当前位置:网站首页>Variables, process control and cursors (MySQL)
Variables, process control and cursors (MySQL)
2022-07-07 03:16:00 【JiaXingNashishua】
Catalog
1.1.1 Classification of system variables
1.1.2 Look at the system variables
1.2.1 User variable classification
1.2.4 Compare session user variables with local variables
Two : Define conditions and handlers
3.3 The cycle structure of LOOP
3.4 The cycle structure of WHILE
3.5 The cycle structure of REPEAT
3.6 Comparison of three cycle structures :
3.7 Jump sentence of LEAVE sentence
3.8 Jump sentence of ITERATE sentence
4.1 What is a cursor ( Or the cursor )
One : Variable
stay MySQL Stored procedures and functions in the database , Variables can be used to store intermediate result data of queries or calculations , Or output the final result data .
stay MySQL In the database , Variables are divided into System variables as well as User defined variables .
1.1 System variables
1.1.1 Classification of system variables
Variables are defined by the system , Not user defined , Belong to The server level . start-up MySQL service , Generate MySQL During the service instance ,MySQL Will be for MySQL Assignment of system variables in server memory , These system variables define the current MySQL Properties of the service instance 、 features . The values of these system variables are either compile MySQL Time parameters The default value of , Or The configuration file ( for example my.ini etc. ) Parameter value in .
System variables are divided into global system variables ( Need to add global keyword ) And session system variables ( Need to add session keyword ), Sometimes global system variables are referred to as global variables , Sometimes the session system variable is also called local Variable . If you don't write , Default session level . Static variables ( stay MySQL Their values cannot be used while service instances are running set Dynamic modification ) Belongs to a special global system variable .
every last MySQL Client successfully connected MySQL After the server , Will produce the corresponding session . During the conversation ,MySQL The service instance will be in MySQL The session system variable corresponding to the session is generated in the server memory , The initial values of these session system variables are copies of the global system variable values . Here's the picture :
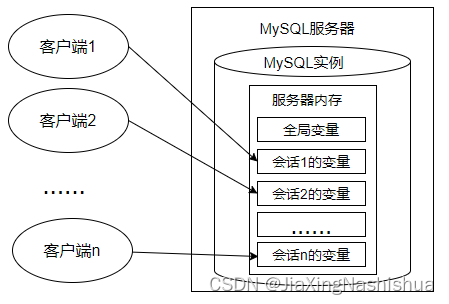
- The global system variable is for all sessions ( Connect ) It works , but Can't cross restart
- The session system variable is only for the current session ( Connect ) It works . During the conversation , Modification of a session system variable value by the current session , It will not affect the value of the same session system variable in other sessions .
- conversation 1 Modifying the value of a global system variable will cause the session to 2 Modification of the same global system variable value in .
stay MySQL in Some system variables can only be global , for example max_connections Used to limit the maximum number of connections to the server ; There are some The scope of system variables can be global or session , for example character_set_client Character set used to set the client ; There are some The scope of the system variable can only be the current session , for example pseudo_thread_id Used to mark the current session MySQL Connect ID.
1.1.2 Look at the system variables
View all or part of the system variables
# See all global variables
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES;
# View all session variables
SHOW SESSION VARIABLES;
or
SHOW VARIABLES;
# Look at some of the system variables that meet the criteria .
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE '% identifier %';
# Look at some session variables that meet the criteria
SHOW SESSION VARIABLES LIKE '% identifier %';
give an example :
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'admin_%';
View the specified system variable
As MySQL Coding standards ,MySQL The system variables in are expressed in Two “@” start , among “@@global” Used only to mark global system variables ,“@@session” Used only to mark the session system variable .“@@” First, mark the session system variable , If the session system variable does not exist , Then mark the global system variable .
# View the value of the specified system variable
SELECT @@global. Variable name ;
# View the value of the specified session variable
SELECT @@session. Variable name ;
# perhaps
SELECT @@ Variable name ; Modify the value of the system variable
Sometimes , The database administrator needs to modify the default value of the system variable , To modify the current session or MySQL Properties of the service instance 、 features . The specific methods :
The way 1: modify MySQL The configuration file , Then modify MySQL The value of the system variable ( This method needs to be restarted MySQL service )
The way 2: stay MySQL During service operation , Use “set” Command to reset the value of the system variable
# Assign a value to a system variable
# The way 1:
SET @@global. Variable name = A variable's value ;
# The way 2:
SET GLOBAL Variable name = A variable's value ;
# It is valid for the current database instance , Once the restart mysql service , Is failure .
# Assign a value to a session variable
# The way 1:
SET @@session. Variable name = A variable's value ;
# The way 2:
SET SESSION Variable name = A variable's value ;
give an example :
SELECT @@global.autocommit;
SET GLOBAL autocommit=0;
SELECT @@session.tx_isolation;
SET @@session.tx_isolation='read-uncommitted';
SET GLOBAL max_connections = 1000;
SELECT @@global.max_connections;
1.2 User variables
1.2.1 User variable classification
User variables are defined by the user , As MySQL Coding standards ,MySQL User variables in One “@” start . Depending on the scope of action , It is divided into Session user variables and local variable .
