当前位置:网站首页>Disk storage chain B-tree and b+ tree
Disk storage chain B-tree and b+ tree
2022-07-07 18:12:00 【cheems~】
Disk storage chain B Trees and B+ Trees
- Preface
- Disk structure analysis and data storage principle
- B The definition of a tree
- B Trees and B+ The difference between trees
- B Two kinds of splitting of tree insertion
- B The borrowing before and after tree deletion is merged with the node
- Keywords are in leaf nodes , Delete directly
- The current node is an inner node , And the left child at least includes M/2 Key words , Then borrow and delete
- The current node is an inner node , And the right child at least includes M/2 Key words , Then borrow backward and delete
- Both children are M/2-1 Key words , Then merge and delete
- Delete merge code
- B Tree insertion , Delete , Traverse , Look for code
Preface
In this paper, b Trees and b+ Trees . Also on b The insertion and deletion of trees are introduced in detail , The code is attached at the end of the text .
The knowledge points of this column are through Zero sound education Online learning , Make a summary and write an article , Yes c/c++linux Readers interested in the course , You can click on the link C/C++ Background advanced server course introduction Check the service of the course in detail .
Disk structure analysis and data storage principle
We know that the common data structures are linked lists , Trees , Pictures and so on , And trees can be divided into binary trees , Multi fork tree and so on . For a linked list , It can find the next node , The tree can not only find the next data node , The tree can find two , Find three , Find more ( Several forks ), If a node has several forks, you can find several nodes , Through a node, you can find n Nodes , This is a tree structure .
So why should there be a multi fork tree ? Academically , Usually interpreted as : The tree is for descending . Then why should we lower the floor ?
For a multitree , Within a node , There may be more than one key, Therefore, multi tree can not improve the efficiency of query ( Compared with a binary tree ). But it has one advantage ,“ Within a node , There may be more than one key”, This means that the number of nodes of a multi tree is relatively small , Since the number of nodes is small , Then the number of times to find nodes is less .
Be careful , The function of multi fork tree : Reduce floor height , Reduce the number of nodes , Then the number of times to find nodes will be reduced .
We know cpu Can directly access memory , Instead of directly accessing the disk . The computer sends an access instruction to the disk , The disk finds the corresponding disk track sector through rotation, and then reads it out and puts it into memory . Why is the disk slow , It's because the disk addressing speed is slow . Every address , The disk will rotate once . One access of memory is about 10ns, One access of disk is 100ms. For in memory , Multi fork tree has little effect , But for disks , If a node is saved 10 individual key, You can address many times less . So the function of multi tree is to reduce the layer height in order to reduce the number of addressing . This is why disk storage is suitable b Tree or b+ The reason for the tree .
Multiforked tree -> Reduce floor height -> Reduce the number of nodes -> Reduce disk IO -> Lifting performance
B The definition of a tree
One M rank B Trees T, The following conditions are met
- Each node has at most M Class subtree
- The root node has at least two subtrees
- Except for the root node , Every other branch node has at least M/2 Class subtree
- All the leaf nodes are on the same layer
- Yes k The branch nodes of Kezi trees exist k-1 Key words , Keywords are sorted in ascending order
- The number of keywords meets ceil( M/2 ) - 1 <= n <= M-1
B Trees and B+ The difference between trees
In the actual disk storage, we often choose b+ Trees
b+ Trees compare with b The advantages of trees :
- Keywords do not save data , Index only , All data is saved in the leaf node (b A tree holds data for each keyword )
- b+ The leaf nodes of the tree have pointers , And the leaf nodes themselves are connected in the order of keywords from small to large ( For range queries )
- b+ The middle node of the tree does not save data , So disk pages can hold more node elements , more “ Short and fat ”
B Two kinds of splitting of tree insertion
b The tree is in the process of inserting , Will check whether the current node can be split from top to bottom , If the keywords are full (k=M-1) Then split first , Insert again . And the insertion will be inserted into the leaf node .b There are two kinds of splits when a tree is inserted , One is root node splitting , One is non root node splitting .
