当前位置:网站首页>JVM the truth you need to know
JVM the truth you need to know
2022-07-07 05:42:00 【Jonny Jiang-zh】
jvm The truth you need to know
- class Approximate file loading process
- jdk+jre+jvm The relationship between
- jvm By default, the compilation interpretation is used to execute at the same time
- jvm Specify four cases of loading classes
- Four ways to create objects
- Parent delegate mechanism
- Hardware layer data consistency
- volatile Realization
- synchrinized Realization
- Object memory layout
- JMM
- jvm Instruction set
- The garbage
- Logical allocation of heap space
- Method area (method area)
- Object on the stack
- When does the subject enter the old age
- Common garbage collectors
- JVM tuning
- Concurrent recycling algorithm
- fibers
class Approximate file loading process
common jvm
- hotspot
- jrocket——IBM
- Microsoft vm
- taobao vm
- azul zing
class file format
compile :
javac xxx.java
see :
- javap -v xxx.class
- idea plug-in unit jclasslib
File identifier | The child version number | Major version number | Number of constant pool elements
cafe babe 0000 0037 0010 0a00 0300 0d07
000e 0700 0f01 0006 3c69 6e69 743e 0100
0328 2956 0100 0443 6f64 6501 000f 4c69
6e65 4e75 6d62 6572 5461 626c 6501 0012
4c6f 6361 6c56 6172 6961 626c 6554 6162
6c65 0100 0474 6869 7301 000b 4c6a 766d
2f44 656d 6f31 3b01 000a 536f 7572 6365
4669 6c65 0100 0a44 656d 6f31 2e6a 6176
610c 0004 0005 0100 096a 766d 2f44 656d
6f31 0100 106a 6176 612f 6c61 6e67 2f4f
626a 6563 7400 2100 0200 0300 0000 0000
0100 0100 0400 0500 0100 0600 0000 2f00
0100 0100 0000 052a b700 01b1 0000 0002
0007 0000 0006 0001 0000 0009 0008 0000
000c 0001 0000 0005 0009 000a 0000 0001
000b 0000 0002 000c
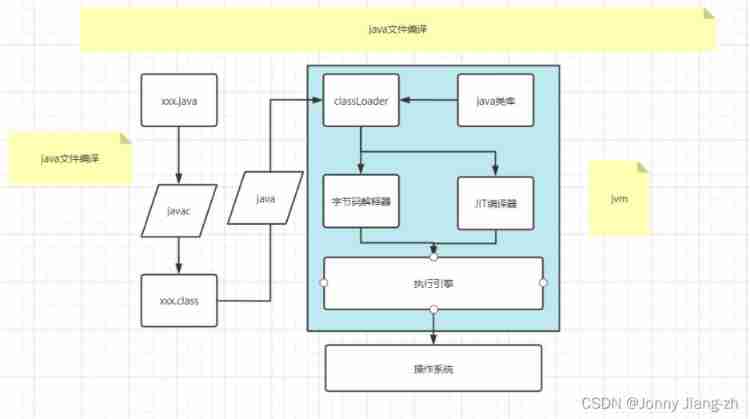
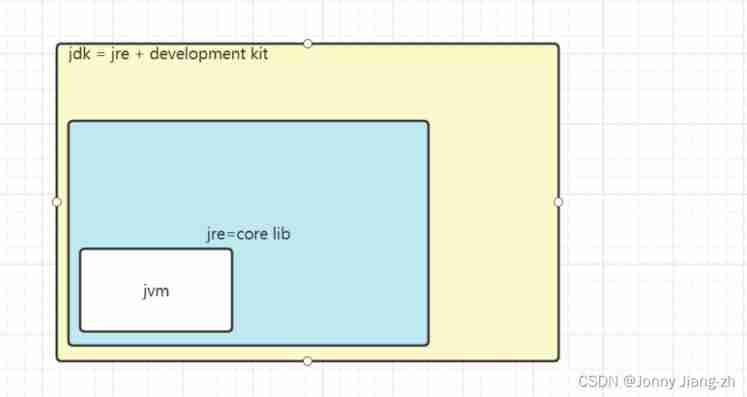
jdk+jre+jvm The relationship between
Class loading process ( Class file +class object )
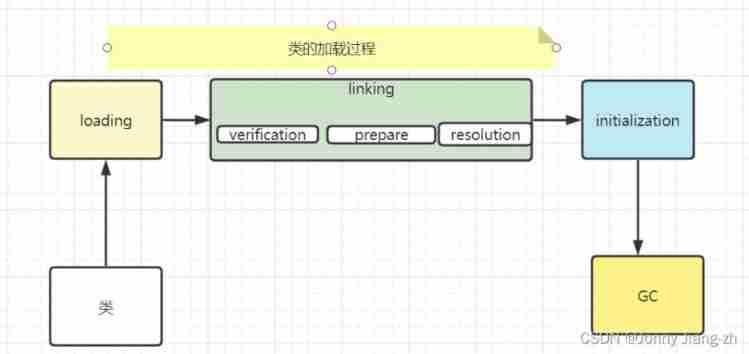
- loading: Load the bytecode file into memory
- linking: Be responsible for the operation before initializing the class
- verification: Verify whether the document is formal class file ( Verify bytecode file )
- prepare: Assign default values to class attributes
- resolution: Convert symbolic references to Memory reference
- initialization: Assign the initial value to the attribute in the class
Class loader
classification
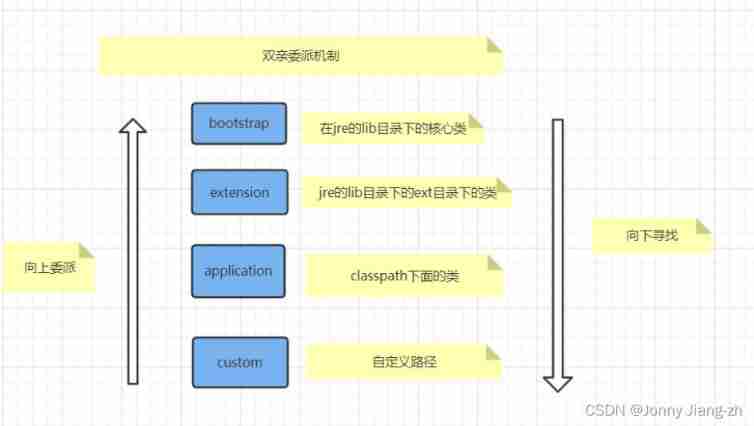
Execute the process ( Parent delegate mechanism )
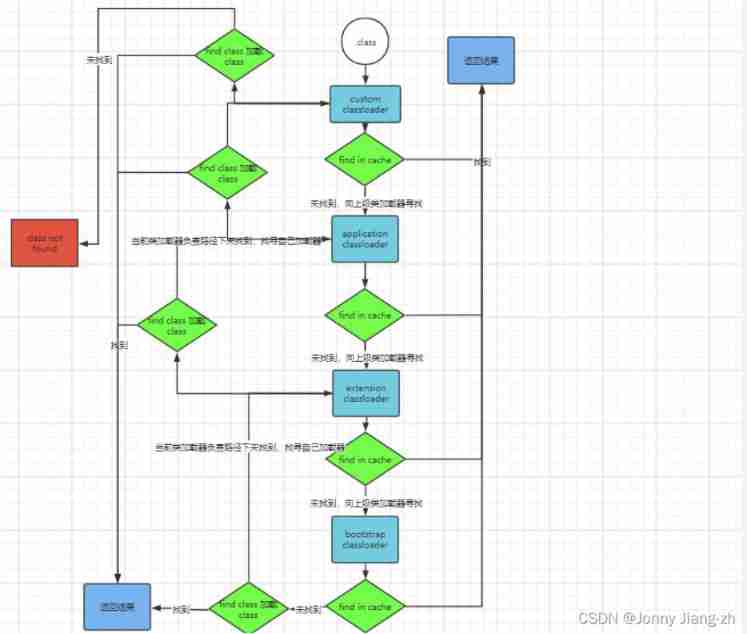
Loading paths of different class loaders
- By looking at “Launcher” The source code of class , The range of different loaders is as follows :
- boostrap => sun.boot.class.path
- extension => java.class.path
- application => java.ext.dirs
- Run the response code to see
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(System.getProperty("sun.boot.class.path").replaceAll(";",System.lineSeparator()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.class.path").replaceAll(";",System.lineSeparator()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.ext.dirs").replaceAll(";",System.lineSeparator()));
}
}
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\resources.jar
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\rt.jar
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\sunrsasign.jar
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\jsse.jar
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\jce.jar
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\charsets.jar
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\jfr.jar
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\classes
