当前位置:网站首页>Numpy Foundation
Numpy Foundation
2022-07-03 10:22:00 【Fully automatic learning robot】
expanded memory bank Numpy brief introduction
Reference material :《Python You can learn this way 》( Dong Fuguo )
This article was originally written in jupyter notebook Upper , Into the .md The format is copied here , If you think this looks inconvenient , need .ipynb Format , Please confide in me :)
Article preview :
- expanded memory bank Numpy brief introduction
- 1. Generating arrays
- 2. Arithmetic operations of arrays and numbers
- 3. Array and array arithmetic operation
- 4. Two dimensional array transpose
- 5. Vector inner product
- 6. Array element access
- 7. Perform functional operations on arrays
- 8. Calculate the elements in different dimensions of the matrix
- 9. Change array size
- 10. Slicing operation
- 11. Boolean operation
- 12. radio broadcast
- 13. Piecewise functions
- 14. Calculate the unique value and the number of occurrences
- 15. Matrix operations
import numpy as np # Import numpy modular
1. Generating arrays
np.array((1,2,3,4,5)) # hold Python Convert list to array
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
np.array(range(5)) # hold range Object to array
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
np.linspace(0,10,11) # Generate an isometric array From 0 To 10 Generate 11 Number
array([ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.])
np.linspace(0,1,11) # Express 0 To 1 Generate 11 Number
array([0. , 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1. ])
np.logspace(0,100,10) # Logarithmic array from 0 To 100 Equal difference takes ten numbers , Do exponentiation . Let the tolerance be d, The ten returned are 10 Of 0 Power 、d Power 、2d Power
array([1.00000000e+000, 1.29154967e+011, 1.66810054e+022, 2.15443469e+033,
2.78255940e+044, 3.59381366e+055, 4.64158883e+066, 5.99484250e+077,
7.74263683e+088, 1.00000000e+100])
np.zeros((3,3)) # whole 0 Two dimensional array
array([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
np.zeros((3,1))
array([[0.],
[0.],
[0.]])
np.zeros((1,3))
array([[0., 0., 0.]])
np.ones((3,3)) # whole 1 Two dimensional array
array([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
np.identity(4) # Unit matrix
array([[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]])
np.empty((3,3)) # An empty array , Only apply for space without initializing , The element value is uncertain
array([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.]])
2. Arithmetic operations of arrays and numbers
x=np.array((1,2,3,4,5)) # Create an array object
x
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
x*2
array([ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
x/2
array([0.5, 1. , 1.5, 2. , 2.5])
x//2
array([0, 1, 1, 2, 2], dtype=int32)
x **3
array([ 1, 8, 27, 64, 125], dtype=int32)
x+2 # Add arrays to numbers
array([3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
x%3 # remainder
array([1, 2, 0, 1, 2], dtype=int32)
3. Array and array arithmetic operation
a = np.array((1,2,3))
b = np.array(([1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]))
c = a*b # Array multiplication ,a Multiply each element in by b Each column element in
c
array([[ 1, 4, 9],
[ 4, 10, 18],
[ 7, 16, 27]])
c/b
array([[1., 2., 3.],
[1., 2., 3.],
[1., 2., 3.]])
c/a
array([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.],
[7., 8., 9.]])
a+a
array([2, 4, 6])
a*a
array([1, 4, 9])
a-a
array([0, 0, 0])
a/a
array([1., 1., 1.])
