当前位置:网站首页>[InstallShield] Introduction
[InstallShield] Introduction
2022-07-07 05:54:00 【BLAZAR'】
Main reference InstallShield 2021 Help Library
Installation Fundamentals
An installation is divided into three levels: products, features, and components. The following diagram illustrates this hierarchy: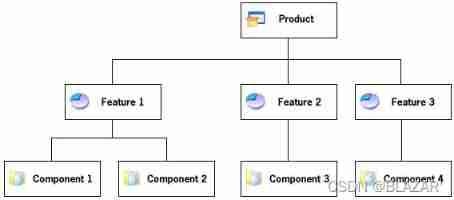
A product is the highest level of organization in an installation project. A product is usually one main application (for example, a word processor) and all of the files and data that the application requires; a suite of applications may also be a product.
A feature is the smallest installable part of a product, from the end user’s perspective.
Each feature in a project is made up of one or more components. A component is the smallest installable part of a product from the installation developer’s perspective; components are invisible to the end user.
When you are designing an installation, the overall task is to separate the product’s files into components based on the files’ destination, operating system, language, and other properties, and to associate each component with one or more features.
Application Lifecycle
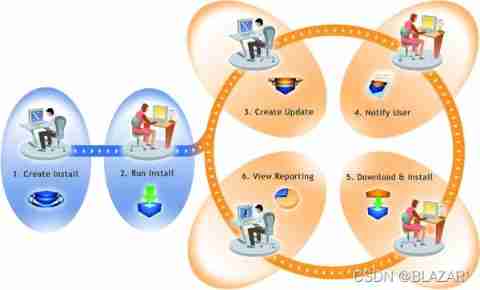
The above diagram illustrates how FlexNet Connect is used to manage the application lifecycle:
- Create Install—InstallShield makes it easy for software developers to create installations that run on any platform.
- Run Install—Installations created with InstallShield technology have successfully installed on over 400 million machines worldwide.
- Create Update—InstallShield enables software developers to rapidly build patches and updates.
- Notify User—FlexNet Connect notifies every user that a new update is ready to be installed.
- Download & Install—FlexNet Connect downloads the update and installs it in one seamless, integrated process.
- View Reporting—FlexNet Connect provides immediate feedback on the update’s adoption rate.
InstallShield project
An InstallShield project specifies the files, folders, and operations that make up the project’s output. A project’s output is one of the following (depending on the project type):
• Installation: creates or updates a copy of your application on the target system
• Redistributable (merge module or InstallShield object): contains logic and files needed to install distinct pieces of functionality when included in an installation
• Transform: enables an administrator to apply modified settings to an Windows Installer installation when deploying the installation
A project can be as simple or as complex as you need to meet your requirements. A simple project might consist of files, components, features, and registry entries. More complex projects might consist of these items plus redistributables, initialization file changes, and calls to external DLL functions.
Project type
With InstallShield, you have the ability to choose between a variety of different installation project types—those that use InstallShield’s powerful InstallScript programming language (InstallScript), those that use the Windows Installer database (Basic MSI), or a combination of the two (InstallScript MSI).
The installation project type you choose depends on the needs of your software installation. InstallShield provides the same intuitive user interface for all project types, so your application’s needs can dictate the project type and your authoring experience does not change. Additionally, the knowledge gained by learning how to create projects of one type is applicable to projects of the other types.
Basic MSI Projects
Suitable for simple projects
Basic MSI projects use the Windows Installer service to drive the entire installation, including calls to any custom actions (InstallScript, VBScript, JScript, .exe files, .dll files, managed code). The Basic MSI project type is recommended when you want to do any of the following:
• You want to meet the Windows logo program requirements.
• You want to maximize compatibility with administrative tools such as Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager, or if your software will be customized by corporate system administrators prior to deployment. The Basic MSI project type gives them the flexibility to create transforms for the installation package and its associated properties, without repackaging your installation.
• You want to avoid writing scripting code and want to instead set properties and make table entries.
• You want to upgrade an existing Basic MSI project.
InstallScript Projects
For the most part
InstallScript projects use InstallScript to control the installation. This project type is recommended for any of the following scenarios:
• You have advanced requirements for the end-user experience (the end-user dialogs), such as multimedia elements.
• You want to use full-screen billboards during the run time of your installation.
• You prefer authoring the project using a procedural language at its core rather than a set of database tables.
• You want to perform actions before or after the main installation has been run.
• You want to upgrade an existing InstallScript project.
