当前位置:网站首页>Custom thread pool rejection policy
Custom thread pool rejection policy
2022-07-07 13:29:00 【Bug Commander】
One . Default deny policy
ThreadPoolExceutor.AbortPolicy : Discard the task and throw it out RejectedExecutionException abnormal .
ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy: Discarding the task , But no exception is thrown . ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy: Discard the top task in the queue , Then resubmit the rejected task
ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy: By the calling thread ( The thread that submitted the task ) Deal with the task
Generally speaking , Default this 4 Type of rejection policy , It is not applicable in some scenarios , For example, we don't want to discard any tasks , So before 3 The two rejection strategies are not applicable
The first 4 This rejection strategy is special , When this policy is implemented , Will give the current thread to The thread that submitted the task To perform this task , For example, you are through The main thread Open thread task , So this rejection strategy is to put Tasks rejected by the thread pool , Backhand to Main thread execution , Scenarios with high concurrency , Will block the main thread , So it is not very applicable , The following uses pseudo code to customize the rejection policy
Two . Custom reject policy
If you don't want to discard the task and leave it to the main thread to execute the task , Can we collect these rejected tasks ? So consider using a cache container , And it must be a concurrency safe cache container , So you can use juc Under bag java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue, Introduce this class first
LinkedBlockingQueue Is a one-way linked list implementation of the blocking queue , The queue by FIFO( fifo ) Sorting elements , The new element is inserted at the end of the queue , And the queue get operation will get the element at the head of the queue , The throughput of linked queues is usually higher than that of array based queues , But in most concurrent applications , Its predictable performance is lower
Besides , LinkedBlockingQueue Or optional capacity ( Prevent excessive expansion ), That is, you can specify the capacity of the queue , If you don't specify , The default capacity size is equal to Integer.MAX_VALUE, I will not specify the capacity of the queue here
LinkedBlockingQueue In the realization of " Mutex access to competing resources by multiple threads " when , For put and take Method operations use different locks , about put operation , adopt " Insert the lock putLock" To synchronize , For the extraction operation , adopt " Take out the lock takeLock" To synchronize
If a thread ( The simulation in the code is SchedulerTask) To retrieve data , The queue is just empty , The thread will execute notEmpty.await() Wait for , When some other thread ( The simulation in the code is the reject task of the thread pool ) After inserting data into the queue , Would call notEmpty.signal() Wake up the "notEmpty On the waiting thread ”, here , ( The simulation in the code is SchedulerTask) Will be awakened to continue to run , Besides , ( The simulation in the code is SchedulerTask) Before the fetch operation , Will get takeLock, Release after the fetch operation is completed takeLock
If a thread ( The simulation in the code is the reject task of the thread pool ) To insert data , The queue is full , Then the thread will execute notFull.await() Wait for , When some other thread ( The simulation in the code is SchedulerTask) After taking out the data , Would call notFull.signal() Wake up the "notFull On the waiting thread ", here , ( The simulation in the code is the reject task of the thread pool ) Will be awakened to continue to run , Besides , ( The simulation in the code is the reject task of the thread pool ) Before performing the insert operation , Will get putLock, It is not released until the insertion operation is completed putLock
2.1 First, customize the rejection policy implementation
Customize a class implementation java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler Interface
public class CustomizeRejectionPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
if (r != null) {
// Tasks that the thread pool does not have time to execute are put into the queue first
ThreadReader.put(r);
}
}
}2.2 Implement an intermediate class , For declaration LinkedBlockingQueue
@Component
public class ThreadReader {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ThreadReader.class);
