当前位置:网站首页>Priority queue (heap)
Priority queue (heap)
2022-07-05 09:07:00 【Herd】
List of articles
- Priority queue ( Pile up )
- Preface
- The sequential storage of binary trees
- Pile up (heap)
- Build a heap ( Big root pile )
- Time complexity of heap building process in heap sorting O(n) How did it come from ?
- Reactor application - priority queue
- Into the heap operation offer
- Out of the heap operation poll
- Topk The problem is not code implementation
- Heap sort
- Priority queue insert element
- Topk problem Code implementation
- [ Look for the smallest K Pairs of numbers ](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-k-pairs-with-smallest-sums/)
- View the source image ](/img/4e/a64e8b39a2c25fb0cff8b78d3ea957.jpg)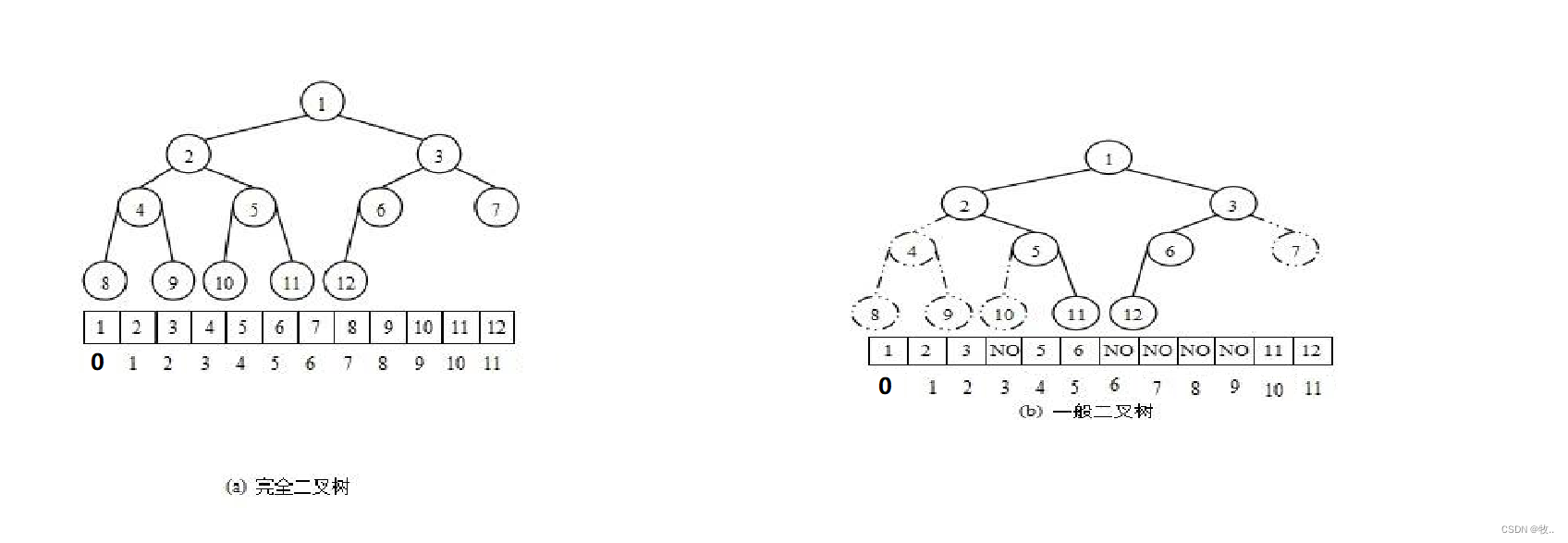
Subscript relation
Known parents (parent) The subscript , be :
Left the child (left) Subscript = 2 * parent + 1;
The right child (right) Subscript = 2 * parent + 2;
Known child ( There's no distinction between left and right )(child) Subscript , be :
Parents (parent) Subscript = (child - 1) / 2;
Pile up (heap)
Concept
The heap is logically a complete binary tree
The heap is physically stored in an array
Satisfy that the value of any node is greater than the value of the node in its subtree , It's called a lot of , Or a big pile , Or the largest heap