Non root node splitting
Non root node splitting process :
1. Create a new node , Set to Z, The original node is set to Y
2. take Y The second half of the keyword and subtree are assigned to Z
3. take Y The key word in the middle key To the parent node
4. Parent node x Add a keyword key And subtree Z
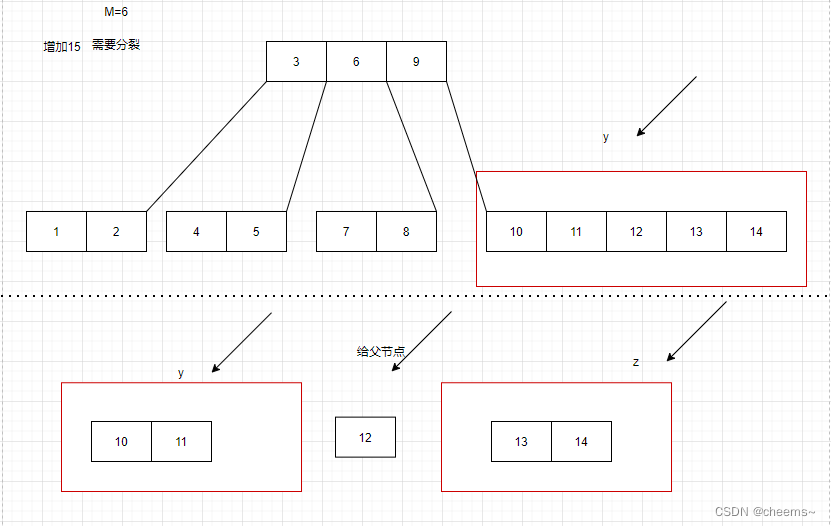
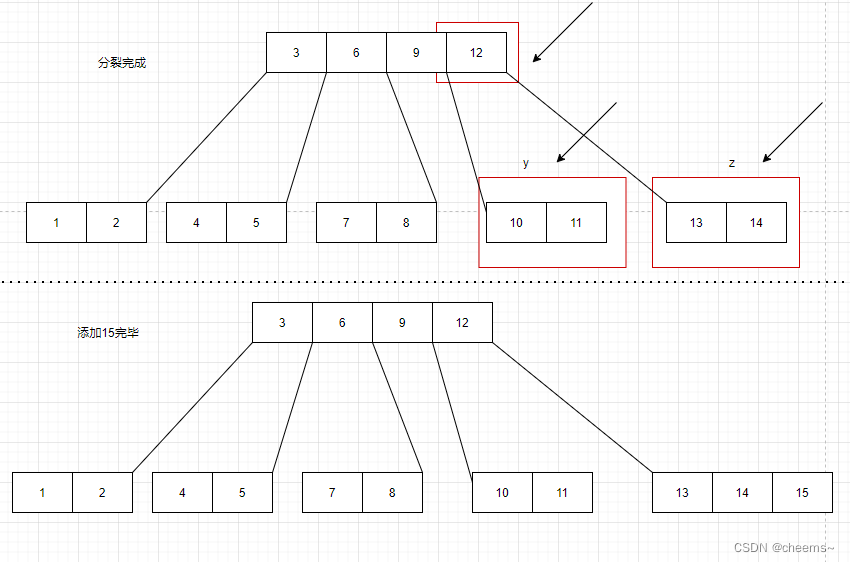
Root node splitting
Root node splitting process :
1. Create a new node , Set to node
2. take b Treelike root Point to node
3. node The first subtree of points to the previous root node
4. Now? , Root node splitting is transformed into non root node splitting
5. Perform the non root node splitting process
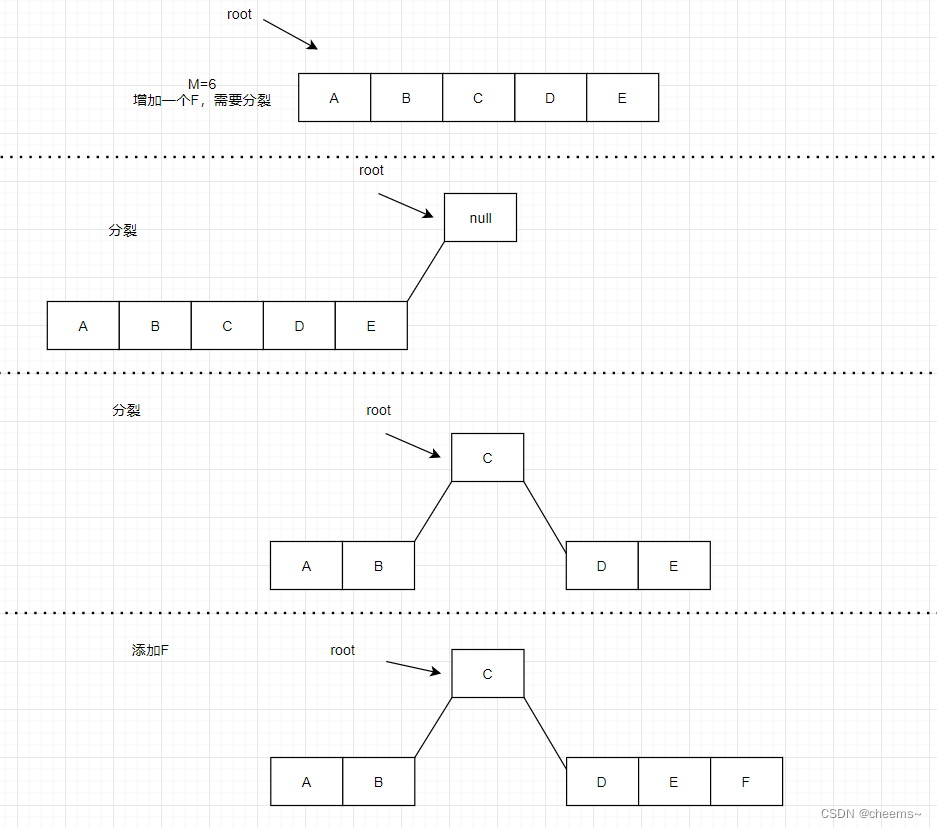
Insert split code
// split
void btree_split_clild(struct btree *T, struct btree_node *x, int i) {
//y Nodes that need to be split
struct btree_node *y = x->children[i];
// New node
struct btree_node *z = btree_create_node(T->t, y->leaf);
int j = 0;
z->num = T->t - 1;
// hold y The second half of key And subtree copy To z in
for (j = 0; j < T->t - 1; j++) {
z->keys[j] = y->keys[j + T->t];
}
if (y->leaf == 0) {
for (j = 0; j < T->t; j++) {
z->children[j] = y->children[j + T->t];
}
}
//y Node modification quantity
y->num = T->t - 1;
// Put the parent node x Add one more key And subtree z
for (j = x->num; j >= i + 1; j--) {
x->children[j + 1] = x->children[j];
}
x->children[i + 1] = z;
for (j = x->num - 1; j >= i; j--) {
x->keys[j + 1] = x->keys[j];
}
x->keys[i] = y->keys[T->t - 1];
x->num++;
}
void btree_insert_nonfull(struct btree *T, struct btree_node *x, KEY_TYPE key) {
int i = x->num - 1;
if (x->leaf) {
while (i >= 0 && x->keys[i] > key) {
x->keys[i + 1] = x->keys[i];
i--;
}
x->keys[i + 1] = key;
x->num++;
}
else {
while (i >= 0 && x->keys[i] > key)i--;
if (x->children[i + 1]->num == 2 * T->t - 1) {
btree_split_clild(T, x, i + 1);
if (key > x->keys[i + 1])i++;
}
btree_insert_nonfull(T, x->children[i + 1], key);
}
}
void btree_insert(struct btree *T, KEY_TYPE key) {
struct btree_node *root = T->root;
// If the root node is full , The root node splits and then inserts
if (root->num == 2 * T->t - 1) {
btree_node *node = btree_create_node(T->t, 0);
T->root = node;
node->children[0] = root;
btree_split_clild(T, node, 0);
int i = 0;
if (key > node->keys[0]) i++;
btree_insert_nonfull(T, node->children[i], key);
}
else {
btree_insert_nonfull(T, root, key);
}
}
B The borrowing before and after tree deletion is merged with the node
Why delete keywords to borrow or merge ? Because we need to meet b The definition of a tree
Determine the number of sub tree keywords
