当前位置:网站首页>HDU 4747 mex "recommended collection"
HDU 4747 mex "recommended collection"
2022-07-07 23:23:00 【Full stack programmer webmaster】
Hello everyone , I meet you again , I'm the king of the whole stack .
The question :
Give a number a Definition mex(l,r) Express a[l]…a[r] The smallest discontinuous number in Find all mex(l,r) And
Ideas :
First of all, I can think of l Start to n Of all numbers mex The value must be increasing Then we can find out with 1 Start to n Of all numbers mex Sweep it from front to back At this time, we can find [1,r] All interval mex and Using the segment tree
Then consider how to find [2,r]、[3,r]…. from [1,r] To [2,r] The change of is nothing more than removing the first number So what is the effect of removing a number ?
For example, remove one 2 Then he can affect the next one at most 2 Where it appears also He just put mex>2 The place was changed to 2 From 2 There's a cut And because of the increasing relationship mentioned before So the range of influence must also be continuous !
Then we can delete one number at a time Use the line segment tree to find out the interval of his influence And cover this interval with the deleted number
Finally, every summation is the answer
Code :
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef __int64 ll;
#define N 201000
#define L(x) (x<<1)
#define R(x) ((x<<1)|1)
struct node
{
int l,r,val,lazy;
ll sum;
}tree[N*4];
int a[N],mex[N],next[N];
int n,l,r;
map<int,int> mp;
ll ans;
void up(int i)
{
tree[i].val=max(tree[L(i)].val,tree[R(i)].val);
tree[i].sum=tree[L(i)].sum+tree[R(i)].sum;
}
void down(int i)
{
if(tree[i].lazy!=-1)
{
tree[L(i)].lazy=tree[i].lazy;
tree[L(i)].val=tree[i].lazy;
tree[L(i)].sum=(tree[L(i)].r-tree[L(i)].l+1)*tree[i].lazy;
tree[R(i)].lazy=tree[i].lazy;
tree[R(i)].val=tree[i].lazy;
tree[R(i)].sum=(tree[R(i)].r-tree[R(i)].l+1)*tree[i].lazy;
tree[i].lazy=-1;
}
}
void init(int l,int r,int i)
{
tree[i].l=l; tree[i].r=r; tree[i].lazy=-1;
if(l==r)
{
tree[i].val=mex[l];
tree[i].sum=mex[l];
return ;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
