当前位置:网站首页>[binocular vision] binocular stereo matching
[binocular vision] binocular stereo matching
2022-07-02 07:48:00 【Silent clouds】
One 、 Binocular stereo matching algorithm
stay opencv There are two kinds of binocular stereo matching algorithms used in :BM and SGBM.SGBM yes BM Optimized version of stereo matching algorithm , It belongs to semi global matching , be relative to BM It takes more time , But the effect is better than BM. This article USES SGBM Semi global matching .
step :
1. Turn on camera , Get the left eye and right eye images ;
2. Correction of distortion ;
3. Image graying ;
4. Stereo matching , Output results .
Code steps
Import the required third-party libraries
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Distortion correction script
import camera_config
Correction of distortion
left_remap = cv2.remap(imgLeft, camera_config.left_map1, camera_config.left_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
right_remap = cv2.remap(imgRight, camera_config.right_map1, camera_config.right_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
Graying
imgL_gray = cv2.cvtColor(left_remap, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
imgR_gray = cv2.cvtColor(right_remap, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
Stereo matching
### Set parameters
# The block size must be odd (3-11)
blockSize = 5
img_channels = 2
num_disp = 16 * 8
param = {
'preFilterCap': 63, # Map filter size , Default 15
"minDisparity" : 0, # Minimum parallax
"numDisparities" : num_disp, # The search range of parallax ,16 Integer multiple
"blockSize" : blockSize,
"uniquenessRatio" : 10, # Unique detectability parameter , The matching discrimination is not enough , Then mismatch (5-15)
"speckleWindowSize" : 0, # The number of pixels in the parallax connected area ( Noise point )(50-200) Or use 0 Disable speckle filtering
"speckleRange" : 1, # Think disconnected (1-2)
"disp12MaxDiff" : 2, # The maximum allowable error value in left-right consistency detection
"P1" : 8 * img_channels * blockSize** 2, # The bigger the value is. , The smoother the parallax , Parallax of adjacent pixels +/-1 Penalty coefficient
"P2" : 32 * img_channels * blockSize** 2, # ditto , Parallax change value of adjacent pixels >1 Penalty coefficient
# 'mode': cv2.STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY
}
## Start to calculate the depth map
left_matcher = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(**param)
left_disp = left_matcher.compute(imgL_gray, imgR_gray)
# Get the depth map
disp = cv2.normalize(dispL, dispL, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
effect 
Two 、wls wave filtering
From the above results , There are many depth maps “ Black areas ”,“ Black areas ” There is no correct match , That is to say, there is no depth information in this part , This situation is “ Not dense enough ”.
stay opencv The expansion pack, opencv-contrib There is a WLS Parallax filtering method , It can make the reconstruction more dense .
The improved part is stereo matching , After stereo matching, do another step :
## Connect the above parameters
left_matcher = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(**param)
right_matcher = cv2.ximgproc.createRightMatcher(left_matcher)
left_disp = left_matcher.compute(imgL_gray, imgR_gray)
right_disp = right_matcher.compute(imgR_gray, imgL_gray)
wls_filter = cv2.ximgproc.createDisparityWLSFilter(left_matcher)
# sigmaColor The typical range value is 0.8-2.0
wls_filter.setLambda(8000.)
wls_filter.setSigmaColor(1.3)
wls_filter.setLRCthresh(24)
wls_filter.setDepthDiscontinuityRadius(3)
filtered_disp = wls_filter.filter(left_disp, imgL_gray, disparity_map_right=right_disp)
disp = cv2.normalize(filtered_disp, filtered_disp, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)