- The two adjacent sub trees are M/2-1 , Then merge
- The left subtree is larger than M/2-1, Borrow to the left
- The right subtree is larger than M/2-1, Borrow right
Keywords are in leaf nodes , Delete directly
Keywords are in leaf nodes
- Delete directly
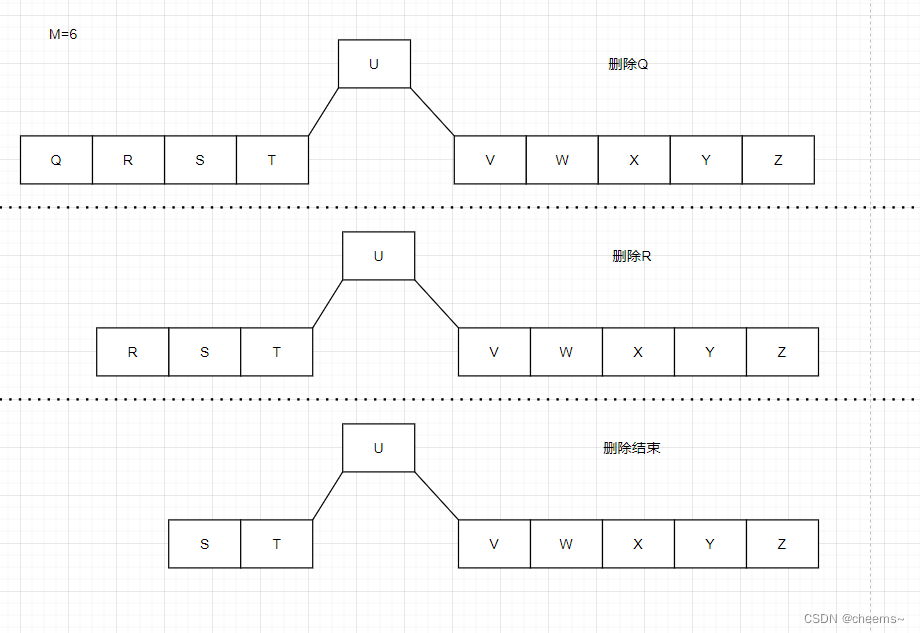
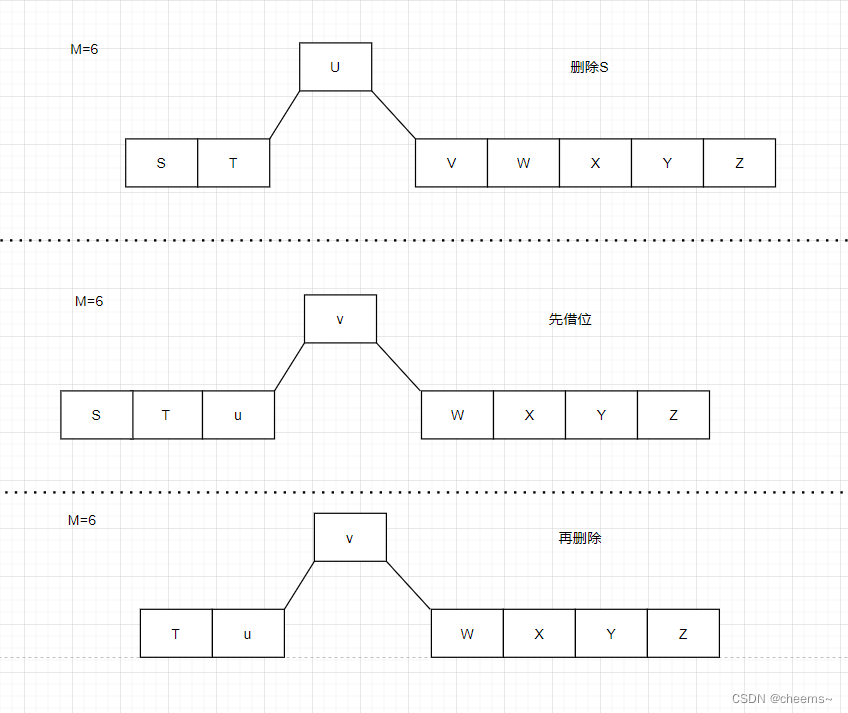
The current node is an inner node , And the left child at least includes M/2 Key words , Then borrow and delete
The current node is an inner node , And the left child at least includes M/2 Key words
- Excuse me first
- In the delete
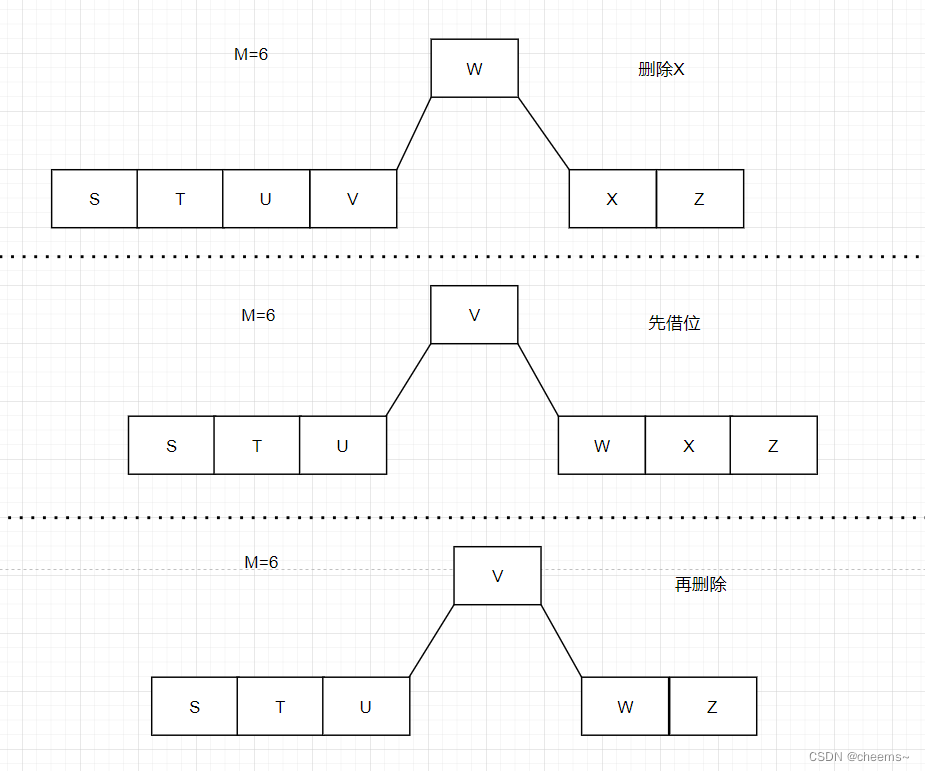
The current node is an inner node , And the right child at least includes M/2 Key words , Then borrow backward and delete
The current node is an inner node , And the right child at least includes M/2 Key words
- Excuse me first
- In the delete
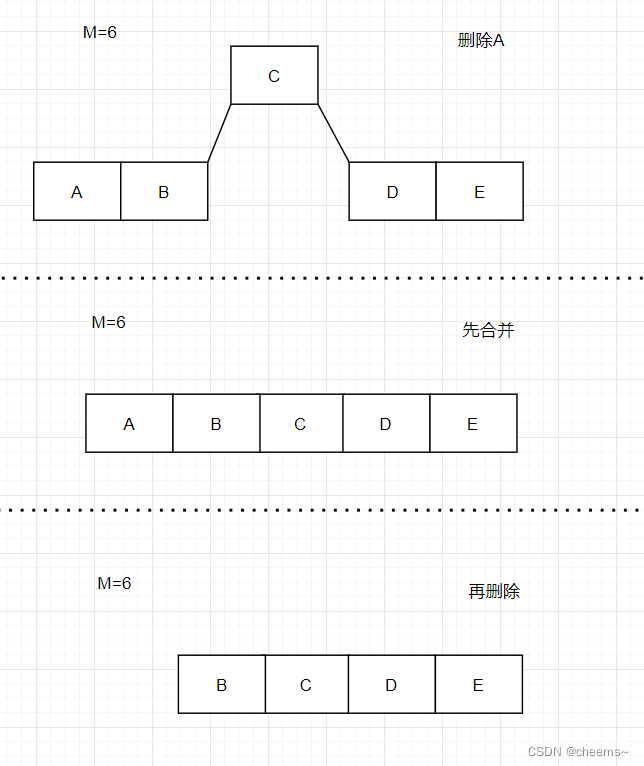
Both children are M/2-1 Key words , Then merge and delete
Both children are M/2-1 The key
- Merge first
- And then delete
Delete merge code
//{child[idx], key[idx], child[idx+1]}
void btree_merge(btree *T, btree_node *node, int idx) {
// Left and right subtrees
btree_node *left = node->children[idx];
btree_node *right = node->children[idx + 1];
int i = 0;
//data merge
left->keys[T->t - 1] = node->keys[idx];
for (i = 0; i < T->t - 1; i++) {
left->keys[T->t + i] = right->keys[i];
}
if (!left->leaf) {
for (i = 0; i < T->t; i++) {
left->children[T->t + i] = right->children[i];
}
}
left->num += T->t;
//destroy right
btree_destroy_node(right);
//node
for (i = idx + 1; i < node->num; i++) {
node->keys[i - 1] = node->keys[i];
node->children[i] = node->children[i + 1];
}
node->children[i + 1] = NULL;
node->num -= 1;
if (node->num == 0) {
T->root = left;
btree_destroy_node(node);
}
}
void btree_delete_key(btree *T, btree_node *node, KEY_TYPE key) {
// If it's deleted null Go straight back to
if (node == NULL) return;
int idx = 0, i;
// find key The location of
while (idx < node->num && key > node->keys[idx]) {
idx++;
}
// If key Is the inner node
if (idx < node->num && key == node->keys[idx]) {
// If the inner node is a leaf node , Direct deletion
if (node->leaf) {
for (i = idx; i < node->num - 1; i++) {
node->keys[i] = node->keys[i + 1];
}
node->keys[node->num - 1] = 0;
node->num--;
if (node->num == 0) {
// If the whole tree is deleted
free(node);
T->root = NULL;
}
return;
}
// Borrow from the previous node
else if (node->children[idx]->num >= T->t) {
btree_node *left = node->children[idx];
node->keys[idx] = left->keys[left->num - 1];
btree_delete_key(T, left, left->keys[left->num - 1]);
}
// The following node borrowing
else if (node->children[idx + 1]->num >= T->t) {
