当前位置:网站首页>Communication between microservices
Communication between microservices
2022-07-06 02:41:00 【Rainy night】
Microservice architecture builds applications based on multiple services , These services must often collaborate to handle various external requests . Because service instances are usually processes running on multiple machines , So they must interact using interprocess communication . therefore , Interprocess communication technology plays a more important role in microservice architecture than in monomer architecture . This article will explore various interprocess communication mechanisms , And discuss how to make a trade-off . Be careful , It needs to be remembered “ There is no silver bullet ” This general principle .
Choosing the appropriate interprocess communication mechanism is an important architectural decision . It affects application availability . what's more , Interprocess communication even interacts with practice management . An ideal microservice architecture should be internally composed of loosely coupled services , These services communicate with each other using asynchronous messages .REST Isochronous protocols are mainly used for communication between services and other external applications .
Overview of communication between microservices
Microservice architecture regards process as a first-class citizen , That is to say, each microservice instance is an independent process . The communication between microservices is the communication between processes . There are many interprocess communication technologies to choose from . Services can use synchronization based requests / The communication mechanism of response , Such as HTTP REST or gRPC. in addition , Asynchronous message based communication mechanisms can also be used , Common message communication protocols are :AMRP or STOMP etc. . This article will start from the interaction of services 、API Definition 、 Message format and other aspects to introduce the communication between microservices .
Interactive mode
Before choosing the interprocess communication mechanism for the service , First of all, we should consider the interaction between the service and the client . Considering the way of interaction will help focus on requirements , And avoid getting caught up in the details of specific interprocess communication technologies . The choice of interaction mode will affect the usability of the application . Besides , Interaction can also help you choose a more appropriate integration testing strategy .
There are many ways for clients to interact with services . Here we introduce from two dimensions . The first dimension focuses on mapping relationships . It can be divided into two categories : One to one and one to many .
(1) one-on-one : Each client request is processed by a service instance .
(2) One to many : Each client request is processed by multiple service instances .
The second dimension focuses on synchronization and asynchrony .
(1) Synchronous mode : The client request requires the server to respond in real time , The client may block while waiting for a response .
(2) Asynchronous mode : Client requests do not block the process , The response of the server can be non real time .

There are several types of one-to-one interaction :
(1) request / Respond to : A client sends a request to the server , Waiting response ; The client expects the server to send a response soon . In a thread based application , Waiting may cause thread blocking .
(2) request / Asynchronous response : Client sends request to server , The server responds to requests asynchronously . The client will not block the thread while waiting for the response , Because the server's response will not return immediately .
(3) notice ( One way notification ): The client's request is sent to the server , But the server is not expected to respond .
There are several types of one to many interactions :
(1) Release / subscribe : The client sends a notification message , Subscribed by zero or more services of interest .
(2) Release / Asynchronous response : The client sends the request message , Then wait for the response from the service of interest .
Each service usually uses a combination of these interaction methods , Instead of using an interactive method alone .
API Definition
API Or interface is the center of software development . An application consists of one or more modules ( For microservice architecture , The module here refers to the component , That is, micro Services ), Each module has an interface , These interfaces define the operations supported by the module . A well-designed interface will expose useful functions and hide implementation details . therefore , The details of the interface implementation can be modified , The interface remains unchanged , This will not affect the client . That is to say , Once the interface is published , In the subsequent maintenance process , The downward compatibility of the interface must be ensured . For incompatible capabilities , You must open a new interface .
For microservice architecture , Service API It is the contract between the service and its client (contract). there API It may contain events published by methods or services provided to clients . The method has a name 、 Parameters and return types . Events have a type and a set of fields , It can be published to the message channel .
For microservice Architecture , The challenge is : The service and its client will not compile together . If you use incompatible API Deploy a new version of the service , Although there will be no errors in the compilation phase , But there will be runtime failures .
No matter which interprocess communication mechanism you choose , Use some interface definition language (Interface Define Language, IDL) Precisely define the API It's all important . In daily development , First, back-end developers write interface definitions , Then work with the designer 、 Client developers review the interface definition document together . Only certain API After the definition , Back end developers and front-end developers really start programming . This pre design helps to build interfaces that meet the needs of the client . This pattern is also called "API Design first mode ". In the stage of front and rear end separation , This method can greatly weaken the dependence of the front end on the back end , Achieve a certain degree of parallel development , Provide efficiency .
