) == -1) {
printf("listen socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
//select
fd_set rfds, rset, wfds, wset;
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_ZERO(&wfds);
FD_SET(listenfd, &rfds);
int max_fd = listenfd;
while (1) {
rset = rfds;
wset = wfds;
int nready = select(max_fd + 1, &rset, &wset, NULL, NULL);
if (FD_ISSET(listenfd, &rset)) {
//
struct sockaddr_in clt_addr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(clt_addr);
if ((connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &clt_addr, &len)) == -1) {
printf("accept socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
FD_SET(connfd, &rfds);
if (connfd > max_fd) max_fd = connfd;
if (--nready == 0) continue;
}
int i = 0;
for (i = listenfd + 1; i <= max_fd; i++) {
if (FD_ISSET(i, &rset)) {
//
n = recv(i, buff, MAX_LEN, 0);
if (n > 0) {
buff[n] = '\0';
printf("recv msg from client: %s\n", buff);
FD_SET(i, &wfds);
}
else if (n == 0) {
//
FD_CLR(i, &rfds);
close(i);
}
if (--nready == 0) break;
}
else if (FD_ISSET(i, &wset)) {
send(i, buff, n, 0);
FD_SET(i, &rfds);
FD_CLR(i, &wfds);
}
}
}
close(listenfd);
return 0;
}
High concurrency server model -poll
poll Introduce
poll Follow select similar , Monitor multiple channels IO, but poll Cannot cross platform . Actually poll Is to put select The set of three file descriptors becomes a set .
int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
Parameter description :
- fds: Incoming and outgoing parameters , It's actually an array of structures
fds.fd: File descriptor to monitor
fds.events:
POLLIN----> Read events
POLLOUT----> Write events
fds.revents: Events returned
- nfds: The number of actual valid contents of the array
- timeout: Timeout time , In milliseconds .
-1: Permanent blocking , Until the monitored event occurs
0: Whether or not there is an incident , Go back to
>0: Until the monitored event occurs or times out
Return value :
- success : Returns the number of ready events
- Failure : return -1. if timeout=0, poll Function does not block , And no event happened , Return at this time -1, also errno=EAGAIN, This should not be considered a mistake .
struct pollfd {
int fd; /* file descriptor */ Monitored file descriptor
short events; /* requested events */ Events to monitor --- Will not be modified
short revents; /* returned events */ Return the changed event --- Returned by kernel
};
explain :
- When poll When the function returns , In the structure fd and events Nothing has changed , Is there any event caused by revents To judge , therefore poll Is the separation of request and return
- struct pollfd In structure fd If the member is assigned -1, be poll Will not monitor
- be relative to select, poll There is no essential change ; however poll Can break through 1024 The limitation of . stay /proc/sys/fs/file-max View what a process can open socket Descriptor upper limit , If necessary, you can modify the configuration file : /etc/security/limits.conf, Add the following configuration information , Then restart the terminal to take effect
* soft nofile 1024
* hard nofile 100000
soft and hard respectively ulimit The minimum and maximum limits that the command can modify
poll Code implementation
#include <errno.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/poll.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define MAX_LEN 4096
#define POLL_SIZE 1024
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int listenfd, connfd, n;
struct sockaddr_in svr_addr;
char buff[MAX_LEN];
if ((listenfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
printf("create socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
memset(&svr_addr, 0, sizeof(svr_addr));
svr_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
svr_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
svr_addr.sin_port = htons(8081);
if (bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &svr_addr, sizeof(svr_addr)) == -1) {
printf("bind socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
if (listen(listenfd, 10) == -1) {
printf("listen socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
//poll
struct pollfd fds[POLL_SIZE] = {
0};
fds[0].fd = listenfd;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
int max_fd = listenfd;
int i = 0;
for (i = 1; i < POLL_SIZE; i++) {
fds[i].fd = -1;
}
while (1) {
int nready = poll(fds, max_fd + 1, -1);
if (fds[0].revents & POLLIN) {
struct sockaddr_in client = {
};
socklen_t len = sizeof(client);
if ((connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &client, &len)) == -1) {
printf("accept socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
printf("accept \n");
fds[connfd].fd = connfd;
fds[connfd].events = POLLIN;
if (connfd > max_fd) max_fd = connfd;
if (--nready == 0) continue;
}
//int i = 0;
for (i = listenfd + 1; i <= max_fd; i++) {
if (fds[i].revents & POLLIN) {
n = recv(i, buff, MAX_LEN, 0);
if (n > 0) {
buff[n] = '\0';
printf("recv msg from client: %s\n", buff);
send(i, buff, n, 0);
}
else if (n == 0) {
//
fds[i].fd = -1;
close(i);
}
if (--nready == 0) break;
}
}
}
}
High concurrency server model -epoll ( a key )
epoll Introduce
Delegate the detection of changes in file descriptors to the kernel , Then the kernel will change the file descriptor corresponding to event Back to the application .