- Session user variables : The scope is the same as the session variable , Only right Current connection Session valid .
- local variable : Only in BEGIN and END Valid in statement block . local variable Only in Stored procedures and functions Use in .
1.2.2 Session user variables
Definition of variables
# The way 1:“=” or “:=”
SET @ User variables = value ;
SET @ User variables := value ;
# The way 2:“:=” or INTO keyword
SELECT @ User variables := expression [FROM Equal clause ];
SELECT expression INTO @ User variables [FROM Equal clause ];
Look at the value of the user variable ( see 、 Compare 、 Operations, etc )
SELECT @ User variables give an example
SET @a = 1;
SELECT @a;
SELECT @num := COUNT(*) FROM employees;
SELECT @num;
SELECT AVG(salary) INTO @avgsalary FROM employees;
SELECT @avgsalary;
SELECT @big; # When viewing an undeclared variable , Will get NULL value
1.2.3 local variable
Definition : have access to DECLARE Statement defines a local variable
Scope : Just defining it BEGIN ... END Effective in
Location : Only on the BEGIN ... END in , And can only be placed in the first sentence
BEGIN
# Declare local variables
DECLARE Variable name 1 Variable data type [DEFAULT Variable defaults ];
DECLARE Variable name 2, Variable name 3,... Variable data type [DEFAULT Variable defaults ];
# Assign values to local variables
SET Variable name 1 = value ;
SELECT value INTO Variable name 2 [FROM Clause ];
# View the value of a local variable
SELECT Variable 1, Variable 2, Variable 3;
END
1. Defining variables
DECLARE Variable name type [default value ]; # without DEFAULT Clause , The initial value is NULL
2. Variable assignment
The way 1: Generally used to assign simple values
SET Variable name = value ;
SET Variable name := value ;
The way 2: It is generally used to assign field values in the table
SELECT Field name or expression INTO Variable name FROM surface ;
3. Using variables ( see 、 Compare 、 Operations, etc )
SELECT Local variable name ;give an example 1: Declare local variables , And assign the values to employees In the table employee_id by 102 Of last_name and salary
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE set_value()
BEGIN
DECLARE emp_name VARCHAR(25);
DECLARE sal DOUBLE(10,2);
SELECT last_name,salary INTO emp_name,sal
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id = 102;
SELECT emp_name,sal;
END //
DELIMITER ;
give an example 2: Declare two variables , Sum and print ( Use session user variables separately 、 Local variables )
# The way 1: Use user variables
SET @m=1;
SET @n=1;
SET @[email protected][email protected];
SELECT @sum;
# The way 2: Use local variables
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE add_value()
BEGIN
# local variable
DECLARE m INT DEFAULT 1;
DECLARE n INT DEFAULT 3;
DECLARE SUM INT;
SET SUM = m+n;
SELECT SUM;
END //
DELIMITER ;
give an example 3: Create stored procedure “different_salary” Check the salary gap between an employee and his leader , And use IN Parameters emp_id Receive employees id, use OUT Parameters dif_salary Output salary gap results .
# Statement
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE different_salary(IN emp_id INT,OUT dif_salary DOUBLE)
BEGIN
# Declare local variables
DECLARE emp_sal,mgr_sal DOUBLE DEFAULT 0.0;
DECLARE mgr_id INT;
SELECT salary INTO emp_sal FROM employees WHERE employee_id = emp_id;
SELECT manager_id INTO mgr_id FROM employees WHERE employee_id = emp_id;
SELECT salary INTO mgr_sal FROM employees WHERE employee_id = mgr_id;
SET dif_salary = mgr_sal - emp_sal;
END //
DELIMITER ;
# call
SET @emp_id = 102;
CALL different_salary(@emp_id,@diff_sal);
# see
SELECT @diff_sal;
1.2.4 Compare session user variables with local variables

Two : Define conditions and handlers
Defined conditions It is to define the problems that may be encountered in the process of program execution in advance , The handler It defines how to deal with problems , And ensure that stored procedures or functions can continue to execute in case of warnings or errors . This can enhance the ability of the stored program to deal with problems , Avoid abnormal program stop .
explain : Define conditions and handlers in stored procedures 、 All storage functions are supported .
