当前位置:网站首页>从FAST TCP到POWERTCP
从FAST TCP到POWERTCP
2022-08-02 14:12:00 【Soonyang Zhang】
POWERTCP[1]的拥塞窗口控制规则是从FAST TCP[2]发展来的,有一些不错的理论分析。
本博客涉及的公式,来自不同的论文,在不同的语境下,相同的符号含义不同。
根据论文[2]的分析,AIMD的拥塞窗口的动态变化,可以总结为:
w ˙ ( t ) = k i ( t ) ( 1 − q i ( t ) u i ( t ) ) (1) \dot w(t)=k_{i}(t)(1-\frac{q_i(t)}{u_{i}(t)})\tag{1} w˙(t)=ki(t)(1−ui(t)qi(t))(1)
- k i ( w i , T i ) k_{i}(w_i,T_{i}) ki(wi,Ti)描述的是算法的响应性——窗口的增长速度(the choice of the gain function determines the dynamic properties such as stability and responsiveness, but does not affect the equilibrium properties)。
- u i ( w i , T i ) u_{i}(w_i,T_{i}) ui(wi,Ti)描述的算法的收敛特性( the choice of the marginal utility function determines equilibrium properties such as the equilibrium rate allocation and its fairness)。
- q i q_i qi是算法使用的拥塞控制信号(in the absence of explicit feedback, the choice of congestion measure q i q_i qi s limited to loss probability or queueing delay)。
博客[3]推导了AIMD算法的随机微分方程( I = 1 w , D = w 2 I=\frac{1}{w},D=\frac{w}{2} I=w1,D=2w)。
x ˙ = 1 r t t Δ w Δ t = w r t t 2 { I ( 1 − p ) − D p } = x r t t { I ( 1 − p ) − D p } (2) \dot x=\frac{1}{rtt}\frac{\Delta w}{\Delta t}=\frac{w}{rtt^2}\{I(1-p)-Dp\}=\frac{x}{rtt}\{I(1-p)-Dp\}\tag{2} x˙=rtt1ΔtΔw=rtt2w{ I(1−p)−Dp}=rttx{ I(1−p)−Dp}(2)
整理为公式(1)的形式( 1 − p ≈ 1 1-p\approx 1 1−p≈1):
w ˙ = Δ w Δ t = w r t t ( I − D p ) = w I r t t ( 1 − D p I ) \dot w=\frac{\Delta w}{\Delta t}=\frac{w}{rtt}(I-Dp)=\frac{wI}{rtt}(1-\frac{Dp}{I}) w˙=ΔtΔw=rttw(I−Dp)=rttwI(1−IDp)
当 x ˙ = 0 \dot x=0 x˙=0,即 I ( 1 − p ) ≈ D p I(1-p)\approx Dp I(1−p)≈Dp,可以求得算法在均衡点的吞吐量:
x = 1 r t t 1 − p p (3) x=\frac{1}{rtt}\sqrt{\frac{1-p}{p}}\tag{3} x=rtt1p1−p(3)
FAST TCP的拥塞控制规则:
w ( t + δ t ) ← min { 2 w ( t ) , ( 1 − γ ) w ( t ) + γ ( b a s e R T T R T T w ( t ) + α ) } (4) w(t+\delta t)\gets \min\{2w(t),(1-\gamma)w(t)+\gamma(\frac{baseRTT}{RTT}w(t)+\alpha)\}\tag{4} w(t+δt)←min{ 2w(t),(1−γ)w(t)+γ(RTTbaseRTTw(t)+α)}(4)
先不考虑 2 w ( t ) 2w(t) 2w(t)的约束项,整理一下上式:
w ( t + δ t ) ← w ( t ) + γ ( α − R T T − b a s e R T T R T T w ( t ) ) (5) w(t+\delta t)\gets w(t)+\gamma(\alpha-\frac{RTT-baseRTT}{RTT}w(t))\tag{5} w(t+δt)←w(t)+γ(α−RTTRTT−baseRTTw(t))(5)
其中 q = R T T − b a s e R T T q=RTT-baseRTT q=RTT−baseRTT描述的链路的缓冲区占用情况。当q较小的时候, α − q R T T w ( t ) ≥ 0 \alpha-\frac{q}{RTT}w(t)\geq0 α−RTTqw(t)≥0,FAST TCP增加窗口值。当q较大的时候,FAST TCP减少窗口值。当 α − q R T T w ( t ) = 0 \alpha-\frac{q}{RTT}w(t)=0 α−RTTqw(t)=0,求得算法在均衡点达到的理论吞吐量:
