当前位置:网站首页>JS --- all knowledge of JS objects and built-in objects (III)
JS --- all knowledge of JS objects and built-in objects (III)
2022-07-06 15:22:00 【Cirrod】
1、 object
stay JavaScript in , An object is an unordered collection of related properties and methods , All things are objects , Like strings 、 The number 、 Array 、 Functions, etc .
Objects are made up of properties and methods :
attribute : The characteristics of things , Use attributes to represent... In objects ( Common nouns )
Method : The behavior of things , Use methods to represent... In objects ( Common verbs )
1.1、 Create objects
stay JavaScript in , At this stage, we can create objects in three ways (object):
Create an object using literals
utilize new Object Create objects
Using constructors to create objects
① Create an object using literals
Object literal : It's curly braces { } It contains the expression of this specific thing ( object ) Properties and methods of
{ } It is expressed in the form of key value pairs
key : Equivalent to property name
value : Equivalent to property value , Can be any type of value ( Numeric type 、 String type 、 Boolean type , Function types, etc )
var star = {
name : 'pink',
age : 18,
sex : ' male ',
sayHi : function(){
alert(' Hello, everyone ~');
}
};// Multiple attributes or methods are separated by commas
// The method colon is followed by an anonymous function
Object call
The properties in the object call : object . Property name , This little point . It means “ Of ”
Another way to call properties in an object : object [‘ Property name ’], Note that the attributes in square brackets must be quoted , We'll use it later
Object : object . Method name () , Note that the method name must be followed by parentheses
console.log(star.name) // Call the name property
console.log(star['name']) // Call the name property
star.sayHi(); // call sayHi Method , Be careful , Make sure you don't forget the parentheses that follow
Variable 、 attribute 、 function 、 Methods to summarize
Variable : Declare the assignment separately , Exist alone
attribute : The variables in the object are called properties , No declaration required , Used to describe the characteristics of the object
function : Existing alone , adopt ==“ Function name ()”== You can call
Method : The functions inside the object are called methods , Methods don't need to be declared , Use ==“ object . Method name ()”== You can call , Method is used to describe the behavior and function of the object .
② utilize new Object Create objects
Just like before new Array() Consistent principle :var Object name = new Object();
Format used : object . attribute = value
var obj = new Object(); // Created an empty object
obj.name = ' Zhang Sanfeng ';
obj.age = 18;
obj.sex = ' male ';
obj.sayHi = function() {
console.log('hi~');
}//1. We use the equal sign assignment method to add objects
//2. Each property and method ends with a semicolon
console.log(obj.uname);
console.log(obj['sex']);
obj.sayHi();③ Using constructors to create objects
Constructors : It's a special function , It's mainly used to initialize objects , That is, to assign initial values to object member variables , It's always related to new Operators . We can extract some common properties and methods from the object , Then encapsulate it into this function .
stay js in , When using constructors, you should pay attention to the following two points :
Constructor is used to create a class of objects , The first letter should be capitalized
Constructors and new It makes sense to use them together
// The syntax format of the constructor
function Constructor name () {
this. attribute = value ;
this. Method = function() {}
}
new Constructor name ();//1. The constructor's first letter should be capitalized
//2. Constructors don't need return You can return the result
//3. Calling the constructor must use new
//4. All we have to do is new Star() Calling the function creates an object
//5. Our properties and methods must be preceded by this
function Star(uname,age,sex) {
this.name = uname;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.sing = function(sang){
console.log(sang);
}
}
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ',18,' male ');
console.log(typeof ldh) // object object , The calling function returns an object
console.log(ldh.name);
console.log(ldh['sex']);
ldh.sing(' Ice rain ');
// Passed the ice rain to sang
var zxy = new Star(' Jacky Cheung ',19,' male ');The constructor's first letter should be capitalized
Before the properties and methods in the function, you need to add this , Represents the properties and methods of the current object .
You don't need... In the constructor return Return results .
When we create objects , Must use new To call the constructor .