2.1 case analysis
case analysis : Create a name “UpdateDataNoCondition” Stored procedure . The code is as follows :
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE UpdateDataNoCondition()
BEGIN
SET @x = 1;
UPDATE employees SET email = NULL WHERE last_name = 'Abel';
SET @x = 2;
UPDATE employees SET email = 'aabbel' WHERE last_name = 'Abel';
SET @x = 3;
END //
DELIMITER ;Calling stored procedure :
mysql> CALL UpdateDataNoCondition();
ERROR 1048 (23000): Column 'email' cannot be null
mysql> SELECT @x;
+------+
| @x |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
You can see , here @x The value of the variable is 1. In conjunction with creating stored procedures SQL Statement code can get : Conditions and handlers are not defined in stored procedures , And when the stored procedure executes SQL When the statement reports an error ,MySQL The database will throw an error , And exit the current SQL Logic , Don't go down .
2.2 Defined conditions
The defining condition is to give MySQL Error code naming in , This helps to make the stored program code clearer . It will be one Wrong name and Specified error condition Connect . This name can then be used to define the handler DECLARE HANDLER In the sentence .
Define conditional usage DECLARE sentence , The syntax is as follows :
DECLARE Wrong name CONDITION FOR Error code ( Or wrong conditions )
Description of error code :
- MySQL_error_code and sqlstate_value All of them can express MySQL Error of .
- MySQL_error_code Is a numeric type error code .
- sqlstate_value yes The length is 5 String type error code .
- for example , stay ERROR 1418 (HY000) in ,1418 yes MySQL_error_code,'HY000' yes sqlstate_value.
- for example , stay ERROR 1142(42000) in ,1142 yes MySQL_error_code,'42000' yes sqlstate_value.
give an example 1: Definition “Field_Not_Be_NULL” Wrong name and MySQL in Violation of non empty constraints The error type of is “ERROR 1048 (23000)” Corresponding .
# Use MySQL_error_code
DECLARE Field_Not_Be_NULL CONDITION FOR 1048;
# Use sqlstate_value
DECLARE Field_Not_Be_NULL CONDITION FOR SQLSTATE '23000';
give an example 2: Definition "ERROR 1148(42000)" error , The name is command_not_allowed.
# Use MySQL_error_code
DECLARE command_not_allowed CONDITION FOR 1148;
# Use sqlstate_value
DECLARE command_not_allowed CONDITION FOR SQLSTATE '42000';2.3 Define handler
It can be for SQL Some type of error that occurs during execution defines a special handler . When defining a handler , Use DECLARE The syntax of the statement is as follows :
DECLARE Processing mode HANDLER FOR Wrong type Processing statements
Processing mode : The treatment methods are 3 A value of :CONTINUE、EXIT、UNDO.
- CONTINUE : Indicates that an error is encountered and will not be processed , Carry on .
- EXIT : Exit immediately in case of an error .
- UNDO : Indicates that the previous operation is withdrawn after an error is encountered .MySQL This operation is not supported in the .
Wrong type ( I.e. conditions ) It can be taken as follows :
- SQLSTATE ' String error code ' : The length is 5 Of sqlstate_value Error code for type ;
- MySQL_error_code : Match numeric type error code ;
- Wrong name : Express DECLARE ... CONDITION Defined error condition name .
- SQLWARNING : Match all to 01 At the beginning SQLSTATE Error code ;
- NOT FOUND : Match all to 02 At the beginning SQLSTATE Error code ;
- SQLEXCEPTION : Match all that have not been SQLWARNING or NOT FOUND The captured SQLSTATE Error code ;
Processing statements : If one of the above conditions occurs , The corresponding processing method is adopted , And execute the specified processing statement . The statement can be
image “ SET Variable = value ” Such a simple statement , It can also be used BEGIN ... END Write compound statements .