init(l,mid,L(i));
init(mid+1,r,R(i));
up(i);
}
void update(int l,int r,int i,int k)
{
if(l==tree[i].l&&r==tree[i].r)
{
tree[i].sum=(tree[i].r-tree[i].l+1)*k;
tree[i].val=k;
tree[i].lazy=k;
return ;
}
down(i);
int mid=(tree[i].l+tree[i].r)>>1;
if(r<=mid) update(l,r,L(i),k);
else if(l>mid) update(l,r,R(i),k);
else
{
update(l,mid,L(i),k);
update(mid+1,r,R(i),k);
}
up(i);
}
void query(int i,int k)
{
if(tree[i].l==tree[i].r)
{
if(tree[i].val>k) l=tree[i].l;
else l=n+1;
return ;
}
down(i);
if(tree[L(i)].val>k) query(L(i),k);
else query(R(i),k);
up(i);
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
if(!n) break;
mp.clear(); // get mex
j=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
mp[a[i]]=1;
while(mp[j]) j++;
mex[i]=j;
}
mp.clear(); // get next
for(i=1;i<=n;i++) mp[a[i]]=n+1;
for(i=n;i>=1;i--)
{
next[i]=mp[a[i]];
mp[a[i]]=i;
}
//for(i=1;i<=n;i++) printf("%d %d\n",mex[i],next[i]);
init(1,n,1);
for(i=1,ans=0;i<=n;i++)
{
ans+=tree[1].sum;
query(1,a[i]);
r=next[i];
//printf("%d %d\n",l,r);
if(l<r)
{
update(l,r-1,1,a[i]);
}
update(i,i,1,0);
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}Publisher : Full stack programmer stack length , Reprint please indicate the source :https://javaforall.cn/116215.html Link to the original text :https://javaforall.cn
边栏推荐
- Oracle database backup and recovery
- Vulnerability recurrence ----- 49. Apache airflow authentication bypass (cve-2020-17526)
- 系统架构设计师备考经验分享:论文出题方向
- Wechat forum exchange applet system graduation design completion (7) Interim inspection report
- Network security -burpsuit
- kubernetes的简单化数据存储StorageClass(建立和删除以及初步使用)
- 微信论坛交流小程序系统毕业设计毕设(1)开发概要
- UE4_UE5全景相机
- 漏洞复现----49、Apache Airflow 身份验证绕过 (CVE-2020-17526)
- 648. 单词替换
猜你喜欢
Matlab SEIR infectious disease model prediction
JMeter interface automated test read case, execute and write back result
【微服务|SCG】gateway整合sentinel
Explain
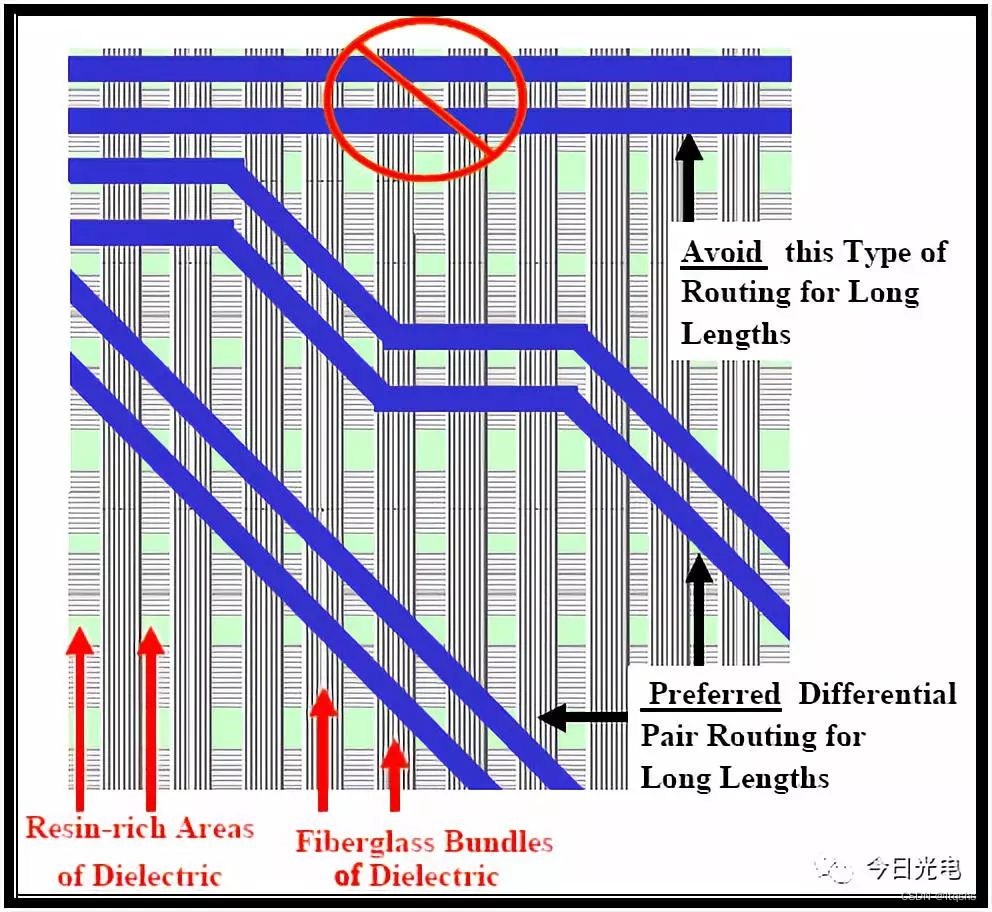
PCI-Express接口的PCB布线规则
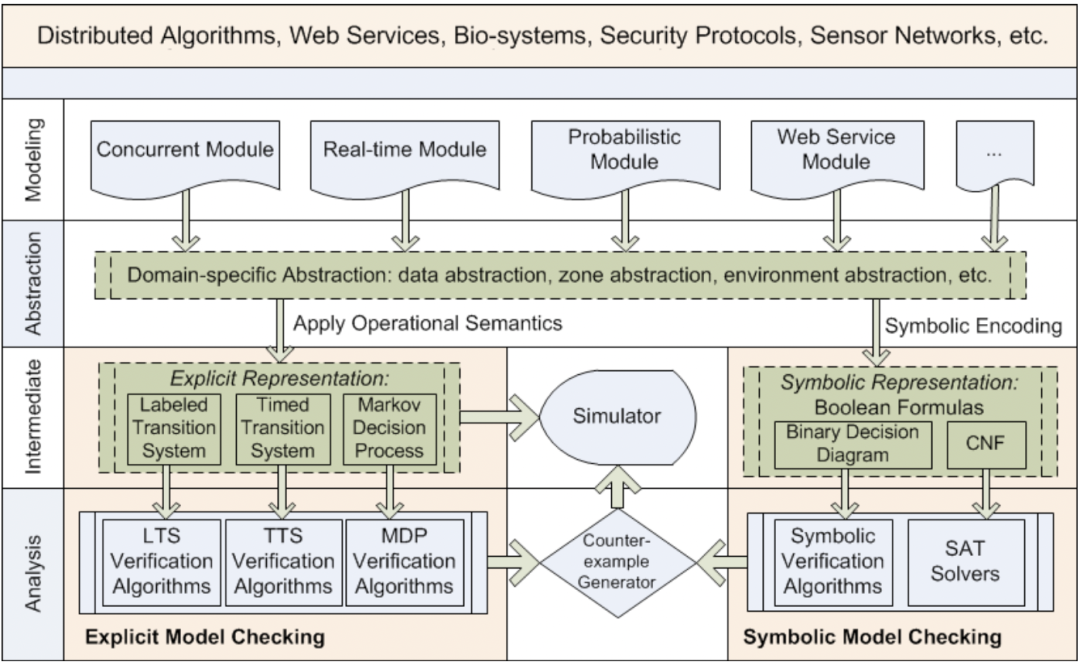
In the field of software engineering, we have been doing scientific research for ten years!