InstallScript MSI Projects
The most complicated , But the function is also the most perfect
InstallScript MSI projects use both the Windows Installer engine and the InstallScript engine to drive the installation. This project type is the most complicated since it uses both of those engines for the installation; it is not recommended for beginners. This project type may be recommended in the following scenarios:
• You want to meet the Windows logo program requirements.
• You have advanced requirements for the end-user experience (the end-user dialogs), such as multimedia elements.
• You prefer authoring the project using a procedural language at its core rather than a set of database tables.
• You want to perform actions before or after the main installation has been run.
• You want to upgrade an existing InstallScript MSI project.
边栏推荐
- [shell] clean up nohup Out file
- 一个简单的代数问题的求解
- Red Hat安装内核头文件
- EMMC print cqhci: timeout for tag 10 prompt analysis and solution
- Red hat install kernel header file
- How to get free traffic in pinduoduo new store and what links need to be optimized in order to effectively improve the free traffic in the store
- [solved] record an error in easyexcel [when reading the XLS file, no error will be reported when reading the whole table, and an error will be reported when reading the specified sheet name]
- 架构设计的五个核心要素
- 常用消息队列有哪些?
- 关于服装ERP,你知道多少?
猜你喜欢

Hcip eighth operation
Message queuing: how to ensure that messages are not lost
判断文件是否为DICOM文件

如何提高网站权重
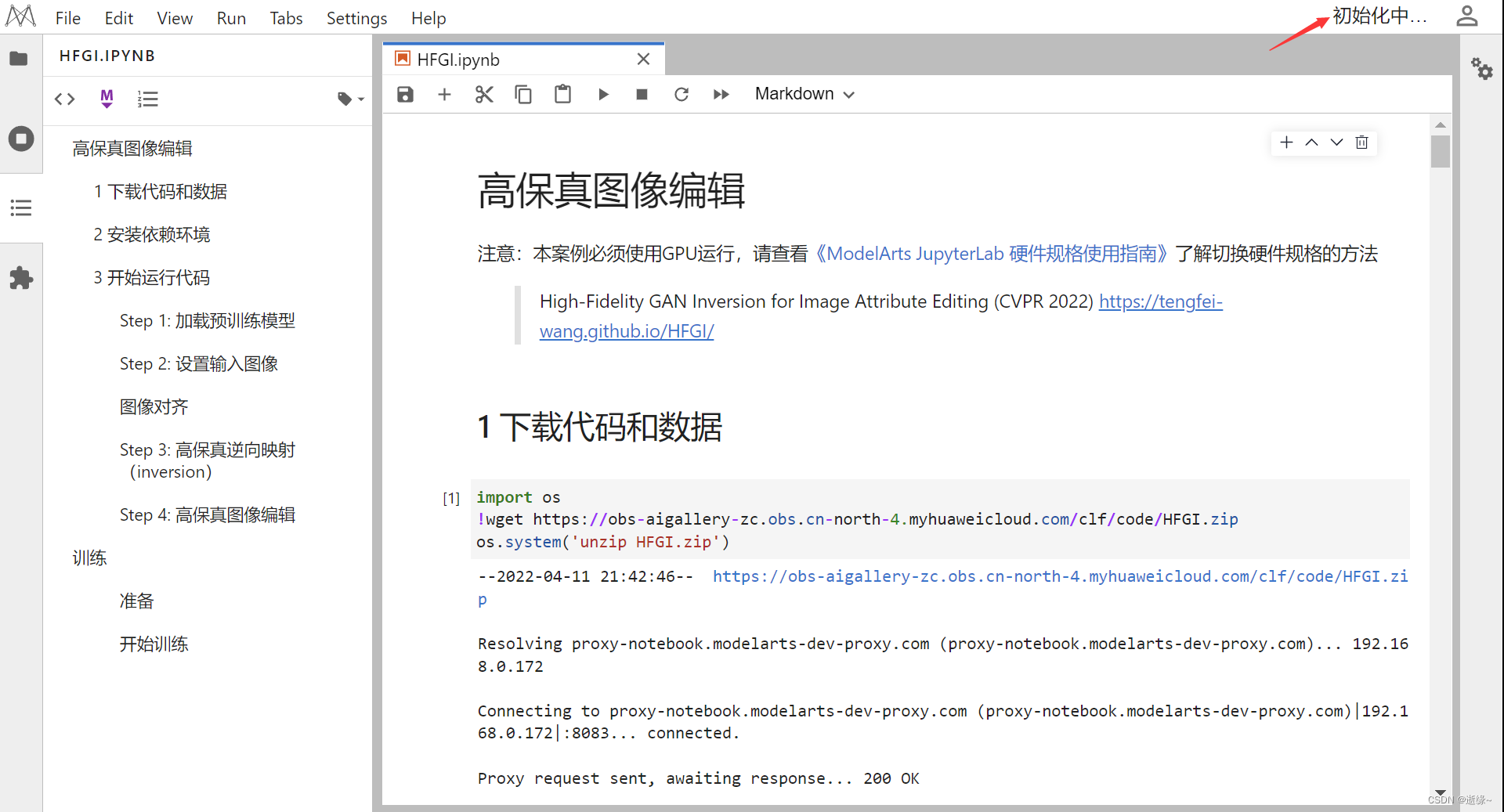
AI人脸编辑让Lena微笑
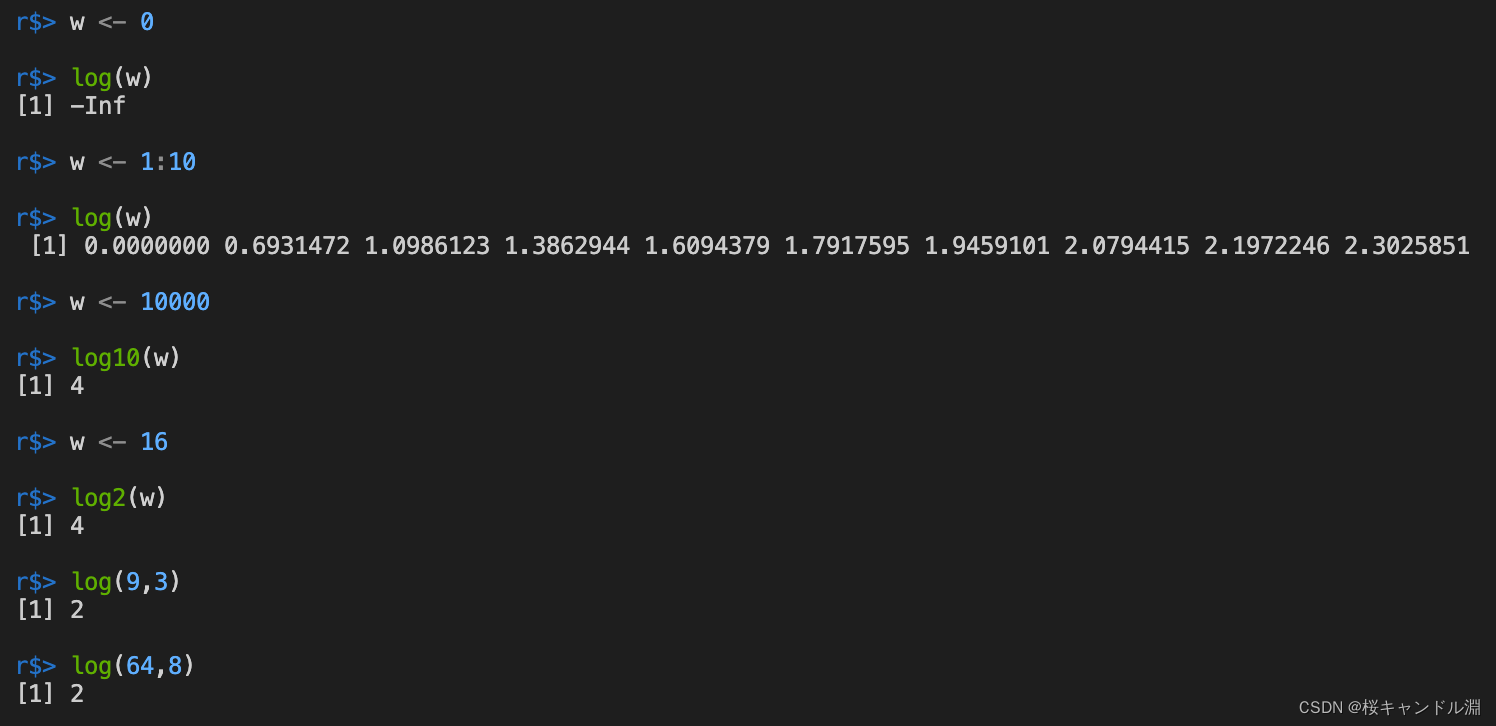
R语言【逻辑控制】【数学运算】

软件测试面试技巧
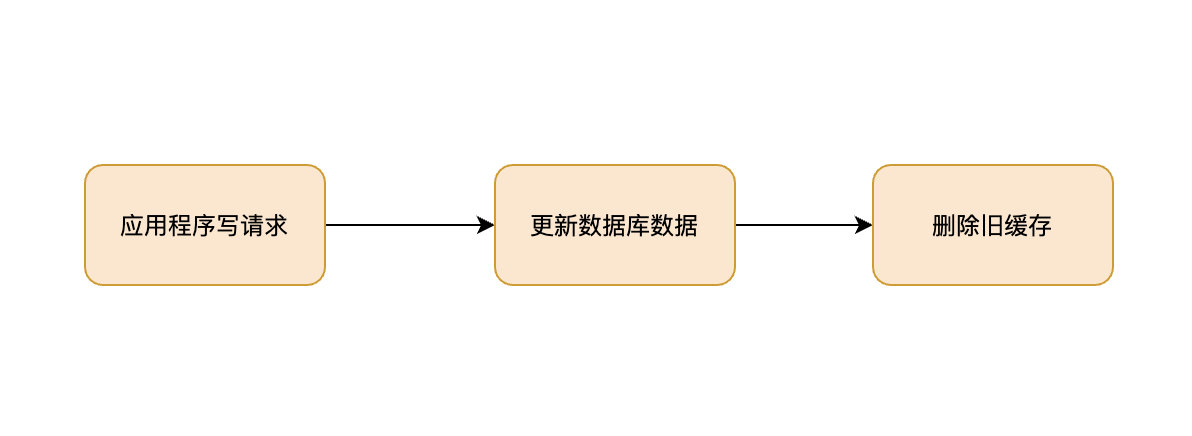
如果不知道这4种缓存模式,敢说懂缓存吗?