Constructors and objects
Constructors , Such as Stars(), Abstracts the common part of the object , Encapsulated in a function , It refers to a general category (class)
Create objects , Such as new Stars(), Especially one , adopt new Keyword the process of creating an object is also called object instantiation

new keyword
new There are four things you can do in execution :
Create a new empty object in memory .
Give Way this Point to this new object .
Execute the code in the constructor , Add properties and methods to this new object
Return to this new object ( So it's not needed in the constructor return)
1.2、 Traversing the properties of an object
for...in Statement is used to loop through the properties of an array or object
The grammar is as follows
for( Variable in Object name ){
// Execute the code here
}The variables in the syntax are custom , It needs to conform to naming conventions , Usually we will write this variable as k perhaps key.
for(var k in obj) {
console.log(k); // there k It's the property name
console.log(obj[k]);// there obj[k] It's property value
}var obj = {
name: ' The qin dynasty sir',
age: 18,
sex: ' male ',
fn:function() {};
};
console.log(obj.name);
console.log(obj.age);
console.log(obj.sex);
//for in Traverse our objects
//for ( Variable in object ){}
// We use for in The variables inside We like writing k perhaps key
for(var k in obj){
console.log(k); // k Variable The output is the attribute name
console.log(obj[k]); // obj[k] What you get is the attribute value
}2、 Built-in objects
JavaScript The objects in are divided into 3 Kind of : Custom object 、 Built-in objects 、 Browser object
Built in objects are JS Some objects that come with language , These objects are used by developers , And provides some common or the most basic and necessary functions
JavaScript Provides multiple built-in objects :Math、 Date 、Array、String etc.
2.1、 Look up the documents
Learn how to use a built-in object , Just learn how to use its common members , We can learn by looking up documents , Can pass MDN/W3C To query
MDN: MDN Web Docs
2.1.1、 How to learn methods in objects
Check the function of this method
Check the meaning and type of parameters inside
Check the meaning and type of the return value
adopt demo To test
3、Math object
Math Object is not a constructor , It has properties and methods of mathematical constants and functions . Operations related to Mathematics ( Find the absolute value , integer 、 Maximum, etc ) have access to Math Members of the .
// Math Mathematical objects , Not a constructor , So we don't need new To call , Instead, you can directly use the properties and methods inside
Math.PI // PI
Math.floor() // Rounding down
Math.ceil() // Rounding up
Math.round() // Round the page Round to the nearest Be careful -3.5 The result is -3
Math.abs() // The absolute value
Math.max()/Math.min() // Find the maximum and minimum
Be careful : The above method must be in parentheses
console.log(Math.PI);
console.log(Math.max(1,99,3)); // 99practice : Encapsulate your own mathematical objects
Using objects to encapsulate their own mathematical objects , There are PI Maximum Minimum value
var myMath = {
PI: 3.141592653,
max: function() {
var max = arguments[0];
for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
if (arguments[i] > max) {
max = arguments[i];
}
}
return max;
},
min: function() {
var min = arguments[0];
for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
if (arguments[i] < min) {
min = arguments[i];
}
}
return min;
}
}
console.log(myMath.PI);
console.log(myMath.max(1, 5, 9));
console.log(myMath.min(1, 5, 9));3.Math Absolute value and three rounding methods
Math.abs() Take the absolute value
Three rounding methods :
Math.floor() : Rounding down
Math.ceil() : Rounding up
Matg.round() : rounding , All other numbers are rounded , however 5 special , It's going big
//1. Absolute value method
console.log(Math.abs(1)); // 1
console.log(Math.abs(-1)); // 1
console.log(Math.abs('-1')); // 1 Implicit conversion , Will put string -1 Convert to digital
//2. Three rounding methods
console.log(Math.floor(1.1)); // 1 Rounding down , To the smallest value floor- The floor