btree_node *right = node->children[idx + 1];
node->keys[idx] = right->keys[0];
btree_delete_key(T, right, right->keys[0]);
}
else {
// Merge
btree_merge(T, node, idx);// Merged on a subtree
btree_delete_key(T, node->children[idx], key);
}
}
else {
//key Not on this floor , Into the lower level
btree_node *child = node->children[idx];
if (child == NULL) {
printf("Cannot del key = %d\n", key);
return;
}
// Explain that you need to borrow
if (child->num == T->t - 1) {
//left child right Three nodes
btree_node *left = NULL;
btree_node *right = NULL;
if (idx - 1 >= 0)
left = node->children[idx - 1];
if (idx + 1 <= node->num)
right = node->children[idx + 1];
// It means that there is a borrowed place
if ((left && left->num >= T->t) || (right && right->num >= T->t)) {
int richR = 0;
if (right) {
richR = 1;
}
// If the right subtree is smaller than the left subtree key many , be richR=1
if (left && right) {
richR = (right->num > left->num) ? 1 : 0;
}
// Borrow from the next
if (right && right->num >= T->t && richR) {
child->keys[child->num] = node->keys[idx];// The key Bring it here , Take the subtree , The first subtree of the right node
child->children[child->num + 1] = right->children[0];
child->num++;
// The parent node borrows the first of the right node key
node->keys[idx] = right->keys[0];
// The right node is borrowed , Delete something
for (i = 0; i < right->num - 1; i++) {
right->keys[i] = right->keys[i + 1];
right->children[i] = right->children[i + 1];
}
right->keys[right->num - 1] = 0;
right->children[right->num - 1] = right->children[right->num];
right->children[right->num] = NULL;
right->num--;
}
// Borrow from the last
else {
for (i = child->num; i > 0; i--) {
child->keys[i] = child->keys[i - 1];
child->children[i + 1] = child->children[i];
}
child->children[1] = child->children[0];
// Bring the last subtree of the left subtree
child->children[0] = left->children[left->num];
// Take the parent node key
child->keys[0] = node->keys[idx - 1];
child->num++;
// The left child tree of the parent node key
node->keys[idx - 1] = left->keys[left->num - 1];
left->keys[left->num - 1] = 0;
left->children[left->num] = NULL;
left->num--;
}
}
// Merge
else if ((!left || (left->num == T->t - 1)) && (!right || (right->num == T->t - 1))) {
// hold node and left Merge
if (left && left->num == T->t - 1) {
btree_merge(T, node, idx - 1);
child = left;
}
// hold node and right Merge
else if (right && right->num == T->t - 1) {
btree_merge(T, node, idx);
}
}
}
// Recursion to the next level
btree_delete_key(T, child, key);
}
}
int btree_delete(btree *T, KEY_TYPE key) {
if (!T->root) return -1;
