当前位置:网站首页>Mongodb learn from simple to deep
Mongodb learn from simple to deep
2022-07-07 20:18:00 【lufei0920】
Mongodb Learn from the simple to the deep
Mongodb brief introduction
MongoDB It is a database based on distributed file storage . It is a product between relational database and non relational database .
The data structure it supports is very loose , Is similar to Json Of Bson Format , Therefore, more complex data types can be stored .
Mongo The biggest feature is that it supports a very powerful query language , Its syntax is somewhat similar to that of an object-oriented query language , You can almost implement most of the functionality of a relational database single table query , It also supports indexing data .
mongodb Is one of the most versatile NoSQL Nonrelational database . from C++ Language writing .
mongodb Provided by itself S End store data , namely server; Also provide C End operation processing ( Such as inquiry, etc ) data , namely client.
SQL and NoSQL The main difference :
stay SQL Middle level relationships : database > surface > data
And in the NoSQL Is in the : database > aggregate > file
No correlation between data :
SQL How to add external associated data in , The normalization is to add a foreign key to the original table , Associate external data tables .
NoSQL You can put the external data directly into the original data set , To improve query efficiency . The disadvantages are obvious , It will be troublesome to update the associated data .
SQL The fields of each data in a table are fixed . and NoSQL A set in ( surface ) Each document in ( data ) Of key( Field ) Can be different from each other .
mongodb As a non relational database, it has advantages over relational database
Easy to expand : NoSQL There are many kinds of databases , But a common feature is the removal of the relational nature of relational databases . There is no relationship between the data , In this way, it is very easy to expand a large amount of data .
High performance : NoSQL Databases all have very high read and write performance , Especially in the case of large amount of data . This is due to its non relational , The structure of the database is simple and flexible data model : NoSQL There is no need to create fields in advance for the data to be stored , You can always store custom data formats . In a relational database , Adding and deleting fields can be a hassle . If it's a very large data table , Adding fields is a nightmare
One 、MongoDB install
1、 System command installation
1)centos System installation
yum -y install https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/7/mongodb-org/4.4/x86_64/RPMS/mongodb-org-mongos-4.4.15-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
yum -y install https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/7/mongodb-org/4.4/x86_64/RPMS/mongodb-org-shell-4.4.15-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
start-up :systemctl start mongod
stop it :systemctl stop mongod
restart :systemctl restart mongod
2) ubuntu Use in apt-get Tool installation
sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org
3) Refer to official documentation https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/tutorial/install-mongodb-on-ubuntu/
2、 Binary installation
wget https://fastdl.mongodb.org/linux/mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-4.4.15.tgz
tar -xf mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-4.4.15.tgz -C /usr/local
cd /usr/local
mv mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-4.4.15 mongodb
cd ./mongodb
mkdir data
mkdir logs
Configure environment variables /etc/profile:
export MONGODB_HOME=/usr/local/mongodb
export PATH=$PATH:$MONGODB_HOME/bin
The configuration file :
cd bin
vim mongodb.conf
## Write the following :
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /usr/local/mongodb/logs/mongodb.log
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 0.0.0.0
maxIncomingConnections: 10000
storage:
dbPath: /usr/local/mongodb/data/db
journal:
enabled: true
wiredTiger:
engineConfig:
cacheSizeGB: 1
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /usr/local/mongodb/logs/mongodb.log
processManagement:
fork: true
security:
authorization: enabled
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 0.0.0.0
maxIncomingConnections: 10000
Start stop :
./mongod -f ./mongo.conf
sudo ./mongod -f ./mongodb.conf --shutdown
Two 、MongoDB Simple use
1、mongodb Client link database
mongo [options] [db address] [file names (ending in .js)]
2、mongodb Common simple commands
View the current database :db( If the database is not switched, it is used by default test database )
View all databases :show dbs /show databases
Switch database :use db_name
db_name by show dbs Database name returned after , If the database is not , Automatically create .