console.log(Math.floor(1.9)); //1
console.log(Math.ceil(1.1)); //2 Rounding up , To the maximum value ceil- The ceiling
console.log(Math.ceil(1.9)); //2
// rounding All other numbers are rounded , however 5 special , It's going big
console.log(Math.round(1.1)); //1 rounding
console.log(Math.round(1.5)); //2
console.log(Math.round(1.9)); //2
console.log(Math.round(-1.1)); // -1
console.log(Math.round(-1.5)); // -14. Random number method rondom()
random() Method can return a decimal at random , Its value range is [0,1), Left closed right away 0 <= x < 1
Get a random integer between two numbers , Including two numbers
// Get a random integer between two numbers , And contain these two integers
function getRandom(min,max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}
console.log(getRandom(1,10));1. Random roll call
var arr = [' Zhang San ', ' Li Si ',' Wang Wu ',' Qin Liu '];
console.log(arr[getRandom(0,arr.length - 1)]);2. Guess the number game

function getRandom(min,max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}
var random = getRandom(1,10);
while(true) { // Dead cycle , Exit loop condition required
var num = prompt(' Please enter 1~10 An integer between :');
if(num > random) {
alert(' You guessed big ');
}else if (num < random) {
alert(' You guess it's small ');
}else {
alert(' You guessed it ');
break; // Exit the whole cycle
}
}4、Data() Date object
Date Objects and Math Different objects , He is a constructor , So we need to instantiate before we can use
Date Instances are used to process date and time
4.1、Date() Use of methods
4.1.1、 To get the current time, you must instantiate
var now = new Date();
console.log(now);4.1.2、Date() Arguments to the constructor
If there is time in parentheses , Just return the time in the parameter . For example, the date format string is ‘2019-5-1’, It can be written. new Date('2019-5-1') perhaps new Date('2019/5/1')
If Date() Don't write parameters , Just go back to the current time
If Date() Parameters written inside , Return the time entered in parentheses
// 1. If there are no parameters , Returns the current time of the current system
var now = new Date();
console.log(now);// 2. Common writing of parameters Digital 2019,10,1 String type '2019-10-1 8:8:8' Minutes and seconds
// If Date() Parameters written inside , Return the time entered in parentheses
var data = new Date(2019,10,1);
console.log(data); // The return is 11 Month is not 10 month
var data2 = new Date('2019-10-1 8:8:8');
console.log(data2);4.2、 Date formatting
We want to 2019-8-8 8:8:8 Format date , do ?
Need to get the part specified by the date , So we have to get this format manually
| Method name | explain | Code |
| getFullYear() | Get the year | dObj.getFullYear() |
| getMonth() | Get the current month (0-11) | dObj.getMonth() |
| getDate | Get date of day | dObj.getDate() |
| getDay() | Get the day of the week ( Sunday 0 Until Saturday 6) | dObj.getDay() |
| getHours() | Get the current hour | dObj.getHours() |
| getMinutes() | Get the current hour | dObj.getMinutes() |
| getSeconds() | Get the current second | dObj.gerSeconds() |
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.getFullYear()); // Returns the year of the current date 2019
console.log(date.getMonth() + 1); // The returned month is one month smaller Remember the month +1
console.log(date.getDate); // What number is returned
console.log(date.getDay()); // Return on Monday 1 Zhou 6 Return to six Return on Sunday 0// Write a 2019 year 5 month 1 Japan Wednesday
var date = new Date();
var year = date.getFullYear();
var month = date.getMonth() + 1;
var dates = date.getDate();
console.log(' It's today ' + year +' year ' + month + ' month ' + dates +' Japan ' );// Encapsulates a function that returns the current hour, minute, and second Format 08:08:08
function getTimer() {
var time = new Date();
var h = time.getHours();
h = h < 10 ? '0' + h : h;
var m = time.getMinutes();
m = m < 10 ? '0' + m : m;
var s = time.getSeconds();
s = s < 10 ? '0' + s : s;
return h + ':' + m + ':' + s;
}
console.log(getTimer());4.3、 Gets the total number of milliseconds of the date