remember ,epoll It's event driven , Its underlying data structure is red black tree , Mangrove key yes fd,val Is the event , What is returned is an event .
epoll There are two working modes ,ET and LT Pattern .
Level trigger LT:
- High level represents 1
- As long as there is data in the buffer , Keep informing
Edge trigger ET:
- If the level changes, it means 1
- If there is data in the buffer, it will be notified only once , After that, new data will be notified ( If you don't finish reading the data , Then the remaining data will not be notified , Until new data comes )
epoll The default is to trigger horizontally LT, In scenarios that require high performance , It can be changed to edge ET Non blocking way to improve efficiency .
In general use LT You can't finish reading data at one time , More data . And you can read it all at once , For small data volume, use edge ET.
ET The mode is only notified once , So when reading, you should read it in cycles , Until the end of reading , But after reading it read It will block , Therefore, the file descriptor should be set to non blocking mode (fcntl function )
read When a function is read in non blocking mode , If returns -1, And errno by EAGAIN, Indicates that the current resource is unavailable , That is, there is no data in the buffer ( The data in the buffer has been read ); Or when read When the returned read data length is less than the requested data length , You can determine that there is no data readable in the buffer at this time , It can be considered that the read event has been processed at this time .
epoll Reactor
Reactor : A small event triggers a series of reactions
epoll The idea of reactor : c++ The idea of encapsulation ( Encapsulate data and operations )
- Will descriptor , event , The corresponding processing methods are encapsulated together
- When the event corresponding to the descriptor occurs , Automatically call processing methods ( In fact, the principle is callback function )
epoll The core idea of the reactor is : Calling epoll_ctl Function , take events When going up the tree , utilize epoll_data_t Of ptr member , Put a file descriptor , Events and callback functions are encapsulated into a structure , And then let ptr Point to this structure . And then call epoll_wait When the function returns , You can get specific events, Then get events In structure events.data.ptr The pointer , ptr There is a callback function in the structure pointed to by the pointer , Finally, you can call this callback function .
struct epoll_event {
uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
};
typedef union epoll_data {
void *ptr;
int fd;
uint32_t u32;
uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;
epoll-api
int epoll_create(int size);
Function description : Create a tree root
Parameter description :
- size: Maximum number of nodes , This parameter is in linux 2.6.8 Has been ignored , But you must pass a greater than 0 Number of numbers , Historical significance , use epoll_create1 It's OK .
- Return value :
success : Return a greater than 0 File descriptor for , Represents the root of the whole tree .
Failure : return -1, And set up errno value .
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
Function description : The node to listen to is in epoll Add... To the tree , Delete and modify
Parameter description :
epfd: epoll The root
op:
EPOLL_CTL_ADD: Add an event node to the tree
EPOLL_CTL_DEL: Delete the event node from the tree
EPOLL_CTL_MOD: Modify the corresponding event node in the tree
- fd: The file descriptor corresponding to the event node
- event: Event node to operate
struct epoll_event {
uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
};
typedef union epoll_data {
void *ptr;
int fd;
uint32_t u32;
uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;
- event.events Commonly used :
EPOLLIN: Read events
EPOLLOUT: Write events
EPOLLERR: Error events
EPOLLET: Edge trigger mode
- event.fd: The file descriptor corresponding to the event to be monitored
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
Function description : Wait for the kernel return event to occur
Parameter description :
- epfd: epoll The root
- events: Out parameter , It is actually an array of event structures
- maxevents: Array size
- timeout:
-1: It means permanent blocking
0: Return immediately
>0: Indicates a timeout wait event
Return value :
- success : Return the number of events
- Failure : if timeout=0, If no event occurs, return ; return -1, Set up errno value
epoll_wait Of events It's an outgoing parameter , call epoll_ctl What value is passed to the kernel , When epoll_wait On return , The kernel returns what value , It won't be right struct event Make any changes to the value of the structure variable of .
epoll Advantages and disadvantages
epoll advantage :
- High performance , Millions of concurrent , and select No way.
