当前位置:网站首页>Storage of data
Storage of data
2022-07-07 03:58:00 【ふり】
List of articles
One 、 Data type introduction
char // Character data type 1
short // Short 2
int // plastic 4
long // Long integer 4(32 position )/8(64 position )
long long // Longer plastic surgery 8 C99
float // Single-precision floating-point 4
double // Double precision floating point 8
The meaning of type :
- Use this type to exploit the size of memory space ( Size determines the range of use ).
- Look at memory space from different perspectives .
1.1 Basic classification of types
(1) Plastic surgery Family

(2) Floating point family

(3) Construction type
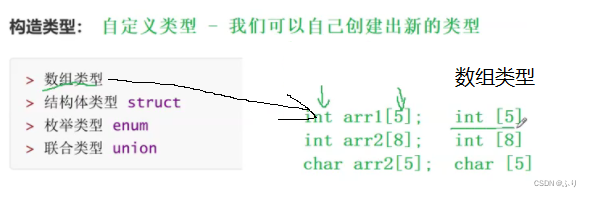
notes : The rest will be explained later
(4) Pointer types

(5) Empty type
- void Indicates empty type ( No type )
- Usually applied to the return type of a function 、 The parameters of the function 、 Pointer types
#include <stdio.h>
// first void Indicates that the function will not return a value ( Function return type )
// the second void Indicates that the function does not require any arguments ( Function parameter type )
void test(void)
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
int main()
{
printf("hehehe\n");
test();
return 0;
}
Two 、 Shaping storage in memory
The creation of a variable is to open up space in memory . The size of space is determined according to different types .
#include <stdio.h>
// Values have different representations
//2 Base number
//8 Base number
//10 Base number
//16 Base number
// Decimal 21
//0b10101
//025
//21
//0x1
int main()
{
int a = 20;
int b = -10;
return 0;
}
2.1 Original code 、 Inverse code 、 Complement code
#include <stdio.h>
// Values have different representations
//2 Base number