How to define API Depends on the interprocess communication mechanism used . Such as using message communication mechanism , be API By the message channel 、 Message type and message format . Based on Kafka In the message communication of ,Protocol Buffers Has become IDL How to recommend . If you use HTTP, be API from URL、HTTP Verbs and request and response forms . Based on Java Web The development of ,Swagger Of yaml Has become IDL How to recommend .
Format of message
The essence of interprocess communication is to exchange messages . Messages usually include data , Therefore, an important design strategy is the format of data . The choice of message format will affect the efficiency of inter process communication 、API The evolution of . For example, for similar HTTP Communication for , You need to select the message format . Some forms of communication , Then the message format is specified , Such as gRPC. For message format , Try to make language irrelevant , In this way, it can be used between heterogeneous systems . The format of messages can be divided into two categories : Text and binary .
Text based message format
There are two main text-based message formats :JSON and XML. at present ,JSON It has become the standard of text message format . The characteristics of text messages are , They are highly readable , It is also self describing . This format allows the recipients of messages to pick only the values they are interested in , And ignore the others . therefore , The modification of message structure can achieve good backward compatibility .
The disadvantage of using text-based messages is that messages are often too verbose , Every delivery of a message must repeatedly contain attribute names other than values , This will cause additional expenses . Another drawback is the extra overhead introduced by parsing text . about JSON The news says , The message sender should serialize , The message receiver needs to deserialize . therefore , In scenarios sensitive to efficiency and performance , You need to consider binary based message formats .
Binary based message format
Common binary based message formats are :Protocol Buffers and Avro. Both formats provide a strongly typed IDL, Used to define the format of the message . The compiler will automatically generate serialization and deserialization code according to these formats . So developers have to adopt API Priority mode to service design . In the development process of using , Only used Protocol Buffers, Comparison and selection of the two , Please also learn by yourself .
Based on synchronous call communication