date.valueOf() : Get the present time distance 1970.1.1 The total number of milliseconds
date.getTime() : Get the present time distance 1970.1.1 The total number of milliseconds
// obtain Date The total number of milliseconds Not the number of milliseconds of the current time But distance 1970 year 1 month 1 How many milliseconds have passed
// Instantiation Date object
var date = new Date();
// 1 . adopt valueOf() getTime() Used to get the original value of the object
console.log(date.valueOf()); // Get the present time distance 1970.1.1 The total number of milliseconds
console.log(date.getTime());
// 2. A simple way of writing
var date1 = +new Date(); // +new Date() The total number of milliseconds is returned ,
console.log(date1);
// 3. HTML5 Method provided in Get the total number of milliseconds Compatibility issues
console.log(Date.now());The countdown effect

function countDown(time) {
var nowTime = +new Date(); // No parameters , Returns the total number of milliseconds of the current time
var inputTime = +new Date(time); // With parameters , Returns the total number of milliseconds of user input time
var times = (inputTime - nowTime) / 1000; //times Is the total number of seconds remaining
var d = parseInt(times / 60 / 60 / 24); // Days
d < 10 ? '0' + d : d;
var h = parseInt(times / 60 / 60 % 24); // Hours
h < 10 ? '0' + h : h;
var m = parseInt(times / 60 % 60); // branch
m < 10 ? '0' + m : m;
var s = parseInt(times % 60); // second
s < 10 ? '0' + s : s;
return d + ' God ' + h + ' when ' + m + ' branch ' + s + ' second ';
}
console.log(countDown('2020-11-09 18:29:00'));
var date = new Date;
console.log(date); // present time 5、 Array objects
5.1、 The creation of array objects
Two ways to create an array object
Literal measure
new Array()
5.2、 Check if it's an array
instanceof Operator , You can determine whether an object belongs to a certain type
Array.isArray() Used to determine whether an object is an array ,isArray() yes HTML5 Method provided in
var arr = [1, 23];
var obj = {};
console.log(arr instanceof Array); // true
console.log(obj instanceof Array); // false
console.log(Array.isArray(arr)); // true
console.log(Array.isArray(obj)); // false5.3、 Add or remove array elements
| Method name | explain | Return value |
| push( Parameters 1…) | Add one or more elements at the end , Pay attention to modifying the original array | And returns the new length |
| pop() | Delete the last element of the array | Returns the value of the element it deleted |
| unshift( Parameters 1…) | Add one or more elements to the beginning of an array , Pay attention to modifying the original array | And returns the new length |
| shift() | Deletes the first element of the array , Array length minus 1, No parameter , Modify the original array | And return the first element |
// 1.push() At the end of our array , Add one or more array elements push PUSH
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
arr.push(4, ' Qin Xiao ');
console.log(arr);
console.log(arr.push(4, ' Qin Xiao '));
console.log(arr);
// push After finishing , The return result is the length of the new array
// 2. unshift At the beginning of our array Add one or more array elements
arr.unshift('red');
console.log(arr);
// pop() It can delete the last element of the array , Only one element can be deleted at a time
arr.pop(); // Without parameters
// shift() It deletes the first element of the array , Only one element can be deleted at a time
arr.shift(); // Without parameters Filter array
There is an array containing wages [1500,1200,2000,2100,1800], The salary in the array is required to exceed 2000 The deletion of , Put the rest in the new array
var arr = [1500, 1200, 2000, 2100, 1800];
var newArr = [];
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < 2000) {
newArr.push(newArr[i]);
}
}
console.log(newArr);
5.4、 Array sorting
| Method name | explain | Whether to modify the original array |
| reverse() | Reverse the order of the elements in the array , No parameter | This method will change the original array , Return a new array |
| sort() | Sort elements of an array | This method will change the original array , Return a new array |