Delete the current database :db.dropDatabase()
show dbs View database name
show collections Check the documents in the existing database ,collections Table for storing documents
show users To view the user
show logs View global log
help
db.help
db.stats(): Database state
db.serverStatus(): mongodb Database server status
db.getCollectionName(): View all collections Documents .
db.collections.help
db.students.insert({name:"tom",age:23}) Insert a students Documents .
show collections View this document collection
show dbs view the database
db.students.stats() see students The state of the table
db.students.insert({name:"jerry",age:40,gender:"M"}) Insert another document data
db.students.find() View this document set
db.students.count() Statistics students How many documents are there in
3、mongodb Commands for collections
Create collections manually :
db.createCollection(name,options)
db.createCollection("stu")
db.createCollection("sub", { capped : true, size : 10 } )
Parameters capped: The default value is false Means no upper limit is set , The value is true Indicates setting the upper limit
Parameters size: Number of bytes occupied by the collection . When capped The value is true when , This parameter needs to be specified , Indicates the upper limit size , When the document reaches the upper limit , Will overwrite the previous data , The unit is byte
View set :show collections
Delete the collection :db. Collection name .drop()
Check whether the set has an upper limit : db. Collection name .isCapped()
4、mongodb Common data types
Object ID: file ID/ Data ID, The primary key of the data
String: character string , The most commonly used , Must be effective UTF-8
Boolean: Store a Boolean value ,true or false
Integer: The whole number can be 32 Bit or 64 position , It depends on the server
Double: Floating point numbers
Arrays: Array / list
Object: mongodb One of the data in / file , That is, documents are nested
Null: Storage null value
Timestamp: Time stamp , From 1970-1-1 The total number of seconds up to now
Date: Storing the current date or time UNIX Time format
Be careful
Every document has an attribute , by _id, Make sure every document is unique ,mongodb By default _id A primary key
You can set it manually _id Value , If not provided , that MongoDB Provides a unique... For each document _id, The type is objectID
objectID It's a 12 Hexadecimal number of bytes , Two bits per byte , Is the total 24 Bit string :
front 4 Bytes are the current timestamp
Next 3 Byte machine ID
Next 2 In bytes MongoDB The service process of id
Last 3 A byte is a simple incremental value
5、mongodb Addition, deletion and modification of
01) insert data
command :db. Collection name .insert(document)
db.stu.insert({name:'gj', gender:1})
db.stu.insert({_id:"20220704", name:'gj', gender:1})
02)mongodb preservation
command :db. Collection name .save(document)
db.stu.save({_id:'20220704', name:'gj', gender:2})
db.stu.save({name:'gj', gender:2})
db.stu.find()
03)mongodb Query for
command :db. Collection name .find()
Method find(): Inquire about
db. Collection name .find({ Condition document })
Method findOne(): Inquire about , Just return the first one
db. Collection name .findOne({ Condition document })
Method pretty(): Format the results ; Unable to join findOne() Use it together !
db. Collection name .find({ Condition document }).pretty()
04) Comparison operator
be equal to : Default is equal to judgment , There are no operators
Less than :$lt (less than)
Less than or equal to :$lte (less than equal)
Greater than :$gt (greater than)
Greater than or equal to :$gte
It's not equal to :$ne
05) Logical operations
and: stay json Write multiple conditions in
The query age is greater than or equal to 18, And the gender is true Of the students
db.stu.find({age:{$gte:18},gender:true})
or: Use $or, Value is an array , Each element in the array is json
Query age is greater than 18, Or gender is false Of the students
db.stu.find({$or:[{age:{$gt:18}},{gender:false}]})
Query age is greater than 18 Or male sex , And the name is Guo Jing
db.stu.find({$or:[{age:{$gte:18}},{gender:true}],name:'gj'})
06) Range operation
Use $in, $nin Determine whether the data is in an array
Query age is 18、 28 Of the students
db.stu.find({age:{$in:[18,28,38]}})
07) regular expression
Use $regex Write regular expressions
Inquire about name With ' yellow ' Initial data
db.stu.find({name:{$regex:'^ yellow '}})
08) Custom query
mongo shell It's a js Execution environment
Use $where Write a function , Return data that meets the criteria
Query age is greater than 30 Of the students
db.stu.find({
$where:function() {
return this.age>30;}
})
09)ship and limit
Method limit(): Used to read a specified number of documents
db. Collection name .find().limit(NUMBER)
Inquire about 2 Student information
db.stu.find().limit(2)
Method skip(): Used to skip a specified number of documents
db. Collection name .find().skip(NUMBER)
db.stu.find().skip(2)
Use at the same time
db.stu.find().limit(4).skip(5)
db.stu.find().skip(5).limit(4)
These two effects are the same , It's all first ship after limit.