When using communication mechanism based on synchronous invocation , Client sends request to server , The server processes the request and sends back a response , The client blocks and waits for a response . The working principle of call communication based on synchronization is as follows :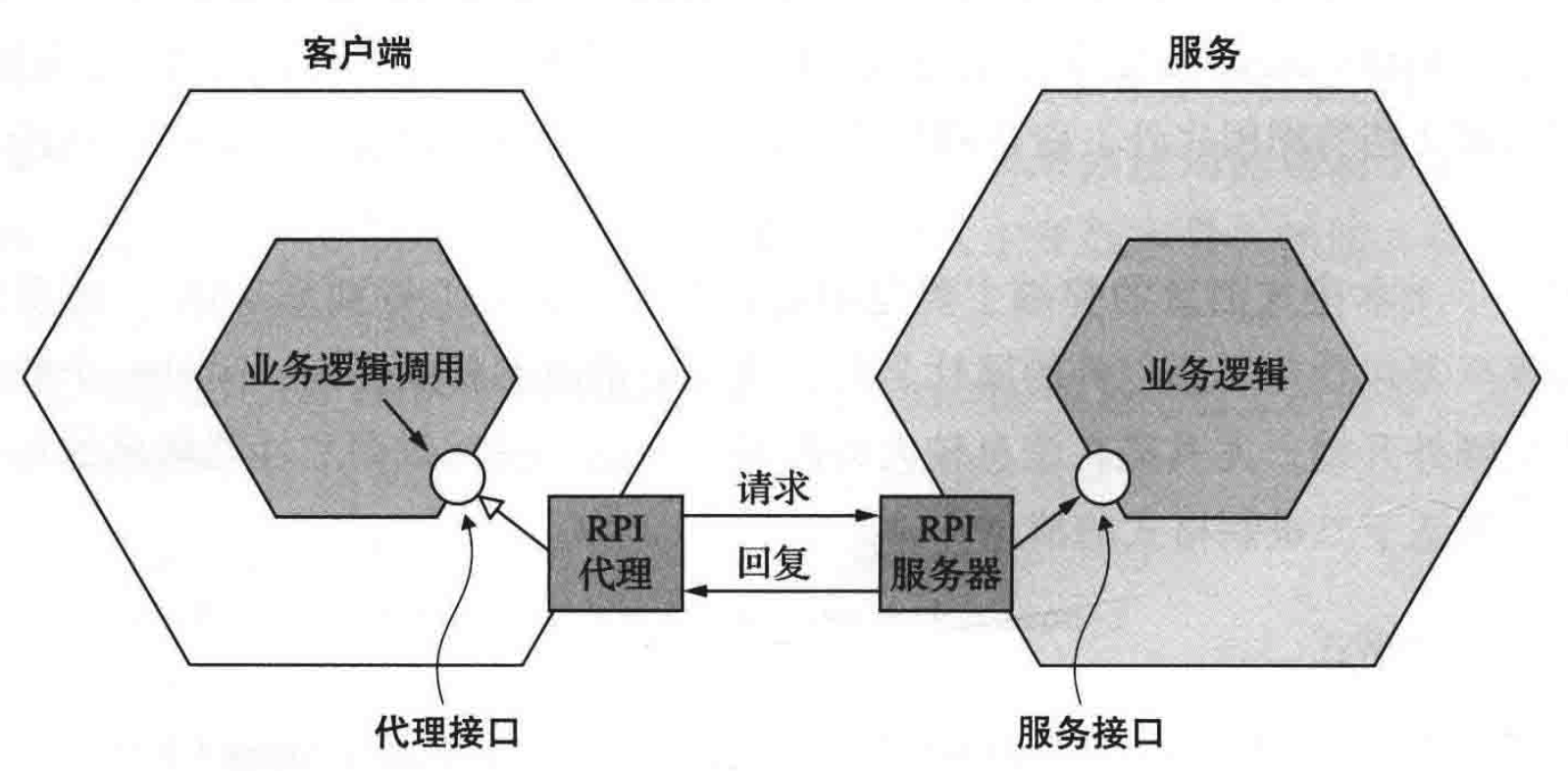
In the diagram above , The business logic in the client calls the proxy interface , This interface is implemented by the proxy adapter class . Proxy sends request to server . The request is handled by the server adapter class , This class calls the business logic of the service through the interface . Then return the response to the client agent , The agent returns the result to the business logic of the client . Careful students can find out , The whole calling process and HTTP Of request-response The models are the same .
here , The proxy interface of the client usually encapsulates the underlying communication protocol . There are many agreements to choose from , The mainstream of REST and gRPC.
REST
Nowadays developers like to use RESTful Style development API.REST It's a use HTTP Interprocess communication mechanism of the protocol ,REST The father of Roy Fielding Once said :
REST Provides a series of architectural constraints , When used as a whole , It emphasizes the extensibility of component interaction 、 Interface versatility 、 Independent deployment of components ,
And middleware that can reduce interaction latency , It enhances security , It can also encapsulate legacy systems .
REST A key concept in is resources , It usually represents a single business object , Like an order , Shopping cart, etc .REST Use HTTP Verb (GET、POST、PUT、DELETE etc. ) Reference these resources . This resource usually uses JSON Object message format .RESTful The style has been successful Web API The de facto standard of development , An article will be written later to introduce .
gRPC
Use REST One of the challenges is , because HTTP Provide only a limited number of verbs , So it can't be used REST Hosting unsupported scenarios , For example, the design supports multiple updates API. An effective alternative is to use gRPC.gRPC Is a protocol based on binary messages , Can be used based on Protocol Buffer Of IDL Definition gRPC API, This is a Google A language neutral mechanism used by the company to serialize structured data .
gRPC API One or more services and requests / The response message definition consists of . In addition to supporting simple requests / Respond to RPC outside ,gRPC Streaming is also supported RPC. The server can reply to the client with message flow . The client can also send message flows to the server .