conversely , It's a small pile , Or a small pile of roots , Or the smallest heap
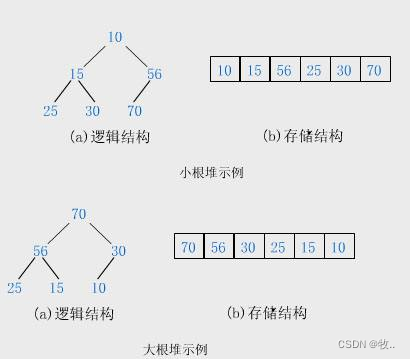
- The root node of each binary tree is less than Left and right child nodes ,
( Heap / The smallest pile )
The root node of each binary tree is larger than the left and right child nodes
( Big root pile / The biggest pile )
Build a heap ( Big root pile )
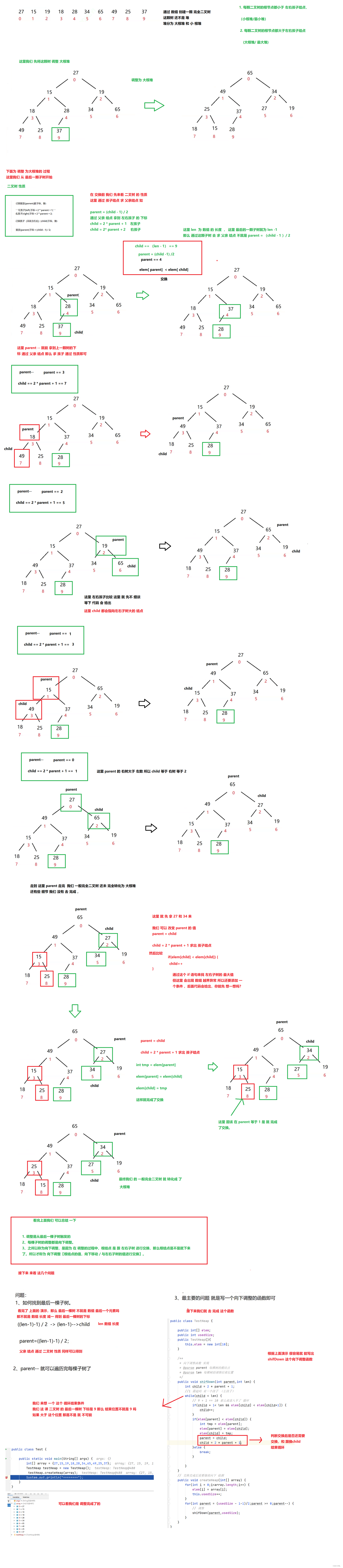
Attach code
public class TestHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public TestHeap(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
/** * Adjust the function down Realization * @param parent The root node of each tree * @param len The adjustment end position of each tree */
public void shifDown(int parent,int len) {
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
//1 Minimum There is a child ( Left the child )
while(child < len) {
// 9 + 1 == 10 Then you can't enter loop
if(child + 1< len && elem[child] < elem[child+1]) {
child++;
}
if(elem[parent] < elem[child]) {
int tmp = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = elem[child];
elem[child] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
// After the exchange is completed, you need to continue down testing