Be careful : First use skip In the use of limit Is more efficient than the former
10) Projection
In the returned result of the query , Select only the necessary fields
command :db. Collection name .find({},{ Field name :1,...})
Parameters are fields and values , The value is 1 Presentation display , The value is 0 Don't show
Particular attention :
about _id Columns are displayed by default , If not shown, it needs to be set to 0
Other fields that are not displayed cannot be set to 0
db.stu.find({},{_id:0,name:1,gender:1})
11) Sort
Method sort(), Used to sort query results according to specified fields
command :db. Collection name .find().sort({ Field :1,...})
Parameters 1 Arrange... In ascending order
Parameters -1 Arrange... In descending order
Descending by sex , And then in ascending order according to age
db.stu.find().sort({gender:-1,age:1})
12) Number of Statistics
Method count() Used to count the number of documents in the result set
command :db. Collection name .find({ Conditions }).count()
command :db. Collection name .count({ Conditions })
db.stu.find({gender:true}).count()
db.stu.count({age:{$gt:20},gender:true})
14)mongodb Update
db. Collection name .update({query}, {update}, {multi: boolean})
Parameters query: Query criteria
Parameters update: Update Operators
Parameters multi: Optional , The default is false, Indicates that only the first data found is updated , The value is true Means to update all the data that meet the conditions
db.stu.update({name:'hr'},{name:'mnc'}) # Overwrite and update the full-text file
db.stu.update({name:'hr'},{$set:{name:'hys'}}) # Specifies the key value update operation
db.stu.update({},{$set:{gender:0}},{multi:true}) # Update all
Be careful :"multi update only works with $ operators"
multi The parameters must be the same as $set Use it together !
15) mongodb The deletion of
db. Collection name .remove({query}, {justOne: boolean})
- Parameters query: Optional , Delete the ? The conditions of the gear
- Parameters justOne: Optional , If it is set to true or 1, Only one , Default false, Delete all
3、 ... and 、MongoDB The aggregation operation of
1、mongodb What is the aggregation of
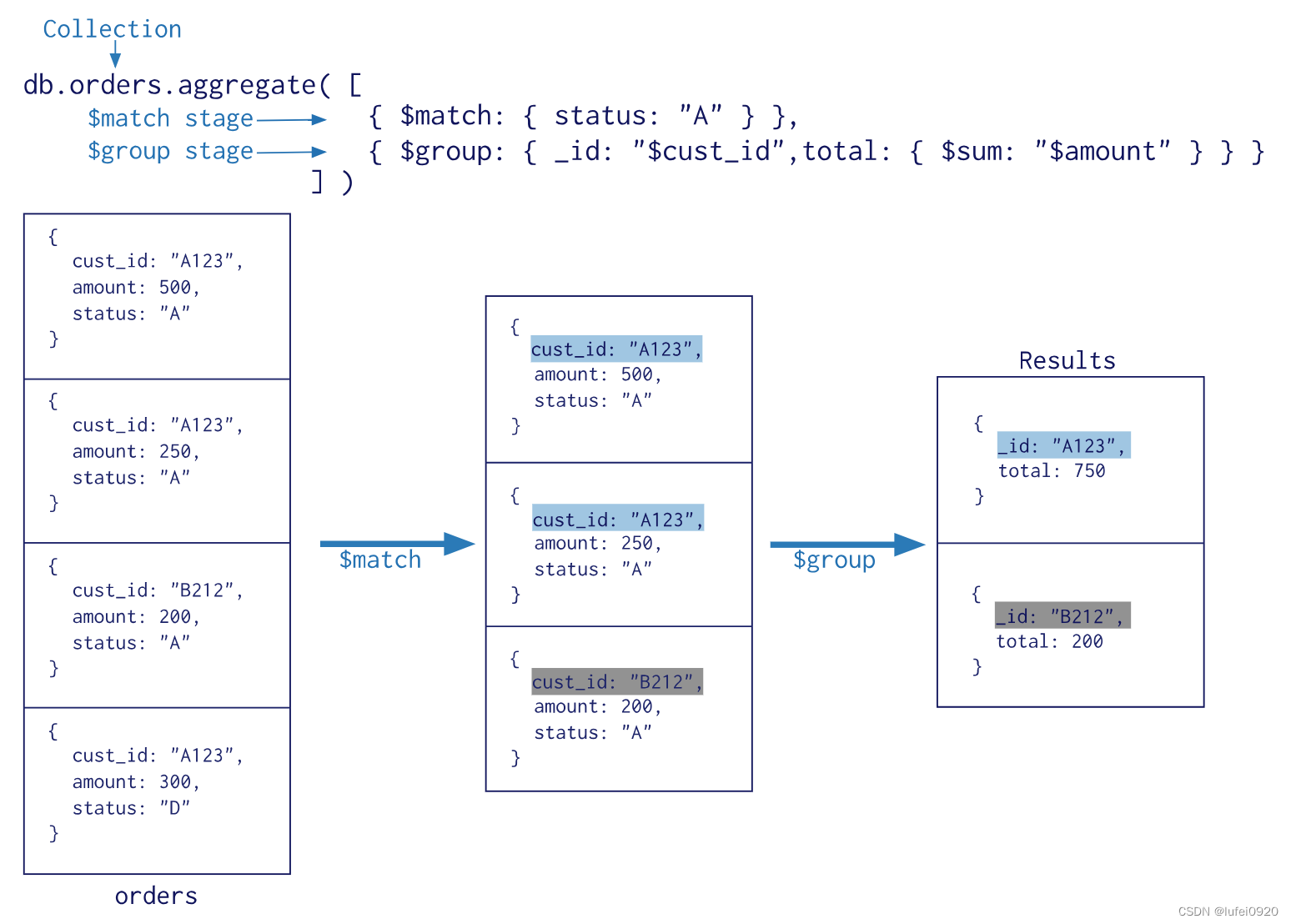