Based on asynchronous call communication
When using communication mechanism based on asynchronous invocation , Messages are exchanged through message channels . The working principle of asynchronous call communication based on message channel is as follows :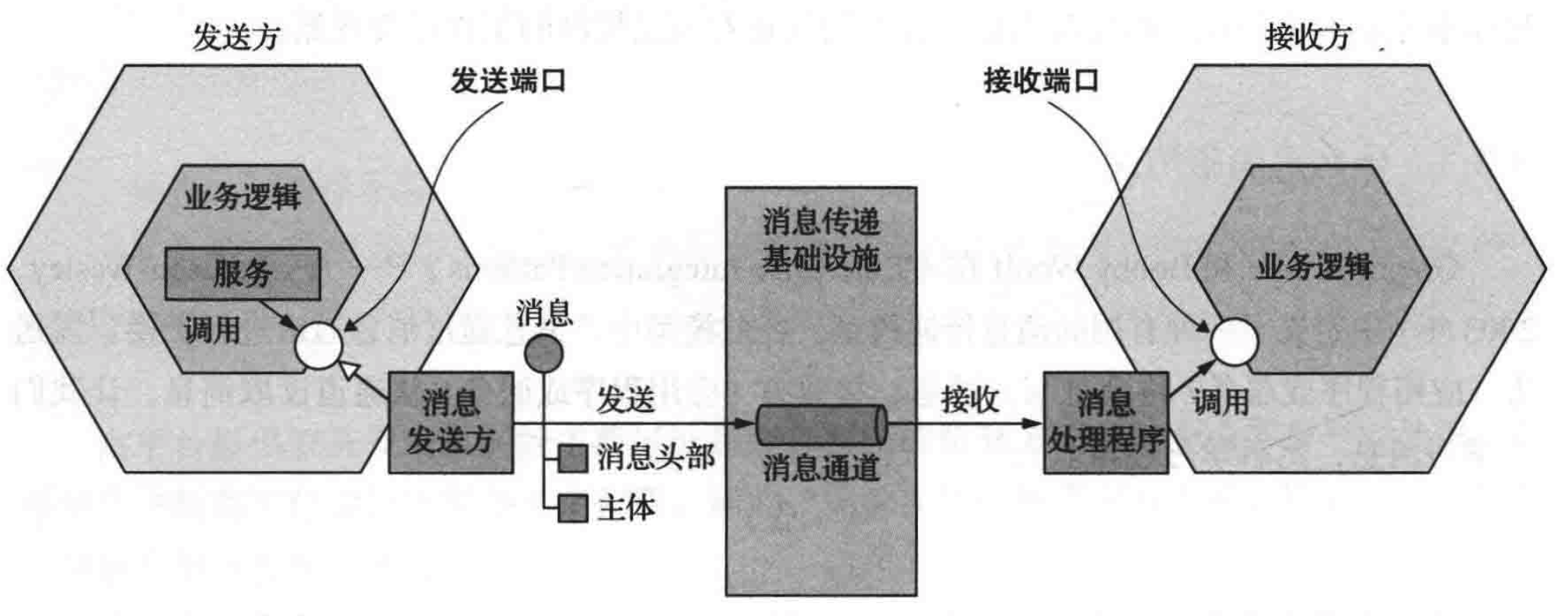
In the diagram above , The business logic in the message sender calls the sender interface , This interface encapsulates the underlying communication mechanism . The sender is implemented by the message sending adapter class . The message sending adapter sends messages to the receiver through the message channel . Message channels are abstractions of messaging infrastructure . The message handler calls the receiver interface implemented by the receiver business logic to process the message .
There are two types of message channels : Point to point (Point to Point, P2P) And release - subscribe (Publish and Subscribe, Pub-Sub).
(1) Point to point channels . The producer delivers a message to a consumer who is reading from the channel . Services use point-to-point channels for one-to-one interaction .
(2) Release - Subscription channel . The message sender sends a message to all subscribers . Service usage publishing - Subscription channel realizes one to many interaction .
Use message mechanism to realize interaction
A valuable feature of the messaging mechanism is that it is flexible enough , It can support all interaction modes . Some interaction methods are directly realized through the message mechanism , Others must be implemented on the message mechanism .
Implement the request / Response and request / Asynchronous response
When clients and servers use requests / Response and request / When interacting with asynchronous responses , The client will send a request , The server will return a response . The difference between the two ways of interaction is , For the request / In response , The client expects the server to respond immediately , And for requests / Asynchronous response , There is no such expectation . The message mechanism is asynchronous in nature , Therefore, only asynchronous responses are provided . But the client can block , Until I get a reply .