x = α q (6) x=\frac{\alpha}{q}\tag{6} x=qα(6)
FAST TCP和Vegas在均衡点的理论吞吐量相同( FAST TCP has the same equilibrium properties as TCP Vegas)[4][5]。博客[4]中的 α \alpha α的单位是毫秒,本文的 α \alpha α的单位是数据包增量。
公式(5)可以不太严谨地整理为公式(1)的形式。
w ˙ = w ( t + δ t ) − w ( t ) δ t = γ α δ t ( 1 − q α × r t t / w ) (7) \dot w=\frac{w(t+\delta t)-w(t)}{\delta t}=\frac{\gamma\alpha}{\delta t}(1-\frac{q}{\alpha\times rtt/w})\tag{7} w˙=δtw(t+δt)−w(t)=δtγα(1−α×rtt/wq)(7)
POWERTCP的拥塞控制规则,是FAST TCP的扩展:
w i ( t + δ t ) ← γ ( w i ( t ) e f ( t ) + α ) + ( 1 − γ ) w i ( t ) (8) w_i(t+\delta t)\gets \gamma(w_i(t)\frac{e}{f(t)}+\alpha)+(1-\gamma)w_i(t)\tag{8} wi(t+δt)←γ(wi(t)f(t)e+α)+(1−γ)wi(t)(8)
f ( t ) f(t) f(t)是从网络中获取的拥塞信号, e e e是某种常量(拥塞控制算法意图靠近的值)。将其整理为公式(1)的形式:
w ˙ = w ( t + δ t ) − w ( t ) δ t = γ α δ t ( 1 − f ( t ) − e α × f ( t ) / w ) (9) \dot w=\frac{w(t+\delta t)-w(t)}{\delta t}=\frac{\gamma\alpha}{\delta t}(1-\frac{f(t)-e}{\alpha\times f(t)/w})\tag{9} w˙=δtw(t+δt)−w(t)=δtγα(1−α×f(t)/wf(t)−e)(9)
论文在附录中有几个论断: - 当 e = B × T , f ( t ) = q l e n + B × T e=B\times T,f(t)=q_{len}+B\times T e=B×T,f(t)=qlen+B×T,当 γ = 1 \gamma=1 γ=1的时候,公式(8)反映的是HPCC[6]的拥塞控制规则(不完全相同,缺少 η \eta η)。
- 当 e = 1 , f ( t ) = q ˙ B + 1 e=1,f(t)=\frac{\dot q}{B}+1 e=1,f(t)=Bq˙+1,即算法采用时延梯度作为网络拥塞信号。公式(8)可以重写为 w i ( t + δ t ) ← w ( 1 − γ q ˙ + B q ˙ ) + γ α w_i(t+\delta t)\gets w(1-\frac{\gamma}{\dot q + B}\dot q)+\gamma\alpha wi(t+δt)←w(1−q˙+Bγq˙)+γα。忽略分母中的 q ˙ \dot q q˙项,公式(8)大致反映的是TIMELY[7]的拥塞控制规则。
根据拥塞控制信号的不同,作者将现有的拥塞控制算法划分为两类:voltage-based CC和current-based CC。voltage-based CC的拥塞信号是网络中的绝对值(loss,delay,ECN),而current-based CC的拥塞信号是网络中的梯度值(rtt gradient)。网络的电压值定义为BDP和缓冲区长度的和,电流值与网络中流速率 ( λ \lambda λ) 相关。网络缓冲区占用长度可以表示为 q ˙ = ( ∑ i λ i ) − B = λ − B \dot q=(\sum_{i}\lambda_{i})-B=\lambda-B q˙=(∑iλi)−B=λ−B。
论文中给出了一个表格。
| quantity | analogy |
|---|---|
| Total transmission rate (network flow) | Current ( λ \lambda λ) |
| BDP+buffered bytes (network effort) | Voltage(V) |
| Current × \times ×Voltage | Power( Γ \Gamma Γ) |
PowerTCP就是一种基于功率的拥塞控制算法,定义 Γ \Gamma Γ函数作为网络拥塞信号。
f ( t ) = Γ ( t ) ⏟ Power = ( q + B × τ ) ⏟ Voltage × λ ⏟ Current (10) f(t)=\underbrace{\Gamma(t)}_{\text{Power}}= \underbrace{(q+B\times \tau)}_{\text{Voltage}}\times \underbrace{\lambda}_{\text{Current}}\tag{10} f(t)=PowerΓ(t)=Voltage(q+B×τ)×Currentλ(10)