btree_delete_key(T, T->root, key);
return 0;
}
B Tree insertion , Delete , Traverse , Look for code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//b tree
#define M 3// Even numbers are better , Easy to split . rank
typedef int KEY_TYPE;
//btree node
struct btree_node {
struct btree_node **children;// subtree
KEY_TYPE *keys;// keyword
int num;// Number of keywords
int leaf;// Is it a leaf node 1yes,0no
};
//btree
struct btree {
struct btree_node *root;
int t;
};
// Create a node
struct btree_node *btree_create_node(int t, int leaf) {
struct btree_node *node = (struct btree_node *) calloc(1, sizeof(struct btree_node));
if (node == NULL)return NULL;
node->num = 0;
node->keys = (KEY_TYPE *) calloc(1, (2 * t - 1) * sizeof(KEY_TYPE));
node->children = (struct btree_node **) calloc(1, (2 * t) * sizeof(struct btree_node *));
node->leaf = leaf;
return node;
}
// Destroy a node
struct btree_node *btree_destroy_node(struct btree_node *node) {
if (node) {
if (node->keys) {
free(node->keys);
}
if (node->children) {
free(node->children);
}
free(node);
}
}
// Create a btree
void btree_create(btree *T, int t) {
T->t = t;
struct btree_node *x = btree_create_node(t, 1);
T->root = x;
}
// split
void btree_split_clild(struct btree *T, struct btree_node *x, int i) {
//y Nodes that need to be split
struct btree_node *y = x->children[i];
// New node
struct btree_node *z = btree_create_node(T->t, y->leaf);
int j = 0;
z->num = T->t - 1;
// hold y The second half of key And subtree copy To z in
for (j = 0; j < T->t - 1; j++) {
z->keys[j] = y->keys[j + T->t];
}
if (y->leaf == 0) {
for (j = 0; j < T->t; j++) {
z->children[j] = y->children[j + T->t];
}
}
//y Node modification quantity
y->num = T->t - 1;
// Put the parent node x Add one more key And subtree z
for (j = x->num; j >= i + 1; j--) {
x->children[j + 1] = x->children[j];
}
x->children[i + 1] = z;
for (j = x->num - 1; j >= i; j--) {
x->keys[j + 1] = x->keys[j];
}
x->keys[i] = y->keys[T->t - 1];
x->num++;
}
void btree_insert_nonfull(struct btree *T, struct btree_node *x, KEY_TYPE key) {
int i = x->num - 1;
if (x->leaf) {
while (i >= 0 && x->keys[i] > key) {
x->keys[i + 1] = x->keys[i];
i--;
}
x->keys[i + 1] = key;
x->num++;
}
else {
while (i >= 0 && x->keys[i] > key)i--;
if (x->children[i + 1]->num == 2 * T->t - 1) {
btree_split_clild(T, x, i + 1);
if (key > x->keys[i + 1])i++;
}
btree_insert_nonfull(T, x->children[i + 1], key);
}
}
void btree_insert(struct btree *T, KEY_TYPE key) {
struct btree_node *root = T->root;
// If the root node is full , Root node splitting
if (root->num == 2 * T->t - 1) {
btree_node *node = btree_create_node(T->t, 0);
T->root = node;
