当前位置:网站首页>Breadth first traversal of graph
Breadth first traversal of graph
2022-07-06 18:33:00 【Wukong doesn't buy vegetables anymore】
This is another way to traverse all vertices in the graph , The name is breadth first traversal (Breadth first search), Let's talk about the specific idea of traversal .
First, let's take a look at a picture :
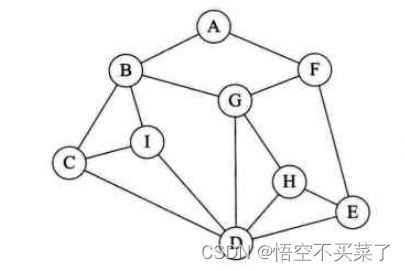
At first glance, this picture , Particularly messy , It seems that after traversing with depth first , There is no idea . But we can sort out this picture as follows
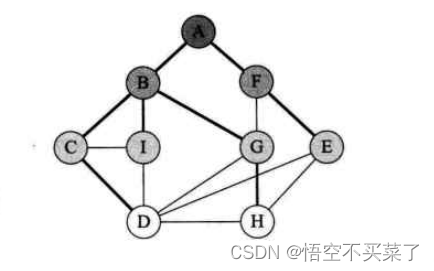
Do you feel a special sense of hierarchy when you see it like this , But the adjacent points of each vertex are not disordered , such as A It's the first floor ,BF It's the second floor ,CIGE It's the third floor ,DH It's the fourth floor , Then the printing order of the last picture is ABFCIGEDH
Now let me use the following figure to analyze its specific ideas :
 Let's use a picture to explain the above idea of entering and leaving the team :
Let's use a picture to explain the above idea of entering and leaving the team :
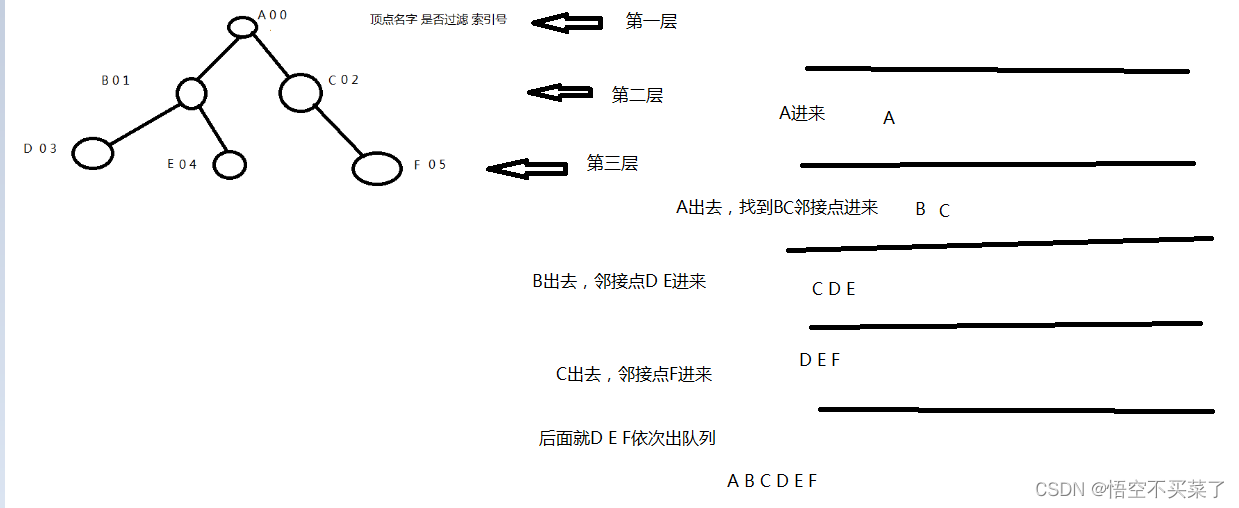 Tell me , Here we need to use the queue , One store int The type of queue , Because the index of each vertex is stored here , Then we need to make this queue into a dynamic library , Then introduce the .
Tell me , Here we need to use the queue , One store int The type of queue , Because the index of each vertex is stored here , Then we need to make this queue into a dynamic library , Then introduce the .