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\charsets.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\deploy.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\access-bridge-64.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\cldrdata.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\dnsns.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\jfxrt.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\nashorn.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\sunec.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\sunpkcs11.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\javaws.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\jce.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\jfr.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\jfxswt.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\jsse.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\management-agent.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\plugin.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\resources.jar
D:\java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\rt.jar
D:\codes\java\review\out\production\review
D:\IntelliJIDEA2021.1.1\lib\idea_rt.jar
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_291\jre\lib\ext
C:\WINDOWS\Sun\Java\lib\ext
Process finished with exit code 0
Custom class loaders
Inherit classLoader Re actualize findClass, The byte stream read uses defineClass
jvm By default, the compilation interpretation is used to execute at the same time
- -Xmix: Specify to execute in a mixed way
- -Xint: Specify to execute in an interpreted way
- -Xcomp: Specifies to execute
jvm Specify four cases of loading classes
- new getstatic putstatic invokestatic Instructions , visit final Variable
- java.lang.reflect Make a reflection call to the class
- When initializing a subclass , The parent class first initializes
- Dynamic language support java.lang.invoke.MethodHandle The result of analysis is REF_getstatic REF_putstatic REF_invokestatic Method handle of
Four ways to create objects
- new
- Reflection
- clone
- serialize
Parent delegate mechanism
break ( be based on jvm In the load .class A copy of the file will be saved in memory .class file + class object )
- how : rewrite classloader Of loadclass Method
- Why? : Due to the existence of parental delegation mechanism, when loading classes with the same path, we always get the class loaded in memory during the loading process , Can't get the latest in time
- when :
- jdk1.2 You have to
- ThreadContextClassloader
- tomat Of classloader, Thermal deployment
Object creation process : Allocate memory space + The default value is + initialization , Class loading process : Load class + The default value is + initialization
DCL
volatile( visibility 、 Orderliness ): Prevent other threads from reading dirty data due to instruction rearrangement
Hardware layer data consistency
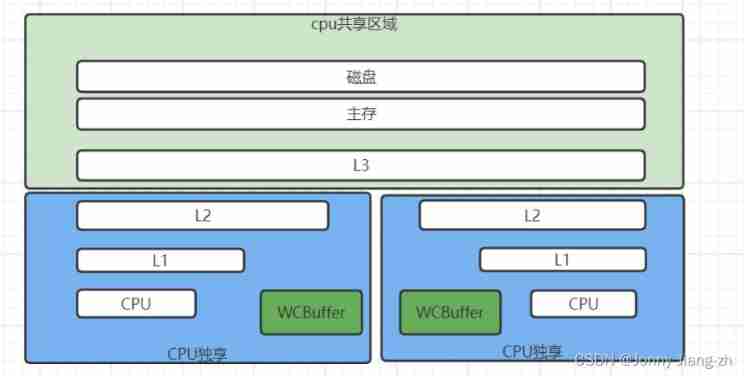
WCBuffer:write combine buffer Merge write
Problems arise
- Lock bus ( When the data in memory is cpu In operation , other cpu Temporarily unable to access memory again )
- Agreement of conformity ( Add different tags through different states )
- MESI:
- modified: Be modified
- exclusive: Only one cpu Read
- share: Multiple cpu Read at the same time
- invalid: When one cpu When reading data, another cpu Modifying data
- MESI:
Basic unit
cpu The basic unit for reading data from memory :cache line -> 64bytes, This may lead to sharing problems
- Problem description : When two adjacent cells store two values , There are two cpu Want to manipulate these two values , But because each read is a cache line It will cause another irrelevant value to be read in , At this time, when modifying a value , Will lead to another cpu The operation of another value is invalid ( False sharing )
- Problem solving : Space for time ( Define multiple Long Type variables populate cache lines )
public class Demo1 {
public volatile long m = 0L; // Unfilled cache line Time is 2000 about