polymerization (aggregate) It's an aggregation pipeline based on data processing , Each document passes through multiple stages (stage) The pipes that make up , The pipes of each stage can be grouped 、 Filtering and other functions , And then through a series of processing , Output the corresponding result .
grammar :db. Collection name .aggregate({ The Conduit :{ expression }})
2、mongodb Pipeline and expression of
1) Common pipeline commands
Common pipeline commands are as follows :
$group: Group documents in a collection , Can be used for statistical results
$match: Filtering data , Output only documents that meet the criteria
$project: Modify the structure of the input document , Such as rename 、 increase 、 Delete field 、 Create calculation results
$sort: Sort the output documents and output
$limit: Limit the number of documents returned by the aggregation pipeline
$skip: Skip the specified number of documents , And return the rest ? files
2) Common expression
grammar : expression :'$ Name '
Common expression :
$sum: Calculate the sum , $sum:1 Said to 1 Multiple count
$avg: Calculate average
$min: Get the minimum
$max: Get the maximum
$push: Insert values into an array in the result document
3、 Pipeline command $group
3.1) Group by a field
$group It is the most used of all aggregation commands , Used to group documents in a collection , Can be used for statistical results
An example is as follows :
db.stu.aggregate(
{$group:
{
_id:"$gender",
counter:{$sum:1}
}
}
)
Among them, pay attention to :
db.db_name.aggregate It's grammar , All pipeline commands need to be written in it
_id Indicate the basis of grouping , By which field , Need to use $gender Indicates that this field is selected for grouping
$sum:1 Means to treat each data as 1 Make statistics , The statistics is the number of data under the group
3.2)group by null
When we need to count the whole document ,$group Another use of is to divide the whole document into a group for Statistics
Examples are as follows :
db.stu.aggregate(
{$group:
{
_id:null,
counter:{$sum:1}
}
}
)
Among them, pay attention to :
_id:null Represents a field that does not specify a grouping , That is, count the whole document , What you get at this time counter Indicates the number of the entire document
3.3) Pivoting
Normally, when statistics are made on data of different genders , Need to know all name, It needs to be observed one by one , Put all... Through some way name Put it together , Then it can be understood as pivoting .