// 1. Flip array
var arr = ['pink','red','blue'];
arr.reverse();
console.log(arr);
// 2. Array sorting ( Bubble sort )
var arr1 = [3,4,7,1];
arr1.sort();
console.log(arr1);
// For double digits
var arr = [1,64,9,61];
arr.sort(function(a,b) {
return b - a; // In descending order
return a - b; // Ascending
}
)5.5、 Array index
| Method name | explain | Return value |
| indexOf() | Find the first index of a given element in the array | Returns the index number if it exists , If it doesn't exist , Then return to -1 |
| lastIndexOf() | At the last index of the array , Index from back to front | Returns the index number if it exists , If it doesn't exist , Then return to -1 |
// Returns the index number method of an array element indexOf( Array elements ) The function is to return the index number of the array element
// It only sends and returns the first index number that meets the condition
// If you can't find an element , Then return to -1
var arr = ['red','green','blue'.'pink','blue'];
console.log(arr.indexOf('blue')); // 2
console.log(arr.lastIndexOf('blue')); // 45.5.1、 Array weight removal
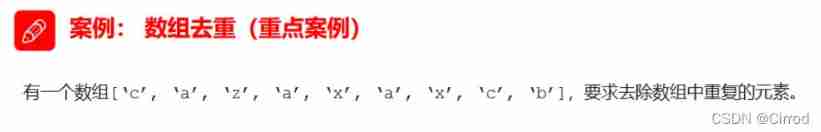
analysis : Select the non repeating elements in the old array and put them in the new array , Duplicate elements retain only one , Put it in the new array to redo .
The core algorithm : We iterate over the old array , Then take the old array element to query the new array , If the element does not appear in the new array , Let's add , Otherwise, do not add .
How do we know that the element does not exist ? utilize New array .indexOf( Array elements ) If the return is -1 Just explain There are no changed elements in the new array
// Encapsulate a de duplication function unique unmatched
function unique(arr) {
var newArr = [];
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (newArr.indexOf(arr[i]) === -1) {
newArr.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return newArr;
}
var demo = unique(['c', 'a', 'z', 'a', 'x', 'a', 'x', 'c', 'b']);
console.log(demo);5.6、 Array to string
| Method name | explain | Return value |
| toString() | Convert an array to a string , Comma separated each item | Returns a string |
| join(‘ Separator ’) | Method is used to convert all elements in the array into a string | Returns a string |
// 1.toString() Convert our array to a string
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(arr.toString()); // 1,2,3// 2.join(' Separator ')
var arr1 = ['green', 'blue', 'red'];
console.log(arr1.join()); // If you don't write, it is separated by commas by default
console.log(arr1.join('-')); // green-blue-red
console.log(arr1.join('&')); // green&blue&red5.7、 Other methods
| Method name | explain | Return value |
| concat() | Connect two or more arrays Does not affect the original array | Returns a new array |
| slice() | Array truncation slice(begin,end) | Returns a new array of intercepted items |
| splice() | Array delete splice( The number of items to be deleted at the beginning ) | Returns a new array of deleted items , This will affect the original array |
6、 String object
6.1、 Basic packaging type
To facilitate the operation of basic data types ,JavaScript Three special reference types are also provided :String、Number and Boolean.
The basic wrapper type is to wrap a simple data type into a complex data type , So the basic data type has properties and methods .
Let's see what's wrong with the following code ?
var str = 'andy';
console.log(str.length);The basic data type has no properties and methods , Objects have properties and methods , But the code above can be executed , This is because js Will wrap basic data types as complex data types , The implementation process is as follows :
// 1. Generate temporary variables , Wrapping simple types into complex data types
var temp = new String('andy');
// 2. Assign to our declared character variable
str = temp;
// 3. Destroy temporary variables
temp = null;6.2、 The immutability of string
It means that the values in it are immutable , Although it seems that the content can be changed , But the address has changed , A new memory space has been opened up in memory .