public volatile long m = 0L,l1,l2,l3,l4,l5,l6; // fill cache line(cache line padding) Time is 800 about
// In filling cache line Every time after cpu Read one cache line
// In unfilled cache line Before , Each read d[0] when , because d[0] The size of is less than 64byte So I will d[1] Read in , So when one is distributed in different cpu Threads of access different d The elements of
It will lead to data consistency problems ( Lock bus 、 Agreement of conformity ), Will reduce performance
// In filling cache line after , Each read d[0] when , because d[0] The size of is close to 64byte Then only the current element will be read and operated , So when located in other cpu Read by other threads d[1] Conduct
Operation does not affect each other , Improve performance
public static Demo1[] d = new Demo1[2];
static{
d[0] = new Demo1();
d[1] = new Demo1();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000_0000L; i++) {
d[0].m = i;
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000_0000L; i++) {
d[1].m = i;
}
});
long start = System.nanoTime();
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println((end - start) / 100_0000L);
}
}
Disorder
- Disordered reading , Only without affecting the final result ,cpu All instructions will be optimized and reordered
- Merge write (WC buffer:write combining buffer -> 4 Bytes ): In every time cpu When the data is calculated and put into memory, it will pass WCBuffer Temporary data , however WCBuffer Only 4 The size of bytes , If the result of data calculation is less than WCBuffer The size of will be directly put into it and flushed back to memory , Otherwise, it will be filled first WCBuffer And flush back to memory at the same time CPU After the calculation, the remaining data will wait WCBuffer Continue to refresh back to memory after idle , Then there will be performance problems
Order guarantees
Hardware memory barrier
- cpu Level ( be based on intel x86):
- sfence(store fence): be located sfence The write command before the instruction occurs first after the instruction
- lfence(load fence): be located lfence The read command before the instruction occurs first in the read command after the instruction
- mfence(storeload fence): be located mfence The read-write command before the instruction occurs first in the read-write command after the instruction
- java Assembly level :lock Instructions
jvm standard
Specific implementation based on hardware
- loadload
- storestore
- storeload
- loadstore
volatile Realization
Bytecode
acc_volatile
jvm
Add a barrier before and after the command
os
win
lock
Linux
barrier +lock
synchrinized Realization
Bytecode
Method
acc_synchronized
Code block
moniterenter moniterexit
jvm
c c++ Call the underlying synchronization mechanism of the operating system
OS
lock comxchg xxx
Object memory layout
Object creation process
- class loading
- class linking(verification prepare resolution)
- class initialization
- Application memory
- Object attributes are given default values
- Call constructor
- Object property initialization
- Call constructor
The composition of objects
Common object
- Object head :markword 8
- classpointer: Class pointer , Point to the class
- The instance data
- padding: The space occupied by filling objects is 8 Integer multiple
Array objects
- Object head :markword 8
- classpointer: Class pointer , Point to the class
- Length of array
- Array data
- padding: The space occupied by filling objects is 8 Integer multiple
Size of object
- Object head :8byte
- classpointer: primary 8 byte ,jvm Default on UseCompressClassPointer after 4byte
- Oops:Ordinary object pointer size, The default is 8 Bytes , By using :XX:+UseCompressOops After compression, it is half
- data size
- fill 8 Integer multiple
Composition of object header

- lock : Lock or not 2bit
- Biased locking :1bit
- Generational age :4bit