You can see that the filtered depth map has become quite dense .
But this method has advantages and disadvantages : The advantage is that the reconstruction becomes dense , The drawback is that this method will erase some details , Make a place from different depths to the same height .
for instance , The cup in the above figure should be cylindrical in actual observation , But after filtering, the whole cup body will become the same height , That is, the original height difference is erased . Therefore, please decide whether to use this method according to the specific situation .
3、 ... and 、open3d Point cloud reconstruction
open3d Provides RGBD The way of reconstruction , The specific implementation is as follows :
First, prepare a camera internal reference file ( It's easier to do this ), Name it camera_intrinsic.json,
According to the internal parameter matrix of the left eye camera :
| fx | 0 | cx |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | fy | cy |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
Write in column order :
{
"width": 960,
"height": 960,
"intrinsic_matrix": [
fx,
0,
0,
0,
fy,
0,
cx,
cy,
1
]
}
preservation , As camera internal reference file . Then continue to access the following code in the main program :
# Get internal parameters
intrinsic = o3d.io.read_pinhole_camera_intrinsic("camera_intrinsic.json")
# Converting images
color_image = o3d.geometry.Image(left_remap)
depth_image = o3d.geometry.Image(disp)
rgbd_image = o3d.geometry.RGBDImage.create_from_color_and_depth(color_image, depth_image, depth_trunc=4.0, convert_rgb_to_intensity=False)
# according to RGBD Image reconstruction
temp = o3d.geometry.PointCloud.create_from_rgbd_image(rgbd_image, intrinsic)
pcd.points = temp.points
pcd.colors = temp.colors
# According to the effect
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries_with_editing([pcd], window_name="3D", width=1280, height=720)

Four 、OpenCV Point cloud reconstruction
In addition, you can also use opencv Bring your own way to rebuild , The reconstruction speed is faster than open3d Much faster .
You need to cut out some unreasonable point cloud data when processing .
# take h×w×3 Array to N×3 Array of
def hw3ToN3(points):
height, width = points.shape[0:2]
points_1 = points[:, :, 0].reshape(height * width, 1)
points_2 = points[:, :, 1].reshape(height * width, 1)
points_3 = points[:, :, 2].reshape(height * width, 1)
points_ = np.hstack((points_1, points_2, points_3))
return points_
def DepthColor2Cloud(points_3d, colors):
rows, cols = points_3d.shape[0:2]
size = rows * cols
points_ = hw3ToN3(points_3d).astype(np.int16)
colors_ = hw3ToN3(colors).astype(np.int64)
# Color information
blue = colors_[:, 0].reshape(size, 1)
green = colors_[:, 1].reshape(size, 1)
red = colors_[:, 2].reshape(size, 1)
# rgb = np.left_shift(blue, 0) + np.left_shift(green, 8) + np.left_shift(red, 16)
rgb = blue + green + red
# Put the coordinates + The colors are superimposed into an array of point clouds
pointcloud = np.hstack((points_, red/255., green/255., blue/255.)).astype(np.float64)
# Delete some inappropriate points
X = pointcloud[:, 0]
Y = pointcloud[:, 1]
Z = pointcloud[:, 2]
remove_idx1 = np.where(Z <= 0)
remove_idx2 = np.where(Z > 1000)
remove_idx3 = np.where(X > 1000)
remove_idx4 = np.where(X < -1000)
remove_idx5 = np.where(Y > 1000)
remove_idx6 = np.where(Y < -1000)
remove_idx = np.hstack((remove_idx1[0], remove_idx2[0], remove_idx3[0], remove_idx4[0], remove_idx5[0], remove_idx6[0]))
pointcloud_1 = np.delete(pointcloud, remove_idx, 0)
return pointcloud_1
The above function can be saved with a script file separately and then imported .
Add the following code to the main script file :
threeD = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disp, camera_config.Q)
pointcloud = DepthColor2Cloud(threeD, left_remap)
# Convert to open3d Point cloud data
pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(pointcloud[:,:3])
pcd.colors = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(pointcloud[:,3:])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries_with_editing([pcd], window_name="3D", width=1280, height=720)

边栏推荐
- 程序的内存模型
- 【MnasNet】《MnasNet:Platform-Aware Neural Architecture Search for Mobile》
- Drawing mechanism of view (I)
- 【Mixed Pooling】《Mixed Pooling for Convolutional Neural Networks》
- Proof and understanding of pointnet principle
- Open failed: enoent (no such file or directory) / (operation not permitted)
- Convert timestamp into milliseconds and format time in PHP
- Regular expressions in MySQL
- 【Paper Reading】
- MMDetection模型微调
猜你喜欢