//8 Base number
//10 Base number
//16 Base number
// Decimal 21
//0b10101
//025
//21
//0x1
//
// The integer 2 There are three representations of base
//1. Positive integer , Original code 、 Inverse code 、 The complement is the same
//2. Negative integer , Original code 、 Inverse code 、 Complement needs to be calculated
// Original code : The binary sequence written directly in positive and negative form is the original code
// Inverse code : The sign bit of the original code remains the same , Other bits are reversed
// Complement code : Inverse code + 1 It's complement
//
int main()
{
int a = 20;
//20
//0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0100
//0x00 00 00 14 Hexadecimal
int b = -10;
//-10
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1010 -- Original code
// 0x80 00 00 00 0a
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 0101 -- Inverse code
// 0xfffffff5
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1010 -- Complement code
//0xfffffff6
return 0;
}
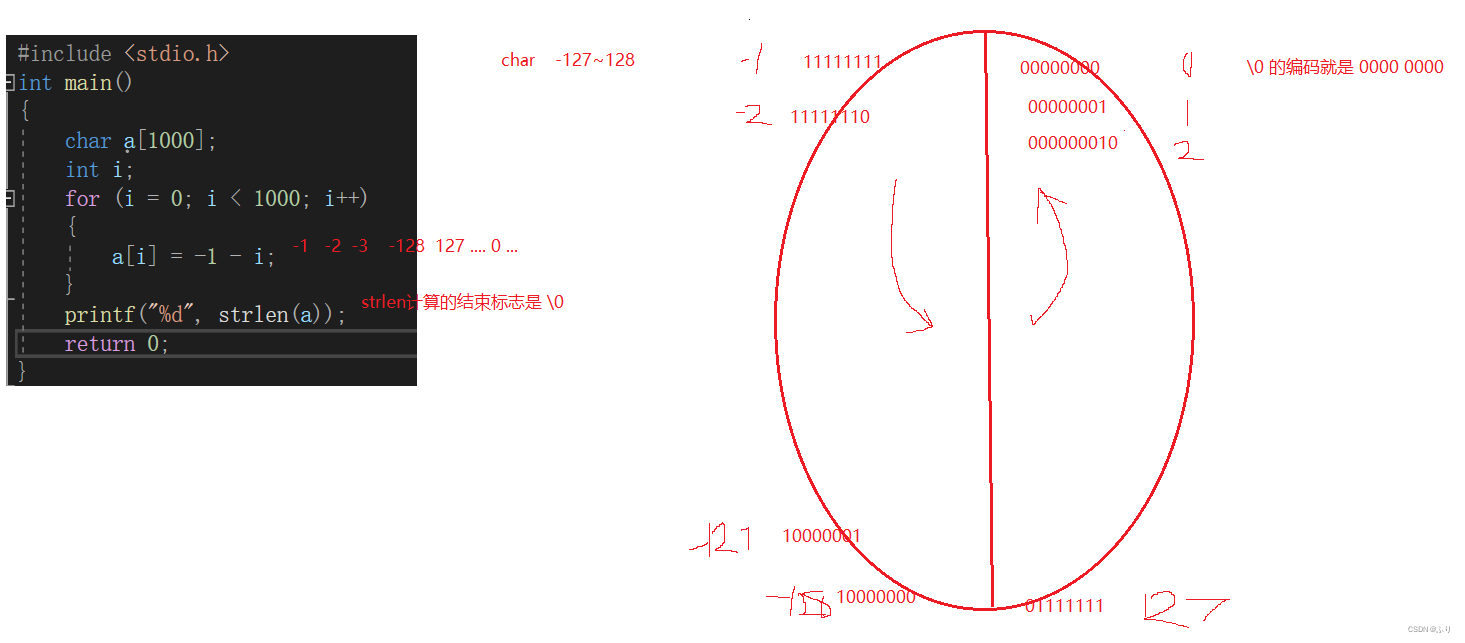
&a
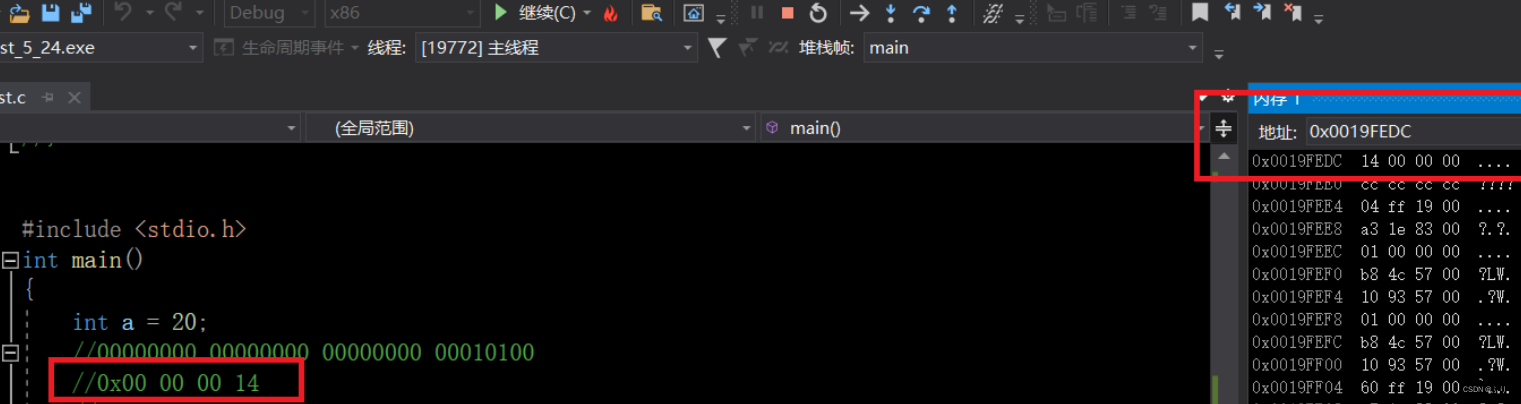

 We can see that for a and b The complement code is stored separately . But we found something wrong with the order .
We can see that for a and b The complement code is stored separately . But we found something wrong with the order .
That's why ?
2.2 Introduction to big and small end
What big end, small end :
- Big end ( Storage ) Pattern , The low bit of data is stored in the high address of memory , And the high end of the data , Stored in a low address in memory ;
- The small end ( Storage ) Pattern , The low bit of data is stored in the low address of memory , And the high end of the data ,, Stored in memory
Address .
