当前位置:网站首页>2020 Zhejiang Provincial Games
2020 Zhejiang Provincial Games
2022-07-07 09:47:00 【moyangxian】
2020 Zhejiang Province competition
- A - AD 2020 ( The prefix and )
- B - Bin Packing Problem( Two points , Line segment tree )
- C - Crossword Validation ( Dictionary tree )
- D
- E - Easy DP Problem( In front of the chairman tree k The great sum )
- F
- G - Gliding( shortest path )
- H - Huge Clouds( The geometric , Calculate the intersection of intervals by difference )
- I - Invoking the Magic ( discretization , Union checking set )
- J
- K - Killing the Brute-force( Sign in )
- L
A - AD 2020 ( The prefix and )
The question : Give two dates , Ask how many days between two dates contain “202” This string .
Answer key : Just deal with the prefix and .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl "\n"
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define int long long
#define max(a,b) ((a>b)?a:b)
#define min(a,b) ((a>b)?b:a)
#define lowbit(x) ((x)&-(x))
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 5e6 + 10;
int days[] = {
0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
int a[N], cnt;
bool check(int y) {
return (y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0) || (y % 400 == 0);
}
void init() {
for (int y = 2000; y < 10000; y++) {
for (int m = 1; m <= 12; m++) {
int d = days[m];
if (check(y) && m == 2) d++;
for (int i = 1; i <= d; i++) {
int x = y * 10000 + m * 100 + i;
string s = to_string(x);
//debug(s);
if (s.find("202") != s.npos) a[++cnt] = x;
}
}
}
}
void solve() {
int y1, m1, d1, y2, m2, d2;
cin >> y1 >> m1 >> d1 >> y2 >> m2 >> d2;
int x = y1 * 10000 + m1 * 100 + d1;
int y = y2 * 10000 + m2 * 100 + d2;
int p1 = lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + cnt, x) - a;
int p2 = upper_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + cnt, y) - a;
cout << p2 - p1 << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
init();
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
B - Bin Packing Problem( Two points , Line segment tree )
The question :n Items and their inscriptions , According to the topic, two methods are given to put it in the volume of c In my box , Ask the number of boxes used in the two methods .
1、 Put the first box on the left every time . If not, add a box on the far right to put .
2、 Each time, the box with the remaining volume closest to the current item , No measurement, add a box on the far right .
Answer key :
1、 Maintain the maximum value of the interval with the line segment tree , Go to the left subtree first every time , Equivalent to the thought of dichotomy .
2、 stay multiset Just two points in .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl "\n"
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define int long long
#define max(a,b) ((a>b)?a:b)
#define min(a,b) ((a>b)?b:a)
#define lowbit(x) ((x)&-(x))
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n, c, ans;
int a[N];
multiset<int>st;
struct SEG {
int t[N << 2];
void up(int p) {
t[p] = max(t[p << 1], t[p << 1 | 1]); }
void build(int p, int l, int r) {
t[p] = c;
if (l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(p << 1, l, mid);
build(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
}
void modify(int p, int l, int r, int v) {
if (l == r) {
if (t[p] == c)ans++;
t[p] -= v;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (t[p << 1] >= v)modify(p << 1, l, mid, v);
else modify(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, v);
up(p);
}
}seg;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> c;
ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
seg.build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
seg.modify(1, 1, n, a[i]);
st.clear();
st.insert(c - a[1]);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
auto p = st.lower_bound(a[i]);
if (p == st.end()) {
st.insert(c - a[i]);
continue;
}
int v = *p - a[i];
st.erase(p);
st.insert(v);
}
cout << ans << " " << st.size() << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
C - Crossword Validation ( Dictionary tree )
The question : Give a n*n Matrix , Ask the weight sum of all words in the matrix .