The client and server realize the request by exchanging a pair of messages / Asynchronous response interaction . The principle is shown in the figure below :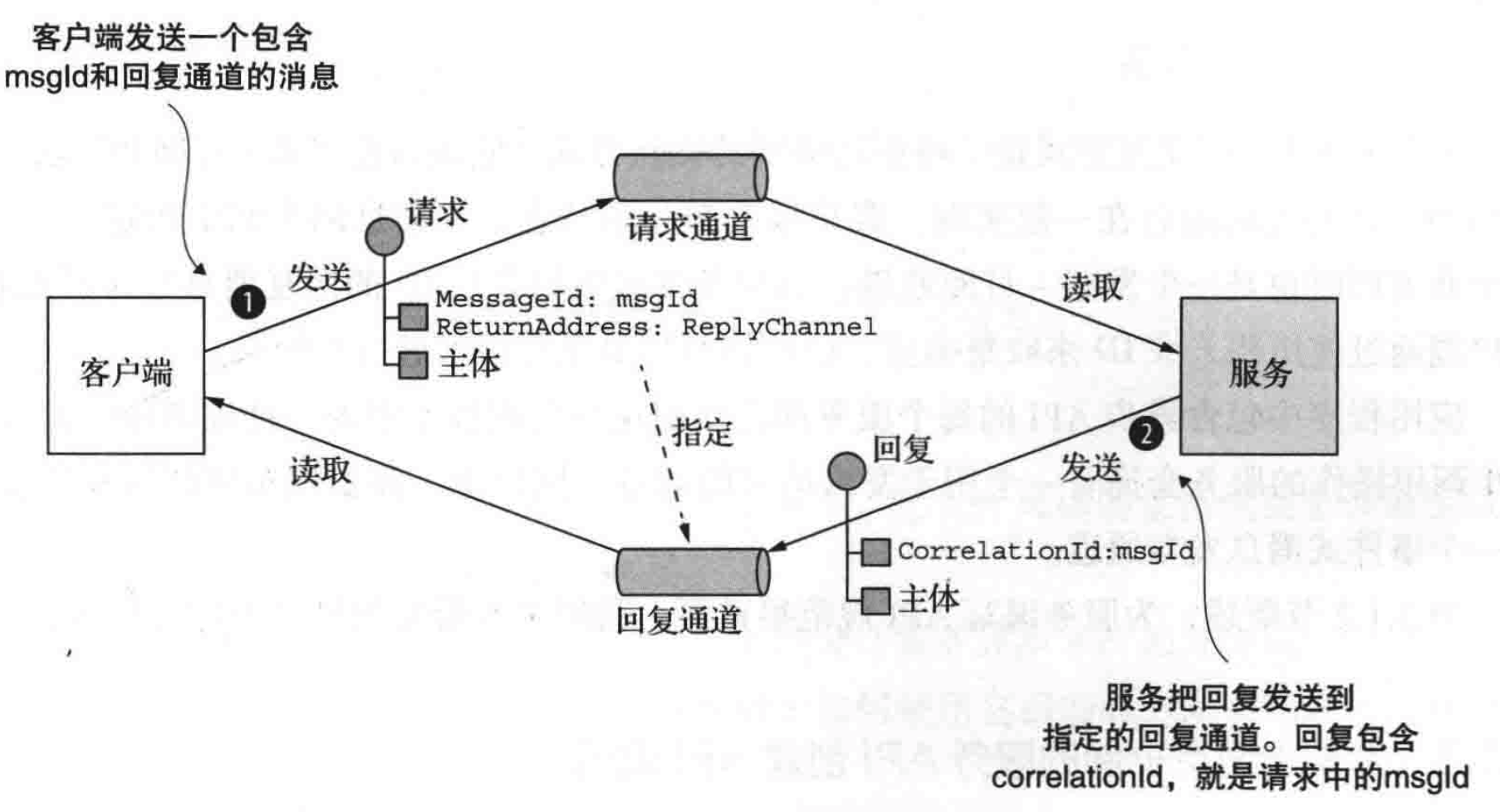
In the diagram above , The client sends a command message , This message specifies the operation and parameters to be performed , These contents are delivered through the peer-to-peer message channel of the server . The server processes the request and sends the message containing the result to the point-to-point channel of the client . Last , The client can receive the message containing the result .
Realize one-way notification
Using asynchronous messages to implement one-way channels is very simple . The client sends the message to the peer-to-peer channel owned by the server . The server subscribes to the channel and processes the message , But the server will not return a response .
Implementation release / subscribe
The message mechanism is built-in for publishing / Subscription support . The sender will produce messages and publish them to publications read by multiple receivers / Subscription channel . The receiver consumes messages from this channel .