Let's first see if there is a dynamic library in our library file
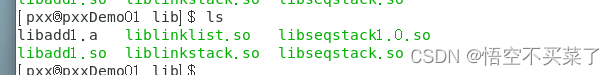
Then I found that there was no such thing , Then we still make a dynamic library by ourselves
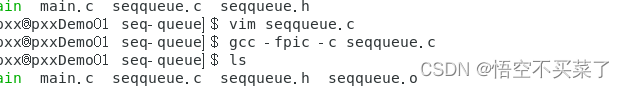
 Then move to the location where we store the library files
Then move to the location where we store the library files
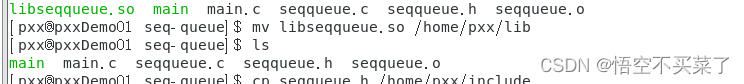 Then you can write the program now
Then you can write the program now
Direct introduction of code undirected_graph.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
extern "C"
{
#include "seqqueue.h"
}
// Maximum number of vertices
#define MAX_VERTEX 30
// Defines whether to filter the array of identities
int visit[MAX_VERTEX];
// Define the graph structure
typedef struct _graph
{
// Vertex array , Store vertex names
char **vertex;
// Array of edges
int edge[MAX_VERTEX][MAX_VERTEX];
// Number of vertices
int vertex_num;
// The number of sides
int edge_num;
}graph;
// Calculate the position of the user input vertex in the array
// Here, for example, enter a v1,v2, So for an undirected graph ,(v1,v2) And (v2,v1) All represent the same side
int calc_vertex_pos(graph &g,char* v)
{
// Traverse the vertex array
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
// This is equivalent to string comparison
if(strcmp(v,g.vertex[i]) == 0) {
return i;// Find and return directly to this location
}
}
return -1;
}
// Create a diagram
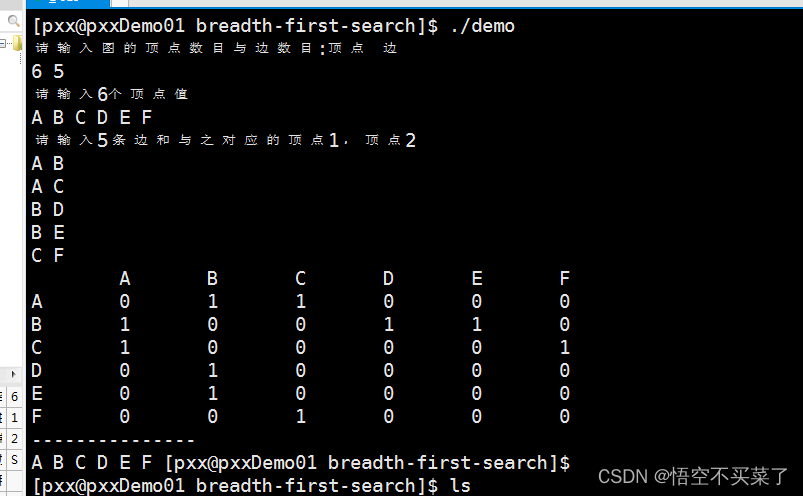
void create_graph(graph &g)
{
printf(" Please enter the number of vertices and edges of the graph : The vertices edge
");
scanf("%d %d",&g.vertex_num,&g.edge_num);
printf(" Please enter %d A peak value
",g.vertex_num);
// Start a loop to assign vertex values to the vertex array
// Before assignment, you need to make room on the heap to store the string
g.vertex = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * g.vertex_num);
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
char str[100] = {0};
scanf("%s",str);
// This array points to an allocated space
g.vertex[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (strlen(str) + 1));
strcpy(g.vertex[i],str);
}
// Initialize the two-dimensional array of edges
// Count by the number of vertices n, To form a n*n Two dimensional array of
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
for(int j = 0;j < g.vertex_num;j++) {
// Initialize all the corresponding edges to 0 Does not exist
g.edge[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// The contents of the above two arrays are initialized
// Let's set the relationship between edges , Is whether there is an edge
printf(" Please enter %d Edges and their corresponding vertices 1, The vertices 2
",g.edge_num);
// Set the relationship between two vertices with edges
char v1[10];
char v2[10];
// How many sides are there , It corresponds to how many vertices there are
for(int i = 0;i < g.edge_num;i++) {
scanf("%s %s",v1,v2);
// Then we calculate the position of the vertex in the array