Why are there big and small ends
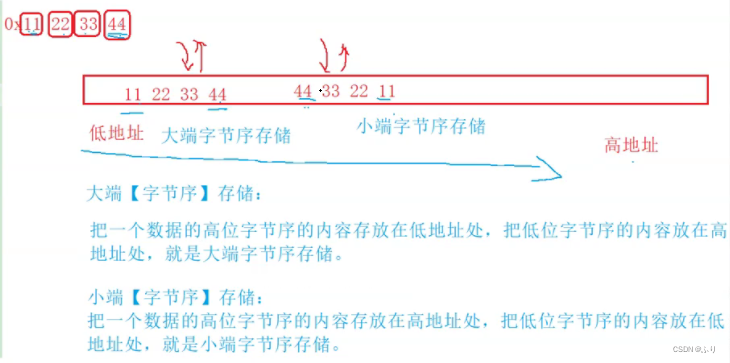
notes :0x 11 22 33 44 The high position is 11 , The low position is 44 , Be similar to 150 , The high position is 1
The low position is 0
Baidu 2015 System Engineer written test questions :
// Please briefly describe the concepts of big end byte order and small end byte order ,
// Design a small program to determine the current machine byte order .(10 branch )
#include <stdio.h>
int check()
{
int i = 1;
//&i Get the first address , Force type to char* Type and then dereference to get 00 still 01
return (*(char*)&i);
}
int main()
{
int ret = check();
if (ret == 1)
{
printf(" The small end \n");
}
else
{
printf(" Big end \n");
}
return 0;
}
2.4 practice
One 、
// What output ?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a= -1;
signed char b=-1;
unsigned char c=-1;
printf("a=%d,b=%d,c=%d",a,b,c);
return 0;
}
Two 、
2.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a = -128;
printf("%u\n",a);
return 0;
}
3、 ... and 、
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a = 128;
printf("%u\n",a);
printf("%d\n", a);
return 0;
}
Four 、
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = -20;
unsigned int j = 10;
return 0;
}
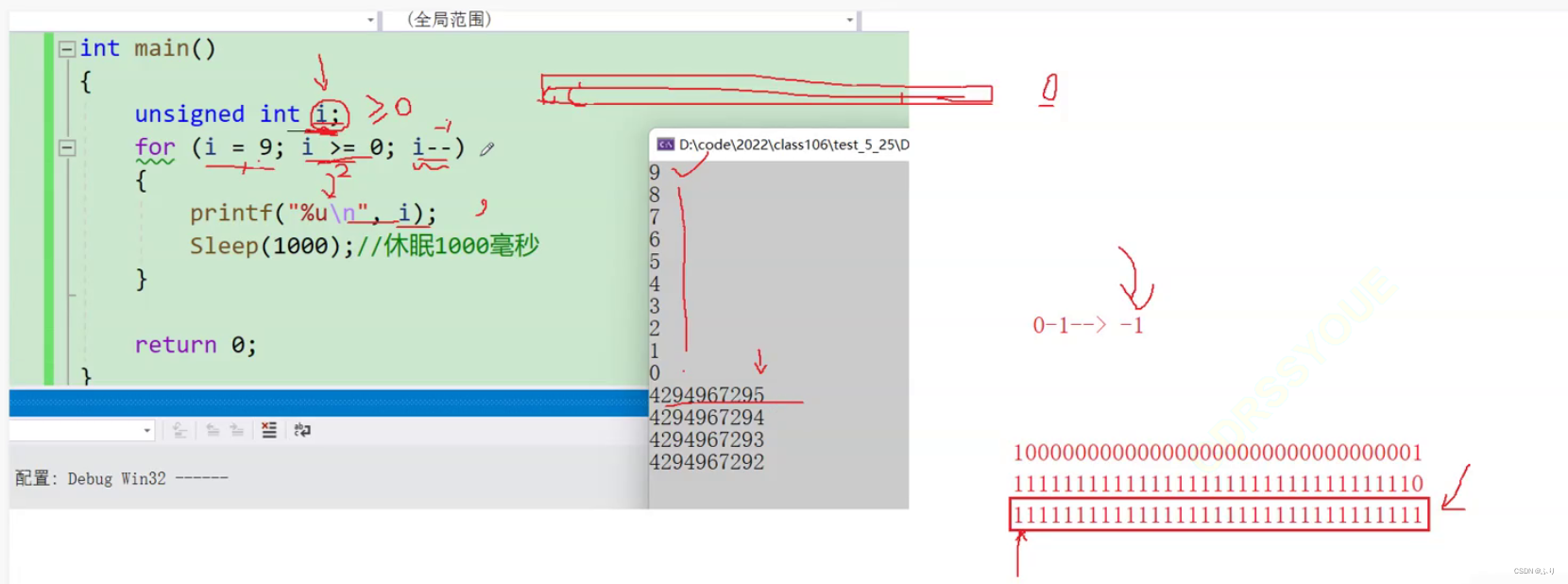
5、 ... and 、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int i;
for (i = 9; i >= 0; i--)
{
printf("%u\n", i);
Sleep(1000);
}
return 0;
}
6、 ... and 、
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a[1000];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
a[i] = -1 - i;
}
printf("%d", strlen(a));
return 0;
}
7、 ... and 、
#include <stdio.h>
unsigned char i = 0;
int main()
{
for (i = 0;i <= 255;i++)
{
printf("hello world\n");
}
return 0;
}
answer
// char Signed number -128 ~ 127
// An unsigned number 0 ~ 255
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a = -1;
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1110
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
// truncation
//11111111 - a %d It's a signed integer
// Improve the overall shape
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 - Complement in memory
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 -> -1
signed char b = -1;
unsigned char c = -1;
// Unsigned integer raised high order direct complement 0
printf("a=%d,b=%d,c=%d", a, b, c);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a = -128;
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0100 0000
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 0111 1111
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1000 0000 - truncation
//10000000 - a
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1000 0000 - promote
//
printf("%u\n", a);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a = 128;