01、 Statistics of students of different genders
db.stu.aggregate(
{$group:
{
_id:null,
name:{$push:"$name"}
}
}
)
02、 Use $$ROOT You can put the entire document into an array
db.stu.aggregate(
{$group:
{
_id:null,
name:{$push:"$$ROOT"}
}
}
)
4、 Pipeline command $match
$match Used for data filtering , Is a command that can be used in aggregation operations , and find The difference lies in $match The operation can pass the result to the next pipeline , and find no way .
Example :
1、 Query age is greater than 20 Of the students
db.stu.aggregate(
{$match:{age:{$gt:20}}}
)
2、 Query age is greater than 20 The number of male and female students
db.stu.aggregate(
{$match:{age:{$gt:20}}},
{$group:{_id:"$gender",counter:{$sum:1}}}
)
5 Pipeline command $project
$project Used to modify the input and output structure of the document , For example, rename , increase , Delete field
An example is as follows :
1、 Query the student's age 、 full name , Output only age and name
db.stu.aggregate(
{$project:{_id:0,name:1,age:1}}
)
2、 Inquire about the life of male and female students , Output number
db.stu.aggregate(
{$group:{_id:"$gender",counter:{$sum:1}}},
{$project:{_id:0,counter:1}}
)
6、 Pipeline command $sort
$sort Used to sort the input documents and output
An example is as follows :
1、 Search for student information , In ascending order of age
db.stu.aggregate({$sort:{age:1}})
2、 Check the number of men and women , In descending order of numbers
db.stu.aggregate(
{$group:{_id:"$gender",counter:{$sum:1}}},
{$sort:{counter:-1}}
)
7、 Pipeline command $skip and $limit
$limit Limit the number of returned data
$skip Skip the specified number of documents , And return the number of remaining documents
Be careful : When used at the same time, use skip In the use of limit
An example is as follows :
1、 Inquire about 2 Student information
db.stu.aggregate(
{$limit:2}
)
2、 Query the student information starting from Article 3
db.stu.aggregate(
{$skip:3}
)
3、 Count the number of male and female students , In ascending order of number of people , Return the second data
db.stu.aggregate(
{$group:{_id:"$gender",counter:{$sum:1}}},
{$sort:{counter:-1}},
{$skip:1},
{$limit:1}
)
Four 、MongoDB Index operation of
1、mongodb Create a simple index method
grammar :db. Collection name .ensureIndex({ attribute :1}),1 Expressing ascending order , -1 Representation of descending order
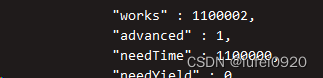
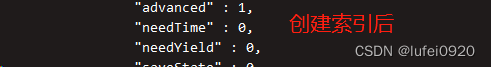
2、 Query speed comparison before and after index creation
test : Insert 100 10000 pieces of data into the database
insert data :
for(i=0;i<1000000;i++){db.t1.insert({name:'test'+i,age:i})}
Before index creation :
db.t1.find({name:'test955342'})
db.t1.find({name:'test955342'}).explain('executionStats') # Show details of the query operation
Create index :
db.t1.ensureIndex({name:1})
After index creation :
db.t1.find({name:'test955342'}).explain('executionStats')
Speed comparison before and after :
3、 Index view
View by :db. Collection name .getIndexes()

4、 Delete index
grammar :db. Collection name .dropIndex({' The index name ':1})
db.t1.dropIndex({name:1})
db.t1.getIndexes()

5、mongodb Create unique index
By default mongdb The value of the index field of can be the same , After creating a unique index , The database will check whether the value of the created index field exists when inserting data , If it exists, the data will not be inserted , But creating an index only improves query speed , At the same time, reduce the speed of database insertion .