public void createHeap(int[] array) {
for(int i = 0;i<array.length;i++) {
elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
for(int parent = (usedSize - 1-1)/2;parent >= 0;parent--) {
// adjustment
shifDown(parent,usedSize);
}
}
}
Set up Big root pile , Next we Take a look at Time complexity of reactor building 
however Time complexity of reactor building by O(n), below The article explains , You can check it out
Time complexity of heap building process in heap sorting O(n) How did it come from ?
To build a small heap, you only need stay Build a lot of foundation Just change it
Attach code
public void shifDown2(int parent,int len) {
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while(child < len) {
if(child + 1 < len && elem[child] > elem[child +1]) {
child++;
}
if(elem[parent] > elem[child]) {
int tmp = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = elem[child];
elem[child] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
Reactor application - priority queue
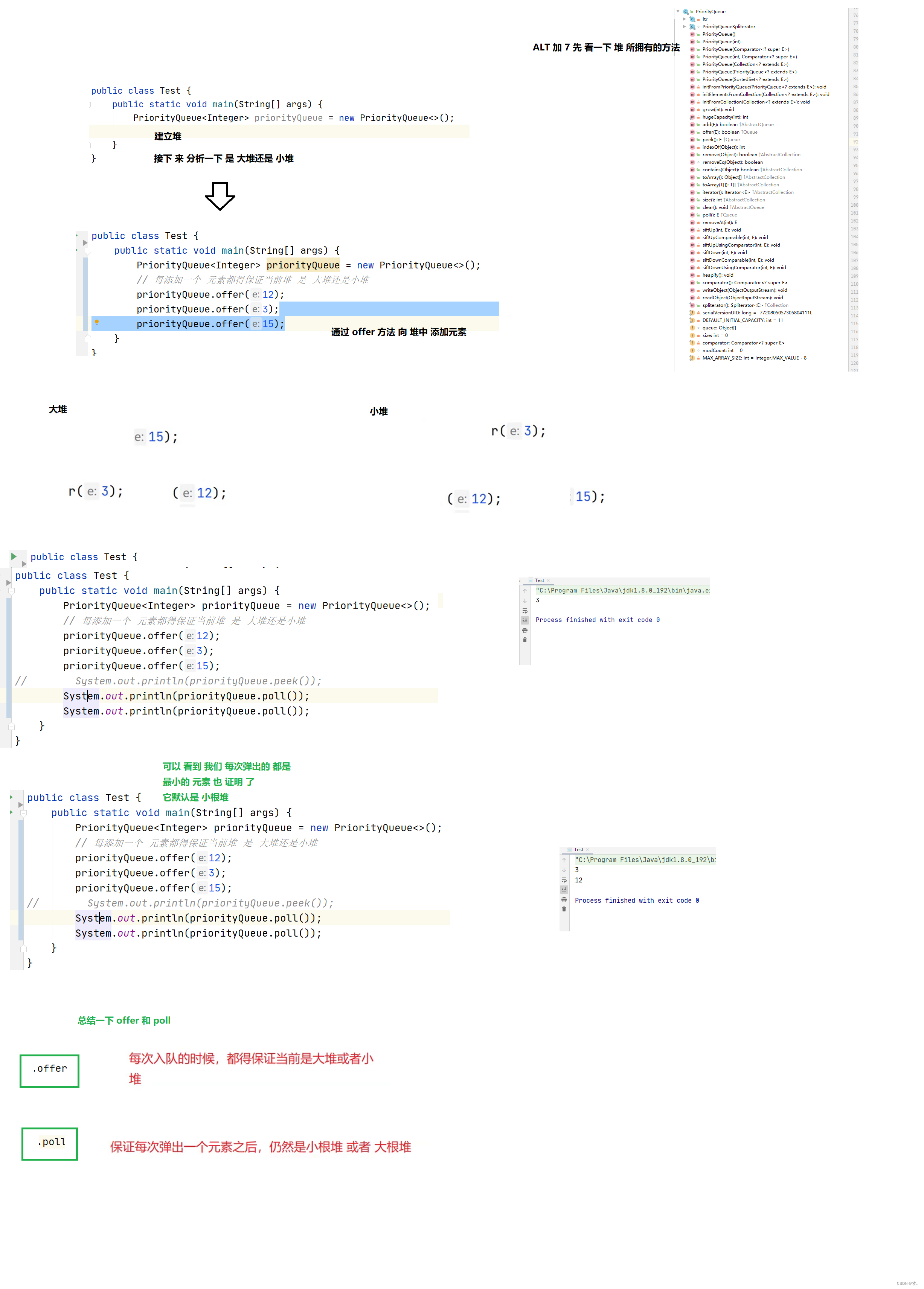
Into the heap operation offer
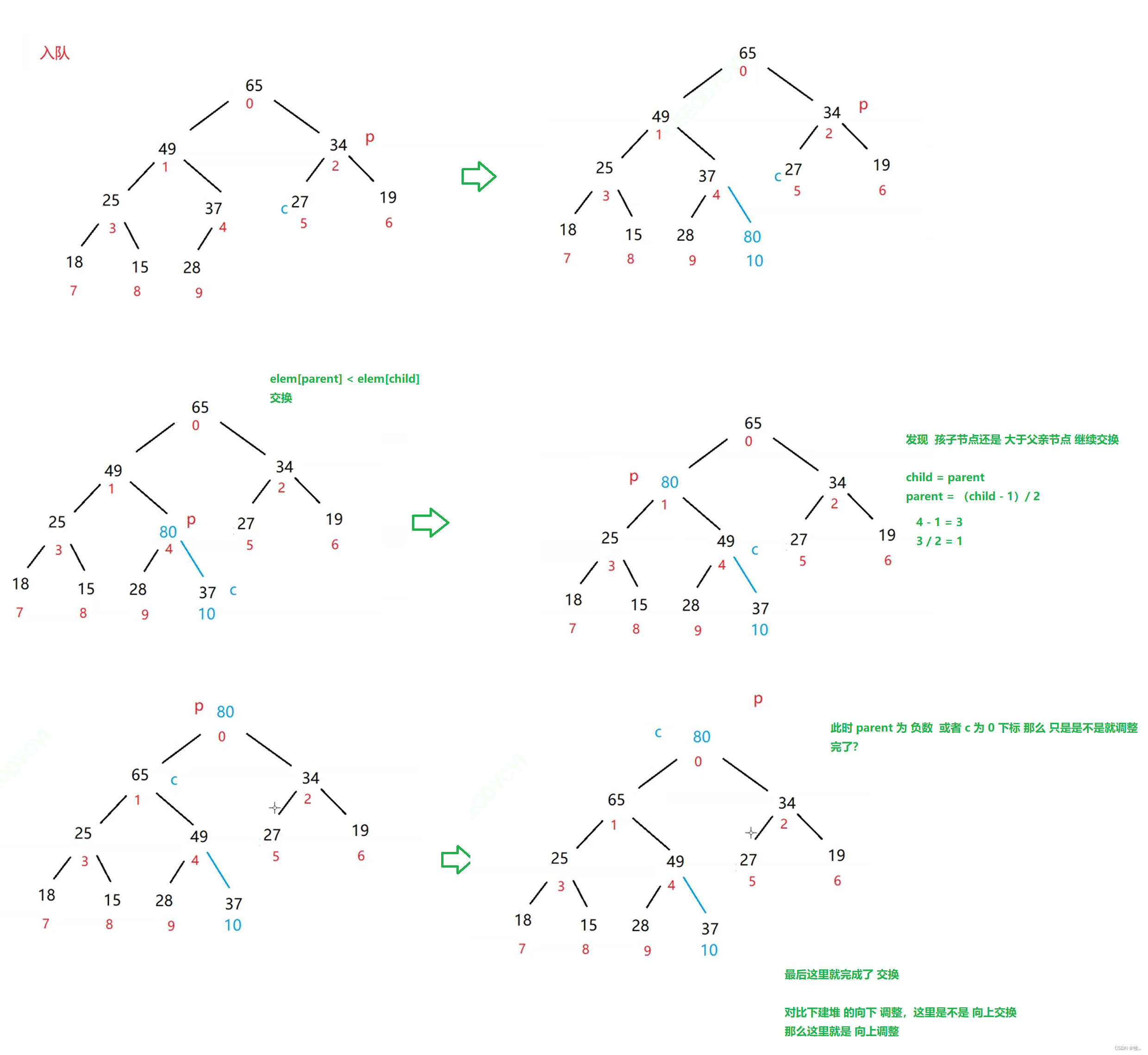
private void shiftUp(int child) {
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while(child != 0) {
if(elem[parent] < elem[child]) {
int tmp = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = elem[child];