var str = 'abc';
str = 'hello';
// When you give str When you assign , Constant 'abc' Will not be modified , Still in memory
// Reassign string , Will re open up space in memory , This feature is the immutability of strings
// Because of the immutability of string , There are efficiency problems when splicing a large number of strings
var str = '';
for(var i = 0; i < 10000; i++){
str += i;
}
console.log(str);
// This result takes a lot of time to show , Because we need to constantly open up new space 6.3、 Return position according to character
String all methods , Will not modify the string itself ( Strings are immutable ), The operation will return a new string
| Method name | explain |
| indexOf(‘ Characters to find ’, Starting position ) | Returns the location of the specified content in the meta string , If you can't find it, go back -1, The starting position is index Reference no. |
| lastIndexOf() | Look backwards , Just find the first match |
// String object Return position according to character str.indexOf(' Characters to find ', [ Starting position ])
var str = ' The spring breeze of reform is sweeping the ground , Spring is coming ';
console.log(str.indexOf(' In the spring ')); // The default from the 0 Start looking for , The result is 2
console.log(str.indexOf(' In the spring ', 3)); // From the index number is 3 Start looking back , The result is 86.3.1、 Returns the character position
Find string “abcoefoxyozzopp” All in o Where and how often
The core algorithm : Find the first one first o Position of appearance
then as long as indexOf The result returned is not -1 Just keep looking back
because indexOf You can only find the first , So the following search , It must be the current index plus 1, To keep looking for
var str = "oabcoefoxyozzopp";
var index = str.indexOf('o');
var num = 0;
// console.log(index);
while (index !== -1) {
console.log(index);
num++;
index = str.indexOf('o', index + 1);
}
console.log('o The number of times is : ' + num);6.4、 Returns the character according to the position
| Method name | explain | Use |
| charAt(index) | Returns the character in the specified position (index The index number of the string ) | str.charAt(0) |
| charCodeAt(index) | Gets the... Of the character at the specified location ASCII code (index Reference no. ) | str.charCodeAt(0) |
| str[index] | Gets the character at the specified location | HTML,IE8+ Support and charAt() equivalent |
Returns the character position
Judging a string “abcoefoxyozzopp” The most frequently used character in , And count the times
The core algorithm : utilize charAt() Traversing this string
Store every character in the object , If the object does not have this property , for 1, If it exists +1
Traversing objects , Get the maximum value and the character
<script>
// There is an object To determine whether there is this attribute object [' Property name ']
var o = {
age: 18
}
if (o['sex']) {
console.log(' There is this attribute ');
} else {
console.log(' No attribute ');
}
// Judging a string 'abcoefoxyozzopp' The most frequently used character in , And count the times .
// o.a = 1
// o.b = 1
// o.c = 1
// o.o = 4
// The core algorithm : utilize charAt() Traversing this string
// Store every character in the object , If the object does not have this property , for 1, If it exists +1
// Traversing objects , Get the maximum value and the character
var str = 'abcoefoxyozzopp';
var o = {};
for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
var chars = str.charAt(i); // chars yes Every character in a string
if (o[chars]) { // o[chars] What you get is the attribute value
o[chars]++;
} else {
o[chars] = 1;
}
}
console.log(o);
// 2. Traversing objects
var max = 0;
var ch = '';
for (var k in o) {
// k Get is Property name
// o[k] What you get is the attribute value
if (o[k] > max) {
max = o[k];
ch = k;
}
}
console.log(max);
console.log(' The most common characters are ' + ch);
</script>6.5、 String operation method
| Method name | explain |
| concat(str1,str2,str3…) | concat() Method is used to connect two or pairs of strings . String concatenation |
| substr(start,length) | from start Position start ( Reference no. ), length Take the number of . |
| slice(start,end) | from start Position start , Intercept to end Location ,end Can't get ( Both are index numbers ) |
| substring(start,end) | from start Position start , Intercept to end Location ,end Can't get ( Basic and slice identical , But don't accept negative ) |
<script>
// 1. concat(' character string 1',' character string 2'....)