node->children[0] = root;
btree_split_clild(T, node, 0);
int i = 0;
if (key > node->keys[0]) i++;
btree_insert_nonfull(T, node->children[i], key);
}
else {
btree_insert_nonfull(T, root, key);
}
}
//{child[idx], key[idx], child[idx+1]}
void btree_merge(btree *T, btree_node *node, int idx) {
// Left and right subtrees
btree_node *left = node->children[idx];
btree_node *right = node->children[idx + 1];
int i = 0;
//data merge
left->keys[T->t - 1] = node->keys[idx];
for (i = 0; i < T->t - 1; i++) {
left->keys[T->t + i] = right->keys[i];
}
if (!left->leaf) {
for (i = 0; i < T->t; i++) {
left->children[T->t + i] = right->children[i];
}
}
left->num += T->t;
//destroy right
btree_destroy_node(right);
//node
for (i = idx + 1; i < node->num; i++) {
node->keys[i - 1] = node->keys[i];
node->children[i] = node->children[i + 1];
}
node->children[i + 1] = NULL;
node->num -= 1;
if (node->num == 0) {
T->root = left;
btree_destroy_node(node);
}
}
void btree_delete_key(btree *T, btree_node *node, KEY_TYPE key) {
// If it's deleted null Go straight back to
if (node == NULL) return;
int idx = 0, i;
// find key The location of
while (idx < node->num && key > node->keys[idx]) {
idx++;
}
// If key Is the inner node
if (idx < node->num && key == node->keys[idx]) {
// If the inner node is a leaf node , Direct deletion
if (node->leaf) {
for (i = idx; i < node->num - 1; i++) {
node->keys[i] = node->keys[i + 1];
}
node->keys[node->num - 1] = 0;
node->num--;
if (node->num == 0) {
// If the whole tree is deleted
free(node);
T->root = NULL;
}
return;
}
// Borrow from the previous node
else if (node->children[idx]->num >= T->t) {
btree_node *left = node->children[idx];
node->keys[idx] = left->keys[left->num - 1];
btree_delete_key(T, left, left->keys[left->num - 1]);
}
// The following node borrowing
else if (node->children[idx + 1]->num >= T->t) {
btree_node *right = node->children[idx + 1];
node->keys[idx] = right->keys[0];
btree_delete_key(T, right, right->keys[0]);
}
else {
// Merge
btree_merge(T, node, idx);// Merged on a subtree
btree_delete_key(T, node->children[idx], key);
}
}
else {
//key Not on this floor , Into the lower level
btree_node *child = node->children[idx];
if (child == NULL) {
printf("Cannot del key = %d\n", key);
return;
}
// Explain that you need to borrow
if (child->num == T->t - 1) {
//left child right Three nodes
btree_node *left = NULL;
btree_node *right = NULL;
if (idx - 1 >= 0)
left = node->children[idx - 1];
if (idx + 1 <= node->num)
right = node->children[idx + 1];
// It means that there is a borrowed place
if ((left && left->num >= T->t) || (right && right->num >= T->t)) {
int richR = 0;