elem[child] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
public void offer(int val) {
if(isFull()) {
// Capacity expansion
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2 * elem.length);
}
elem[usedSize++] = val;
// Be careful here Incoming parameter usedSize - 1
shiftUp(usedSize - 1);
}
public boolean isFull() {
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
You can see us Join the team and I become In exchange for
Out of the heap operation poll
Attach code
public class TestHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public TestHeap(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
/** * Adjust the function down Realization * @param parent The root node of each tree * @param len The adjustment end position of each tree */
public void shifDown(int parent,int len) {
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
//1 Minimum There is a child ( Left the child )
while(child < len) {
// 9 + 1 == 10 Then you can't enter loop
if(child + 1< len && elem[child] < elem[child+1]) {
child++;
}
if(elem[parent] < elem[child]) {
int tmp = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = elem[child];
elem[child] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
// After the exchange is completed, you need to continue down testing
public void createHeap(int[] array) {
for(int i = 0;i<array.length;i++) {
elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
for(int parent = (usedSize - 1-1)/2;parent >= 0;parent--) {
// adjustment
shifDown(parent,usedSize);
}
}
private void shiftUp(int child) {
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while(child != 0) {
if(elem[parent] < elem[child]) {
int tmp = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = elem[child];
elem[child] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
public void offer(int val) {
if(isFull()) {
// Capacity expansion
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2 * elem.length);
}
elem[usedSize++] = val;
// Be careful here Incoming parameter usedSize - 1
shiftUp(usedSize - 1);
}
public boolean isFull() {
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
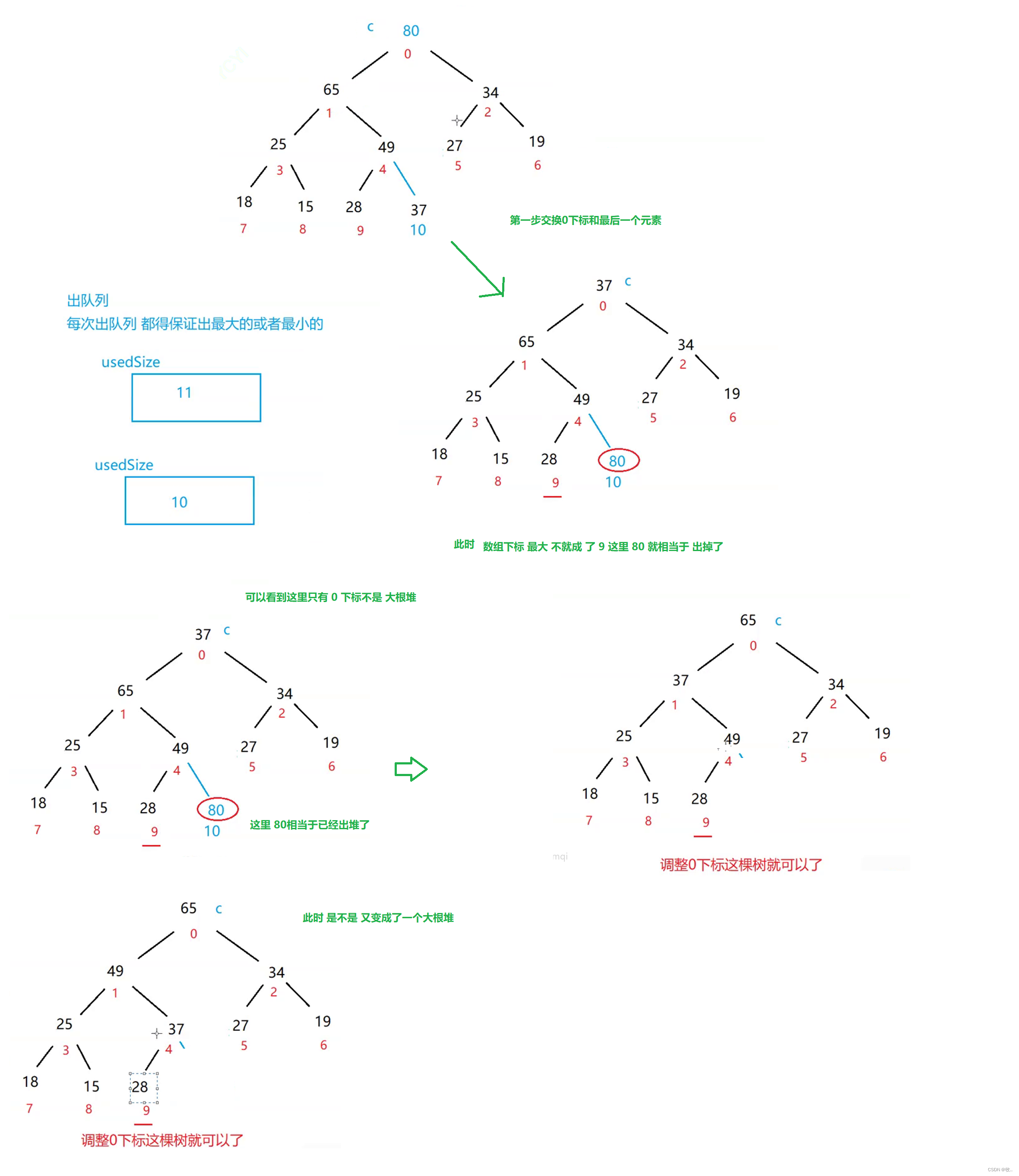
// Out of the heap operation
public int poll() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException(" Priority queue is empty !");
}
// In exchange for 0 Subscripts and Last An element
int tmp = elem[0];
elem[0] = elem[usedSize-1];
elem[usedSize-1] = tmp;
usedSize--;
// adjustment 0 Subscript element
shifDown(0,usedSize);
return tmp;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return usedSize == 0;
