当前位置:网站首页>浅谈Label Smoothing技术
浅谈Label Smoothing技术
2022-07-05 09:01:00 【aelum】
作者简介:非科班转码,正在不断丰富自己的技术栈
️ 博客主页:https://raelum.blog.csdn.net
主要领域:NLP、RS、GNN
如果这篇文章有帮助到你,可以关注️ + 点赞 + 收藏 + 留言,这将是我创作的最大动力

目录
一、从 One-Hot 到 Label Smoothing
考虑单个样本的交叉熵损失
H ( p , q ) = − ∑ i = 1 C p i log q i H(p,q)=-\sum_{i=1}^C p_i\log q_i H(p,q)=−i=1∑Cpilogqi
其中 C C C 代表类别个数, p i p_i pi 是真实分布(即 target), q i q_i qi 是预测分布(即神经网络输出的 prediction)。
如果真实分布采用传统的 One-Hot 向量,则其分量非 0 0 0 即 1 1 1。不妨设第 k k k 个位置是 1 1 1,其余位置是 0 0 0,此时交叉熵损失变为
H ( p , q ) = − log q k H(p,q)=-\log q_k H(p,q)=−logqk
从上面的表达式不难发现一些问题:
- 真实标签跟其他标签之间的关系被忽略了,一些有用的知识无法学到;
- One-Hot 倾向于让模型过度自信(Overconfidence),容易造成过拟合,进而导致泛化性能降低;
- 误标注的样本(即
target错误)更容易对模型的训练产生影响; - One-Hot 对 “模棱两可” 的样本表征较差。
缓解这些问题的方法就是采用 Label Smoothing 的技术,它也是一种正则化的技巧,具体如下:
p i : = { 1 − ϵ , i = k ϵ / ( C − 1 ) , i ≠ k p_i:= \begin{cases} 1-\epsilon,& i=k \\ \epsilon/(C-1),&i\neq k\\ \end{cases} pi:={ 1−ϵ,ϵ/(C−1),i=ki=k
其中 ϵ \epsilon ϵ 是一个小正数。
例如,设原始 target 为 [ 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 ] [0,0,1,0,0,0] [0,0,1,0,0,0],取 ϵ = 0.1 \epsilon=0.1 ϵ=0.1,则经过 Label Smoothing 后 target 变为 [ 0.02 , 0.02 , 0.9 , 0.02 , 0.02 , 0.02 ] [0.02,0.02,0.9,0.02,0.02,0.02] [0.02,0.02,0.9,0.02,0.02,0.02]。
原始的 One-Hot 向量通常称为 Hard Target(或 Hard Label),经过标签平滑后通常称为 Soft Target(或 Soft Label)
二、Label Smoothing 的简单实现
import torch
def label_smoothing(label, eps):
label[label == 1] = 1 - eps
label[label == 0] = eps / (len(label) - 1)
return label
a = torch.tensor([0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], dtype=torch.float)
print(label_smoothing(a, 0.1))
# tensor([0.0200, 0.0200, 0.9000, 0.0200, 0.0200, 0.0200])
三、Label Smoothing 的优缺点
优点:
- 一定程度上可以缓解模型 Overconfidence 的问题,此外也具有一定的抗噪能力;
- 提供了训练数据中类别之间的关系(数据增强);
- 可能在一定程度上增强了模型的泛化能力。
缺点:
- 单纯地添加随机噪音,也无法反映标签之间的关系,因此对模型的提升有限,甚至有欠拟合的风险;
- 某些场景下 Soft Label 并不能帮助我们构建更好的神经网络(表现不如 Hard Label)。
四、什么时候使用 Label Smoothing?
- 庞大的数据集难免存在噪音(即标注错误),为了避免模型学到这些噪音可以加入 Label Smoothing;
- 对于模糊的 case 而言可以引入 Label Smoothing(比如猫狗分类任务中,可能存在一些图片既像狗又像猫);
- 防止模型 Overconfidence。
边栏推荐
- Wechat H5 official account to get openid climbing account
- Halcon shape_ trans
- Redis implements a high-performance full-text search engine -- redisearch
- Kubedm series-00-overview
- location search 属性获取登录用户名
- Summary of "reversal" problem in challenge Programming Competition
- Basic number theory - fast power
- 使用arm Neon操作,提高内存拷贝速度
- Return of missing persons
- Blogger article navigation (classified, real-time update, permanent top)
猜你喜欢
![3D reconstruction open source code summary [keep updated]](/img/ec/984aede7ef9e758abd52fb5ff4e144.jpg)
3D reconstruction open source code summary [keep updated]
Use and programming method of ros-8 parameters

嗨 FUN 一夏,与 StarRocks 一起玩转 SQL Planner!
![Introduction Guide to stereo vision (5): dual camera calibration [no more collection, I charge ~]](/img/68/6bfa390b0bedcdbc4afba2f9bd9c0f.jpg)
Introduction Guide to stereo vision (5): dual camera calibration [no more collection, I charge ~]
Attention is all you need

微信H5公众号获取openid爬坑记
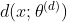
生成对抗网络

IT冷知识(更新ing~)
Ros- learn basic knowledge of 0 ROS - nodes, running ROS nodes, topics, services, etc
Nodejs modularization
随机推荐
Applet (subcontracting)
Multiple linear regression (sklearn method)
OpenFeign
The location search property gets the login user name
Pearson correlation coefficient
微信H5公众号获取openid爬坑记
RT thread kernel quick start, kernel implementation and application development learning with notes
编辑器-vi、vim的使用
Multiple solutions to one problem, asp Net core application startup initialization n schemes [Part 1]
ORACLE进阶(三)数据字典详解
Understanding rotation matrix R from the perspective of base transformation
ECMAScript6介绍及环境搭建
c#比较两张图像的差异
Beautiful soup parsing and extracting data
Install the CPU version of tensorflow+cuda+cudnn (ultra detailed)
Meta标签详解
Blogger article navigation (classified, real-time update, permanent top)
Golang foundation -- map, array and slice store different types of data
Ros- learn basic knowledge of 0 ROS - nodes, running ROS nodes, topics, services, etc
nodejs_ 01_ fs. readFile