var str = 'andy';
console.log(str.concat('red'));
// 2. substr(' Intercept start position ', ' Intercept a few characters ');
var str1 = ' The spring breeze of reform is sweeping the ground ';
console.log(str1.substr(2, 2)); // first 2 It's the index number 2 the second 2 Is to take a few characters
</script>6.6、replace() Method
replace() Method is used to replace some characters with others in a string
Its use format :replace( Replaced characters , String to replace with )
<script>
// 1. Replace character replace(' Replaced characters ', ' Replace with the new character ') It will only replace the first character
var str = 'andyandy';
console.log(str.replace('a', 'b'));
// There's a string 'abcoefoxyozzopp' Ask for all the inside o Replace with *
var str1 = 'abcoefoxyozzopp';
while (str1.indexOf('o') !== -1) {
str1 = str1.replace('o', '*');
}
console.log(str1);
</script>6.7、split() Method
split() Method is used to segment strings , It splits strings into arrays . After the segmentation , It returns a new array .
For example, the following code :
var str = 'a,b,c,d';
console.log(str.split(','));
// It returns an array [a, b, c, d]<script>
// 2. Character to array split(' Separator ') We learned about join Convert an array to a string
var str2 = 'red, pink, blue';
console.log(str2.split(','));
var str3 = 'red&pink&blue';
console.log(str3.split('&'));
</script>6.8、 toggle case
toUpperCase() Convert a capital
toLowerCase() Convert lowercase
7、 Simple types are better than complex types
Simple types are also called basic data types or value types , Complex types are also called reference types .
Value type : Simple data type / Basic data type , In storage time, the value itself is stored in the variable , So it's called value type
string ,number,boolean,undefined,null
Reference type : Complex data type , At the time of storage, only the address is stored in the variable ( quote ), So it's called reference data type
adopt new Keyword created objects ( System object 、 Custom object ), Such as Object、Array、Date etc.
7.1、 Heap and stack
Stack space allocation difference :
Stack ( operating system ): The operating system automatically allocates and releases the parameter values of stored functions 、 The value of a local variable, etc . It operates like a stack in a data structure ;
Simple data types are stored in the stack
Pile up ( operating system ): Store complex types ( object ), Release is usually assigned by the programmer , If programmers don't release , Recycling by garbage collection mechanism .
Complex data types are stored in the heap
Be careful :JavaScript There is no concept of stack in , By stack , It can make it easier for you to understand some of the execution methods of the code , Easy to learn other languages in the future .
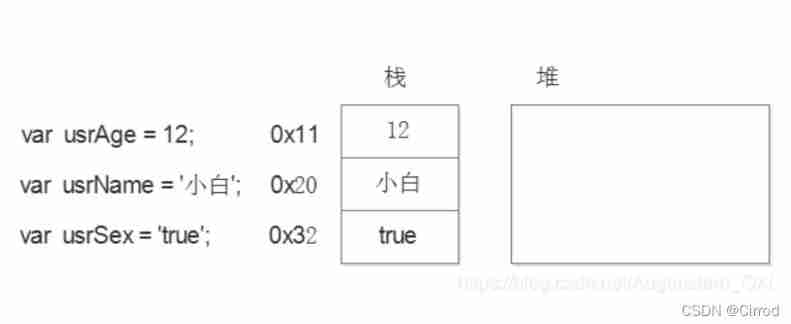
7.2、 Simple type of memory allocation
Value type ( Simple data type ): string ,number,boolean,undefined,null
The data of the value type variable is directly stored in the variable ( Stack space ) in
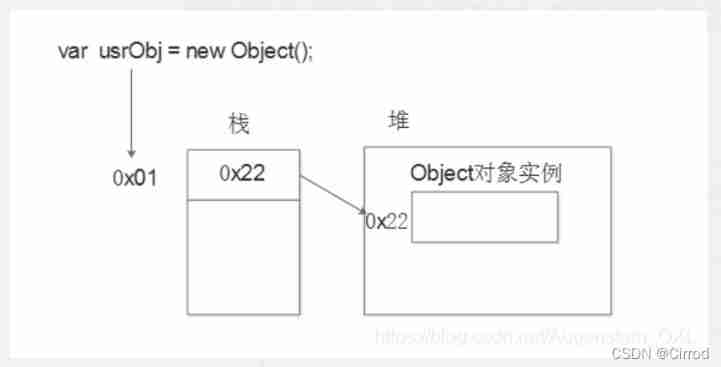
Reference type ( Complex data type ): adopt new Keyword created objects ( System object 、 Custom object ), Such as Object、Array、Date etc.