}
}
Topk The problem is not code implementation
Next two Let's first get to know topk problem
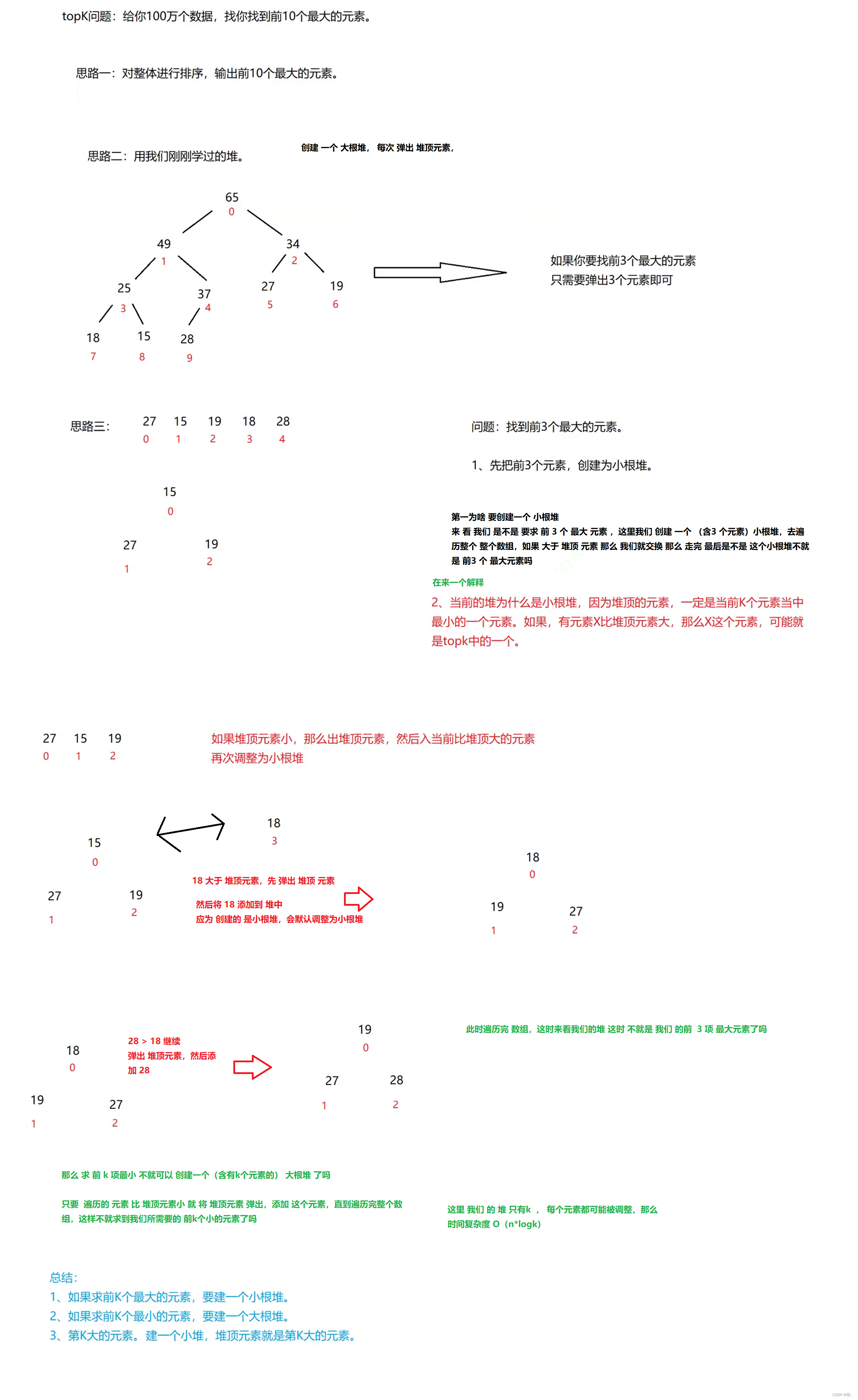
We First come Learn about heap sorting , After learning , We can better understand of topk problem Of oj topic 、
Heap sort
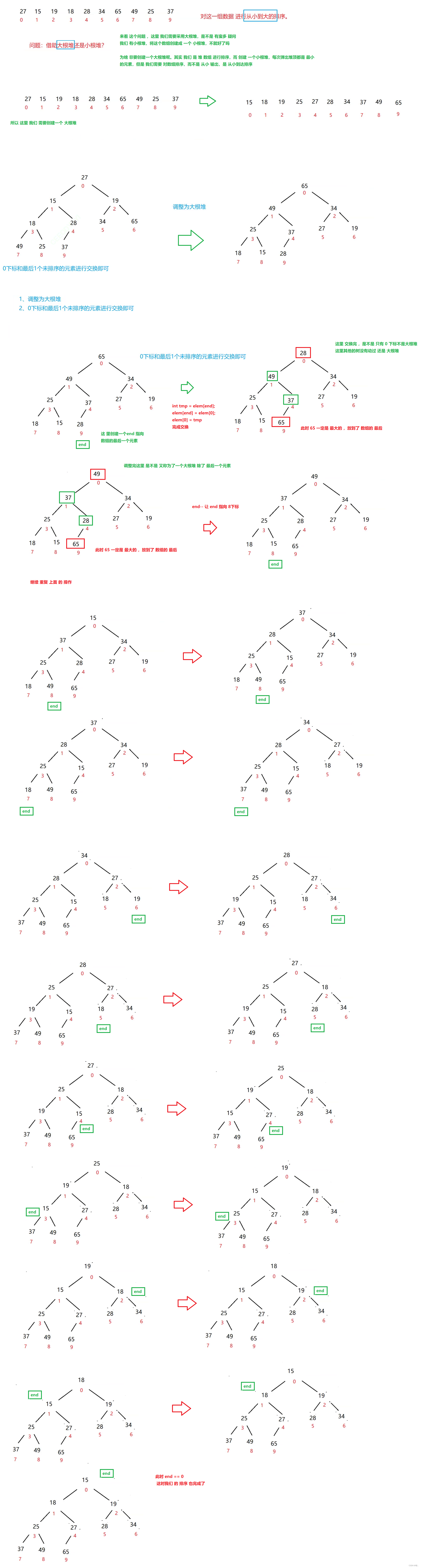
Next we To code
public void shifDown(int parent,int len) {
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
//1 Minimum There is a child ( Left the child )
while(child < len) {
// 9 + 1 == 10 Then you can't enter loop
if(child + 1< len && elem[child] < elem[child+1]) {
child++;
}
if(elem[parent] < elem[child]) {
int tmp = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = elem[child];
elem[child] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
public void heapSort() {
int end = usedSize - 1;
while(end > 0) {
int tmp = elem[0];
elem[0] = elem[end];
elem[end] = tmp;
shifDown(0,end);
end--;
}
}
Analysis finished In some code is not very simple
Next we Come on complete
Priority queue insert element
The priority queue has a requirement when inserting elements : The inserted element cannot be null Or elements must be able to compare , For the sake of simplicity , We just inserted Integer type , Can I insert custom type objects into the priority queue ?