grammar :db. Collection name .ensureIndex({" Field name ":1}, {"unique":true})
Use unique index to de duplicate data :
The value of the field specified by the unique index , If the same , Can't insert data
db.t1.ensureIndex({"name":1}, {"unique":true})
db.t1.insert({name: 'test10000'})
6、 Build composite index
In the process of data De duplication , A domain may be used to guarantee the uniqueness of data , At this time, we can consider building composite index to realize .
for example : Catch the full post information , It is not advisable to de duplicate the data by using the name of the post as the only index , Because there may be many posts with the same name
Syntax for building composite indexes :db.collection_name.ensureIndex({ Field 1:1, Field 2:1})
Be careful :
Choose whether you need to create a unique index based on your needs
Whether index fields are in ascending or descending order does not affect query efficiency in the case of a single index , But with a composite index there is an impact
Only when the amount of data is huge and the read-out operation of the database is very frequent can the index be created , If write operations are very frequent , Creating an index affects write speed
for example : If the field is 1 You need to sort the output in ascending order , Field 2 You need to sort the output in descending order , At this time, the establishment of the composite index needs to put the fields 1 Set to 1, Field 2 Set to -1
5、 ... and 、MongoDB Authority management
1、 Why do you need to set permission management
Just installed mongodb By default, permission authentication is not used to start , And MySQL Different ,mongodb No permissions were set during installation , However, the public network operating system needs to set permissions to ensure data security , So we have to learn mongodb Authority management .
2、mongodb Authority management scheme of
MongoDB There is no default administrator account , So add the administrator account first , also mongodb The server needs to turn on authentication mode when running
Users can only log in to the database where they are ( Create the user's database ), Including administrator account .
Administrators can manage all databases , But you can't directly manage other databases , Certification is required before .
3、mongodb Super administrator account creation
3.1 Create a superuser
Use admin database ( Super administrator account must be created on this database )
use admin
Create a superuser
db.createUser({"user":"pytest","pwd":"python","roles":["root"]})

Log in through super user
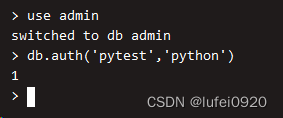
explain :python Users are created in admin So the database has to come to admin Authentication on the database
Successful authentication will return 1, Failure to return 0
If you don't switch users and login account password , Then the operation does not show any .
4、 Create a normal user
4.1 Select the database that needs to create users
use test
4.2 Create user
db.createUser({"user":"user1", "pwd":"pwd1", roles:["read"]}) # Create a normal user user1, The user is on test1 The permissions on are read-only
db.createUser({"user":"user2", "pwd":"pwd1", roles:["readWrite"]}) # Create a normal user user1, The user is on test1 The permissions on are read and write
4.3 stay admin Create ordinary users on the user database
use admin
db.createUser({"user":"python1", "pwd":"python1", roles:[{"role":"read","db":"dbname1"},{"role":"readWrite","db":"dbname2"}]})
stay admin To create a python1 user ,python1 There are two permissions for users , One more dbname1 Read only on , The other is in dbname2 Read and write on
5、 View created users
show users
6、 Delete user
use db_name # Enter the database where the account is located
db.dropUser('python') # Delete the corresponding account you want to delete
边栏推荐
- 机械臂速成小指南(十二):逆运动学分析
- Force buckle 1790 Can two strings be equal by performing string exchange only once
- 网络原理(1)——基础原理概述
- About cv2 dnn. Readnetfromonnx (path) reports error during processing node with 3 inputs and 1 outputs [exclusive release]
- c语言如何判定是32位系统还是64位系统
- The boundary of Bi: what is bi not suitable for? Master data, Martech? How to expand?