private static final BlockingQueue<Runnable> BLOCKING_QUEUE = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
@Qualifier("thread-pool")
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor;
public static void put(Runnable runnable) {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> blockingQueue = getBlockingQueue();
try {
blockingQueue.put(runnable);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
public void take() {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> blockingQueue = getBlockingQueue();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(blockingQueue)) {
return;
}
try {
Runnable runnable = blockingQueue.take();
logger.info(LogUtils.format(" Fetch the tasks that the current thread pool has not been able to execute , runnable=<{0}>", runnable));
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//
}
}
public static BlockingQueue<Runnable> getBlockingQueue() {
return BLOCKING_QUEUE;
}
}2.3 Define the fetch class of the queue , Single thread is used here , No longer the main thread
@Component
public class CustomizeScheduler implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Autowired
private ThreadReader threadReader;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
ThreadFactory threadFactory =
new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setThreadFactory(new NamedThreadFactory("SchedulerTask")).build();
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutor =
new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, threadFactory, new CustomizeRejectionPolicy());
// After every 1 Second, there is no time to execute tasks in the execution queue
scheduledExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> threadReader.take(), 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}2.4 Simulation test
First Thread pool The configuration is as follows , And then use jmeter simulation 2000 A request
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
@Bean("thread-pool")
public static ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor() {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(8, 16,1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100),
new NamedThreadFactory("common-service"), new CustomizeRejectionPolicy());
threadPoolExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
return threadPoolExecutor;
}
}
Then check the console , You can see the log printing , You can find Single thread every other 1 Seconds from the queue Tasks rejected by the thread pool , And add the task back to the thread pool , Re execution 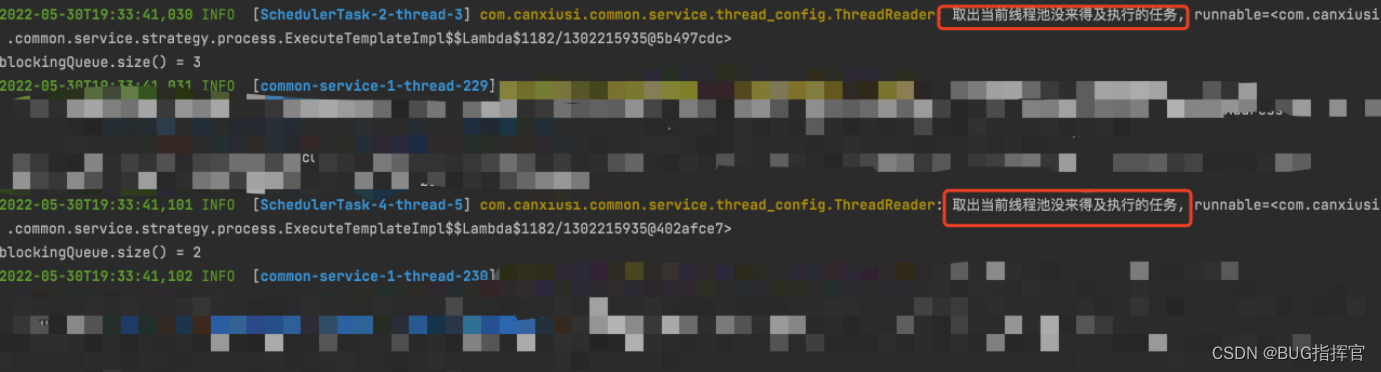
3、 ... and . Related design patterns
The classic design pattern of multithreading is used here , Producer-Consumer Pattern , The thread pool submits a task that is denied execution , He is equivalent to a producer , Single thread is equivalent to consumer , Deal with these tasks , Intermediate class ThreadReader amount to Channel passageway , This design pattern can be explained in detail in the blog : Multithreading based design patterns Producer-Consumer Pattern
Why not directly introduce a single thread into the rejection policy to execute the rejected task ?
In this way, the performance of the program will be reduced , The thread pool only needs to add the rejected tasks to the queue , There is no need to care about how a single thread is scheduled , There is no need to wait for a single thread to process these tasks , You can immediately put the next task in the queue
边栏推荐
- Pcap learning notes II: pcap4j source code Notes
- Read PG in data warehouse in one article_ stat
- [untitled]
- Why can basic data types call methods in JS
- Scrapy教程经典实战【新概念英语】
- Realbasicvsr test pictures and videos
- PAcP learning note 1: programming with pcap
- Write it down once Net a new energy system thread surge analysis
- 单片机原理期末复习笔记
- ESP32系列专栏
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
[QNX hypervisor 2.2 user manual]6.3.4 virtual register (guest_shm.h)
RealBasicVSR测试图片、视频
单片机学习笔记之点亮led 灯
Test next summary
线程池拒绝策略最佳实践
10 pictures open the door of CPU cache consistency
如何让electorn打开的新窗口在window任务栏上面
Show the mathematical formula in El table
Mongodb replication (replica set) summary
为租客提供帮助
Talk about pseudo sharing
简单好用的代码规范
单片机原理期末复习笔记
如何让join跑得更快?
Problems that cannot be accessed in MySQL LAN
Esp32 construction engineering add components
PAcP learning note 3: pcap method description
[QNX Hypervisor 2.2用户手册]6.3.4 虚拟寄存器(guest_shm.h)
Go language learning notes - structure
[Presto profile series] timeline use