Several ways to define handlers , The code is as follows :
# Method 1: Capture sqlstate_value
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR SQLSTATE '42S02' SET @info = 'NO_SUCH_TABLE';
# Method 2: Capture mysql_error_value
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR 1146 SET @info = 'NO_SUCH_TABLE';
# Method 3: Define the conditions first , Call again
DECLARE no_such_table CONDITION FOR 1146;
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NO_SUCH_TABLE SET @info = 'NO_SUCH_TABLE';
# Method 4: Use SQLWARNING
DECLARE EXIT HANDLER FOR SQLWARNING SET @info = 'ERROR';
# Method 5: Use NOT FOUND
DECLARE EXIT HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET @info = 'NO_SUCH_TABLE';
# Method 6: Use SQLEXCEPTION
DECLARE EXIT HANDLER FOR SQLEXCEPTION SET @info = 'ERROR';2.4 Case solving
In the stored procedure , Define handler , Capture sqlstate_value value , When you meet MySQL_error_code The value is 1048 when , perform CONTINUE operation , And will @proc_value Is set to -1.
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE UpdateDataNoCondition()
BEGIN
# Define handler
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR 1048 SET @proc_value = -1;
SET @x = 1;
UPDATE employees SET email = NULL WHERE last_name = 'Abel';
SET @x = 2;
UPDATE employees SET email = 'aabbel' WHERE last_name = 'Abel';
SET @x = 3;
END //
DELIMITER ;
# call
mysql> CALL UpdateDataWithCondition();
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> SELECT @x,@proc_value;
+------+-------------+
| @x | @proc_value |
+------+-------------+
| 3 | -1 |
+------+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3、 ... and : Process control
It is impossible to solve complex problems through a SQL Sentence completion , We need to perform multiple SQL operation . The function of process control statement is to control the stored procedure SQL The order in which statements are executed , Is an essential part of our complex operations . As long as the program is executed , Processes are divided into three categories :
- Sequential structure : The program runs from top to bottom
- Branching structure : The program is selected and executed according to conditions , Select one of two or more paths to execute
- Loop structure : When the program meets certain conditions , Repeat a set of statements
Aim at MySQL The main flow control statements are 3 class . Be careful : Can only be used to store programs .
- Conditional statements :IF Statement and CASE sentence
- Loop statement :LOOP、WHILE and REPEAT sentence
- Jump statements :ITERATE and LEAVE sentence
3.1 Branching structure IF
IF The grammatical structure of the statement is :
IF expression 1 THEN operation 1
[ELSEIF expression 2 THEN operation 2]……
[ELSE operation N]
END IF
The result of the expression is TRUE or FALSE Execute the corresponding statement . here “[]” The content in is optional .
characteristic :① Different expressions correspond to different operations ② Use in begin end in
give an example 1:
IF val IS NULL
THEN SELECT 'val is null';
ELSE SELECT 'val is not null';
END IF;
give an example 2:
Declaring stored procedures “update_salary_by_eid1”, Definition IN Parameters emp_id, Enter employee number . Judge the employee
If the salary is lower than 8000 Yuan and has been employed for more than 5 year , Just raise your salary 500 element ; Otherwise, it will remain the same .
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE update_salary_by_eid1(IN emp_id INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE emp_salary DOUBLE;
DECLARE hire_year DOUBLE;
SELECT salary INTO emp_salary FROM employees WHERE employee_id = emp_id;
SELECT DATEDIFF(CURDATE(),hire_date)/365 INTO hire_year
FROM employees WHERE employee_id = emp_id;
IF emp_salary < 8000 AND hire_year > 5
THEN UPDATE employees SET salary = salary + 500 WHERE employee_id = emp_id;
END IF;
END //
DELIMITER ;
3.2 Branching structure CASE
CASE The grammatical structure of a sentence 1:
# Situation 1 : Be similar to switch
CASE expression
WHEN value 1 THEN result 1 Or words 1( If it's a statement , Need semicolon )
WHEN value 2 THEN result 2 Or words 2( If it's a statement , Need semicolon )
...
ELSE result n Or words n( If it's a statement , Need semicolon )
END [case]( If it's on begin end Need to add case, If you put it in select There is no need for )
CASE The grammatical structure of a sentence 2:
# Situation two : Similar to multiple if
CASE
WHEN Conditions 1 THEN result 1 Or words 1( If it's a statement , Need semicolon )
WHEN Conditions 2 THEN result 2 Or words 2( If it's a statement , Need semicolon )
...
ELSE result n Or words n( If it's a statement , Need semicolon )
END [case]( If it's on begin end Need to add case, If you put it in select There is no need for )
give an example 1:
Use CASE The... Of the process control statement 1 format , Judge val The value is equal to 1、 be equal to 2, Or both .