4. Two dimensional array transpose
b = np.array(([1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]))
b
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])
b.T
array([[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[3, 6, 9]])
a=np.array((1,2,3,4))
a
array([1, 2, 3, 4])
a.T # The transposed one-dimensional array is the same as the original
array([1, 2, 3, 4])
5. Vector inner product
a=np.array((5,6,7))
b=np.array((6,6,6))
a.dot(b) # Vector inner product
(108, 108)
np.dot(a,b) # Vector inner product
108
c = np.array(([1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]))
cT=c.T
c.dot(a)
array([ 38, 92, 146])
c[0].dot(a)
38
c[1].dot(a)
92
a.dot(cT[2])
114
6. Array element access
b=np.array(([1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]))
b
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])
b[0]
array([1, 2, 3])
b[0][0]
1
Multi element simultaneous access
x=np.arange(0,100,10)
x
array([ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90])
index = np.random.randint(1,len(x),5)
index
array([6, 6, 2, 3, 7])
x[index]
array([60, 60, 20, 30, 70])
x[index] = [1,2,3,4,5] # Modify the values of multiple elements at the same time
x
array([ 0, 10, 3, 4, 40, 50, 2, 5, 80, 90])
x[[1,2,3]] # Access the values of multiple elements at the same time
array([10, 3, 4])
7. Perform functional operations on arrays
x=np.arange(0,100,10)
np.sin(x) # Find the sine of all elements in a one-dimensional array
array([ 0. , -0.54402111, 0.91294525, -0.98803162, 0.74511316,
-0.26237485, -0.30481062, 0.77389068, -0.99388865, 0.89399666])
b=np.array(([1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]))
np.cos(b)
array([[ 0.54030231, -0.41614684, -0.9899925 ],
[-0.65364362, 0.28366219, 0.96017029],
[ 0.75390225, -0.14550003, -0.91113026]])
np.round(np.cos(b)) # rounding
array([[ 1., -0., -1.],
[-1., 0., 1.],
[ 1., -0., -1.]])
x=np.random.rand(10)
x*=10
x
array([0.72528784, 7.46094155, 0.94747503, 2.10896222, 9.50620225,
2.64778271, 0.68896693, 1.19711742, 7.17753355, 0.93906123])
np.floor(x) # Rounding down
array([0., 7., 0., 2., 9., 2., 0., 1., 7., 0.])
np.ceil(x) # Rounding up
array([ 1., 8., 1., 3., 10., 3., 1., 2., 8., 1.])
8. Calculate the elements in different dimensions of the matrix
x=np.arange(0,10).reshape(2,5) # Create a 2D array
x
array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]])
np.sum(x) # Sum up
45
np.sum(x,axis = 0)# Longitudinal summation
array([ 5, 7, 9, 11, 13])
np.sum(x,axis = 1) # Horizontal summation
array([10, 35])
np.mean(x,axis = 0) # Calculate the arithmetic mean longitudinally
array([2.5, 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.5])
np.mean(x,axis = 1) # Calculate the arithmetic mean horizontally
array([2., 7.])
weight = [0.3,0.7] # The weight
np.average(x,axis = 0,weights = weight) # The weighted average value of two-dimensional array is calculated vertically
array([3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.5, 7.5])
np.max(x)
9
np.max(x,axis = 0) # Find the maximum value longitudinally , That is, the maximum value of each column
array([5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
x=np.random.randint(1,10,size=(3,3))
x
array([[8, 1, 6],
[1, 4, 1],
[8, 7, 9]])
np.std(x) # Find the standard deviation of all elements
3.1269438398822866
np.std(x,axis=1) # Horizontal standard deviation That is, the standard deviation of each line of elements
array([2.94392029, 1.41421356, 0.81649658])
np.var(x,axis = 0) # Vertical variance That is, the variance of each column of elements
array([10.88888889, 6. , 10.88888889])
np.sort(x,axis = 0) # Arrange vertically From small to large
array([[1, 1, 1],