Implementation of yolov5 single image detection based on pytorch
【Batch】learning notes

open3d学习笔记三【采样与体素化】
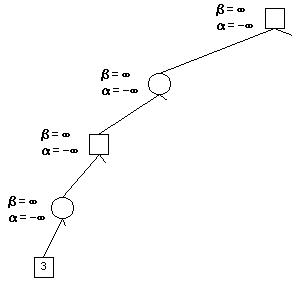
Alpha Beta Pruning in Adversarial Search
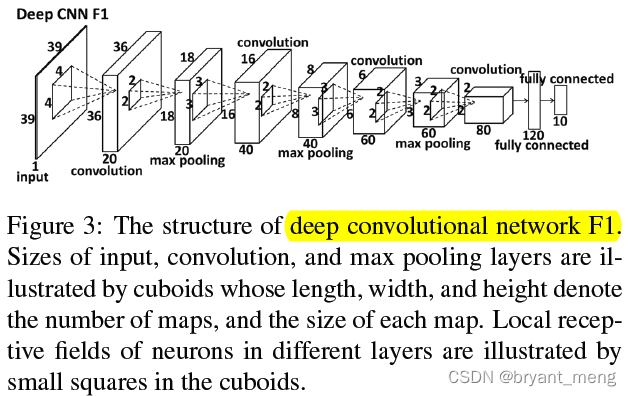
【Cascade FPD】《Deep Convolutional Network Cascade for Facial Point Detection》
![[Sparse to Dense] Sparse to Dense: Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth samples and a Single Image](/img/05/bf131a9e2716c9147a5473db4d0a5b.png)
[Sparse to Dense] Sparse to Dense: Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth samples and a Single Image

Deep learning classification Optimization Practice

【AutoAugment】《AutoAugment:Learning Augmentation Policies from Data》

机器学习理论学习:感知机
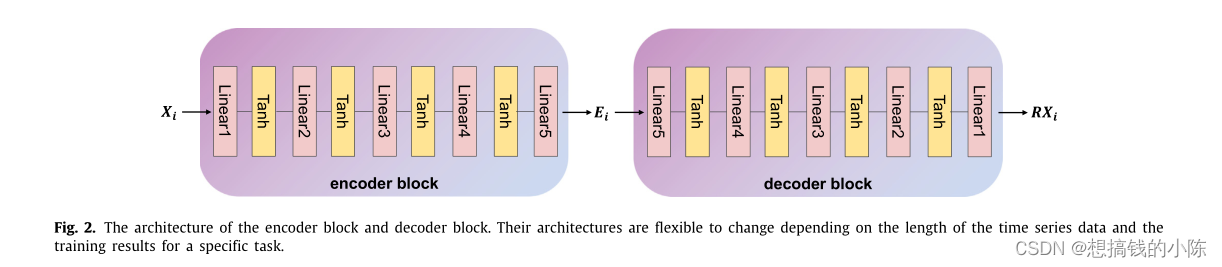
TimeCLR: A self-supervised contrastive learning framework for univariate time series representation
随机推荐
conda常用命令
【Hide-and-Seek】《Hide-and-Seek: A Data Augmentation Technique for Weakly-Supervised Localization xxx》
【FastDepth】《FastDepth:Fast Monocular Depth Estimation on Embedded Systems》
TimeCLR: A self-supervised contrastive learning framework for univariate time series representation
【Paper Reading】
【Random Erasing】《Random Erasing Data Augmentation》
Win10 solves the problem that Internet Explorer cannot be installed
PHP returns the corresponding key value according to the value in the two-dimensional array
Jordan decomposition example of matrix
MMDetection安装问题
The difference and understanding between generative model and discriminant model
Proof and understanding of pointnet principle
半监督之mixmatch
win10+vs2017+denseflow编译
Using compose to realize visible scrollbar
latex公式正体和斜体
Sorting out dialectics of nature
MMDetection模型微调
【TCDCN】《Facial landmark detection by deep multi-task learning》
Pointnet understanding (step 4 of pointnet Implementation)