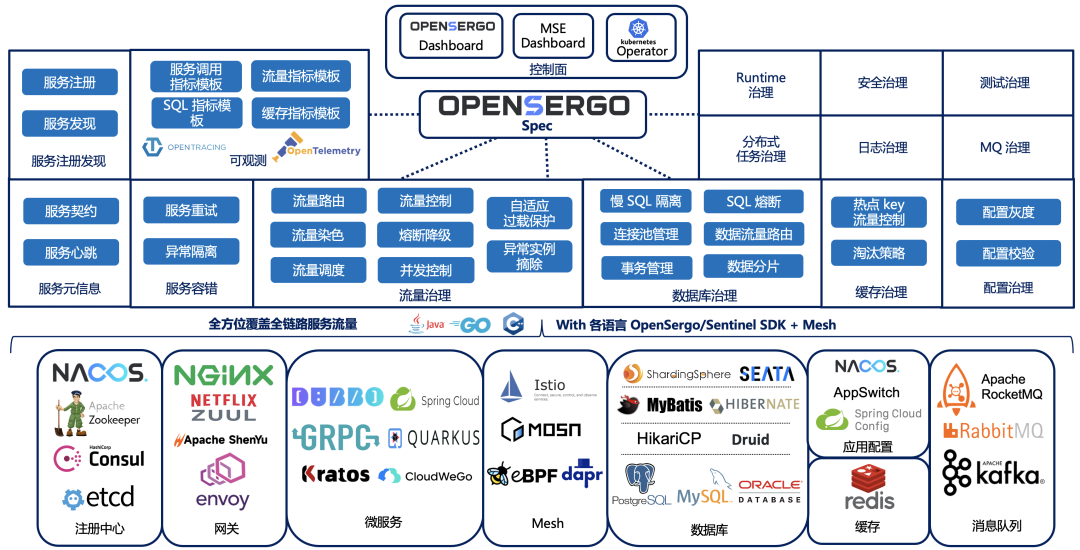
Opensergo is about to release v1alpha1, which will enrich the service governance capabilities of the full link heterogeneous architecture
![Reading the paper [sensor enlarged egocentric video captioning with dynamic modal attention]](/img/db/feb719e2715c7b9c669957995e1d83.png)
Reading the paper [sensor enlarged egocentric video captioning with dynamic modal attention]
随机推荐
Opensergo is about to release v1alpha1, which will enrich the service governance capabilities of the full link heterogeneous architecture
yarn入门(一篇就够了)
[shell] clean up nohup Out file
How much do you know about clothing ERP?
C#可空类型
Nvisual network visualization
The 2022 China low / no code Market Research and model selection evaluation report was released
[cloud native] what is the microservice architecture?
PowerPivot——DAX(函数)
Interview skills of software testing
如果不知道这4种缓存模式,敢说懂缓存吗?
How to improve website weight
Flink SQL realizes reading and writing redis and dynamically generates hset key
AI人脸编辑让Lena微笑
pytorch_ 01 automatic derivation mechanism
Paper reading [MM21 pre training for video understanding challenge:video captioning with pre training techniqu]
判断文件是否为DICOM文件
404 not found service cannot be reached in SAP WebService test
数字IC面试总结(大厂面试经验分享)
Unity keeps the camera behind and above the player