- Once an object is calculated identityhashcode You cannot enter the locked state
Object positioning
- Handle to the pool
- Direct to
JMM
Basic division
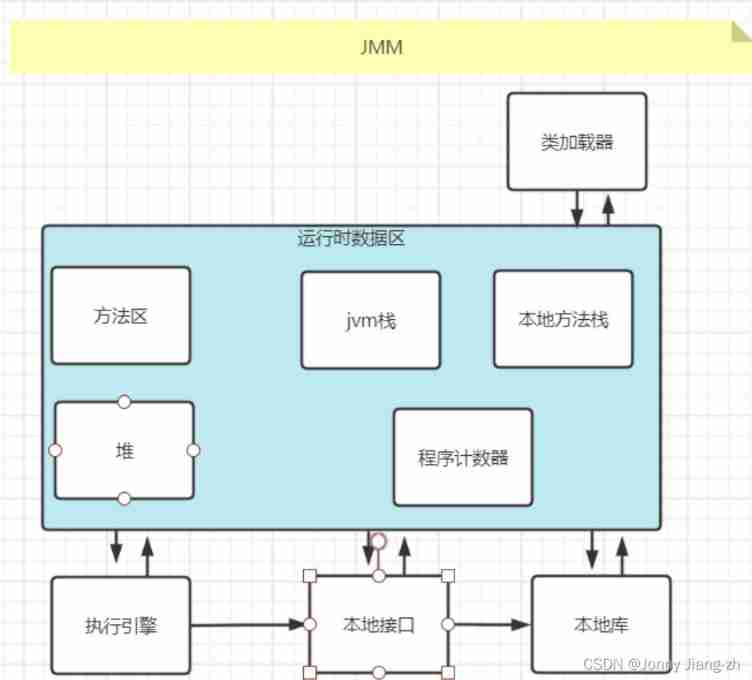
Method area
- 8 Before : Forever permanent gen,fgc No recovery
- 1.8 after : Meta space meta space
jvm Stack ( The sub elements are stack frames )
Local variable table
Include parameter list 、 Custom parameters 、this( Example method )
The stack of operands
Record the value of the operation
Dynamic links
Implement value reference conversion when checking that there is a symbol reference that is converted to a value reference
Method return address
Record the address to which the returned value should be returned
Interview questions
Code 1:
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 8;
i = i++; // i++ It is the self increment of the variable value on the local variable table , and i = xx, Is to pop up the value at the top of the operand stack and assign it to i, This is why the result is still 8
System.out.println(i); // The result is 8
}
}
Bytecode 1:
0 bipush 8 // Like putting values in the operand stack
2 istore_1 // Pop up the value at the top of the operand stack and assign it to the local variable table with the subscript 1 On variables of
3 iload_1 // Subscript the local variable table as 1 The value of the variable of is pushed into the operand stack
4 iinc 1 by 1 // Subscript the local variable table as 1 Add one to the value of the variable of
7 istore_1 // Pop up the value at the top of the operand stack and assign it to the local variable table with the subscript 1 On variables of
8 getstatic #2 <java/lang/System.out : Ljava/io/PrintStream;>
11 iload_1
12 invokevirtual #3 <java/io/PrintStream.println : (I)V>
15 return
Code 2:
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 8;
i = ++i; // ++i It is the self increment of the variable value on the local variable table , and i = xx, Is to pop up the value at the top of the operand stack and assign it to i, This is why the result is 9
System.out.println(i); // The result is 8
}
}
Bytecode 2:
0 bipush 8 // take 8 Into the stack of operands
2 istore_1 // Subscript the local variable table as 1 The variable of gives the value of the top of the operand stack
3 iinc 1 by 1 // Subscript the local variable table as 1 The value of the variable plus 1
6 iload_1 // The following table in the local variable table is 1 The value of the variable of is put into the operand stack
7 istore_1 // Pop up the value of the element at the top of the operand stack and assign it to the local variable table. The following table is 1 Value
8 getstatic #2 <java/lang/System.out : Ljava/io/PrintStream;>
11 iload_1
12 invokevirtual #3 <java/io/PrintStream.println : (I)V>
15 return
jvm Instruction set
invoke series
invoke_static
Call static methods
invoke_virtual
Call methods that support polymorphism ( Include final Examples of embellishments )
invoke_special
call private Method or construction method
invoke_dynamic
adopt lambda Expression related methods . Be careful :() -> {} Will create a in the current class Lambda Inner class and create an inner class again in this inner class
The garbage
Definition
No reference to the object
The way of judging
Quoting Technology (python)
The circular reference problem cannot be solved
The root can reach
Can be used as the type of root :
- Thread stack variables : One method calls another
- Static variables
- Constant pool
- JNI The pointer (java native interface)
Garbage collection algorithm
Mark —— eliminate (mark sweep)
Scan first and then remove the garbage
It is applicable to the situation where there are many surviving objects
Need to traverse twice , Low efficiency , And will produce a lot of space debris
Copy (copy)—— The new generation