CASE val
WHEN 1 THEN SELECT 'val is 1';
WHEN 2 THEN SELECT 'val is 2';
ELSE SELECT 'val is not 1 or 2';
END CASE;
give an example 2:
Use CASE The... Of the process control statement 2 format , Judge val Is it empty 、 Less than 0、 Greater than 0 Or equal to 0.
CASE
WHEN val IS NULL THEN SELECT 'val is null';
WHEN val < 0 THEN SELECT 'val is less than 0';
WHEN val > 0 THEN SELECT 'val is greater than 0';
ELSE SELECT 'val is 0';
END CASE;
3.3 The cycle structure of LOOP
LOOP Loop statements are used to repeat certain statements .LOOP The statements in the loop are repeated until the loop is exited ( Use LEAVE Clause ), Jump out of the loop process .
LOOP The basic format of the statement is as follows :
loop_label:] LOOP
Statements executed in a loop
END LOOP [loop_label]among ,loop_label Express LOOP Of the statement Label name , This parameter can be omitted .
give an example 1:
Use LOOP Statement ,id Less than 10 The loop process is repeated .
DECLARE id INT DEFAULT 0;
add_loop:LOOP
SET id = id +1;
IF id >= 10 THEN LEAVE add_loop;
END IF;
END LOOP add_loop;
3.4 The cycle structure of WHILE
WHILE Statement creates a loop with conditional judgment .WHILE When executing a statement , First judge the specified expression , If it is true , Just execute the statements in the loop , Otherwise exit the loop .WHILE The basic format of the statement is as follows :
while_label:] WHILE The loop condition DO
The loop body
END WHILE [while_label];while_label by WHILE The annotation name of the statement ; If the result of the loop condition is true ,WHILE A statement or group of statements within a statement is executed , Until the cycle condition is false , Exit loop .
give an example :
WHILE Statement example ,i Less than 10 when , The loop process... Will be repeated , The code is as follows :
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE test_while()
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
WHILE i < 10 DO
SET i = i + 1;
END WHILE;
SELECT i;
END //
DELIMITER ;
# call
CALL test_while();
3.5 The cycle structure of REPEAT
REPEAT Statement creates a loop with conditional judgment . And WHILE The difference between cycles is ,REPEAT The loop first executes a loop , And then in UNTIL To judge the expression , If the conditions are met, exit , namely END REPEAT; If the conditions are not met , Then it will continue to execute the loop , Until the exit conditions are met .
REPEAT The basic format of the statement is as follows :
[repeat_label:] REPEAT
The statement of the loop body
UNTIL Conditional expression to end the loop
END REPEAT [repeat_label]
repeat_label by REPEAT The annotation name of the statement , This parameter can be omitted ;REPEAT A statement or group of statements within a statement is repeated , until expr_condition It's true .
give an example :
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE test_repeat()
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
REPEAT
SET i = i + 1;
UNTIL i >= 10
END REPEAT;
SELECT i;
END //
DELIMITER ;
3.6 Comparison of three cycle structures :
1、 All three loops can omit the name , But if you add a loop control statement to the loop (LEAVE or ITERATE) You must add a name .
2、 LOOP: Commonly used in Simple implementation " die " loop
WHILE: First Execute after judgment
REPEAT: Execute before judge , Unconditionally execute at least once
3.7 Jump sentence of LEAVE sentence
LEAVE sentence : Can be used in loop statements , Or with BEGIN and END Wrapped program body , Represents the operation of jumping out of the loop or out of the program body . If you have experience with process oriented programming languages , You can take LEAVE Understood as a break.
The basic format is as follows :
LEAVE Tagnames
among ,label The parameter represents the flag of the loop .LEAVE and BEGIN ... END Or loops are used together .
give an example : Create stored procedure “leave_begin()”, Statement INT Type of IN Parameters num. to BEGIN...END Tagging , And in
BEGIN...END Use in IF Sentence judgment num The value of the parameter .
If num<=0, Then use LEAVE Statement exit BEGIN...END;
If num=1, Then check “employees” The average salary of the table ;
If num=2, Then check “employees” The minimum salary of the table ;
If num>2, Then check “employees” The highest salary in the table .
IF Query at the end of the statement “employees” The total number of people in the table .
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE leave_begin(IN num INT)
begin_label: BEGIN
IF num<=0
THEN LEAVE begin_label;
ELSEIF num=1
THEN SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees;
ELSEIF num=2
THEN SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees;
ELSE
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees;
END IF;
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees;
END //
DELIMITER ;
3.8 Jump sentence of ITERATE sentence
ITERATE sentence : Can only be used in loop statements (LOOP、REPEAT and WHILE sentence ) Inside , Means to restart the cycle , Move the execution order to the beginning of the statement segment . If you have experience with process oriented programming languages , You can take ITERATE Understood as a continue, You mean for “ Cycle again ”.
