当前位置:网站首页>Sparse matrix storage
Sparse matrix storage
2022-07-02 08:06:00 【programmercherry】
C++ Triple storage
//C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100
#define ERROR 0
#define OK 1
typedef int Status; // Function result state type
typedef struct {
int row, col; // The line number of the triple 、 Column number
int item; // The value of triples
} Triple;
// Definition TripleMatrix class , Every TripleMatrix Object to access the information of a matrix
class TripleMatrix {
private:
Triple data[MAX]; // Nonzero triples
int mu, nu, num; // The number of rows in a matrix 、 Number of columns and The number of nonzero elements
public:
TripleMatrix();
TripleMatrix(int m, int n); // When you create an object , Complete the initialization of the property
~TripleMatrix();
Status setItem(int row, int col, int item); // According to line number 、 Column number Nonzero element , Add a ternary at the end Elements
int getItem(int row, int col); // According to line number Column number , Get the matrix element value
void printMatrix(); // Print sparse matrix as matrix
void printTriple(); // Print an array of triples
friend bool matrixAdd(TripleMatrix a, TripleMatrix b, TripleMatrix& result);
friend bool matrixMulty(TripleMatrix a, TripleMatrix b, TripleMatrix& result);
};
TripleMatrix::TripleMatrix() {
// The number of rows of the initialization matrix 、 Number of columns The number of nonzero elements
mu = 0;
nu = 0;
num = 0;
}
TripleMatrix::TripleMatrix(int m, int n) {
// The number of rows of the initialization matrix 、 Number of columns The number of nonzero elements
mu = m;
nu = n;
num = 0;
}
TripleMatrix::~TripleMatrix() {
}
/* According to line number Column number Nonzero element Get the matrix element value */
int TripleMatrix::getItem(int row, int col) {
if (row > mu || col > nu) // Out of range, return directly 0
return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
// Traverse triples num Is the number of non-zero elements
// If you find triples with matching row and column numbers , Then return the non-zero element value
if (data[i].row == row && data[i].col == col) {
return data[i].item;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* This member function stores an element of a sparse matrix into a triple Because triples are by line Column From small to large , So you need to find the position to insert first Then consider moving the element back , Then insert */
Status TripleMatrix::setItem(int row, int col, int item) {
if (row > mu || col > nu) // Exceeding the scope , return ERROR
return ERROR;
// Store a non-zero element in a triple
if (num == MAX) // Number of saved elements num Reach the maximum range that triples can store
return ERROR;
if (item == 0) // The input array element value is 0, Then do nothing and return directly
return OK;
// utilize while loop First find the right storage location
int index = 0;
while (index < num) {
// If you want to find row col Larger than the row and column value of the existing triples , Then continue to move back
if (row > data[index].row) {
index++;
}
else if (row == data[index].row && (col > data[index].col)) {
index++;
}
else {
break;
}
}
if ((row == data[index].row) && (col == data[index].col)) {
// If the current line The column number element already exists , Replace the newly entered data with item
data[index].item = item;
}
else {
// otherwise Insert new elements
//index All subsequent elements of move by one unit , Vacate index The location of
for (int i = num; i > index; i--) {
data[i].row = data[i - 1].row;
data[i].col = data[i - 1].col;
data[i].item = data[i - 1].item;
}
// stay index Place new elements
data[index].row = row;
data[index].col = col;
data[index].item = item;
// Element number num Add 1
num++;
}
return OK;
}
/* Print sparse matrix */
void TripleMatrix::printMatrix() {
int tripleIndex = 0; //triple Used to control triples data Index of the array