Divide the space into two pieces , First traverse to determine which objects are not garbage , Then copy to another space , Then clear the whole space
You need to traverse it once , More efficient , But it will change the address of the object in memory , There is a little trouble in the follow-up
Mark —— Compress (mark compact)
Gather all objects that cannot be cleared
Two iterations , Low efficiency , It is better to
Generational garbage collection algorithms
except Epsilon ZGC Shenandoah All the others use logical generational models
G1 Use logical generation , Physics has no generations
In addition, they are all logical generations 、 Physical generation
- The new generation : Copy algorithm
- Old age : Clearly marked 、 Tag compression
Logical allocation of heap space
Old age : The new generation =2:1
eden:survivor=8:2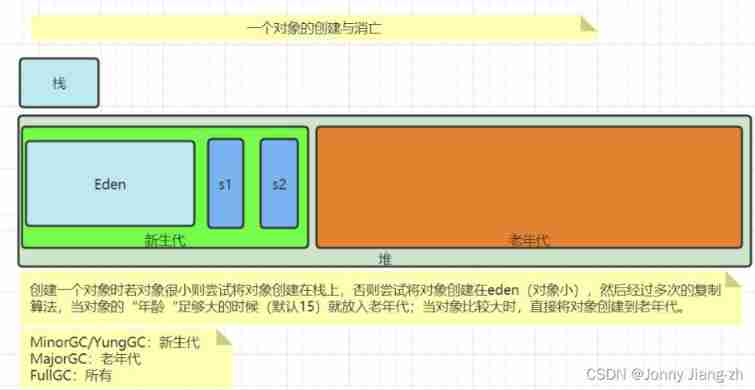
Method area (method area)
Forever perm gen(1.8 Before )
Meta space meta space(1.8 after )
Object on the stack
On the stack
Small objects
No escape analysis
Scalar substitution
Thread local cache TLAB(thread local allocate buffer)
Forever
eden
When does the subject enter the old age
- When you are older than XX:MaxTenuringThreshold Put it in the old generation
- Dynamic allocation : When survivor When the total age of the surviving objects exceeds half, they will enter the elderly generation
- Distribution guarantee : When survivor When there is not enough space , Space guarantee allocation enters the elderly generation
Common garbage collectors
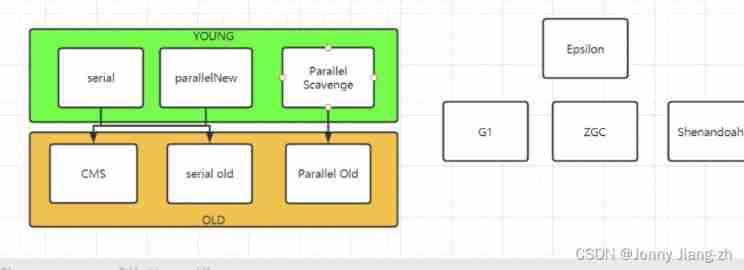
serial
Single thread call recycling ,stop-the-world
serialOld
Single thread recycling ,stop-the-world
Parallel Scavenge
Concurrent recovery ,stop-the-world
Parallel Old
Concurrent recovery ,stop-the-world
ParallelNew
be based on parallel scavenge enhance , In combination with CMS
CMS(concurrent mark sweep)
Concurrent tags 、 Clear away rubbish
The process
- Initial marker
- Concurrent Tags
- Re label
- Concurrent cleanup ( Mark clear )
problem
- memory fragment( Using tags —— Compression algorithm )
- -XX:+UseCompactAtFullCollection -XX:+CMSGCsBeforeCompaction
- floating garbage( During concurrent cleanup )
- Concurrent Mode Failure
- Lower the departure CMS The threshold of :-XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction Default 92%
- PromotionFaild
- The solution is similar to , Keep enough space for the elderly
- Concurrent Mode Failure
G1
1.8 mature ,1.9 Default
Use tricolor markers
ZGC
Shenandoah
Epsilon
Use GC
- -XX:+UseSerialGC => Serial + SerialOld
- -XX:+UseParallelGC => ParallelScavenge + SerialOld (ParallelScavenge +ParallelOld 1.8 Default )
- -XX:+UseParallelOldGC => Parallel Scavenge + Parallel Old
- -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC => ParaNew + CMS + SerialOld( When cms When there is too much debris space in the implementation process, it will be used SerialOld)
- -XX:+UseG1GC
JVM tuning
Command Introduction
classification
- -xxxxx: Represents a standard command
- -x:xxx: Indicates the command used in a specific version
- -xx:xxx: Indicates instability , The next version may not support
Basic concepts
- throughput : User program execution time / ( User program execution time + Garbage collection time )
- response time :STW,stw The less response time, the higher
- Pursue throughput :Parallel Scavenger + Parallel + Old, Pursue response time :(1.8)G1、ParallelNew + CMS, You can also improve throughput when the response time meets
What is tuning
- According to the needs jvm Planning and pre tuning
- Optimize operation jvm Environmental Science
- solve jvm All kinds of problems in the process of operation (OOM)
Problem solving
- CPU Utilization rate reaches 100%
- Through the first top Check the occupation of that process cpu The most resources top
- Find the thread in the process CPU The most resources top -Hp
- adopt jstack Save the stack of threads