// yes 0 ah ,1 ah , still 2 Ah, wait, such a relationship
int m = calc_vertex_pos(g,v1);// such as v1=0
int n = calc_vertex_pos(g,v2);//v2 = 1 (0,1) It means there is an edge , Set the position value to 1
// meanwhile (1,0) This position should also be set to 1, After all, it is an undirected graph
g.edge[m][n] = 1;
g.edge[n][m] = 1;
}
}
// Print a picture
void print_graph(graph& g)
{
// To print a graph is to print this two-dimensional array
printf(" ");
// Loop horizontal vertex header
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
printf("%s ",g.vertex[i]);
}
// Loop through the contents of a two-dimensional array
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
// Print horizontal vertex header
printf("
");// Change one line at a time
printf("%s ",g.vertex[i]);
// Then output a line of content
for(int j = 0;j < g.vertex_num;j++) {
printf("%d ",g.edge[i][j]);
}
}
printf(" ");
}
// Breadth first traversal
void BFSTraverse(graph &g)
{
// Initialize the filter ID array to 0
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
visit[i] = 0;
}
// Create a queue
t_seq_queue* queue = create_queue();
// Traverse every node
for(int j = 0;j < g.vertex_num;j++) {
// Then check whether the node has been accessed
if(!visit[j]) {
// Print
// And change the access ID to 1
printf("%s ",g.vertex[j]);
visit[j] = 1;
// At the same time, put the index of this vertex into the queue , To find its adjacency
push_queue(queue,j);
// Next, we are going to find the adjacency point of the next layer
// As long as the queue is not empty , Just keep cycling and printing data
while(!is_empty(queue)) {
// First get the team leader index
int index = get_front(queue);
pop_queue(queue);
// Then cycle to determine the vertex associated with it , Let it print and join the team
for(int n = 0;n < g.vertex_num;n++) {
if(g.edge[index][n] == 1 && !visit[n]) {
printf("%s ",g.vertex[n]);
push_queue(queue,n);
visit[n] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
// Build a diagram
void test01()
{
graph g;
create_graph(g);
print_graph(g);
printf("
---------------
");
BFSTraverse(g);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
But there is another problem when compiling in the middle , Just can't find the function reference of the queue
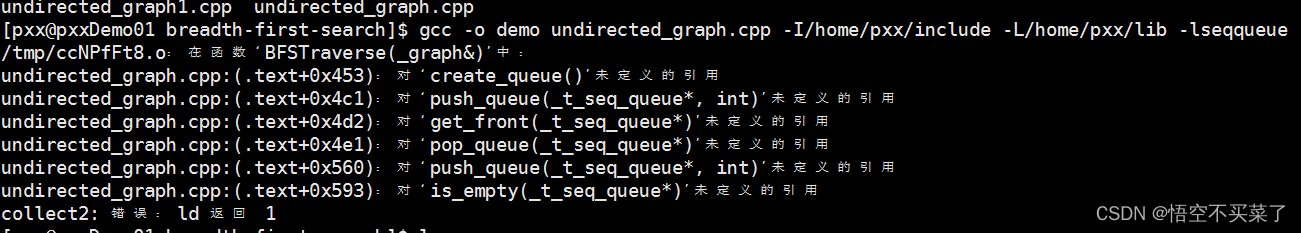 But I checked the dynamic library , It is indeed compiled , Before .c There are basically no errors in file import , At this time, I was wondering if cpp The file import c There will be problems when writing functions in the dynamic library , So a problem will be introduced here , Is how to cpp The file import c Write dynamic library ?
But I checked the dynamic library , It is indeed compiled , Before .c There are basically no errors in file import , At this time, I was wondering if cpp The file import c There will be problems when writing functions in the dynamic library , So a problem will be introduced here , Is how to cpp The file import c Write dynamic library ?