Reference type variable ( Stack space ) There's an address in it , Real object instances are stored in heap space
<script>
// Simple data type null It returns an empty object object
var timer = null;
console.log(typeof timer);
// If there is a variable, we plan to store it as an object later , I haven't figured out what to put , I'll give it to you at this time null
// 1. Simple data type It's stored in the stack It directly opens up a space to store the value
// 2. Complex data type First, store the address in the stack Hexadecimal representation Then this address points to the data in the heap
</script>7.3、 Simple type transfer reference
The formal parameter of a function can also be regarded as a variable , When we pass a value type variable as a parameter to a function's formal parameter , In fact, the value of the variable in the stack space is copied to the formal parameter , Then make any changes to the formal parameters within the method , Will not affect the external variables of .
<script>
// Simple data type parameters
function fn(a) {
a++;
console.log(a);
}
var x = 10;
fn(x);
console.log(x);
</script>7.4、 Complex type parameters
The formal parameter of a function can also be regarded as a variable , When we pass a reference type variable to a formal parameter , In fact, it copies the heap address stored in the stack space of the variable to the formal parameter , Formal parameters and arguments actually store the same heap address , So it operates on the same object .
<script>
// Complex data type transfer parameters
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
function f1(x) { // x = p
console.log(x.name); // 2. What does this output ? Lau Andy
x.name = " Jacky Cheung ";
console.log(x.name); // 3. What does this output ? Jacky Cheung
}
var p = new Person(" Lau Andy ");
console.log(p.name); // 1. What does this output ? Lau Andy
f1(p);
console.log(p.name); // 4. What does this output ? Jacky Cheung
</script>
边栏推荐
- MySQL数据库(三)高级数据查询语句
- Iterators and generators
- Introduction to variable parameters
- Eigen User Guide (Introduction)
- Leetcode simple question: check whether the numbers in the sentence are increasing
- MySQL transactions
- LeetCode#19. Delete the penultimate node of the linked list
- CSAPP shell lab experiment report
- 软件测试行业的未来趋势及规划
- CSAPP homework answers chapter 789
猜你喜欢

Investment operation steps
The wechat red envelope cover designed by the object is free! 16888
Stc-b learning board buzzer plays music 2.0
Lab 8 file system
ucore lab2 物理内存管理 实验报告

C4D quick start tutorial - creating models
Do you know the performance testing terms to be asked in the software testing interview?
Want to change jobs? Do you know the seven skills you need to master in the interview software test

Winter vacation daily question - maximum number of balloons
12306: mom, don't worry about me getting the ticket any more (1)
随机推荐
Take you to use wxpy to create your own chat robot (plus wechat interface basic data visualization)
Collection collection and map collection
ucore lab6 调度器 实验报告
JDBC介绍
转行软件测试必需要知道的知识
Mysql database (V) views, stored procedures and triggers
MySQL development - advanced query - take a good look at how it suits you
MySQL数据库(五)视 图 、 存 储 过 程 和 触 发 器
Knowledge that you need to know when changing to software testing
The wechat red envelope cover designed by the object is free! 16888
Introduction to variable parameters
MySQL数据库(三)高级数据查询语句
Do you know the performance testing terms to be asked in the software testing interview?
基于485总线的评分系统双机实验报告
CSAPP家庭作業答案7 8 9章
What are the commonly used SQL statements in software testing?
ucore lab7 同步互斥 实验报告
Currently, mysql5.6 is used. Which version would you like to upgrade to?
Emqtt distribution cluster and node bridge construction
Winter vacation daily question - maximum number of balloons