if (right) {
richR = 1;
}
// If the right subtree is smaller than the left subtree key many , be richR=1
if (left && right) {
richR = (right->num > left->num) ? 1 : 0;
}
// Borrow from the next
if (right && right->num >= T->t && richR) {
child->keys[child->num] = node->keys[idx];// The key Bring it here , Take the subtree , The first subtree of the right node
child->children[child->num + 1] = right->children[0];
child->num++;
// The parent node borrows the first of the right node key
node->keys[idx] = right->keys[0];
// The right node is borrowed , Delete something
for (i = 0; i < right->num - 1; i++) {
right->keys[i] = right->keys[i + 1];
right->children[i] = right->children[i + 1];
}
right->keys[right->num - 1] = 0;
right->children[right->num - 1] = right->children[right->num];
right->children[right->num] = NULL;
right->num--;
}
// Borrow from the last
else {
for (i = child->num; i > 0; i--) {
child->keys[i] = child->keys[i - 1];
child->children[i + 1] = child->children[i];
}
child->children[1] = child->children[0];
// Bring the last subtree of the left subtree
child->children[0] = left->children[left->num];
// Take the parent node key
child->keys[0] = node->keys[idx - 1];
child->num++;
// The left child tree of the parent node key
node->keys[idx - 1] = left->keys[left->num - 1];
left->keys[left->num - 1] = 0;
left->children[left->num] = NULL;
left->num--;
}
}
// Merge
else if ((!left || (left->num == T->t - 1)) && (!right || (right->num == T->t - 1))) {
// hold node and left Merge
if (left && left->num == T->t - 1) {
btree_merge(T, node, idx - 1);
child = left;
}
// hold node and right Merge
else if (right && right->num == T->t - 1) {
btree_merge(T, node, idx);
}
}
}
// Recursion to the next level
btree_delete_key(T, child, key);
}
}
int btree_delete(btree *T, KEY_TYPE key) {
if (!T->root) return -1;
btree_delete_key(T, T->root, key);
return 0;
}
void btree_traverse(btree_node *x) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < x->num; i++) {
if (x->leaf == 0)
btree_traverse(x->children[i]);
printf("%C ", x->keys[i]);
}
if (x->leaf == 0) btree_traverse(x->children[i]);
}
void btree_print(btree *T, btree_node *node, int layer) {
btree_node *p = node;
int i;
if (p) {
printf("\nlayer = %d keynum = %d is_leaf = %d\n", layer, p->num, p->leaf);
for (i = 0; i < node->num; i++)
printf("%c ", p->keys[i]);
printf("\n");
#if 0
printf("%p\n", p);
for(i = 0; i <= 2 * T->t; i++)
printf("%p ", p->childrens[i]);
printf("\n");
#endif
layer++;
for (i = 0; i <= p->num; i++)
if (p->children[i])
btree_print(T, p->children[i], layer);
}
else printf("the tree is empty\n");
}
int btree_bin_search(btree_node *node, int low, int high, KEY_TYPE key) {