Answer key : The dictionary tree records and gives m Weight of words , Then traverse the total weight of all words .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl "\n"
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//#define int long long
#define max(a,b) ((a>b)?a:b)
#define min(a,b) ((a>b)?b:a)
#define lowbit(x) ((x)&-(x))
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1010, M = 4e6 + 10;
char a[N][N], t[N];
int n, m;
struct Trie {
struct Node {
int p[26];
int v, cnt;
void init() {
memset(p, -1, sizeof(p));
v = cnt = 0;
}
}t[M];
int root, tot;
int newNode() {
++tot;
t[tot].init();
return tot;
}
void init() {
tot = 0;
root = newNode();
}
void insert(char* s, int v) {
int len = strlen(s);
int now = root;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int c = s[i] - 'a';
if (t[now].p[c] == -1)
t[now].p[c] = newNode();
now = t[now].p[c];
}
t[now].v += v;
t[now].cnt++;
}
int query(char* s) {
int len = strlen(s);
int now = root;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int c = s[i] - 'a';
if (t[now].p[c] == -1) return -1;
now = t[now].p[c];
}
if (t[now].cnt == 0) return -1;
return t[now].v;
}
}trie;
void solve() {
trie.init();
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> (a[i] + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int v;
cin >> t >> v;
trie.insert(t, v);
}
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
int len = 0;
if (a[i][j] == '#') continue;
while (a[i][j] != '#' && j <= n) {
t[len++] = a[i][j];
j++;
}
t[len] = 0;
ll sum = trie.query(t);
if (sum == -1) {
cout << "-1" << endl;
return ;
}
ans += sum;
}
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int len = 0;
if (a[i][j] == '#') continue;
while (a[i][j] != '#' && i <= n) {
t[len++] = a[i][j];
i++;
}
t[len] = 0;
ll sum = trie.query(t);
if (sum == -1) {
cout << "-1" << endl;
return;
}
ans += sum;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
D
E - Easy DP Problem( In front of the chairman tree k The great sum )
The question : Take out a continuous subsequence every time dp, ask dp[m][k] Value .
. : Simulate the example to know that the final answer must be 1 To m Sum of squares of , All can put dp In the equation i2 Ignore first , such dp The equation becomes a former k Daiwa dp equation . Use the chairman tree to maintain the front k Big sum ,1 To m The sum of squares of can be preprocessed , Do you , Add it every time you ask .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e5 + 9;
int n, q, a[N], rt[N], b[N], m;
struct Data {
int ls, rs, val, siz;
};
struct SegmentTree {
int tot;
std::vector<Data> s;
SegmentTree(int n) :
tot(0), s(n << 5)
{
}
int update(int rt, int pre, int L, int R, int pos, int val) {
rt = ++tot;
s[rt] = s[pre];
s[rt].siz++;
s[rt].val += val;
if (L == R) return rt;
int mid = (L + R) >> 1;
if (pos <= mid) s[rt].ls = update(s[rt].ls, s[pre].ls, L, mid, pos, val);
else s[rt].rs = update(s[rt].rs, s[pre].rs, mid + 1, R, pos, val);
return rt;
}
int query(int rt1, int rt2, int L, int R, int k) {
if (L == R) return b[L] * k;
int siz = s[s[rt2].rs].siz - s[s[rt1].rs].siz;
int val = s[s[rt2].rs].val - s[s[rt1].rs].val;
int mid = (L + R) >> 1;
if (k <= siz) return query(s[rt1].rs, s[rt2].rs, mid + 1, R, k);
else return val + query(s[rt1].ls, s[rt2].ls, L, mid, k - siz);
}
};
int s[N];
void solve() {
scanf("%lld", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
b[i] = a[i];
rt[i] = 0;
s[i] = s[i - 1] + i * i;
}
std::sort(b + 1, b + 1 + n);
m = std::unique(b + 1, b + 1 + n) - b - 1LL;
SegmentTree segt(m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int pos = std::lower_bound(b + 1, b + 1 + m, a[i]) - b;
rt[i] = segt.update(rt[i], rt[i - 1], 1, m, pos, a[i]);
}
scanf("%lld", &q);
while (q--) {
int l, r, k;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &l, &r, &k);
int sum = segt.query(rt[l - 1], rt[r], 1, m, k);
sum = sum + s[r - l + 1];
printf("%lld\n", sum);
}
return;
}
signed main() {
int T = 1;
scanf("%lld", &T);
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
F
G - Gliding( shortest path )
The question : A little
Answer key : A little
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
const int N = 4e3 + 9;
const int INF = 100000000;
int n;
int xs, ys, xe, ye;
int vf, vp, vh;
int xx[N], yy[N], vv[N];
int du[N];
double dis[N];
struct edge {
int to; double w;
};
std::vector<edge> e[N];
double dist(int xa, int ya, int xb, int yb) {
return sqrt((xa - xb) * (xa - xb) + (ya - yb) * (ya - yb));
}
void solve() {
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &xs, &ys, &xe, &ye);
scanf("%d%d%d", &vf, &vp, &vh);
scanf("%d", &n); n++;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &xx[i], &yy[i], &vv[i]);
e[i].clear();
du[i] = 0;
dis[i] = INF;
}
e[n + 1].clear();