[8, 4, 6],
[8, 7, 9]])
9. Change array size
a=np.arange(1,11,1)
a
array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
a.shape = 2,5 # Change to two rows and five columns
a
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
a.shape=5,-1 # -1 Indicates automatic calculation
a
array([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 6],
[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10]])
b=a.reshape(2,5) #reshape() Method to return a new array
b
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
10. Slicing operation
a=np.arange(10)
a
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
a[::-1] # Reverse slice
array([9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0])
a[::2] # Take one element after another
array([0, 2, 4, 6, 8])
a[:5] # The first five elements
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
c=np.arange(25)
c.shape=5,5
c
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
c[0,2:5] # The first 0 Middle subscript [2,5) Between the elements
array([2, 3, 4])
c[1] # The first 0 All elements in the row
array([5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
c[2:5,2:5] # Both row and column subscripts conclude [2,5) The element values between
array([[12, 13, 14],
[17, 18, 19],
[22, 23, 24]])
11. Boolean operation
x=np.random.rand(10) #10 A random array of numbers
x
array([0.66334709, 0.82328621, 0.41857429, 0.28620644, 0.26740633,
0.95842834, 0.94531951, 0.6467254 , 0.41522248, 0.64909167])
x>0.5 # Compare whether the value of each element in the array is greater than 0.5
array([ True, True, False, False, False, True, True, True, False,
True])
x[x>0.5] # Gets an array greater than 0.5 The elements of
array([0.66334709, 0.82328621, 0.95842834, 0.94531951, 0.6467254 ,
0.64909167])
a=np.array([1,2,3])
b=np.array([3,2,1])
a>b # Compare the size of elements in the corresponding position
array([False, False, True])
a[a>b]
array([3])
a ==b
array([False, True, False])
a[a==b]
array([2])
12. radio broadcast
a = np.arange(0,60,10).reshape(-1,1) # Column vector , -1 Indicates automatic calculation
a
array([[ 0],
[10],
[20],
[30],
[40],
[50]])
b=np.arange(0,6)
b
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
a+b # radio broadcast
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45],
[50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55]])
a*b
array([[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50],
[ 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100],
[ 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150],
[ 0, 40, 80, 120, 160, 200],
[ 0, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250]])
13. Piecewise functions
x=np.arange(10)
x
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
np.where(x<5,0,1) # Less than 5 The element value of corresponds to 0, Other correspondence 1
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
np.piecewise(x,[x<4,x>7],[lambda x:x*2,lambda x:x*3]) # Satisfaction is less than 4 Greater than 7 Multiply the number of by 3, Multiply the others by 2
array([ 0, 2, 4, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 24, 27])
14. Calculate the unique value and the number of occurrences
x= np.random.randint(0,10,7)
x
array([3, 5, 7, 6, 4, 2, 7])
a=np.bincount(x)# The number of times an element appears , This is not easy to say If you forget, check bincount()
a
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2], dtype=int64)
np.sum(a) # The sum of the occurrences of all elements is equal to the length of the array
7
len(x)
7
np.unique(x) # Return the unique element value
array([2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
x=np.random.randint(0,10,10)