Implementation release / Asynchronous response
Release / Asynchronous response interaction is a more advanced interaction , This interactive way releases / Subscribe and request / The elements that respond to these two ways are combined to implement . The client sends a message , Specify the reply channel in the header of the message , This channel is also a release - Subscription channel . The server will contain dependencies ID Write the reply message to the reply channel . The client uses dependencies ID To collect responses , This matches the reply message to the request .
Communication exception handling
Distributed system , When a service sends a synchronization request to another service , Always face the risk of local failure . Because the client and server are independent processes , The server may not be able to respond to the client's request in a limited time . The server may be suspended due to failure or maintenance . perhaps , The server may also become extremely slow to respond to requests due to overload . Besides the server itself , Network is also a factor that cannot be ignored , For details, please refer to the author Previous post .
For synchronous requests , The client is blocked waiting for a response , The risk that this may bring is the transmission between other clients or third-party applications using services , And cause service disruption .
The transmission and diffusion of faults in the whole application should be prevented by reasonably designing services , This is crucial . Whenever a service synchronously calls another service , It should use current limiting 、 Overtime 、 Fuse and other technologies to protect yourself .
Current limiting
Flow limiting refers to limiting the number of requests made by the client to the server . Specifically, the server sets a request upper limit , If the request reaches the upper limit , Subsequent more requests will immediately fail .
Overtime
Timeout refers to limiting the response time of the server . Specifically, set a response timeout limit for the server , If the server does not respond within the specified time , It will also fail immediately .
Fusing mode
Fusing mode refers to monitoring the number of successful and failed requests sent by the client , If the failure rate exceeds the threshold , Just start the fuse , Let subsequent requests fail immediately . After a certain period of time , Continue to receive client requests , If the call succeeds , Then release the fuse .
Reference resources
Microservice design Sam Newman Writing , Cui Liqiang etc. translate
Microservice architecture design pattern Chris Richardson Writing , Chen Bin etc. translate
https://itdks.su.bcebos.com/307ea09e7ef34bbfa58b845bf0f3d74b.pdf Microservice architecture development and platform evolution