du[n + 1] = 0;
dis[n + 1] = INF;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (vv[i] <= vp) continue;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (i == j) continue;
if (vv[j] <= vp) continue;
if (vv[j] <= vv[i]) continue;
double dis = dist(xx[i], yy[i], xx[j], yy[j]);
double x = dis / vh;
double h = x * vp;
double y = h / (vv[i] - vp);
e[i].emplace_back(edge{
j, x + y });
du[j]++;
}
double dis = dist(xx[i], yy[i], xe, ye);
double x = dis / vh;
double h = x * vp;
double y = h / (vv[i] - vp);
e[i].emplace_back(edge{
n + 1, x + y });
du[n + 1]++;
}
dis[1] = 0;
std::queue<int> que;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (du[i] == 0) {
que.push(i);
}
}
while (!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < (int)e[u].size(); i++) {
int v = e[u][i].to;
double w = e[u][i].w;
dis[v] = std::min(dis[v], dis[u] + w);
du[v]--;
if (du[v] == 0) {
que.push(v);
}
}
}
printf("%.15lf\n", dis[n + 1]);
return;
}
signed main() {
int T = 1;
std::cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
H - Huge Clouds( The geometric , Calculate the intersection of intervals by difference )
The question :n A light source ( spot ),m A board ( Line segment ), Ask the shadow area of the ground .
Answer key : For each point, find the interval where each line segment can cause shadow , Then merge the intervals . Finally, the answer is to join the corresponding intervals of different points .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl "\n"
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define int long long
#define max(a,b) ((a>b)?a:b)
#define min(a,b) ((a>b)?b:a)
#define lowbit(x) ((x)&-(x))
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
const double eps = 1e-8;
const double INF = 1e18;
const int N = 510;
int sgn(double x) {
if (fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
else return x < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
struct Point {
double x, y;
Point() {
}
Point(double x, double y) :x(x), y(y) {
}
Point operator + (Point B) {
return Point(x + B.x, y + B.y); }
Point operator - (Point B) {
return Point(x - B.x, y - B.y); }
Point operator * (double k) {
return Point(x * k, y * k); }
Point operator / (double k) {
return Point(x / k, y / k); }
};
struct Line {
Point p1, p2;
Line() {
}
Line(Point p1, Point p2) :p1(p1), p2(p2) {
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
double Cross(Vector A, Vector B) {
return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x; }
double Dot(Vector A, Vector B) {
return A.x * B.x + A.y * B.y; }
Point a[N], c[N * N];
Line b[N];
bool Point_on_seg(Point p, Line v) {
return sgn(Cross(p - v.p1, v.p2 - v.p1)) == 0 && sgn(Dot(p - v.p1, p - v.p2)) <= 0;
}
Point Cross_point(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) {
double s1 = Cross(b - a, c - a);
double s2 = Cross(b - a, d - a);
return Point(c.x * s2 - d.x * s1, c.y * s2 - d.y * s1) / (s2 - s1);
}
int Point_line_relation(Point p, Line v) {
int c = sgn(Cross(p - v.p1, v.p2 - v.p1));
if (c < 0) return 1;
if (c > 0) return 2;
return 0;
}
Point get(int x, int y) {
if (Point_on_seg(a[x], b[y])) return Point(-INF, INF);
//if(a[x].y<b[y].p1.y&&a[x].y<b[y].p2.y) return Point(-INF,INF);
Line e(Point(0, 0), Point(INF, 0));
if (a[x].y > b[y].p2.y) {
Point l = Cross_point(a[x], b[y].p1, e.p1, e.p2);
Point r = Cross_point(a[x], b[y].p2, e.p1, e.p2);
if (l.x > r.x) swap(l, r);
return Point(l.x, r.x);
}
else if (a[x].y > b[y].p1.y) {
int v = Point_line_relation(a[x], b[y]);
if (v == 0) return Point(-INF, INF);
Point l = Cross_point(a[x], b[y].p1, e.p1, e.p2);
if (v == 1) return Point(l.x, INF);
else return Point(-INF, l.x);
}
else return Point(0, 0);
}
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> b[i].p1.x >> b[i].p1.y >> b[i].p2.x >> b[i].p2.y;
if (b[i].p1.y > b[i].p2.y) swap(b[i].p1, b[i].p2);
}
map<double, int> m1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
map<double, int> m2;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
Point t = get(i, j);
m2[t.x]++;
m2[t.y]--;
}
int sum = 0;
bool flag = false;
double p = 0;
for (auto x : m2) {
sum += x.se;
if (sum > 0 && !flag) {
p = x.fi;
flag = true;
}
else if (sum == 0 && flag) {
m1[p]++;
m1[x.first]--;
flag = false;
}
}
}
int sum = 0;
bool flag = false;
double p = 0, ans = 0;
for (auto x : m1) {
sum += x.se;
if (sum == n && !flag) {
p = x.fi;
flag = true;
}
else if (sum < n && flag) {
ans += x.first - p;
flag = false;
}
}
if (ans > 1e9) printf("-1\n");
else printf("%.10f\n", ans);
}
signed main() {
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
I - Invoking the Magic ( discretization , Union checking set )
The question :n Pairs of socks , It can be operated every time k Match the socks ( Perfect match ), Ask the smallest k.