//0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000 0000
//0111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 0111 1111
//0111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1000 0000 - truncation
//1000 0000 - a
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1000 0000 - promote
printf("%u\n", a);
//1000 0000 - a
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1000 0000 - promote
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0111 1111
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000 0000
printf("%d\n", a);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = -20;
// -20
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0100
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1110 1011
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1110 1100 -> -20 Complement
unsigned int j = 10;
//0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1010
printf("%d\n", i + j);
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1110 1100
//0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 1010
//1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 0110
//
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1001
//1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1010
return 0;
}
 6.
6. 7 .
7 .
#include <stdio.h>
unsigned char i = 0;
//unsigned char Type value range 0~255 So Heng holds
int main()
{
for (i = 0;i <= 255;i++)
{
printf("hello world\n");
}
return 0;
}
// Dead cycle
important
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
if (strlen("abc") - strlen("abcdef") > 0)
{
//strlen The type returned by the function is an unsigned integer , For two unsigned reshapes, see the result or unsigned reshape
printf(">\n");
printf("%u\n", strlen("abc") - strlen("abcdef")); //4294967293
}
else
{
printf("<\n");
}
return 0;
}
// If you want to calculate, you can force type conversion from integer or comparison size
3、 ... and 、 Floating point storage in memory
Common floating point numbers :
3.14159
1E10 1.0*pow(10,10)
The family of floating-point numbers includes : float、double、long double type .
The range represented by floating point numbers : float.h In the definition of
They are included in these header files 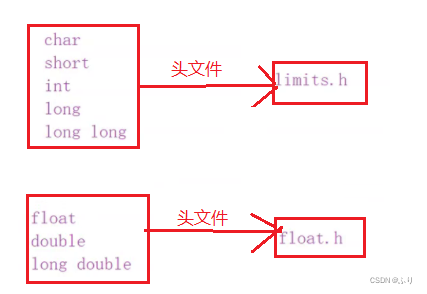
3.1 An example
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 9;
float* pFloat = (float*)&n;
printf("n The value of is :%d\n", n);
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%f\n", *pFloat);
*pFloat = 9.0;
printf("num The value of is :%d\n", n);
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%f\n", *pFloat);
return 0;
}
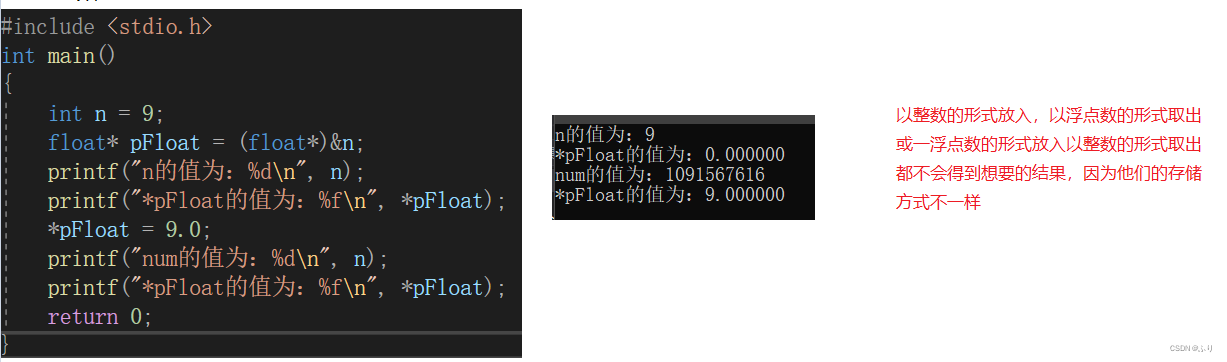
3.2 Floating point storage rules
num and *pFloat It's the same number in memory , Why are the interpretation results of floating-point numbers and integers so different ?
