当前位置:网站首页>Redis Foundation
Redis Foundation
2022-07-06 06:38:00 【Protogram Technology】
One 、Redis brief introduction
Redis Is a high-performance key-value database
Two 、Redis Characteristics
Support data persistence
Rich data types
3、 ... and 、redis data type
string( character string ),hash( Hash ),list( list ),set( aggregate ) And zset(sorted set: Ordered set )
1、string( character string )
# Set up
SET runoob " Novice tutorial "
# obtain
GET runoob
2、Hash( Hash )
# Set up
HMSET runoob field1 "Hello" field2 "World"
# obtain
HGET runoob field1
HGET runoob field2
3、List( list )
# Set up
lpush runoob redis
lpush runoob mongodb
lpush runoob rabbitmq
# obtain
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> lrange runoob 0 10
1) "rabbitmq"
2) "mongodb"
3) "redis"
4、Set( aggregate )
# grammar
sadd key member
# Set up
sadd runoob redis
sadd runoob mongodb
sadd runoob rabbitmq
sadd runoob rabbitmq
# obtain
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers runoob
1) "redis"
2) "rabbitmq"
3) "mongodb"
5、zset(sorted set: Ordered set )
# grammar
zadd key score member
# Set up
zadd runoob 0 redis
zadd runoob 0 mongodb
zadd runoob 0 rabbitmq
zadd runoob 0 rabbitmq
# obtain
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGEBYSCORE runoob 0 1000
1) "mongodb"
2) "rabbitmq"
3) "redis"
notes : Delete use DEL key
Four 、Redis Publish subscribe
Redis Publish subscribe (pub/sub) It's a message communication mode : sender (pub) Send a message , subscriber (sub) receive messages .
5、 ... and 、Redis Business
1、 A transaction goes through the following three stages from the beginning to the execution :
Start business .
Order to join the team .
Perform transactions .
2、 example
Start with MULTI Start a transaction , Then queue multiple commands into the transaction , Finally by EXEC Command triggers transaction , Execute all the commands in the transaction
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> MULTI
OK
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SET book-name "Mastering C++ in 21 days"
QUEUED
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> GET book-name
QUEUED
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SADD tag "C++" "Programming" "Mastering Series"
QUEUED
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS tag
QUEUED
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> EXEC
1) OK
2) "Mastering C++ in 21 days"
3) (integer) 3
4) 1) "Mastering Series"
2) "C++"
3) "Programming"
6、 ... and 、Redis Stream
Redis Stream It is mainly used for message queuing (MQ,Message Queue),Redis There is one in itself Redis Publish subscribe (pub/sub) To realize the function of message queuing , But it has a drawback that messages are not persistent , If there is a network disconnect 、Redis Downtime, etc , The message will be discarded .
Simply put, publish subscribe (pub/sub) You can distribute messages , But we can't record historical information .
and Redis Stream It provides message persistence and primary / secondary replication functions , Any client can access data at any time , And remember the location of each client's access , It also ensures that the message is not lost .
Message queuing related commands :
XADD - Add the message to the end
XTRIM - Pruning the convection , Limit length
XDEL - removal message
XLEN - Gets the number of elements contained in the stream , The message length
XRANGE - Get message list , Will automatically filter deleted messages
XREVRANGE - Get the message list in reverse ,ID From big to small
XREAD - Get a list of messages in a blocking or non blocking way
Consumer group related orders :
XGROUP CREATE - Create consumer groups
XREADGROUP GROUP - Read messages from consumer groups
XACK - Mark the message as " Disposed of "
XGROUP SETID - Set up a new last delivery message for the consumer group ID
XGROUP DELCONSUMER - Delete consumer
XGROUP DESTROY - Delete consumer group
XPENDING - Displays information about the message to be processed
XCLAIM - Transfer ownership of messages
XINFO - View information about streams and consumer groups ;
XINFO GROUPS - Print information about consumer groups ;
XINFO STREAM - Print stream information
7、 ... and 、Redis Data backup and recovery
1、 Backup
Redis SAVE Command to create a backup of the current database
example :
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SAVE
OK
The order will be in redis Create... In the installation directory dump.rdb file .
2、 recovery
If you need to recover data , Just back up the files (dump.rdb) Move to redis Install the directory and start the service . obtain redis The directory can be used CONFIG command , As shown below :
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET dir
1) "dir"
2) "/usr/local/redis/bin"
The above order CONFIG GET dir Output redis Installation directory is /usr/local/redis/bin.
8、 ... and 、Redis Security
1、 example
We can check whether password verification is set through the following command :
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG get requirepass
1) "requirepass"
2) ""
By default requirepass Parameter is empty , This means that you can connect to... Without password verification redis service .
You can modify this parameter with the following command :
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG set requirepass "runoob"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG get requirepass
1) "requirepass"
2) "runoob"
After setting the password , Client connection redis The service needs password verification , Otherwise, the command cannot be executed .
grammar
AUTH The basic syntax of the command is as follows :
127.0.0.1:6379> AUTH password
example
127.0.0.1:6379> AUTH "runoob"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> SET mykey "Test value"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> GET mykey
"Test value"
Nine 、Redis Pipeline technology
Redis It's a client based - Server model and request / In response to the protocol TCP service . This means that normally a request follows these steps :
The client sends a query request to the server , And monitor Socket return , Usually in blocking mode , Waiting for the server to respond .
The server handles commands , And return the result to the client .
Redis Pipeline technology can be used when the server is not responding , The client can continue to send requests to the server , And finally read all the server's responses at once .
Advantages of Pipeline Technology : The most significant advantage of pipeline technology is the improvement of redis Service performance .
Ten 、Redis Partition
Partitioning is dividing data into multiple Redis The process of the instance , So each instance only saves key A subset of .
11、 ... and 、 other
Redis Queue real-time and non real-time : Real time and non real time are mainly aimed at consumers , Message producers produce messages after ,Redis These messages are stored in the queue , When to consume is our concern , Non real time means , At the back end, there is a rotation service to get messages from the queue regularly , This has a certain delay ; Real time means building on the consumer side Tcp A long connection , When the queue has data, consume it immediately , When there is no data, the thread is in a suspended waiting state !
边栏推荐
- How effective is the Chinese-English translation of international economic and trade contracts
- SSO流程分析
- Black cat takes you to learn UFS protocol Chapter 18: how UFS configures logical units (Lu Management)
- Data security -- 13 -- data security lifecycle management
- Black cat takes you to learn UFS Protocol Part 8: UFS initialization (boot operation)
- [English] Verb Classification of grammatical reconstruction -- English rabbit learning notes (2)
- ECS accessKey key disclosure and utilization
- How much is it to translate Chinese into English for one minute?
- Simulation volume leetcode [general] 1143 Longest common subsequence
- Simulation volume leetcode [general] 1109 Flight reservation statistics
猜你喜欢