| symbol | meaning |
|---|---|
| λ \lambda λ | 网络数据流速率和 |
| B B B | 网络瓶颈链路容量 |
| τ \tau τ | 链路往返传播时延 |
| q q q | 网络缓冲区占用长度 |
算法定义 e = B 2 τ e=B^2\tau e=B2τ。PowerTCP定义的拥塞信号需要网络路由设备反馈信息,是一种应用于数据中心的拥塞控制算法。而其扩展版本 θ − P o w e r T C P \theta{-}PowerTCP θ−PowerTCP可以不依赖这些信息。
e f = B 2 τ ( q + B × τ ) × ( q ˙ + B ) = τ ( q / B + τ ) × ( q ˙ / B + 1 ) (11) \frac{e}{f}=\frac{B^2\tau}{(q+B\times \tau)\times(\dot q+B)}=\frac{\tau}{(q/B+\tau)\times(\dot q/B+1)}\tag{11} fe=(q+B×τ)×(q˙+B)B2τ=(q/B+τ)×(q˙/B+1)τ(11)
其中, R T T ( t ) = q ( t ) B + τ RTT(t)=\frac{q(t)}{B}+\tau RTT(t)=Bq(t)+τ,对其求导,可得 R ˙ T T ( t ) = q ˙ ( t ) B \dot RTT(t)=\frac{\dot q(t)}{B} R˙TT(t)=Bq˙(t)。RTT和RTT的梯度可以在终端侧估计。
效果如何?我没有做仿真实验,不做评价。
Reference
[1] POWERTCP: Pushing the Performance Limits of Datacenter Networks
[2] FAST TCP: motivation, architecture, algorithms, performance
[3] AIMD吞吐量公式的推导
[4] tcp拥塞控制vegas的数学分析
[5] 漫谈TCP Vegas如何收敛到公平
[6] HPCC: high precision congestion control
[7] TIMELY: RTT-based Congestion Control for the Datacenter
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Introduction to MATLAB drawing functions ezplot explanation
cmake configure libtorch error Failed to compute shorthash for libnvrtc.so
Doubled and sparse tables

饥荒联机版Mod开发——准备工具(一)

How to simulate 1/3 probability with coins, and arbitrary probability?

Unity-Post Processing

开心一下,9/28名场面合集
Installation and configuration of Spark and related ecological components - quick recall
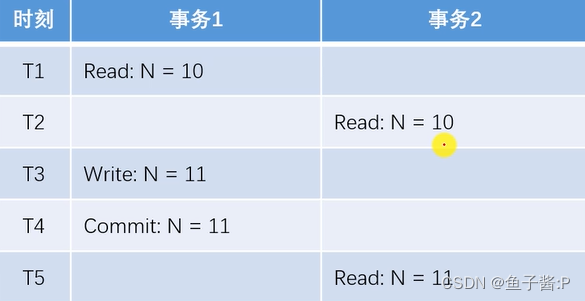
5. Transaction management
Unity-PlayMaker
随机推荐
Introduction to C language function parameter passing mode
MATLAB drawing command fimplicit detailed introduction to drawing implicit function graphics
Software Testing Basics (Back)
MMD->Unity一站式解决方案
饥荒联机版Mod开发——配置代码环境(二)
Open the door of electricity "Circuit" (1): voltage, current, reference direction
LeetCode 2354. 优质数对的数目 二进制01表示和集合之间的转换
Detailed explanation of MATLAB drawing function fplot
质数相关问题-小记
队列与栈
项目:数据库表的梳理
企业的电子签名、私钥签名
Introduction to in-order traversal (non-recursive, recursive) after binary tree traversal
1. Development community homepage, register
[STM32 Learning 1] Basic knowledge and concepts are clear
Knapsack Problem - Dynamic Programming - Theory
开源一个golang写的游戏服务器框架
泰伯效应.
Unity插件-NGUI
Qt | 实现一个简单的可以转动的仪表盘