To understand this result , Be sure to understand the representation of floating-point numbers in the computer .
Detailed interpretation :
According to international standards IEEE( Institute of electrical and Electronic Engineering ) 754, Any binary floating point number V It can be expressed in the following form :
- (-1)^S * M * 2^E
- (-1)^s The sign bit , When s=0,V Is a positive number ; When s=1,V It's a negative number .
- M Represents a significant number , Greater than or equal to 1, Less than 2.
- 2^E Indicates the index bit .
for instance :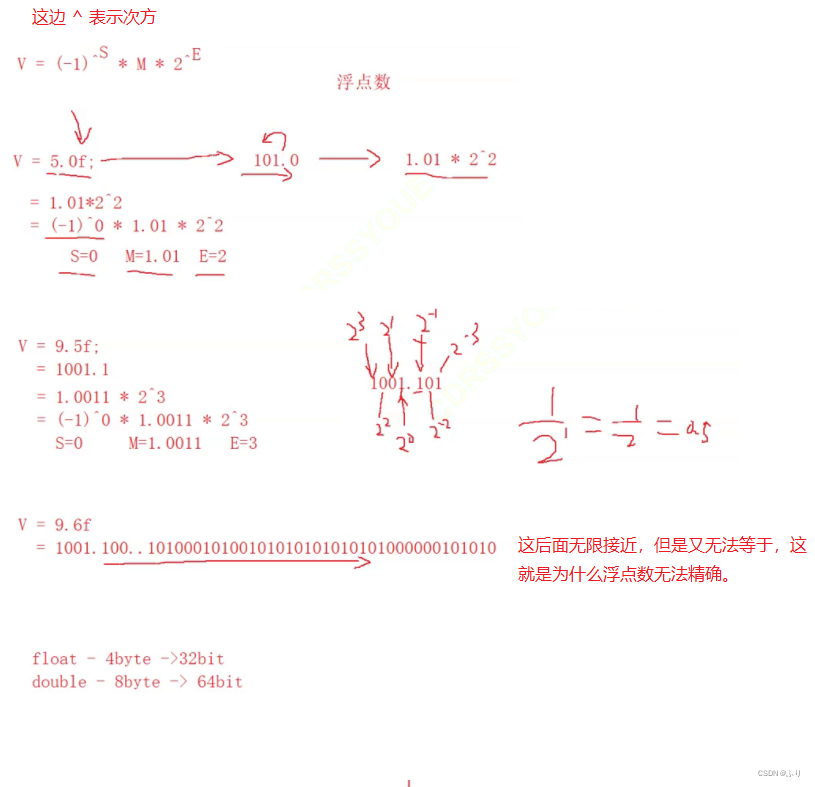

First ,E For an unsigned integer (unsigned int)
- It means , If E by 8 position , Its value range is 0 ~ 255;
- If E by 11 position , Its value range is 0~2047.
- however , We know , In scientific counting E You can have negative numbers , therefore IEEE754 Regulations :
Deposit in Memory time E The true value of must be added with an intermediate number ,
about 8 Bit E, The middle number is 127;
about 11 Bit E, The middle number is 1023.such as ,2^10 Of E yes 10, So save it as 32 When floating-point numbers are in place , Must be saved as 10+127=137, namely 10001001.
