当前位置:网站首页>Special training of C language array
Special training of C language array
2022-07-05 06:50:00 【An embedded enthusiast】
C Special training of language array
The first question is
If there is a statement char s1[10], s2[10] = {“books”}; The string books Store in array s1 The correct sentence for is ( )
A、strcpy(s1, s2);
B、s1 = {“books”};
C、s1 = s2;
D、strcpy(s2, s1);
answer :A
analysis : The array name represents the first address of the array , It's an address constant , So you can't assign values to array names ,C error .strcpy The function prototype is as follows
char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src)
The second question is
The linear table is ________.
A、 A finite sequence , Can be null
B、 A finite sequence , Do not be empty
C、 An infinite sequence , Can be null
D、 An infinite sequence , Do not be empty
answer :A
analysis : Linear lists include linked list arrays , Arrays are finite , Linear tables can be initialized to null , When there are no elements in the linear table , Is an empty table .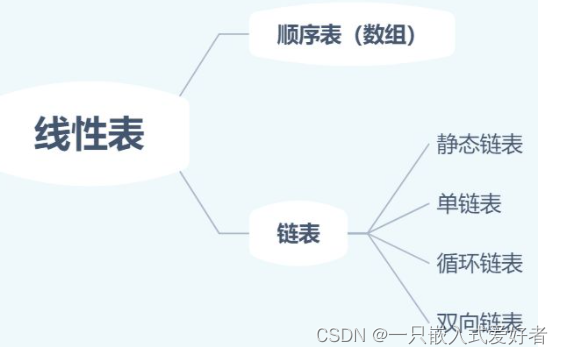
Recommended reading : Logical structure and physical structure
Third question
Which of the following correctly defines a one-dimensional array .()
A、char a[] = {‘0’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘\0’};
B、char a = {‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’};
C、int a[] = “0123”;
D、int a[3] = {0, 1, 2, 3};
answer :A
analysis :B In the options a Not defined as an array , It's characters , Will make mistakes ;C Option integer array cannot be assigned string ;D The number of initial values defined by the option exceeds the length of the array ;
Fourth question
The keyword sequence with sequence table is {1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99}, When the binary search method is used, the key value is 35 When the node of , the () Search succeeded after comparison .
answer :4
analysis :
The first 1 Time
1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99
left=0,right=13,mind=6; mid The value is 42, Too big
The first 2 Time
1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99
left=0,right=5,mind=2; mid The value is 6, Too small
The first 3 Time
1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99
left=3,right=5,mind=4; mid The value is 18, Too small
The first 4 Time
1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99
left=5,right=5,mind=5; mid The value is 35, eureka
Fifth question
There are two general compression storage methods for sparse matrix , namely ()
A、 Two dimensional array and three-dimensional array
B、 Triples and hashes
C、 Triples and cross linked lists
D、 Hash and cross linked list
answer :C
analysis : A triple is an element that holds three pieces of information , Row numbers in the matrix , Column number and value , In this way, the value of 0 The elements of , Achieve compression . Cross linked list is equivalent to the set of adjacency table and inverse adjacency table , In an element, the values, the outgoing and incoming tables are stored , In this way, there is no need to store a large number of 0 Elements , And finding the incoming node of a node is as fast as finding the node .
A two-dimensional cross linked list is a list of elements that link left and right horizontal neighbors and up and down vertical neighbors at the same time .
Typically used for sparse matrix storage , Each element of the matrix is the following five tuples :
typedef struct OLNode
{
int LineNumber, ColumneNumber; // Line and column numbers
ElemType value; // value
struct OLNode *right, *down; // Colleague 、 Pointer to the next element in the same column
} OLNode, *OList;
Sixth question
Of the following options , Which option correctly defines a two-dimensional array ()
A、char a[2][2] = ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’;
B、int a[][] = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}};
C、int a[2][] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
D、int a[][4] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
answer :D
analysis : When defining a character array, it is not allowed to directly use “ character constants ” Give initial value in the way of ,C Language policy , It is not allowed to omit the length of the second dimension when defining a two-dimensional array , So options A、B、C error . It is allowed to omit the length of the first dimension when defining a two-dimensional array , So options D correct .