- Finding out which method is more time-consuming jstack
- CPU Memory usage is soaring
- Export heap memory (jmap)
- analysis (jprofiler、jstat、jvisualvm..)
- monitor CPU
- jprofiler、jstat、jvisualvm
Specifically
- View object creation (OOM)
- jmap => OOM
- -histo Check how many objects are created
- -dump Create dump file , Generally, the memory is too big, and there is a jam , When there is a polymorphic server backup , have access to
- The graphical interface : Generally used for testing (jconsole、jvisualvm、jprofiler)
- arthas Online monitoring
- jmap => OOM
- Check thread operation
- jstack
command
-XX:+PrintCommandLineFlags
-XX:+PrintContainerInfo
-XX:+TraceClassLoading
-XX:+TraceClassResolution
-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError
-XX:HeapDumpPath=path
-XX:+DisableExplicitGC
-XX:+PrintGC
-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC
-XX:+UseG1GC
-XX:+UseParallelGC
-XX:+UseParallelOldGC
-XX:+UseParNewGC
-XX:+UseSerialGC
-XX:+PrintFlagsFinal
Concurrent recycling algorithm
G1
Tri-colour marking ( Concurrent Tags )
There are different states for objects
- Concept
- black : Indicates that the object itself and the attributes within the object are marked as non garbage
- gray : Indicates that the object itself is marked as non garbage, But the attributes in the object are not marked as non garbage
- white : Indicates that the object is not marked as non garbage
- problem :
- Missing mark : Indicates that during the marking process, the reference that originally points to a white object suddenly disappears , And there is a black object pointing to this object
- Necessary condition : The current white object is pointed by a black marker , The reference that was originally associated with the gray object disappears
- problem : Because the black object has been marked , So the object pointed by the black object will not be scanned again when re marking , So the white object will be regarded as garbage It's recycled ( No reference points to )
- resolvent :
- increment update(CMS): Record the added references , And modify the color of the current object , So when you mark again, you will find the white object again , And mark , It won't be recycled , This method will scan the whole heap to find the direction of the original black object
- SATB(snapshot at the begining)(G1): Record deleted references , And put it on its own stack , combination CSet, In the process of re marking, the record in the stack of the object will be scanned and the white object will be found , White objects are based on their own Rset Find a black object pointing to yourself , So it will be re marked and will not be recycled
- Why? G1 Use SATB: because g1 The implementation of is to divide the heap into different region, therefore , To reduce scanning all region, So I'll use satb combination CSet You only need to scan the objects related to yourself
- Missing mark : Indicates that during the marking process, the reference that originally points to a white object suddenly disappears , And there is a black object pointing to this object
Color pointer
card table
When doing fgc You need to scan the whole old District , More time-consuming , Therefore, based on bitmap Of cardtable It was born , If old There are objects pointing to y The area will be marked dirtycard, When scanning, you only need to scan cardtable that will do
CSet(collection set)
Records other object references that the object points to
Rset(Remember Set)
Records all other object references to this object
fibers
Threads vs fibers
- One in kernel mode 、 One is in user mode
- A lightweight 、 A heavyweight
边栏推荐
- [paper reading] semi supervised left atrium segmentation with mutual consistency training
- Egr-20uscm ground fault relay
- English语法_名词 - 所有格
- C nullable type
- 关于服装ERP,你知道多少?