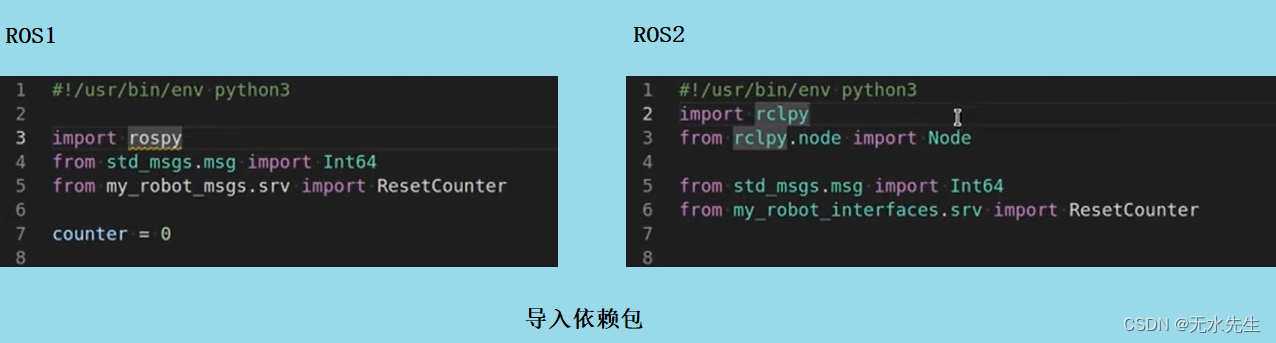
ROS2专题(03):ROS1和ROS2的区别【01】

三问TDM
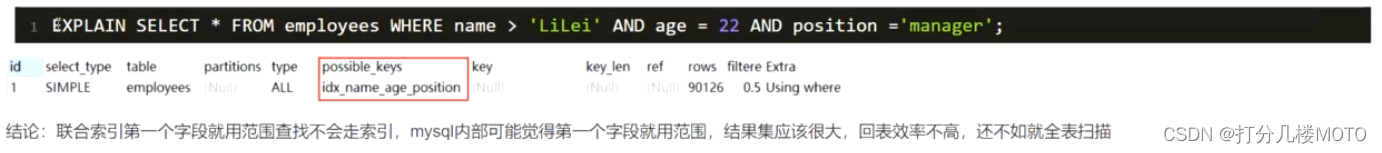
Mysql索引优化实战一
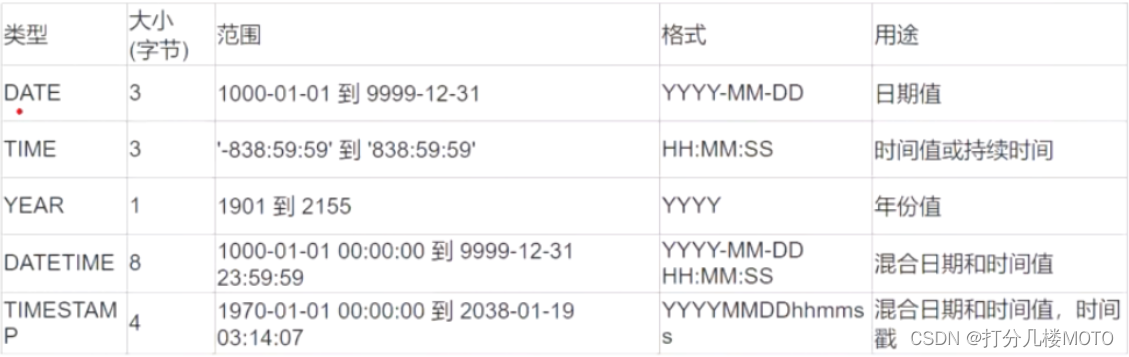
Mysql索引优化实战二
随机推荐
在软件工程领域,搞科研的这十年!
Adrnoid Development Series (XXV): create various types of dialog boxes using alertdialog
Network security -burpsuit
LDO稳压芯片-内部框图及选型参数
树后台数据存储(採用webmethod)[通俗易懂]
伸展树(一) - 图文解析与C语言实现
UE4_UE5全景相机
kubernetes的简单化数据存储StorageClass(建立和删除以及初步使用)
Cloud native is devouring everything. How should developers deal with it?
Unity3d Learning Notes 6 - GPU instantiation (1)
Dynamics 365 find field filtering
The 19th Zhejiang Provincial Collegiate Programming Contest VP记录+补题
智慧社区和智慧城市之间有什么异同
PMP项目管理考试过关口诀-1
Binary tree
LeeCode -- 6. Z 字形变换
PHP uses Alibaba cloud storage
FreeLink开源呼叫中心设计思想
Dynamic agent explanation (July 16, 2020)
Gee (IV): calculate the correlation between two variables (images) and draw a scatter diagram