- 力扣 912.排序数组
- Jenkins 用户权限管理
- Force buckle 599 Minimum index sum of two lists
- CIS芯片测试到底怎么测?
猜你喜欢
机械臂速成小指南(十二):逆运动学分析
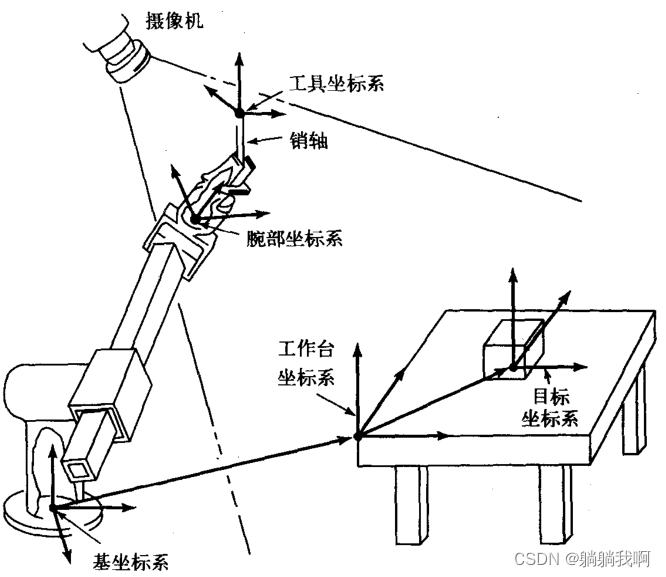
机械臂速成小指南(十一):坐标系的标准命名
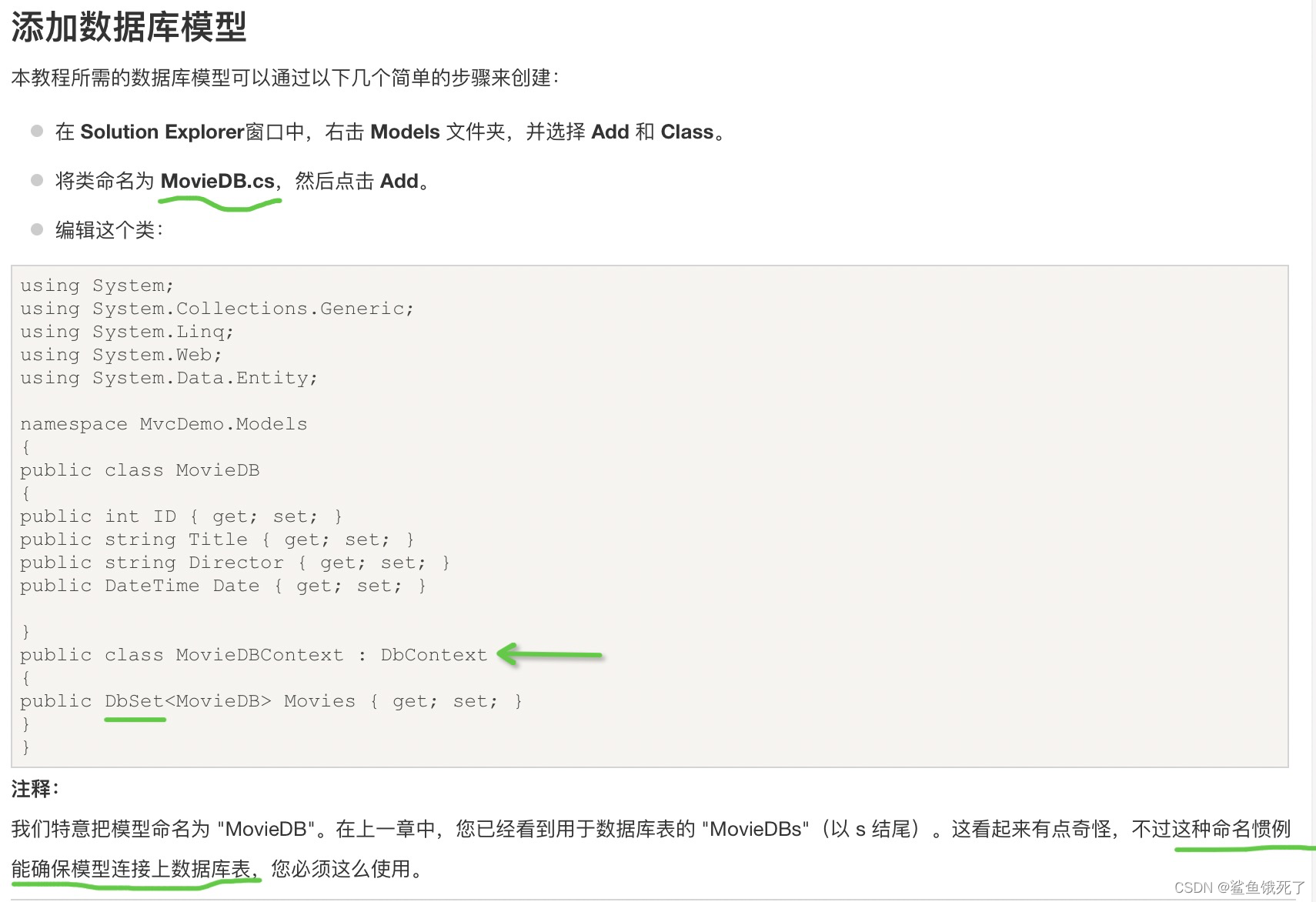
ASP. Net learning & ASP's one word

九章云极DataCanvas公司摘获「第五届数字金融创新大赛」最高荣誉!
Force buckle 2319 Judge whether the matrix is an X matrix
The boundary of Bi: what is bi not suitable for? Master data, Martech? How to expand?

Open source heavy ware! Chapter 9 the open source project of ylarn causal learning of Yunji datacanvas company will be released soon!
Leetcode force buckle (Sword finger offer 36-39) 36 Binary search tree and bidirectional linked list 37 Serialize binary tree 38 Arrangement of strings 39 Numbers that appear more than half of the tim
让这个CRMEB单商户微信商城系统火起来,太好用了!
Mrs offline data analysis: process OBS data through Flink job
随机推荐