int mid;
if (low > high || low < 0 || high < 0) {
return -1;
}
while (low <= high) {
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (key > node->keys[mid]) {
low = mid + 1;
}
else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
int main() {
btree T = {
0};
btree_create(&T, 3);
srand(48);
int i = 0;
char key[27] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
for (i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
//key[i] = rand() % 1000;
printf("%c ", key[i]);
btree_insert(&T, key[i]);
}
btree_print(&T, T.root, 0);
for (i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
printf("\n---------------------------------\n");
btree_delete(&T, key[25 - i]);
//btree_traverse(T.root);
btree_print(&T, T.root, 0);
}
}
边栏推荐
- Machine vision (1) - Overview
- 通过 Play Integrity API 的 nonce 字段提高应用安全性
- 【demo】循环队列及条件锁实现goroutine间的通信
- golang 客户端服务端登录
- [OKR target management] case analysis
- Debian10 compile and install MySQL
- [OKR target management] value analysis
- Face recognition attendance system based on Baidu flying plasma platform (easydl)
- 【蓝桥杯集训100题】scratch从小到大排序 蓝桥杯scratch比赛专项预测编程题 集训模拟练习题第17题
- 2021-06-28
猜你喜欢

zdog. JS rocket turn animation JS special effects
![[deep learning] 3 minutes introduction](/img/d9/acaff84dbe6bc97885b41766aa841d.png)
[deep learning] 3 minutes introduction
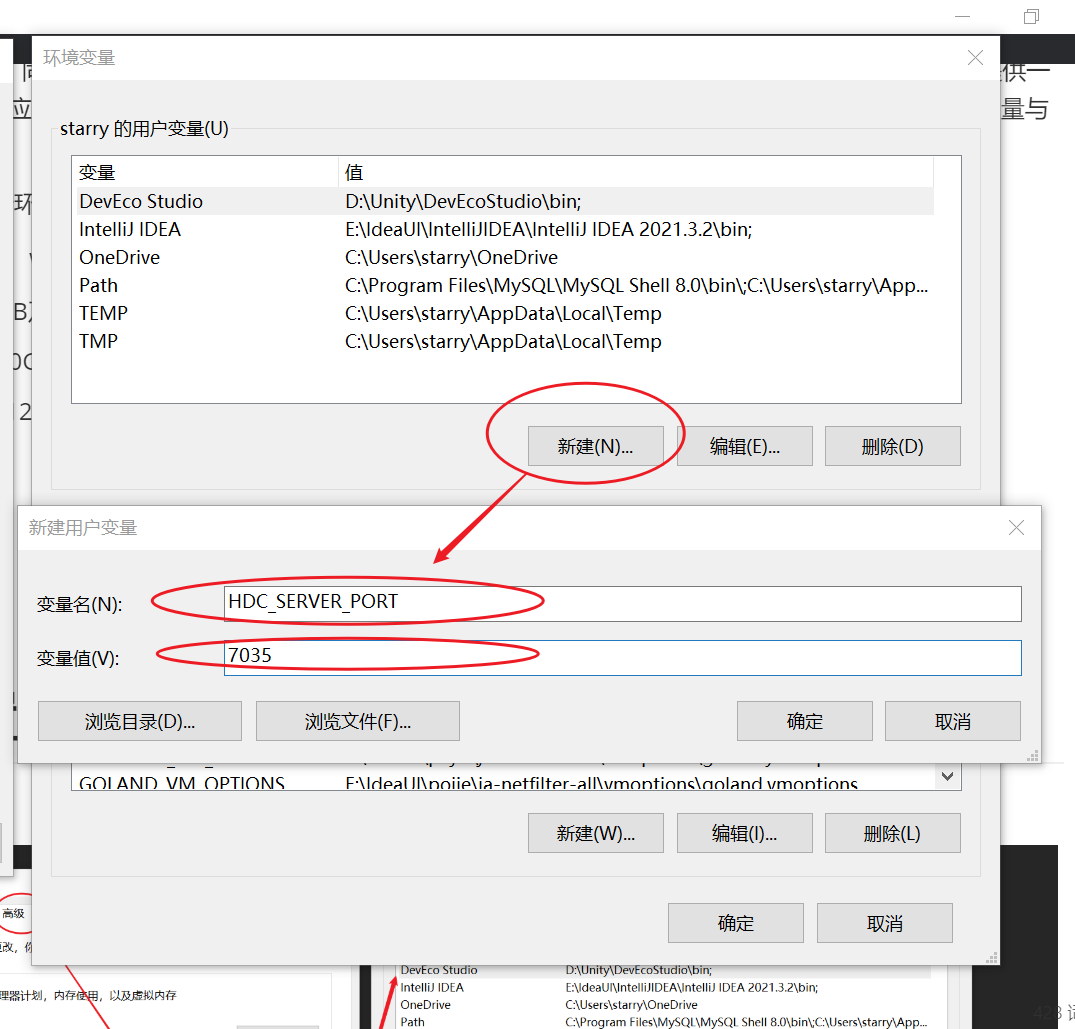
『HarmonyOS』DevEco的下载安装与开发环境搭建

Backup Alibaba cloud instance OSS browser
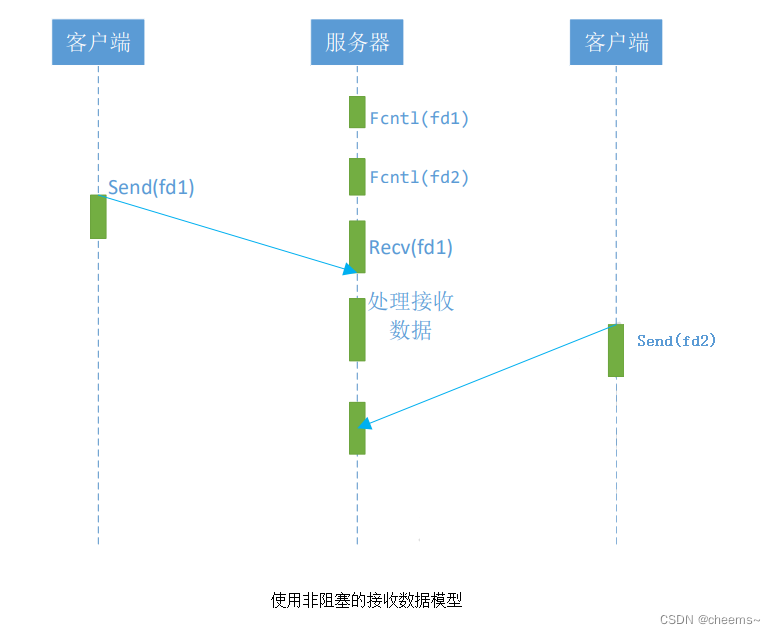
五种网络IO模型
数学分析_笔记_第11章:Fourier级数

磁盘存储链式的B树与B+树
Cartoon | who is the first ide in the universe?

AI 击败了人类,设计了更好的经济机制
Vscode three configuration files about C language
随机推荐
Native JS verification code
[tpm2.0 principle and Application guide] Chapter 1-3
Based on pytorch, we use CNN to classify our own data sets
Use seven methods to enhance all the images in a folder
Understanding of 12 methods of enterprise management
Youth experience and career development
漫画 | 宇宙第一 IDE 到底是谁?
基于百度飞浆平台(EasyDL)设计的人脸识别考勤系统
目标检测1——YOLO数据标注以及xml转为txt文件脚本实战
三仙归洞js小游戏源码
线上比赛相关规则补充说明
直播软件搭建,canvas文字加粗
Tips of this week 135: test the contract instead of implementation
Summary of debian10 system problems
Main work of digital transformation
Five simple ways to troubleshoot with Stace
SD_DATA_RECEIVE_SHIFT_REGISTER
Unlike the relatively short-lived industrial chain of consumer Internet, the industrial chain of industrial Internet is quite long
Deep learning machine learning various data sets summary address
Afghan interim government security forces launched military operations against a hideout of the extremist organization "Islamic state"