Insert , And switching operations Of Source code analysis
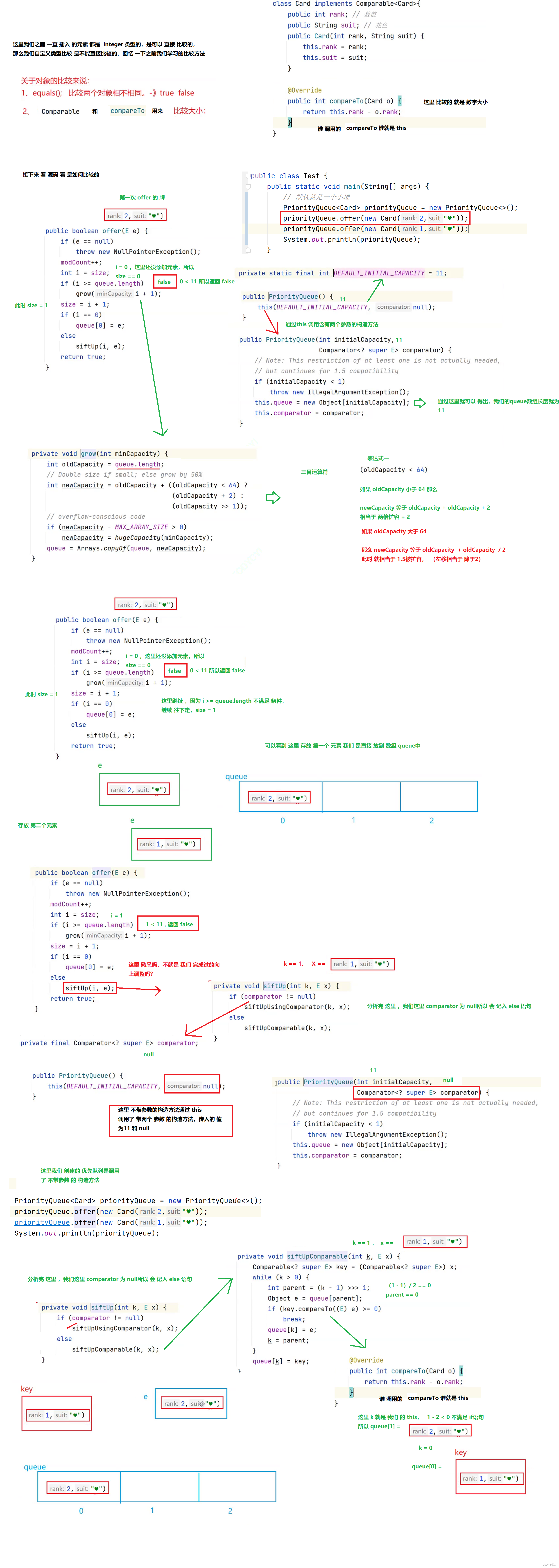
Attach code
class Card implements Comparable<Card> {
public int rank; // The number
public String suit; // Design and color
public Card(int rank, String suit) {
this.rank = rank;
this.suit = suit;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Card o) {
return this.rank - o.rank;
// here Switch to 0.rank - this.rank, It's just A lot
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Card{" +
"rank=" + rank +
", suit='" + suit + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The default is a small pile
PriorityQueue<Card> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.offer(new Card(2,""));
priorityQueue.offer(new Card(1,""));
System.out.println(priorityQueue);
}
}
recall Comparable Interface , Is he Too intrusive to class , Once it's done , According to that rule comparison, it can't be easily modified .
So here I We are here Sure Use A separate Write Some comparators .
class RankComparator implements Comparator<Card> {
@Override
public int compare(Card o1, Card o2) {
return o1.rank - o2.rank;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Card card1 = new Card(1,"");
Card card2 = new Card(2,"");
RankComparator rankComparator = new RankComparator();
int ret = rankComparator.compare(card1,card2);
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
After recalling these , that We Use priority queue Sure , Pass in the comparator to complete the comparison . It's obviously possible here
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RankComparator rankComparator = new RankComparator();
Card card1 = new Card(1,"");
Card card2 = new Card(2,"");
// Direct in The comparator
PriorityQueue<Card> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(rankComparator);
priorityQueue.offer(card1);
priorityQueue.offer(card2);
System.out.println(priorityQueue);
}
}
here except The comparator and Use Comparable in compareTo Besides method comparison, it can also be written like this
public static void main(String[] args) {
RankComparator rankComparator = new RankComparator();
Card card1 = new Card(1,"");
Card card2 = new Card(2,"");
PriorityQueue<Card> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Card>() {
@Override
public int compare(Card o1, Card o2) {
return o1.rank - o2.rank;
}
});
priorityQueue.offer(card1);
priorityQueue.offer(card2);
System.out.println(priorityQueue);
}
here There is no need to establish The comparator Can also compare ,
here Equivalent to An inner class , Rewrote compare Method .