Let's start with C++ And C Language function processing ,C++ Is an object-oriented programming language , Then it has a feature that it can realize function overloading , That is, the function with the same name depends on the number of parameters , Reload in different positions ,C Language doesn't work , let me put it another way ,C++ When compiling functions , In order to solve the problem of function polymorphism , The function name and parameters will be combined to generate an intermediate function name , and C Language can't , because C++ Introduction in C The function of will not be found , So we need to put C The header file of the language is enclosed
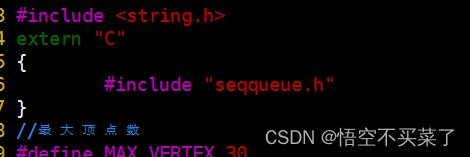 This extern "C" {} It means that the functions introduced here follow C In the way of language , So the compilation is successful
This extern "C" {} It means that the functions introduced here follow C In the way of language , So the compilation is successful
Running results :
 Let's talk about a depth first traversal of the adjacency table
Let's talk about a depth first traversal of the adjacency table
The analysis idea is the same , It's just that their memory forms are different
Go straight to the code
undirected_graph1.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"
{
#endif
#include "seqqueue.h"
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
// The maximum number of vertices that can be stored
#define MAX_VERTEX 100
// Store a vertex filter ID array
int visit[MAX_VERTEX];
struct edge_node {
int position;// The said vertex Which node index in the array
edge_node *next;// Store the pointer of the next adjacent contact
// The weight here can be written or not
};
struct vertex {
char *name;// Store vertex names , The first level pointer points to the space allocated on a heap
// There is also the storage of each adjacent first adjacent contact , In fact, here it is equivalent to the head node
edge_node *first_node;
};
// Finally, you need the structure of the whole graph
// To store the information of the corresponding diagram
struct graph {
// Store all the information of the vertex
vertex head[MAX_VERTEX];
// Number of vertices and edges
int vertex_num;
int edge_num;
};
// Let's determine the vertex position
int find_pos(graph &g,char *v)// here v If there is a point, you can print , I mean scanf It's impossible to assign values directly
{
for (int i = 0; i < g.vertex_num; i++) {
// Loop the space where the vertex names are stored
if (strcmp(g.head[i].name, v) == 0) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Let's create a diagram first
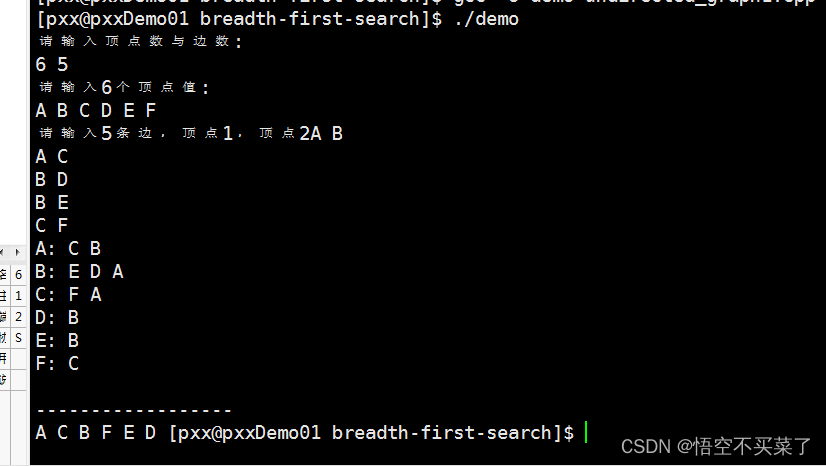
void create_graph(graph &g)
{
printf(" Please enter the number of vertices and edges :
");
scanf("%d %d", &g.vertex_num, &g.edge_num);
// Cycle through the values of the vertices
printf(" Please enter %d A peak value :
", g.vertex_num);
// Loop to assign values to vertices
for (int i = 0; i < g.vertex_num; i++){
char str[30] = { 0 };
scanf("%s", str);
// pure scanf("%s",&g.head[i].name) Definitely not , This name It's a two-level pointer
g.head[i].name = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (strlen(str) + 1));
strcpy(g.head[i].name, str);// In which index position to store the vertex
// In addition to the assignment string , You also need to initialize the address of an adjacent node
g.head[i].first_node = NULL;// Similar to every overhead point next Is full of NULL
}
// Let's start by entering edges , That is, two vertices
printf(" Please enter %d side , The vertices 1, The vertices 2", g.edge_num);
char v1[10];
char v2[10];
// Loop to assign values to edges
for (int i = 0; i < g.edge_num; i++) {
scanf("%s %s", v1,v2);
int m = find_pos(g, v1);
int n = find_pos(g, v2);
// Number of each vertex found in memory
// And then for example m Is it the head representing a vertex , Here you can.