Answer key : Discretize it, and then use the union search set to deal with it .(map Will timeout )
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl "\n"
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define int long long
#define max(a,b) ((a>b)?a:b)
#define min(a,b) ((a>b)?b:a)
#define lowbit(x) ((x)&-(x))
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
unordered_map<int, int>mp;
int cnt;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int f[N], s[N];
int ans;
int getnum(int x) {
if (mp[x] == 0) mp[x] = ++cnt;
return mp[x];
}
int find(int x) {
return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]); }
void merge(int x, int y) {
x = find(x), y = find(y);
if (x != y) {
f[y] = x;
s[x] += s[y];
ans = max(ans, s[x]);
}
}
void solve() {
mp.clear();
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
f[i] = i, s[i] = 1;
ans = cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
x = getnum(x);
y = getnum(y);
merge(x, y);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
J
K - Killing the Brute-force( Sign in )
The question : A little
Answer key : A little
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl "\n"
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define int long long
#define max(a,b) ((a>b)?a:b)
#define min(a,b) ((a>b)?b:a)
#define lowbit(x) ((x)&-(x))
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N], b[N];
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i];
int ans = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (b[i] > a[i] * 3) {
ans = i;
break;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
L
边栏推荐
- Unity shader (to achieve a simple material effect with adjustable color attributes only)
- PostgreSQL创建触发器的时候报错,
- Impression notes finally support the default markdown preview mode
- 在EXCEL写VBA连接ORACLE并查询数据库中的内容
- 哈夫曼编码压缩文件
- Write VBA in Excel, connect to Oracle and query the contents in the database
- 基于智慧城市与储住分离数字家居模式垃圾处理方法
- 进程间的通信方式
- In fact, it's very simple. It teaches you to easily realize the cool data visualization big screen
- How to use Mongo shake to realize bidirectional synchronization of mongodb in shake database?
猜你喜欢
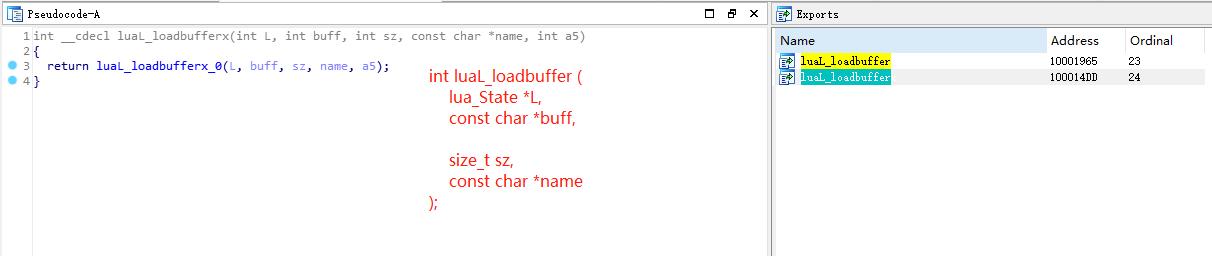
【frida实战】“一行”代码教你获取WeGame平台中所有的lua脚本
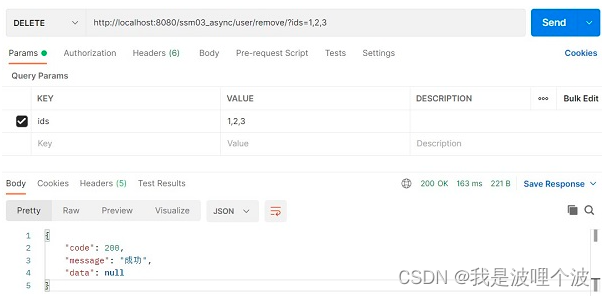
Over 100000 words_ Ultra detailed SSM integration practice_ Manually implement permission management

小程序滑动、点击切换简洁UI
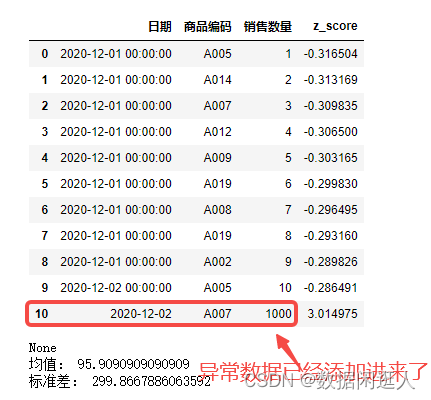
数据建模中利用3σ剔除异常值进行数据清洗
Flex flexible layout
Sqlplus garbled code problem, find the solution

iNFTnews | 时尚品牌将以什么方式进入元宇宙?