Question seven
It is known that int a[3][4]; Then the following can mean a[1][2] The value of the element is ()
A、*( *(a+1)+2)
B、 *(a+1+2)
C、(&a[0]+1)[2]
D、 *(a[0]+1)
answer :A
analysis : In a two-dimensional array , The array name is the address of the first array , Note that there a Not the address of the first element , It's the address of the first dimension array ,a[0][0] Is the address of the first element of the one-dimensional array . Address + 1 Move down one layer .
A, a It's a secondary pointer , Not a first level pointer ,*(a+1) The address of the second array of the
B, * (a+1+2) be equal to *(a+3), It's a int *, It means No 4 An array a[3] The address of , and **(a+3) Express a[3][0] Value , *((int *)(a+3)) It can also express a[3][0] Value
C. (&a[0]+1) It means No 2 An array a[1] The address of ,(&a[0]+1)[2] It's actually an array a[3] The address of , Change to ((int *)(&a[0]+1))[2] That's right
D. *(a[0]+1) yes a[0][1] Value
The eighth question
What results will be output by executing the following code snippet .()
int a[][3] = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
char k;
for (k = 0; k < 3; k ++)
printf("%d ",a[k][2-k]);
A、1 3 5
B、3 5 7
C、3 6 9
D、 Compilation error or nothing else
answer :B
analysis : A two-dimensional array must specify the number of columns , The topic has been specified and does not cross the boundary , So there's no mistake .
a[0][0]=1 a[0][1]=2 a[0][2]=3
a[1][0]=4 a[1][1]=5 a[1][2]=6
a[2][0]=7 a[2][1]=8 a[2][2]=9
for Loop output a[0][2]=3 a[1][1]=5 a[2][0]=7
Question 9
int A[2][3]={1,2,3,4,5,6}; be A[1][0] and *(*(A+1)+1) The values of ()
A、4 5
B、4 3
C、3 5
D、3 4
answer :A
analysis : Array A altogether 2 That's ok 3 Column , The first 0 Behavior 123, The first 1 Behavior 456.A[1][0] For the first time 1 Xing di 0 Column number 4. * (A+1) Point to array number 1 Xing di 0 Elements , * (A+1)+1 Point to array number 1 Xing di 1 Elements , Retake * It is the first 1 Xing di 1 The value of the elements 5, Therefore 4,5.
Question 10
The following statement is correct ()
A、 An array that is more than two dimensions is actually a special generalized table
B、 Once the array is created , The number of elements of the structure and the physical storage relationship between elements will not change
C、 Arrays are linear structures , Therefore, it can only be used to store linear tables
D、 Arrays are represented by sequential storage
answer :A B D
analysis : On this subject , We need to distinguish between the physical and logical structure of the data . Physical structure mainly refers to storage mode , Including linear storage and chain storage , It is considered from the perspective of computer storage . Logical structure refers to the relationship between data , There are linear relations and chain relations , Mainly from the perspective of artificial definition . An array is a table defined as a linear relationship , As for its storage structure , It can be stored by linear storage or chain storage .
Recommended reading : Logical structure and physical structure
Eleventh questions
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Redis-01. First meet redis
Vant Weapp SwipeCell设置多个按钮
Orin 两种刷机方式
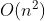
Rehabilitation type force deduction brush question notes D1
confidential! Netease employee data analysis internal training course, white whoring! (attach a data package worth 399 yuan)
Game theory acwing 892 Steps Nim game
Pycahrm reports an error: indentation error: unindent does not match any outer indentation

Volcano resource reservation feature

程序中的负数存储及类型转换
ROS2——安装ROS2(三)
随机推荐
Technical conference arrangement
Error: “MountVolume.SetUp failed for volume pvc 故障处理
[Chongqing Guangdong education] 1185t administrative leadership reference test of National Open University in autumn 2018
Integer to 8-bit binary explanation (including positive and negative numbers) scope of application -127~+127
CGroup CPU group source code analysis
[algorithm post interview] interview questions of a small factory
namespace
6-2 sequence table operation set
VLAN experiment
H5内嵌App适配暗黑模式
cgroup_ memcg
*P++, (*p) + +, * (p++) differences
6-3 find the table length of the linked table
ROS2——node节点(七)
kata container
[nvidia] CUDA_ VISIBLE_ DEVICES
Orin 安装CUDA环境
MQClientException: No route info of this topic: type_ topic
.net core踩坑实践
Ret2xx---- common CTF template proposition in PWN