cout << " Print sparse matrix :" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= mu; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= nu; j++) {
// If you find triples with matching row and column numbers , Then the output is non-zero
if (i == data[tripleIndex].row && j == data[tripleIndex].col) {
cout << data[tripleIndex].item << "\t";
tripleIndex++;
}
else {
// otherwise , Output 0
cout << "0\t";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << " The matrix has " << mu << " That's ok " << nu << " Column , common " << num << " A non-zero element " << endl;
return;
}
/* Print an array of triples */
void TripleMatrix::printTriple() {
cout << " Print an array of triples :" << endl;
cout << "row\tcol\titem" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
cout << data[i].row << "\t" << data[i].col << "\t" << data[i].item << endl;
}
}
void inputMatrix(int m, int n, int num, TripleMatrix& triple) {
int row, col, item;
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
cout << " Please enter lines in sequence , Column And non-zero yuan :";
cin >> row >> col >> item;
if (item != 0) {
if (triple.setItem(row, col, item) == ERROR) {
cout << " The row number and column number are incorrect , Or the triple array is full , Cannot store correctly !";
break;
}
}
}
}
bool matrixAdd(TripleMatrix a, TripleMatrix b, TripleMatrix& result) {
if (a.mu != b.mu || b.mu != result.mu || a.nu != b.nu || b.nu != result.nu) // The row and column are incorrect , Matrices cannot be added
{
return false;
}
else {
for (int i = 1; i <= a.mu; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= a.nu; j++) {
int item = a.getItem(i, j) + b.getItem(i, j);
if (item != 0) {
result.setItem(i, j, item);
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
bool matrixMulty(TripleMatrix a, TripleMatrix b, TripleMatrix& result) {
int i, j, k;
// If a Columns of It's not equal to b The number of rows , Then return to false
if (a.nu != b.mu) {
return false;
}
// initialization result Row and column values of
result.mu = a.mu;
result.nu = b.nu;
// Multiplication
for (int i = 1; i <= a.mu; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= b.nu; j++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int k = 1; k <= a.nu; k++) {
sum += a.getItem(i, k) * b.getItem(k, j);
}
// If the calculated value is not 0 Then insert into the sparse matrix
if (sum != 0) {
result.setItem(i, j, sum);
}
}
}
return true;
}
/* Triple test code */
/* 3 4 4 1 1 2 3 4 1 1 1 3 2 2 -1 */
void tripleTest() {
int m, n, num;
cout << " Please enter the row of the matrix Column Number of non-zero elements :";
cin >> m >> n >> num;
TripleMatrix triple(m, n);
inputMatrix(m, n, num, triple);
triple.printMatrix();
triple.printTriple();
}
// Matrix addition test code
void matrixAddTest() {
int m, n, num;
cout << " Please enter the row of the first matrix , Column , Number of non-zero elements ";
cin >> m >> n >> num;
cout << " The first matrix :" << endl;
TripleMatrix tripleA(m, n);
inputMatrix(m, n, num, tripleA);
tripleA.printMatrix();
cout << " Please enter the row of the second matrix , Column , Number of non-zero elements ";
cin >> m >> n >> num;
cout << " The second matrix :" << endl;
TripleMatrix tripleB(m, n);
inputMatrix(m, n, num, tripleB);
tripleB.printMatrix();
TripleMatrix tripleResult(m, n);
if (matrixAdd(tripleA, tripleB, tripleResult)) {
cout << endl << " After matrix addition :" << endl;
tripleResult.printMatrix();
}
else{
cout << " Matrices cannot be added " << endl;
}
}
// Matrix multiplication test code
void matrixMultyTest() {
int m, n, num;
cout << " Please enter the row of the first matrix , Column , Number of non-zero elements ";
cin >> m >> n >> num;
cout << " The first matrix :" << endl;
TripleMatrix tripleA(m, n);
inputMatrix(m, n, num, tripleA);
tripleA.printMatrix();
