当前位置:网站首页>Creative mode 1 - single case mode
Creative mode 1 - single case mode
2022-07-05 23:13:00 【Dutkig】
After learning C++ Knowledge about static members of , Let's first understand the simplest design pattern : The singleton pattern .
The motivation of the singleton model
For some classes of a software system , There is no need to create multiple instantiated objects , Like Windows System task manager or recycle bin , No matter how many times we click, only one window will pop up , Because if multiple windows pop up , It's actually a repeating object , It is bound to waste system resources , Therefore, we need to ensure that there is only one instance of a class in the system , When this instance is created successfully , We can no longer create other objects of the same type , All operations can only be based on this unique instance , For example, ensure the uniqueness of objects , We propose a singleton pattern .
From the perspective of concrete implementation :
- Singleton mode only provides private constructors ;
- The class definition contains a static private object of the class ;
- This class provides a static common function to create or obtain its own static private object .
1、 The hungry man mode
An example of the hungry man model is The main function has been generated before it runs ( This is because the initialization of static data members is completed before the main function runs ), Because it's hungry , Very anxious .^ _ ^…
class Object
{
private:
int value;
static Object instance;
private:
Object(int x = 0):value(x){
}// Objects cannot be built outside anywhere else
Object(const Object & obj) = delete;// Prevent copying construction objects
Object & operator=(const Object & obj) = delete;// Prevent building objects through assignment statements
public:
static Object & GetInstance()// If you do not return by reference here, you will transfer the copy structure as a transition
{
// But our copy structure has been deleted , Unable to complete . Another solution is to return with a pointer
return instance;
}
};
// Static member initialization
Object Object::instance();
int main()
{
Object & obja = Object::GetInstance();
Object & objb = obja.GetInstance();
cout<<&obja<<endl;
cout<<&objb<<endl;
}
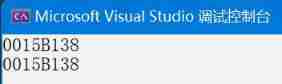
We can see ,obja and objb All represent the same object :
Be careful : The above way Objects created : yes Thread safety Of , When two threads modify it respectively , It's not thread safe .
such as : Put the following two functions into two threads
void funa()
{
Object & obja = Object::GetInstance();
cout<<&obja<<endl;
}
void funb()
{
Object & objb = Object::GetInstance();
cout<<&objb<<endl;
}
#include<thread>
int main()
{
thread thra(funa);
thread thrb(funb);
thra.join();
thrb.join();
return 0;
}
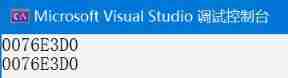
No matter how many threads call , When building objects, we all get unique instantiated objects
summary :
experience : Why should we define this design pattern as hungry man singleton pattern ?
namely : Like a hungry man , Create instances whether you need them or not , That is, create a good instance when the class is generated , This is a practice of exchanging space for time . As a hungry man , Embodies its essence ——“ All I want ”.
- advantage : Instantiate when the program is loaded , After that, the operation efficiency will be higher
- shortcoming : Because the program is instantiated when it is loaded , If there is no further operation on this class , Will lead to a waste of memory .
Lazy singleton mode
An example of lazy mode is lazy , So only when someone wants to use an instance new, Have to build .
class Object
{
private:
int value;
static Object *pobj;
private:
Object(int x = 0):value(x){
}
Object(const Object & obj) = delete;
Object & operator=(const Object & obj) = delete;
public:
static Object * GetInstance()
{
if(pobj == nullptr)
{
pobj = new Object();
}
return pobj;
}
};
// Static member initialization
Object* Object::pobj = nullptr;
void funa()
{
Object * pobja = Object::GetInstance();
cout<<pobja<<endl;
}
void funb()
{
Object * pobjb = Object::GetInstance();
cout<<pobjb<<endl;
}
int main()
{
thread thra(funa);
thread thrb(funb);
thra.join();
thrb.join();
return 0;
}
In our opinion, even if the running result is ok , But this code is actually thread unsafe .
Because there have been many object constructions , This is inconsistent with the original principle of the simple interest single case model
Explain in detail :
In a single thread , This kind of writing can be used correctly , But not in multithreading , This method is thread unsafe .