The basic format of the statement is as follows :
ITERATE label
label The parameter represents the flag of the loop .ITERATE Statement must precede the loop flag .
give an example : Defining local variables num, The initial value is 0. Execute in a loop structure num + 1 operation .
If num < 10, Then continue to execute the loop ;
If num > 15, Then exit the loop structure ;
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE test_iterate()
BEGIN
DECLARE num INT DEFAULT 0;
my_loop:LOOP
SET num = num + 1;
IF num < 10
THEN ITERATE my_loop;
ELSEIF num > 15
THEN LEAVE my_loop;
END IF;
SELECT ' Silicon Valley : Let the world have no hard to learn technology ';
END LOOP my_loop;
END //
DELIMITER ;
Four : The cursor
4.1 What is a cursor ( Or the cursor )
Although we can also pass the screening criteria WHERE and HAVING, Or a keyword that limits the return record LIMIT Return a record , however , But it can't be like a pointer in the result set , Position a record forward 、 Position a record backward , Or is it Randomly locate a record , And process the recorded data .
This is the time , You can use a cursor . The cursor , It provides a flexible operation mode , Enables us to locate each record in the result set , A data structure that operates on the data in the pointed record . Cursor let SQL This set oriented language has the ability of process oriented development .
stay SQL in , A cursor is a temporary database object , Can point to the data row pointer stored in the database table . Here's the cursor Acts as a pointer , We can manipulate data rows by manipulating cursors .
MySQL Cursors can be used in stored procedures and functions .
such as , We checked employees The salary in the data sheet is higher than 15000 What are your employees :
SELECT employee_id,last_name,salary FROM employees
WHERE salary > 15000;
Here we can manipulate data rows through cursors , As shown in the figure, the line where the cursor is located is “108” The record of , We can also scroll the cursor over the result set , Point to any row in the result set .
4.2 Using cursor steps
The cursor must be declared before the handler is declared , And variables and conditions must also be declared before declaring cursors or handlers .
If we want to use cursors , It usually takes four steps . Different DBMS in , The syntax for using cursors may be slightly different .
First step , declare cursor
stay MySQL in , Use DECLARE Keyword to declare the cursor , The basic form of its grammar is as follows :
DECLARE cursor_name CURSOR FOR select_statement;
This grammar applies to MySQL,SQL Server,DB2 and MariaDB. If it is to use Oracle perhaps PostgreSQL, Need to be written :
DECLARE cursor_name CURSOR IS select_statement;
To use SELECT Statement to get the data result set , At this time, the traversal of the data has not started , here select_statement It stands for SELECT sentence , Returns a result set used to create the cursor .
such as :
DECLARE cur_emp CURSOR FOR
SELECT employee_id,salary FROM employees;
The second step , Open cursor
The syntax for opening a cursor is as follows :
OPEN cursor_name
When we define the cursor , If you want to use a cursor , The cursor must be opened first . When opening the cursor SELECT The query result set of the statement will be sent to the cursor workspace , For the following cursor Read one by one Prepare the records in the result set .
OPEN cur_emp ;
The third step , Use cursors ( Get data from cursor )
The grammar is as follows :
FETCH cursor_name INTO var_name [, var_name] ...
The function of this sentence is to use cursor_name Use this cursor to read the current row , And save the data to var_name In this variable , The cursor pointer points to the next line . If the data row read by the cursor has multiple column names , It's in INTO Assign a value to multiple variable names after the keyword .
Be careful :var_name The cursor must be defined before it is declared .
FETCH cur_emp INTO emp_id, emp_sal ;
Be careful : The number of fields in the query result set of the cursor , Must follow INTO The following variables are the same , otherwise , When the stored procedure executes ,MySQL It will give you an error .
Step four , Close cursor
CLOSE cursor_nameYes OPEN There will be CLOSE, That is, open and close the cursor . When we finish using the cursor, we need to close the cursor . Because the cursor will occupy system resources , If you don't close it in time , The cursor remains until the end of the stored procedure , Affect the efficiency of system operation . And closing the cursor , The system resources occupied by the cursor will be released .
After closing the cursor , We can no longer retrieve the data rows in the query results , If you need to retrieve, you can only open the cursor again .