x
array([5, 3, 7, 5, 7, 6, 1, 4, 8, 8])
y = np.random.rand(10) # Random decimal , Simulation weight
y = np.round_(y,1) # Keep one decimal place
y
array([0.2, 0.3, 0.7, 0.9, 0.3, 0.2, 0.4, 0.2, 0. , 0.2])
np.sum(x*y)/np.sum(np.bincount(x)) # Weighted sum / Total number of occurrences or elements
1.7399999999999998
15. Matrix operations
a_list=[3,5,7]
a_mat=np.matrix(a_list)
a_mat
matrix([[3, 5, 7]])
a_mat.T
matrix([[3],
[5],
[7]])
a_mat.shape # Matrix shape
(1, 3)
a_mat.size
3
b_mat=np.matrix((1,2,3))
b_mat
matrix([[1, 2, 3]])
a_mat * b_mat.T # matrix multiplication
matrix([[34]])
a_mat.mean() # Average value of elements
5.0
a_mat.sum() # Sum up
15
a_mat.max()
7
c_mat=np.matrix([[1,5,3],[2,9,6]]) # Create a two-dimensional matrix
c_mat
matrix([[1, 5, 3],
[2, 9, 6]])
c_mat.argsort(axis =0) # Sequence number of elements after vertical sorting
matrix([[0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1]], dtype=int64)
c_mat.argsort(axis = 1) # Sequence number of elements after horizontal sorting
matrix([[0, 2, 1],
[0, 2, 1]], dtype=int64)
d_mat=np.matrix([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
d_mat
matrix([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])
d_mat.diagonal() # Diagonal elements
matrix([[1, 5, 9]])
d_mat.flatten() # Matrix tiling
matrix([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]])
`
边栏推荐
- LeetCode - 919. 完全二叉树插入器 (数组)
- 2018 y7000 upgrade hard disk + migrate and upgrade black apple
- Tensorflow2.0 save model
- 20220531 Mathematics: Happy numbers
- 20220610其他:任务调度器
- LeetCode - 919. Full binary tree inserter (array)
- LeetCode - 508. Sum of subtree elements with the most occurrences (traversal of binary tree)
- [LZY learning notes -dive into deep learning] math preparation 2.5-2.7
- Leetcode - 5 longest palindrome substring
- 2312. Selling wood blocks | things about the interviewer and crazy Zhang San (leetcode, with mind map + all solutions)
猜你喜欢
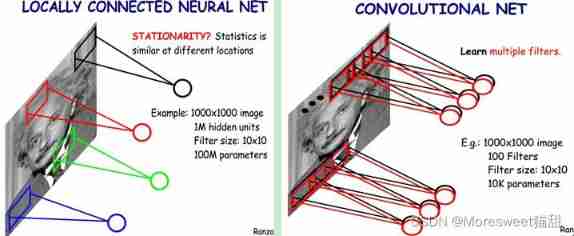
CV learning notes convolutional neural network

一步教你溯源【钓鱼邮件】的IP地址
![[LZY learning notes dive into deep learning] 3.1-3.3 principle and implementation of linear regression](/img/ce/8c2ede768c45ae6a3ceeab05e68e54.jpg)
[LZY learning notes dive into deep learning] 3.1-3.3 principle and implementation of linear regression

1. Finite Markov Decision Process

Leetcode - 895 maximum frequency stack (Design - hash table + priority queue hash table + stack)*
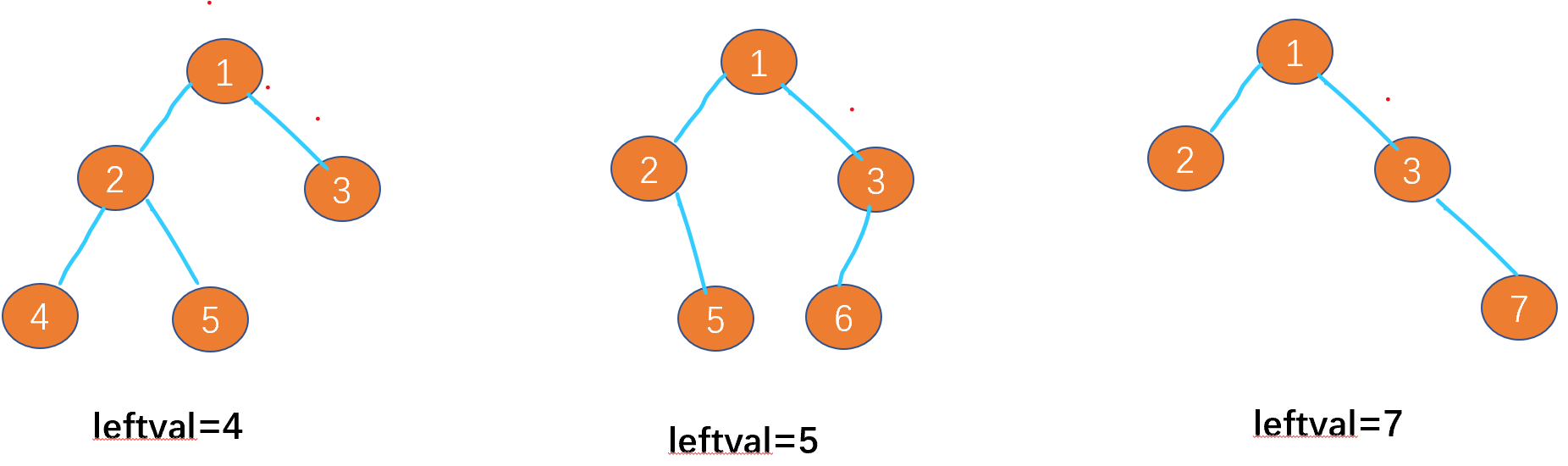
Leetcode-513:找树的左下角值
2018 Lenovo y7000 black apple external display scheme
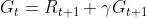
3.1 Monte Carlo Methods & case study: Blackjack of on-Policy Evaluation

Leetcode-106:根据中后序遍历序列构造二叉树

CV learning notes - BP neural network training example (including detailed calculation process and formula derivation)
随机推荐
CV learning notes ransca & image similarity comparison hash
Leetcode-100: same tree
Deep Reinforcement learning with PyTorch
Matplotlib drawing
Leetcode-112: path sum
On the problem of reference assignment to reference
Leetcode-404: sum of left leaves
LeetCode - 1670 設計前中後隊列(設計 - 兩個雙端隊列)
Opencv feature extraction - hog
Boston house price forecast (tensorflow2.9 practice)
Leetcode-513: find the lower left corner value of the tree
Tensorflow built-in evaluation
Leetcode - 1670 conception de la file d'attente avant, moyenne et arrière (conception - deux files d'attente à double extrémité)
Secure in mysql8.0 under Windows_ file_ Priv is null solution
Standard library header file
Synchronous vs asynchronous
LeetCode - 933 最近的请求次数
CV learning notes alexnet
20220602数学:Excel表列序号
Leetcode - 933 number of recent requests