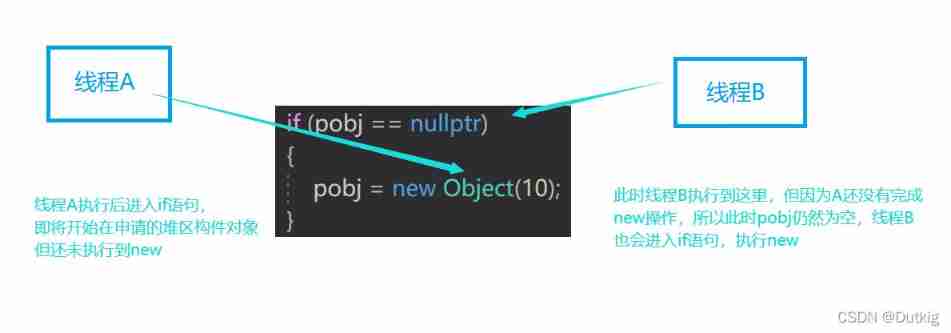
(1) If a thread A And thread B, These two threads need to access getInstance function , Threads A Get into getInstance function , And detect if Conditions , Because it is the first time to enter ,value_ It's empty ,if Conditions established , Ready to create an object instance .
(2) however , Threads A It's possible to be OS The scheduler of is interrupted and sleep is suspended , And give control to the thread B.
(3) Threads B Also came to if Conditions , Find out value_ Still for NULL, Because the thread A It was interrupted before it could be constructed . At this point, suppose the thread B Finished creating the object , And return smoothly .
(4) After that thread A Awakened , Carry on new Create the object again , thus , Two threads build two object instances , This destroys uniqueness .
in addition , There are also memory leaks ,new What comes out has never been released
So how to solve this problem ??—— Join in Thread mutex
#include<mutex>
std::mutex mtx;// Build a lock object
class Object
{
private:
int value;
static Object* pobj;
private:
Object(int x = 0) :value(x) {
}
Object(const Object& obj) = delete;
Object& operator=(const Object& obj) = delete;
public:
static Object* GetInstance()
{
if (pobj == nullptr)
{
lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
if (pobj == nullptr)// Judge again , Ensure that multiple threads will not enter at the same time during locking
{
pobj = new Object(10);
}
}
return pobj;
}
};
// Static member initialization
Object* Object::pobj = nullptr;
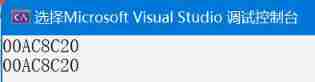
At this time, we found that : The problem is really solved 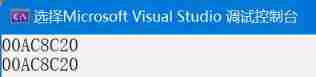
Actually , At present, the lazier style is more popular, and the following one is more concise Writing : it Take advantage of static Keyword features .
class Object
{
private:
int value;
static Object* pobj;
private:
Object(int x = 0) :value(x) {
}
Object(const Object& obj) = delete;
Object& operator=(const Object& obj) = delete;
public:
static Object* GetInstance()
{
static Object instance;
return &instance;
}
};
This is thread safe , Because this instance allocates memory in the global data area , The object is initialized only once when it is created , Go deeper The explanation is : Compiler for static Initialization of static local variables , It will automatically lock and unlock .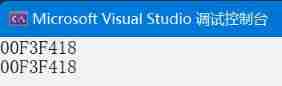
experience : Why should we define this design pattern as lazy singleton pattern ?
namely : Like a lazy man , You need to use the program to create instances , You don't need to create an instance program “ Don't bother ” To create instances , This is a time for space approach , This is reflected. “ Lazy nature ”.