边栏推荐
- What should we pay attention to when using the built-in tool to check the health status in gbase 8C database?
- LeetCode 103. Binary tree zigzag level order transverse - Binary Tree Series Question 5
- Ue4- how to make a simple TPS role (II) - realize the basic movement of the role
- 07 单件(Singleton)模式
- 解决:AttributeError: ‘str‘ object has no attribute ‘decode‘
- 2345 file shredding, powerful file deletion tool, unbound pure extract version
- 3D drawing ()
- CobaltStrike-4.4-K8修改版安装使用教程
- Redis delete policy
- Microsoft speech synthesis assistant v1.3 text to speech tool, real speech AI generator
猜你喜欢
Black high-end responsive website dream weaving template (adaptive mobile terminal)
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 12](/img/b1/926d9b3d7ce9c5104f3e81974eef07.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 12
![[untitled] a query SQL execution process in the database](/img/de/700ee20934fc2cd4a019f761148ef9.png)
[untitled] a query SQL execution process in the database
Li Kou today's question -729 My schedule I

Which ecology is better, such as Mi family, graffiti, hilink, zhiting, etc? Analysis of five mainstream smart brands
A copy can also produce flowers
Introduction to robotframework (II) app startup of appui automation
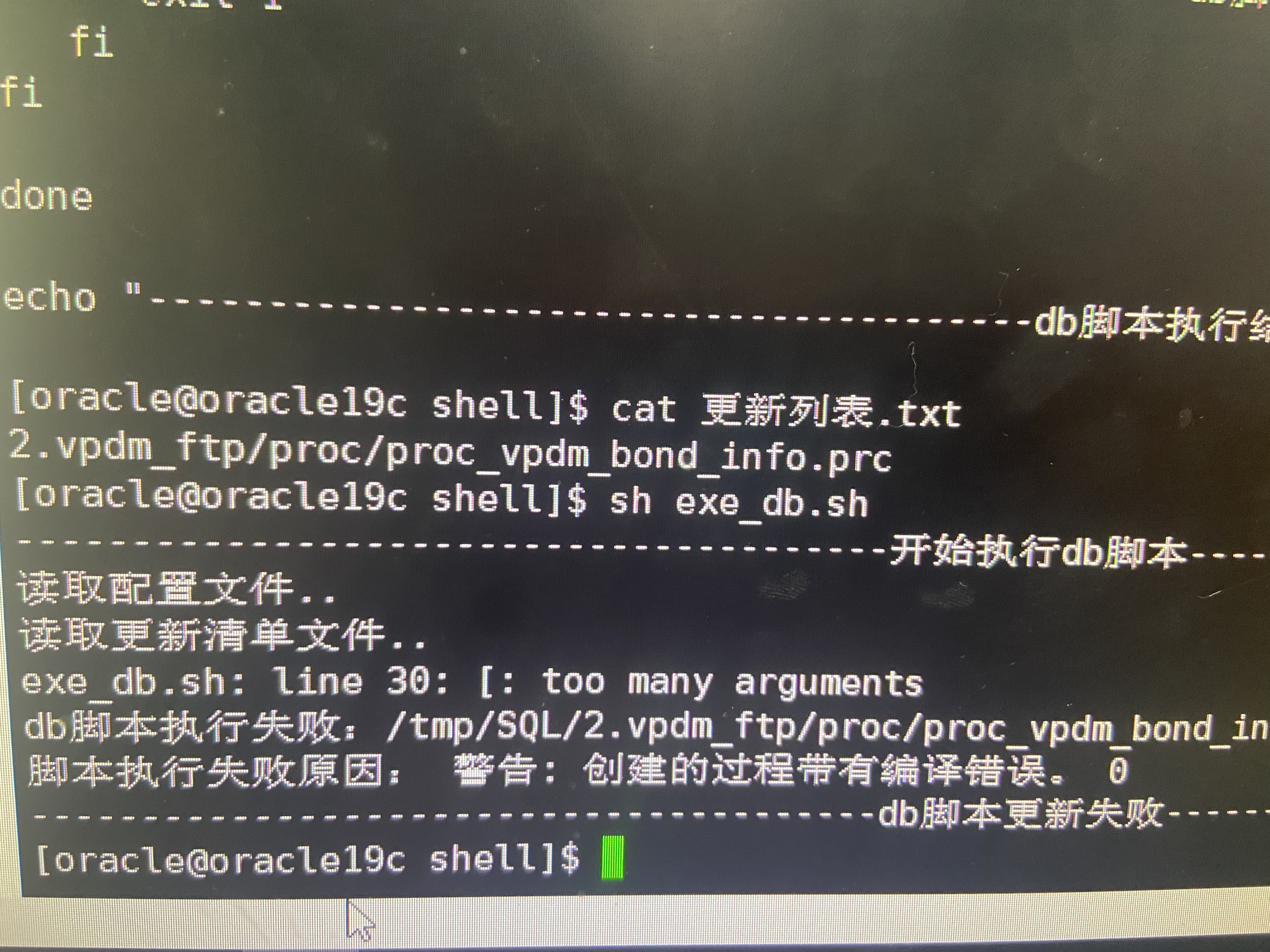
Shell脚本更新存储过程到数据库
![[Digital IC manual tearing code] Verilog asynchronous reset synchronous release | topic | principle | design | simulation](/img/e4/890e84ab8326e029c4915163904d85.jpg)
[Digital IC manual tearing code] Verilog asynchronous reset synchronous release | topic | principle | design | simulation

Looking at the trend of sequence modeling of recommended systems in 2022 from the top paper
随机推荐
3D drawing ()
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 11
Redis skip table
QT release exe software and modify exe application icon
There are so many giants, why should we independently develop POS store cashier system?
零基础自学STM32-复习篇2——使用结构体封装GPIO寄存器
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 21
Which ecology is better, such as Mi family, graffiti, hilink, zhiting, etc? Analysis of five mainstream smart brands
2.13 simulation summary
微软语音合成助手 v1.3 文本转语音工具,真实语音AI生成器
[Wu Enda machine learning] week5 programming assignment EX4 - neural network learning
Apt installation ZABBIX
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 19
Zero basic self-study STM32 wildfire review of GPIO use absolute address to operate GPIO
Httprunnermanager installation (III) - configuring myql Database & initialization data under Linux
Template_ Quick sort_ Double pointer
ReferenceError: primordials is not defined错误解决
Qt发布exe软件及修改exe应用程序图标
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 22
MySQL winter vacation self-study 2022 11 (9)