// As the head of the linked list
// Then we implement header insertion , To express a connection
// Finally, we implement an interaction of the relationship , This is for an undirected graph v1 And v2 and v2 And v1 Same relationship
// Create a new adjacency point
edge_node *p_new = (edge_node*)malloc(sizeof(edge_node));
// Then start inserting... In the head , This head is m spot
p_new->position = n;
// here p_new Must first refer to
p_new->next = g.head[m].first_node;
g.head[m].first_node = p_new;
// Then implement v0 And v1 An alternation of , It means
edge_node *p_new1 = (edge_node*)malloc(sizeof(edge_node));
// In fact, it is to achieve a m And n Alternation of
p_new1->position = m;
p_new1->next = g.head[n].first_node;
g.head[n].first_node = p_new1;
}
}
// Print this picture
void print_graph(graph &g)
{
for (int i = 0; i < g.vertex_num; i++) {
printf("%s: ", g.head[i].name);
// Get the head node to traverse a single linked list
edge_node *p_node = g.head[i].first_node;
while (p_node != NULL) {
// Get is n, Looking for it m
int index = p_node->position;
printf("%s ", g.head[index].name);
p_node = p_node->next;
}
// Line break
printf("
");
}
}
void BFSTraverse(graph &g)
{
// Initialization nodes are not traversed
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
visit[i] = 0;
}
// Then create a queue , It is still to traverse every vertex
t_seq_queue* queue = create_queue();
for(int j = 0;j < g.vertex_num;j++) {
// Determine whether to be visited
if(!visit[j]) {
// Change access identity , Print , The team
visit[j] = 1;
printf("%s ",g.head[j].name);
push_queue(queue,j);
// Then start walking in the queue
while(!is_empty(queue)) {
// Get the team leader element
int index = get_front(queue);
// Outgoing queue
pop_queue(queue);
// Get this vertex first_node
edge_node *p_node = g.head[index].first_node;
// Start cycle and index All vertices associated with this vertex
// After all, this is a linked list
while(p_node != NULL) {
// Finding this vertex is still the old rule to judge whether it is traversed
int n = p_node->position;
if(!visit[n]) {
printf("%s ",g.head[n].name);
visit[n] = 1;
// Press this vertex into the opposite column
push_queue(queue,n);
}
p_node = p_node->next;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
graph g;
create_graph(g);
print_graph(g);
printf("
------------------
");
BFSTraverse(g);
return 0;
}
Running results :
 Let's talk about the time complexity , Compare depth first with breadth first , These two are the same in algorithm time , Deal with different realities , You can choose the right algorithm .
Let's talk about the time complexity , Compare depth first with breadth first , These two are the same in algorithm time , Deal with different realities , You can choose the right algorithm .
边栏推荐
- 使用block实现两个页面之间的传统价值观
- Alibaba cloud international ECS cannot log in to the pagoda panel console
- Redis的五种数据结构
- celery最佳实践
- Bonecp uses data sources
- Atcoder a mountaineer
- Introduction and case analysis of Prophet model
- 复现Thinkphp 2.x 任意代码执行漏洞
- 使用cpolar建立一个商业网站(1)
- J'aimerais dire quelques mots de plus sur ce problème de communication...
猜你喜欢
std::true_type和std::false_type

Recursive way
![Jerry is the custom background specified by the currently used dial enable [chapter]](/img/32/6c22033bda8ff1b53993bacef254cd.jpg)
Jerry is the custom background specified by the currently used dial enable [chapter]
Declval of template in generic programming
Grafana 9.0 is officially released! It's the strongest!
阿里云国际版ECS云服务器无法登录宝塔面板控制台
十、进程管理
Windows连接Linux上安装的Redis
CSRF vulnerability analysis
Use cpolar to build a business website (1)
随机推荐
Ms-tct: INRIA & SBU proposed a multi-scale time transformer for motion detection. The effect is SOTA! Open source! (CVPR2022)...
Transfer data to event object in wechat applet
【.NET CORE】 请求长度过长报错解决方案
[the 300th weekly match of leetcode]
当保存参数使用结构体时必备的开发技巧方式
STM32+ESP8266+MQTT协议连接OneNet物联网平台
CSRF漏洞分析
从交互模型中蒸馏知识!中科大&美团提出VIRT,兼具双塔模型的效率和交互模型的性能,在文本匹配上实现性能和效率的平衡!...
[.Net core] solution to error reporting due to too long request length
C语言自动预订飞机票问题
atcoder它A Mountaineer
Reprint: defect detection technology of industrial components based on deep learning
J'aimerais dire quelques mots de plus sur ce problème de communication...
30 分钟看懂 PCA 主成分分析
MySQL查询请求的执行过程——底层原理
echart简单组件封装
虚拟机VirtualBox和Vagrant安装
287. Find duplicates
This article discusses the memory layout of objects in the JVM, as well as the principle and application of memory alignment and compression pointer
STM32+HC05串口蓝牙设计简易的蓝牙音箱