How effective is the Chinese-English translation of international economic and trade contracts
LeetCode 739. Daily temperature

Biomedical English contract translation, characteristics of Vocabulary Translation

Drug disease association prediction based on multi-scale heterogeneous network topology information and multiple attributes
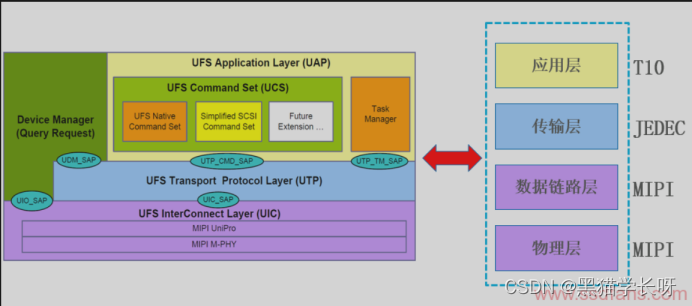
Black cat takes you to learn UFS protocol Chapter 4: detailed explanation of UFS protocol stack
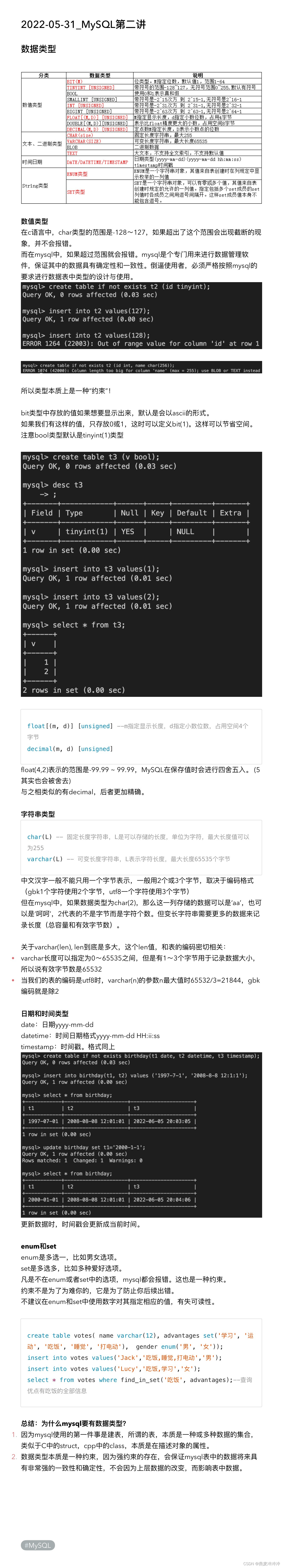
Data type of MySQL

翻译公司证件盖章的价格是多少
Suspended else

Changes in the number of words in English papers translated into Chinese
Private cloud disk deployment
随机推荐
Modify the list page on the basis of jeecg boot code generation (combined with customized components)
翻译生物医学说明书,英译中怎样效果佳
My creation anniversary
ECS accessKey key disclosure and utilization
Day 248/300 关于毕业生如何找工作的思考
Thesis abstract translation, multilingual pure human translation
删除外部表源数据
Chinese English comparison: you can do this Best of luck
The whole process realizes the single sign on function and the solution of "canceltoken" of undefined when the request is canceled
CS certificate fingerprint modification
Phishing & filename inversion & Office remote template
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
org. activiti. bpmn. exceptions. XMLException: cvc-complex-type. 2.4. a: Invalid content beginning with element 'outgoing' was found
SSO流程分析
[ 英語 ] 語法重塑 之 動詞分類 —— 英語兔學習筆記(2)
JDBC requset corresponding content and function introduction
CS-证书指纹修改
Simulation volume leetcode [general] 1143 Longest common subsequence
In English translation of papers, how to do a good translation?
翻译公司证件盖章的价格是多少