- AI人脸编辑让Lena微笑
- Digital innovation driven guide
- Getting started with DES encryption
- JVM (XX) -- performance monitoring and tuning (I) -- Overview
- 爬虫练习题(三)
猜你喜欢
什么是消息队列?
Mapbox Chinese map address
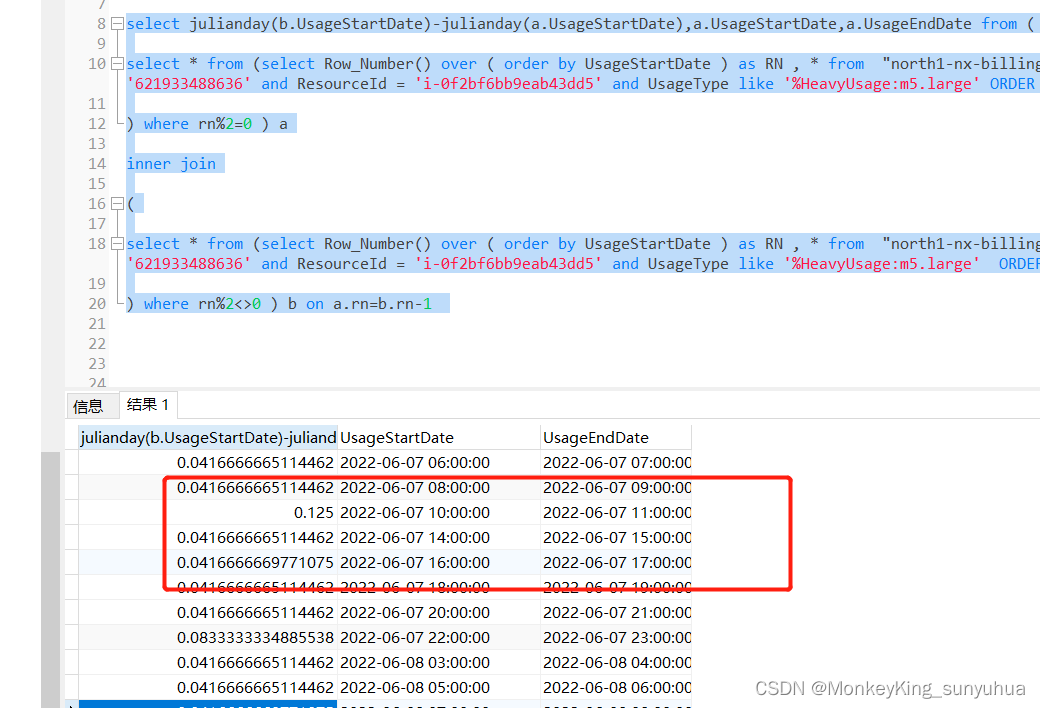
sql查询:将下一行减去上一行,并做相应的计算
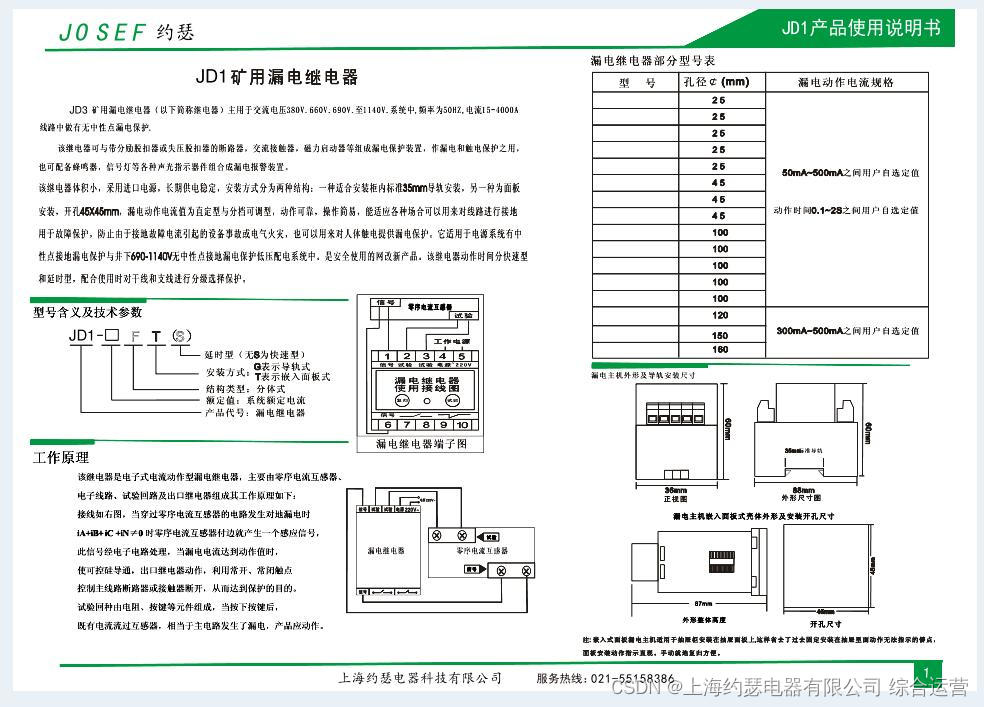
Leakage relay jd1-100
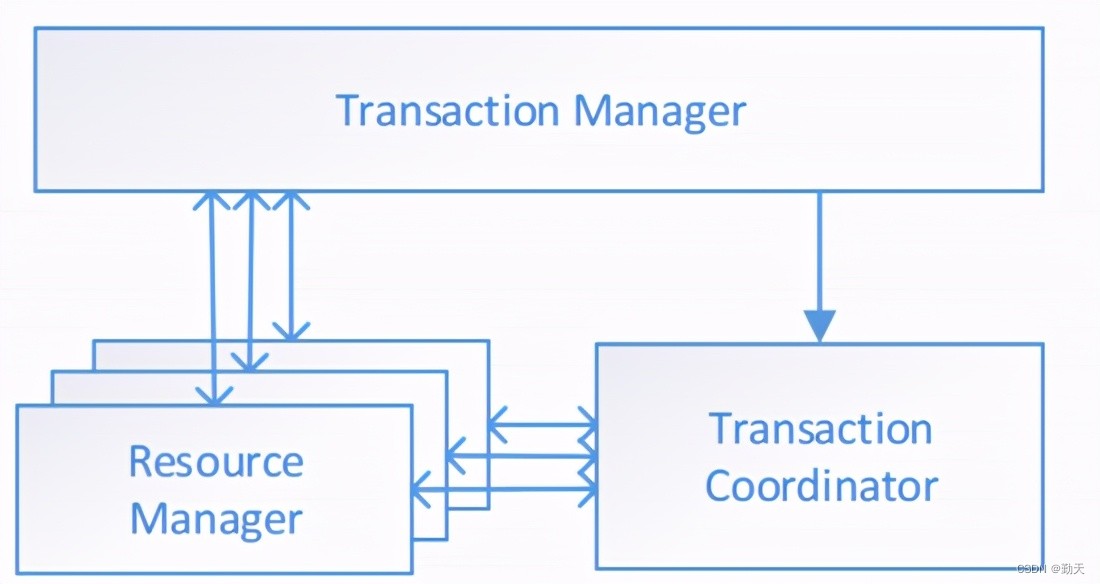
2pc of distributed transaction solution
Lombok插件
AI face editor makes Lena smile

Zhang Ping'an: accelerate cloud digital innovation and jointly build an industrial smart ecosystem
LabVIEW is opening a new reference, indicating that the memory is full
Design, configuration and points for attention of network specified source multicast (SSM) simulation using OPNET
随机推荐
消息队列:消息积压如何处理?
Mapbox Chinese map address
Preliminary practice of niuke.com (9)
基于NCF的多模块协同实例
什么是消息队列?
Pinduoduo product details interface, pinduoduo product basic information, pinduoduo product attribute interface
Most commonly used high number formula
Common skills and understanding of SQL optimization
How Alibaba cloud's DPCA architecture works | popular science diagram
async / await
AI人脸编辑让Lena微笑
Différenciation et introduction des services groupés, distribués et microservices
If you want to choose some departments to give priority to OKR, how should you choose pilot departments?
Use Zhiyun reader to translate statistical genetics books
Unity让摄像机一直跟随在玩家后上方
Mybaits multi table query (joint query, nested query)
LabVIEW is opening a new reference, indicating that the memory is full
TabLayout修改自定义的Tab标题不生效问题
1.AVL树:左右旋-bite
sql优化常用技巧及理解