CLOSE cur_emp;
边栏推荐
- 迷失在MySQL的锁世界
- HDU 4337 King Arthur&#39; S Knights it outputs a Hamiltonian circuit
- Leetcode 77: combination
- 变量、流程控制与游标(MySQL)
- Optimization of application startup speed
- Household appliance industry under the "retail is king": what is the industry consensus?
- Domcontentloaded and window onload
- The first symposium on "quantum computing + application of financial technology" was successfully held in Beijing
- Redis getting started complete tutorial: client management
- C language string sorting
猜你喜欢
知识图谱构建全流程
杰理之在非蓝牙模式下,手机连接蓝牙不要跳回蓝牙模式处理方法【篇】

首届“量子计算+金融科技应用”研讨会在京成功举办
![Jerry's broadcast has built-in flash prompt tone to control playback pause [chapter]](/img/8c/e8f7e667e4762a4815e97c36a2759f.png)
Jerry's broadcast has built-in flash prompt tone to control playback pause [chapter]
尚硅谷JVM-第一章 类加载子系统
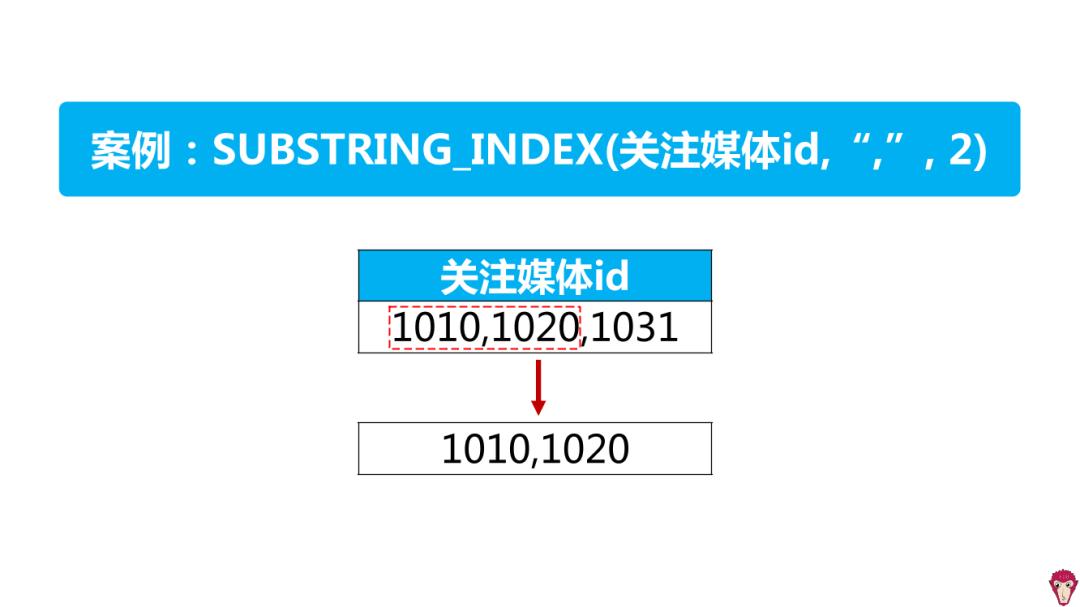
如何分析粉丝兴趣?