cout << " Please enter the row of the second matrix , Column , Number of non-zero elements ";
cin >> m >> n >> num;
cout << " The second matrix :" << endl;
TripleMatrix tripleB(m, n);
inputMatrix(m, n, num, tripleB);
tripleB.printMatrix();
TripleMatrix tripleResult;
if (matrixMulty(tripleA, tripleB, tripleResult)) {
cout << endl << " After multiplying matrices :" << endl;
tripleResult.printMatrix();
}
else {
cout << " Matrices cannot be multiplied " << endl;
}
}
int main() {
//tripleTest();
//matrixAddTest();
matrixMultyTest();
return 0;
}
Java Example
public class SparseMatrix {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. Create a 2D array 11 * 11 0 No chess pieces 1 The spots 2 An albino
int[][] array1 = new int[11][11];
array1[1][2] = 1;
array1[2][3] = 2;
// Output original array
System.out.println(" Output the original array :");
for (int[] ints : array1) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("==========================");
// Convert to sparse array to save
// Get the number of valid values
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
if(array1[i][j] != 0)
sum++;
}
}
System.out.println(" The number of valid values :" + sum);
//2. Create an array of sparse arrays
int[][] array2 = new int[sum + 1][3];
array2[0][0] = 11;
array2[0][1] = 11;
array2[0][2] = sum;
//3. ergodic matrix
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array1[0].length; j++) {
if(array1[i][j] != 0){
count++;
array2[count][0] = i;
array2[count][1] = j;
array2[count][2] = array1[i][j];
}
}
}
//4. Output sparse array
System.out.println(" Output sparse array :");
for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(array2[i][0] + "\t" + array2[i][1] + "\t" + array2[i][2]);
}
// Reduction matrix
System.out.println("==========================");
System.out.println(" Reduction matrix ");
//1. Read sparse arrays
int[][] array3 = new int[array2[0][0]][array2[0][1]];
//2. Restore its value to the element in it
for (int i = 1; i < array2.length; i++) {
array3[array2[i][0]][array2[i][1]] = array2[i][2];
}
//3. Print
for (int[] ints : array3) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
边栏推荐
- AR系统总结收获
- VS Code配置问题
- Global and Chinese market of medicine cabinet 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Open3d learning note 4 [surface reconstruction]
- 【MagNet】《Progressive Semantic Segmentation》
- Programmers can only be 35? The 74 year old programmer in the United States has been programming for 57 years and has not retired
- [C # note] the data in DataGridView saved in WinForm is excel and CSV
- 【双目视觉】双目立体匹配
- On the confrontation samples and their generation methods in deep learning
- 【Cascade FPD】《Deep Convolutional Network Cascade for Facial Point Detection》
猜你喜欢

联邦学习下的数据逆向攻击 -- GradInversion
Eklavya -- infer the parameters of functions in binary files using neural network

Nacos service registration in the interface

【雙目視覺】雙目矯正
Matlab数学建模工具
利用超球嵌入来增强对抗训练

图像增强的几个方法以及Matlab代码
【MobileNet V3】《Searching for MobileNetV3》
What if the notebook computer cannot run the CMD command
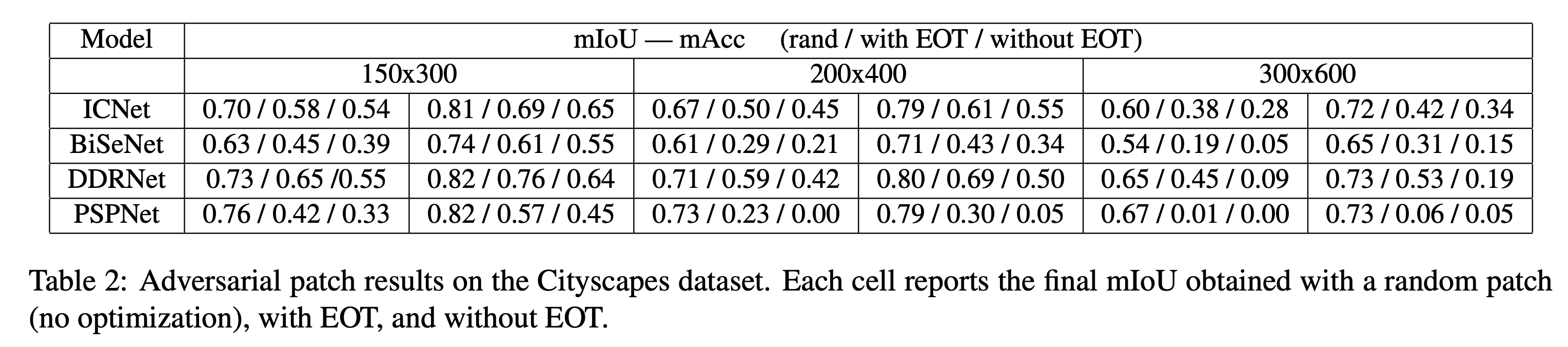
针对语义分割的真实世界的对抗样本攻击
随机推荐
乐理基础(简述)
Meta Learning 简述
【Mixed Pooling】《Mixed Pooling for Convolutional Neural Networks》
OpenCV常用方法出处链接(持续更新)
SQLyog远程连接centos7系统下的MySQL数据库
SQL操作数据库语法
力扣每日一题刷题总结:链表篇(持续更新)
用MLP代替掉Self-Attention
Brief introduction of prompt paradigm
业务架构图
How gensim freezes some word vectors for incremental training
使用Matplotlib绘制图表初步
On the back door of deep learning model
Cvpr19 deep stacked hierarchical multi patch network for image deblurring paper reproduction
高中数学必修一
Array and string processing, common status codes, differences between PHP and JS (JS)
Global and Chinese markets for Salmonella typhi nucleic acid detection kits 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Feature Engineering: summary of common feature transformation methods
力扣每日一题刷题总结:字符串篇(持续更新)
Organigramme des activités