Index E Fetching from memory can be further divided into three cases :
At this time , Floating point numbers are represented by the following rules , The index E The calculated value of minus 127( or 1023), Get the real value , then
Significant figures M Add the first 1.
such as :
0.5(1/2) The binary form of is 0.1, Since it is stipulated that the positive part must be 1, That is to move the decimal point to the right 1 position , Then for 1.0*2^(-1), Its order code is -1+127=126, Expressed as 01111110, And the mantissa 1.0 Remove the integer part and make it 0, A filling 0 To 2300000000000000000000000, Then its binary representation is :
0 01111110 00000000000000000000000
E All for 0
At this time , The exponent of a floating point number E be equal to 1-127( perhaps 1-1023) That's the true value ,
Significant figures M No more first 1, It's reduced to 0.xxxxxx Decimals of . This is to show that ±0, And close to
0 A very small number of .
E All for 1
At this time , If the significant number M All for 0, Express ± infinity ( It depends on the sign bit s);
Explain the previous topic :
Why? 0x00000009 Restore to floating point number , became 0.000000 ?
First , take 0x00000009 Split , Get the first sign bit s=0, Back 8 Bit index E=00000000 , Last 23 A significant number of bits M=000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1001.
9 -> 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1001
Because the index E All for 0, So the second case in the previous section . therefore , Floating point numbers V The just :

obviously ,V It's a very small one, close to 0 Positive number of , So the decimal number is 0.000000.
Let's look at the second part of the example .
Floating point number 9.0, How to express... In binary ? How much is it to restore to decimal ?
9.0 -> 1001.0 ->(-1)01.00123 -> s=0, M=1.001,E=3+127=130
First , Floating point numbers 9.0 Equal to binary 1001.0, namely 1.001×2^3.
that , The first sign bit s=0, Significant figures M be equal to 001 Add... To the back 20 individual 0, Cramming 23 position , Index E etc. 3+127=130, namely 10000010.
therefore , Written in binary form , Should be s+E+M, namely
0 10000010 001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
This 32 The binary number of bits , Restore to decimal , It is 1091567616 .
边栏推荐
- Summer 2022 daily question 1 (1)
- Enter the rough outline of the URL question (continuously updated)
- 链表面试常见题
- Hongmi K40S root gameplay notes
- cuda编程
- Create commonly used shortcut icons at the top of the ad interface (menu bar)
- 使用 BR 备份 TiDB 集群到 GCS
- Ggplot facet detail adjustment summary
- 【mysql】mysql中行排序
- VHDL implementation of arbitrary size matrix addition operation
猜你喜欢

21. (article ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS rectangular acquisition (sketchviewmodel)
再AD 的 界面顶部(菜单栏)创建常用的快捷图标
![[leetcode] 450 and 98 (deletion and verification of binary search tree)](/img/89/dd7ac0d886e6bbca5a439386c576bb.jpg)
[leetcode] 450 and 98 (deletion and verification of binary search tree)
力扣------路径总和 III

2022夏每日一题(一)
链表面试常见题

map和set的实现
QT 项目 表格新建列名称设置 需求练习(找数组消失的数字、最大值)
VHDL implementation of single cycle CPU design

19. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS line acquisition (sketchviewmodel)
随机推荐
Tencent cloud native database tdsql-c was selected into the cloud native product catalog of the Academy of communications and communications
海思3559万能平台搭建:RTSP实时播放的支持
Baidu map JS development, open a blank, bmapgl is not defined, err_ FILE_ NOT_ FOUND
U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory, "exploring the vulnerability and robustness of deep learning systems", the latest 85 page technical report in 2022
About Tolerance Intervals
Introduction to opensea platform developed by NFT trading platform (I)
Can the applet run in its own app and realize live broadcast and connection?
Ggplot facet detail adjustment summary
Redis源码学习(30),字典学习,dict.h
Mobile measurement and depth link platform - Branch
使用 TiDB Lightning 恢复 GCS 上的备份数据
Flutter3.0, the applet is not only run across mobile applications
My brave way to line -- elaborate on what happens when the browser enters the URL
QT thread and other 01 concepts
QT opens a file and uses QFileDialog to obtain the file name, content, etc
大白话高并发(二)
【开发软件】 tilipa开发者软件
二进制、八进制、十六进制
How to detect whether the MySQL code runs deadlock +binlog view
再AD 的 界面顶部(菜单栏)创建常用的快捷图标