边栏推荐
- Element operation and element waiting in Web Automation
- Use of metadata in golang grpc
- UART Application Design and Simulation Verification 2 - TX Module Design (Stateless machine)
- 一文搞定class的微观结构和指令
- 3D point cloud slam
- Thoroughly understand JVM class loading subsystem
- 3:第一章:认识JVM规范2:JVM规范,简介;
- 基于脉冲神经网络的物体检测
- 二叉树递归套路总结
- 透彻理解JVM类加载子系统
猜你喜欢
Getting started stm32--gpio (running lantern) (nanny level)
Three. Js-01 getting started

Hainan Nuanshen tea recruits warmhearted people: recruitment of the product experience recommender of Nuanshen multi bubble honey orchid single cluster
一文搞定class的微观结构和指令
利用LNMP实现wordpress站点搭建
Leetcode weekly The 280 game of the week is still difficult for the special game of the week's beauty team ~ simple simulation + hash parity count + sorting simulation traversal

3: Chapter 1: understanding JVM specification 2: JVM specification, introduction;
一文搞定JVM常见工具和优化策略
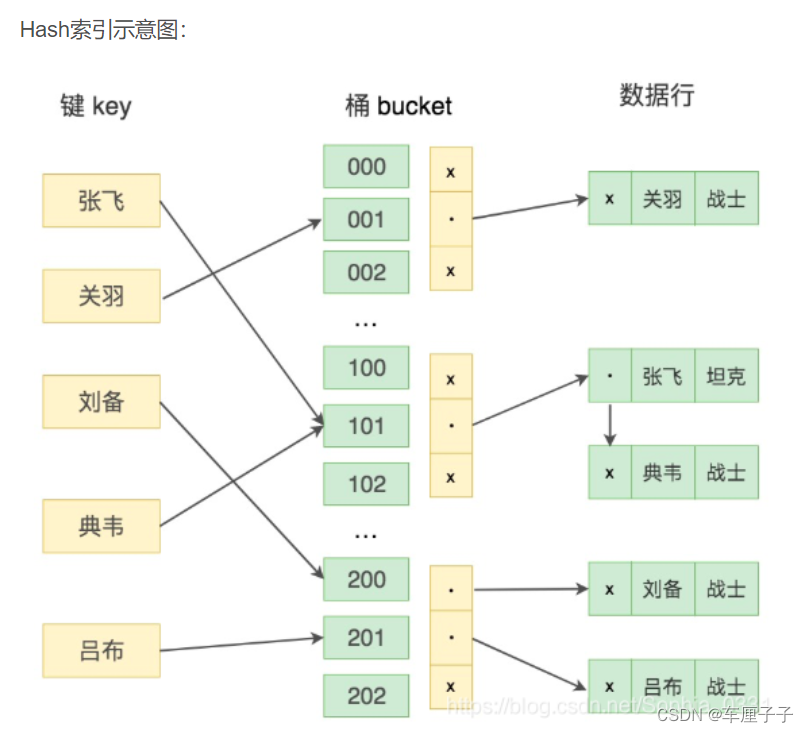
数据库基础知识(面试)
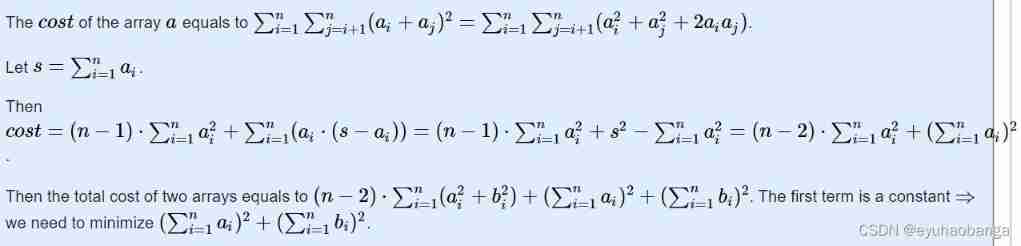
Codeforces Global Round 19
随机推荐
CJ mccullem autograph: to dear Portland
CorelDRAW plug-in -- GMS plug-in development -- new project -- macro recording -- VBA editing -- debugging skills -- CDR plug-in (2)
Dynamic memory management (malloc/calloc/realloc)
Go language implementation principle -- lock implementation principle
Thoroughly understand JVM class loading subsystem
Shell: operator
数学公式截图识别神器Mathpix无限使用教程
Marginal probability and conditional probability
TypeError: this. getOptions is not a function
LeetCode——Add Binary
Leetcode daily question 1189 The maximum number of "balloons" simple simulation questions~
Leetcode buys and sells stocks
派对的最大快乐值
One article deals with the microstructure and instructions of class
Vision Transformer (ViT)
PLC编程基础之数据类型、变量声明、全局变量和I/O映射(CODESYS篇 )
(4) UART application design and simulation verification 2 - TX module design (stateless machine)
Global and Chinese markets of industrial pH meters 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
2:第一章:认识JVM规范1:JVM简介;
What is the process of building a website