In addition to the above These methods We You can also rewrite equals Methods to compare 
Three ways of comparison difference

Topk problem Code implementation
above We Have analyzed Topk Of Ideas , here Code implementation
public class Topk2 {
/** * Find the first K The smallest element * @param array * @param k * @return * use Big root pile */
public static int[] topk(int[] array,int k){
// 1. Create a size of k Big root pile
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// This comparison is a lot
return o2 - o1;
}
});
// 2. Traverse the elements in the array , front k Put elements in the heap
for(int i = 0;i<array.length;i++){
if(maxHeap.size() < k) {
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
}else {
int tmp = maxHeap.peek();
if(tmp > array[i]) {
// First pop up
maxHeap.poll();
// On deposit
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
int[] arr = new int[k];
for(int i = 0;i < k;i++) {
arr[i] = maxHeap.poll();
}
return arr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {
18,21,8,10,34,12};
int[] ret = topk(array,3);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ret));
}
}
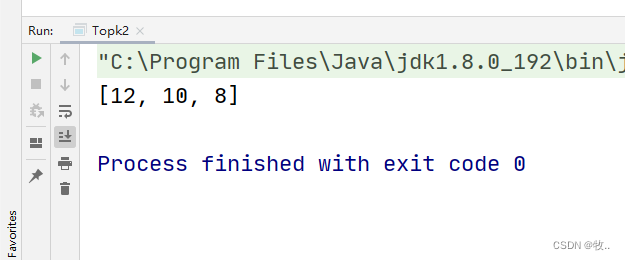
Next, let's finish one of topk Of oj topic
Look for the smallest K Pairs of numbers

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
PriorityQueue<List<Integer>> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<List<Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(List<Integer> o1, List<Integer> o2) {
// Create a large root heap The comparison method of
return (o2.get(0)+o2.get(1)) - (o1.get(0)+o1.get(1));
}
});
for(int i = 0;i< Math.min(k,nums1.length);i++) {
for(int j = 0;j< Math.min(k,nums2.length);j++) {
if(maxHeap.size() < k) {
List<Integer> tmpList = new ArrayList<>();
tmpList.add(nums1[i]);
tmpList.add(nums2[j]);
maxHeap.offer(tmpList);
}else {
int top = maxHeap.peek().get(0) + maxHeap.peek().get(1);
if(top > (nums1[i] + nums2[j])) {
List<Integer> tmpList = new ArrayList<>();
maxHeap.poll();
tmpList.add(nums1[i]);
tmpList.add(nums2[j]);
maxHeap.offer(tmpList);
}
}
}
}
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
// here Be careful k If Greater than Number pair To judge , Is the heap empty
for(int i = 0;i<k && !maxHeap.isEmpty();i++) {
ret.add(maxHeap.poll());
}
return ret;
}
}
边栏推荐
- 浅谈Label Smoothing技术
- Solutions of ordinary differential equations (2) examples
- Ecmascript6 introduction and environment construction
- Multiple solutions to one problem, asp Net core application startup initialization n schemes [Part 1]
- Halcon color recognition_ fuses. hdev:classify fuses by color
- [technical school] spatial accuracy of binocular stereo vision system: accurate quantitative analysis
- Rebuild my 3D world [open source] [serialization-3] [comparison between colmap and openmvg]
- Alibaba cloud sends SMS verification code
- Blogger article navigation (classified, real-time update, permanent top)
- TF coordinate transformation of common components of ros-9 ROS
猜你喜欢

It cold knowledge (updating ing~)
Codeworks round 639 (Div. 2) cute new problem solution
信息與熵,你想知道的都在這裏了
Attention is all you need
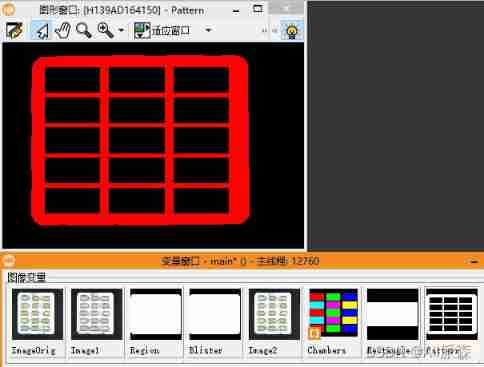
Halcon: check of blob analysis_ Blister capsule detection
深度学习模型与湿实验的结合,有望用于代谢通量分析
![[daiy4] copy of JZ35 complex linked list](/img/bc/ce90bb3cb6f52605255f1d6d6894b0.png)
[daiy4] copy of JZ35 complex linked list
容易混淆的基本概念 成员变量 局部变量 全局变量
Huber Loss
Programming implementation of ROS learning 5-client node
随机推荐
特征工程
浅谈Label Smoothing技术
Array, date, string object method
Solution to the problem of the 10th Programming Competition (synchronized competition) of Harbin University of technology "Colin Minglun Cup"
2311. 小于等于 K 的最长二进制子序列
皮尔森相关系数
Solution to the problems of the 17th Zhejiang University City College Program Design Competition (synchronized competition)
scipy. misc. imread()
Halcon: check of blob analysis_ Blister capsule detection
深度学习模型与湿实验的结合,有望用于代谢通量分析
golang 基础 —— golang 向 mysql 插入的时间数据和本地时间不一致
Oracle advanced (III) detailed explanation of data dictionary
kubeadm系列-00-overview
OpenFeign
[daiy4] copy of JZ35 complex linked list
Jenkins pipeline method (function) definition and call
golang 基础 ——map、数组、切片 存放不同类型的数据
Programming implementation of ROS learning 6 -service node
Ministry of transport and Ministry of Education: widely carry out water traffic safety publicity and drowning prevention safety reminders
Codeforces Round #648 (Div. 2) E.Maximum Subsequence Value