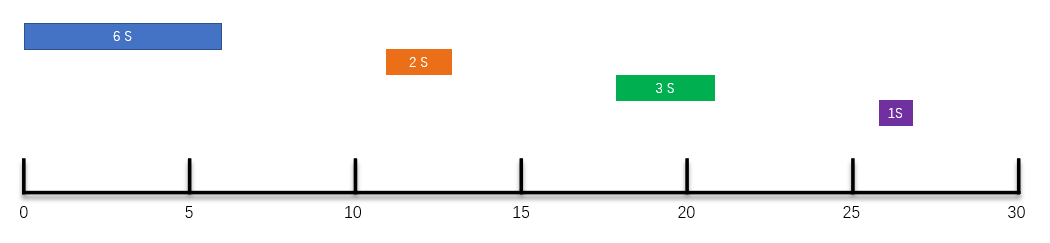
When you go to the toilet, you can clearly explain the three Scheduling Strategies of scheduled tasks
![[2022 national tournament simulation] polygon - computational geometry, binary answer, multiplication](/img/09/b9d50f7a10e6898ac4088ee005d00b.png)
[2022 national tournament simulation] polygon - computational geometry, binary answer, multiplication
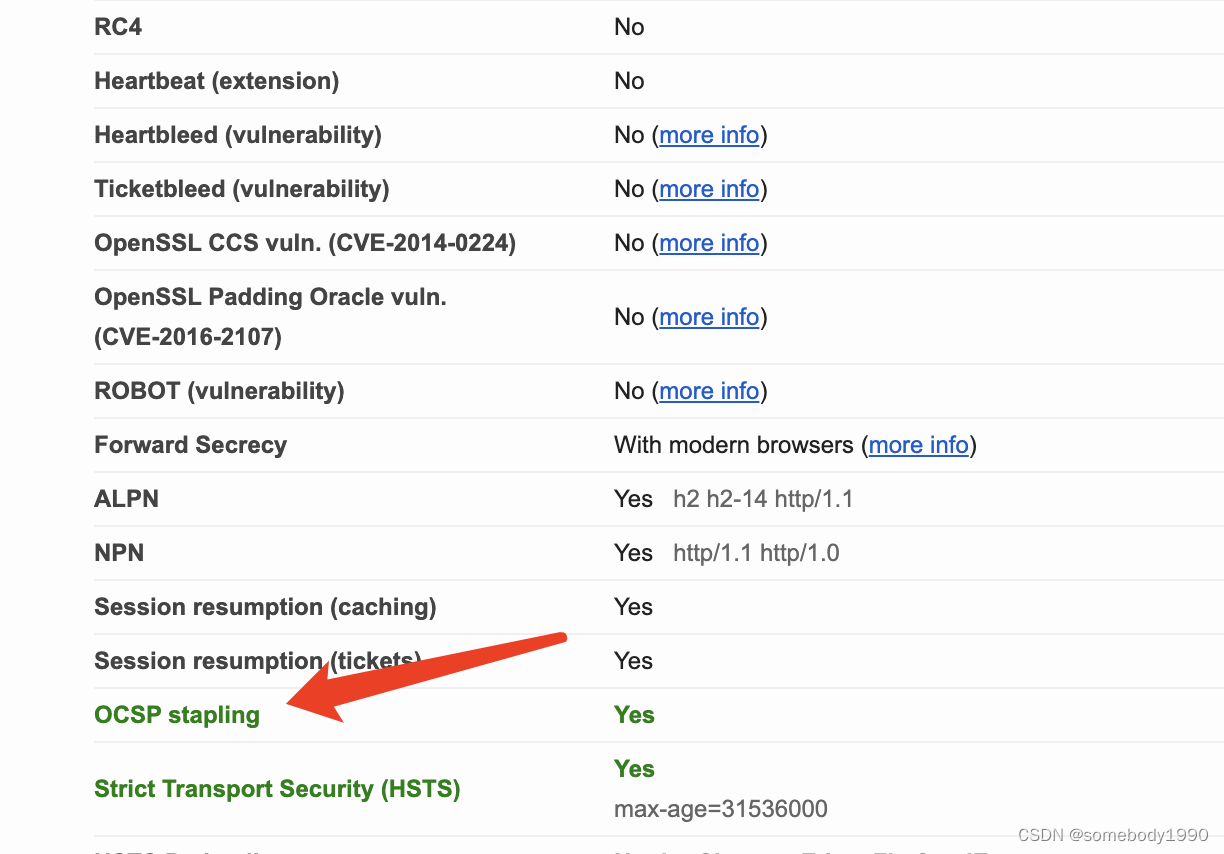
密码学系列之:在线证书状态协议OCSP详解

uniapp的表单验证
随机推荐
unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x10b34e810
杰理之RTC 时钟开发【篇】
Redis introduction complete tutorial: replication principle
The solution of unable to create servlet file after idea restart
腾讯云原生数据库TDSQL-C入选信通院《云原生产品目录》
尚硅谷JVM-第一章 类加载子系统
Install redis from zero
oracle连接池长时间不使用连接失效问题
Do you know the five most prominent advantages of E-bidding?
“零售为王”下的家电产业:什么是行业共识?
美国空军研究实验室《探索深度学习系统的脆弱性和稳健性》2022年最新85页技术报告
2022 spring recruitment begins, and a collection of 10000 word interview questions will help you
Flink Task退出流程与Failover机制
Jerry's RTC clock development [chapter]
硬件之OC、OD、推挽解释
Unity uses maskablegraphic to draw a line with an arrow
Oauth2协议中如何对accessToken进行校验
杰理之播内置 flash 提示音控制播放暂停【篇】
商城商品的知识图谱构建
Centerx: open centernet in the way of socialism with Chinese characteristics