Prometheus remote_write InfluxDB,unable to parse authentication credentials,authorization failed
Creation of kubernetes mysql8
Force buckle 674 Longest continuous increasing sequence
Implement secondary index with Gaussian redis
I wrote a markdown command line gadget, hoping to improve the efficiency of sending documents by garden friends!
《数字图像处理原理与实践(MATLAB版)》一书之代码Part2[通俗易懂]
Version selection of boot and cloud
Micro service remote debug, nocalhost + rainbow micro service development second bullet
sql 常用优化
Force buckle 599 Minimum index sum of two lists
Force buckle 1037 Effective boomerang
4G设备接入EasyGBS平台出现流量消耗异常,是什么原因?
MSE API学习
力扣 989. 数组形式的整数加法
Vulnhub's funfox2
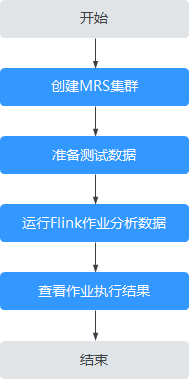
MRS离线数据分析:通过Flink作业处理OBS数据
Traversal of Oracle stored procedures
力扣 1961. 检查字符串是否为数组前缀
Force buckle 599 Minimum index sum of two lists
基于深度学习的目标检测的更新迭代总结(持续更新ing)