epoll shortcoming :
- Cannot cross platform ,linux Under the
epoll Code implementation
#include <errno.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/poll.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define POLL_SIZE 1024
#define MAX_LEN 4096
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int listenfd, connfd, n;
char buff[MAX_LEN];
struct sockaddr_in svr_addr;
memset(&svr_addr, 0, sizeof(svr_addr));
svr_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
svr_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
svr_addr.sin_port = htons(8081);
if ((listenfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
printf("create socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
if (bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &svr_addr, sizeof(svr_addr)) == -1) {
printf("bind socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
if (listen(listenfd, 10) == -1) {
printf("listen socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
int epfd = epoll_create(1); //int size
struct epoll_event events[POLL_SIZE] = {
0};
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = listenfd;
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, listenfd, &ev);
while (1) {
int nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, POLL_SIZE, 5);
if (nready == -1) {
continue;
}
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < nready; i++) {
int actFd = events[i].data.fd;
if (actFd == listenfd) {
struct sockaddr_in cli_addr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(cli_addr);
if ((connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &cli_addr, &len)) == -1) {
printf("accept socket error: %s(errno: %d)\n", strerror(errno), errno);
return 0;
}
printf("accept\n");
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = connfd;
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, connfd, &ev);
}
else if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
n = recv(actFd, buff, MAX_LEN, 0);
if (n > 0) {
buff[n] = '\0';
printf("recv msg from client: %s\n", buff);
send(actFd, buff, n, 0);
}
else if (n == 0) {
//
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, actFd, NULL);
close(actFd);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- MRS离线数据分析:通过Flink作业处理OBS数据
- yolo训练过程中批量导入requirments.txt中所需要的包
- Youth experience and career development
- 【4500字归纳总结】一名软件测试工程师需要掌握的技能大全
- TaffyDB开源的JS数据库
- 元宇宙带来的创意性改变
- 直播软件搭建,canvas文字加粗
- Automated testing: a practical skill that everyone wants to know about robot framework
- Tear the Nacos source code by hand (tear the client source code first)
- Tips of this week 135: test the contract instead of implementation
猜你喜欢
【4500字归纳总结】一名软件测试工程师需要掌握的技能大全
Import requirements in batches during Yolo training Txt
mui侧边导航锚点定位js特效
Chapter 2 build CRM project development environment (database design)
![[trusted computing] Lesson 13: TPM extended authorization and key management](/img/96/3089e80441949d26e39ba43306edeb.png)
[trusted computing] Lesson 13: TPM extended authorization and key management

Sanxian Guidong JS game source code
Pro2: modify the color of div block

Pro2:修改div块的颜色
![[4500 word summary] a complete set of skills that a software testing engineer needs to master](/img/82/acae52928b3ab48e9ecbf4ec436e5e.jpg)
[4500 word summary] a complete set of skills that a software testing engineer needs to master
![[PaddleSeg源码阅读] PaddleSeg Validation 中添加 Boundary IoU的计算(1)——val.py文件细节提示](/img/f2/b6a0e5512b35cf1b695a8feecd0895.png)
[PaddleSeg源码阅读] PaddleSeg Validation 中添加 Boundary IoU的计算(1)——val.py文件细节提示
随机推荐
Personal best practice demo sharing of enum + validation
深入浅出【机器学习之线性回归】
Sanxian Guidong JS game source code
财富证券证券怎么开户?通过链接办理股票开户安全吗
[trusted computing] Lesson 11: TPM password resource management (III) NV index and PCR
Test for 3 months, successful entry "byte", my interview experience summary
[re understand the communication model] the application of reactor mode in redis and Kafka
Year SQL audit platform
Chapter 3 business function development (to remember account and password)
手撕Nacos源码(先撕客户端源码)
三仙归洞js小游戏源码
SD_DATA_SEND_SHIFT_REGISTER
直播软件搭建,canvas文字加粗
socket编程之常用api介绍与socket、select、poll、epoll高并发服务器模型代码实现
数学分析_笔记_第11章:Fourier级数
AI defeated mankind and designed a better economic mechanism
Cf:c. factors and powers of two [DP + sort + Select Board + select several numbers equal to the minimum number of known sums]
cf:C. Factorials and Powers of Two【dp + 排序 + 选不选板子 + 选若干个数等于已知和的最少数】
原生js验证码
自动化测试:Robot FrameWork框架大家都想知道的实用技巧