H5 web player easyplayer How does JS realize live video real-time recording?
其实特简单,教你轻松实现酷炫的数据可视化大屏
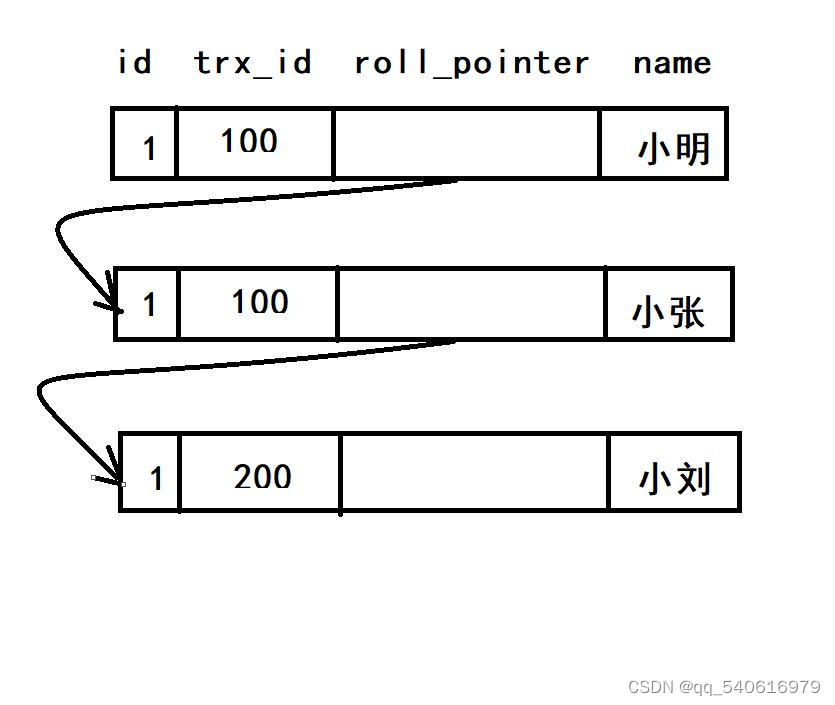
细说Mysql MVCC多版本控制
随机推荐
沙龙预告|GameFi 领域的瓶颈和解决方案
IIS redirection redirection appears eurl axd
Binary tree high frequency question type
flink. CDC sqlserver. 可以再次写入sqlserver中么 有连接器的 dem
【BW16 应用篇】安信可BW16模组/开发板AT指令实现MQTT通讯
H5网页播放器EasyPlayer.js如何实现直播视频实时录像?
Oracle安装增强功能出错
What development models did you know during the interview? Just read this one
In fact, it's very simple. It teaches you to easily realize the cool data visualization big screen
Octopus future star won a reward of 250000 US dollars | Octopus accelerator 2022 summer entrepreneurship camp came to a successful conclusion
Arthas simple instructions
VSCode+mingw64+cmake
基于智慧城市与储住分离数字家居模式垃圾处理方法
Netease Cloud Wechat applet
ComputeShader
JMeter JDBC batch references data as input parameters (the simplest method for the whole website)
数据建模中利用3σ剔除异常值进行数据清洗
Use 3 in data modeling σ Eliminate outliers for data cleaning
剑指 Offer II 107. 矩阵中的距离
Create an int type array with a length of 6. The values of the array elements are required to be between 1-30 and are assigned randomly. At the same time, the values of the required elements are diffe