当前位置:网站首页>Do you choose pandas or SQL for the top 1 of data analysis in your mind?
Do you choose pandas or SQL for the top 1 of data analysis in your mind?
2022-07-05 07:06:00 【AI technology base camp】

author | Junxin
source | About data analysis and visualization
Today, Xiaobian is going to talk about Pandas and SQL Grammatical differences between , I believe for many data analysts , Whether it's Pandas Module or SQL, They are all very many tools used in daily study and work , Of course, we can also be in Pandas From the module SQL sentence , By calling read_sql() Method .

Building a database
First we pass SQL Statement is creating a new database , I'm sure everyone knows the basic grammar ,
CREATE TABLE Table name (
Field name data type ...
)Let's take a look at the specific code
import pandas as pd
import sqlite3
connector = sqlite3.connect('public.db')
my_cursor = connector.cursor()
my_cursor.executescript("""
CREATE TABLE sweets_types
(
id integer NOT NULL,
name character varying NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
... Limited space , Refer to the source code for details ...
""")At the same time, we also insert data into these new tables , The code is as follows
my_cursor.executescript("""
INSERT INTO sweets_types(name) VALUES
('waffles'),
('candy'),
('marmalade'),
('cookies'),
('chocolate');
... Limited space , Refer to the source code for details ...
""") We can view the new table through the following code , And convert it to DataFrame Data set in format , The code is as follows
df_sweets = pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM sweets;", connector)output
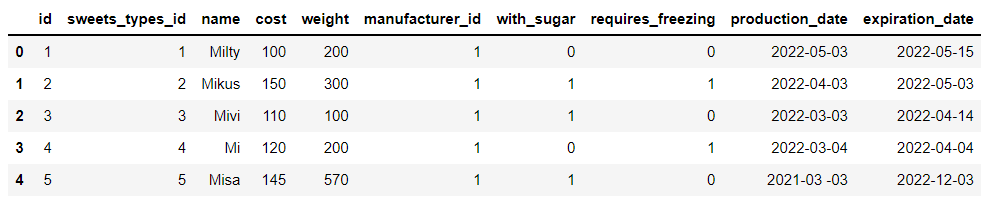
We have built a total of 5 Data sets , It mainly involves desserts 、 Types of desserts and data of processing and storage , For example, the data set of desserts mainly includes the weight of desserts 、 Sugar content 、 Production date and expiration time 、 Cost and other data , as well as :
df_manufacturers = pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM manufacturers", connector)output
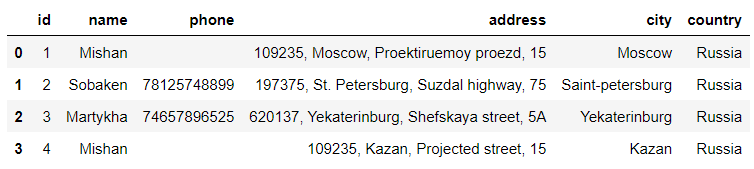
The data set of processing involves the main person in charge and contact information of the factory , The warehouse data set involves the detailed address of the warehouse 、 City location, etc .
df_storehouses = pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM storehouses", connector)output

And the dessert category data set ,
df_sweets_types = pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM sweets_types;", connector)output
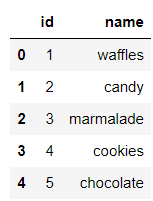

Data screening
Screening of simple conditions
Next, let's do some data screening , For example, the weight of desserts is equal to 300 The name of dessert , stay Pandas The code in the module looks like this
# Convert data type
df_sweets['weight'] = pd.to_numeric(df_sweets['weight'])
# Output results
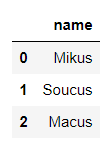
df_sweets[df_sweets.weight == 300].nameoutput
1 Mikus
6 Soucus
11 Macus
Name: name, dtype: object Of course, we can also pass pandas In the middle of read_sql() Method to call SQL sentence
pd.read_sql("SELECT name FROM sweets WHERE weight = '300'", connector)output
Let's look at a similar case , The screening cost is equal to 100 The name of dessert , The code is as follows
# Pandas
df_sweets['cost'] = pd.to_numeric(df_sweets['cost'])
df_sweets[df_sweets.cost == 100].name
# SQL
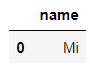
pd.read_sql("SELECT name FROM sweets WHERE cost = '100'", connector)output
MiltyFor text data , We can also further screen out the data we want , The code is as follows
# Pandas
df_sweets[df_sweets.name.str.startswith('M')].name
# SQL
pd.read_sql("SELECT name FROM sweets WHERE name LIKE 'M%'", connector)output
Milty
Mikus
Mivi
Mi
Misa
Maltik
Macus Of course. SQL Wildcards in statements ,% Means to match any number of letters , and _ Means to match any letter , The specific differences are as follows
# SQL
pd.read_sql("SELECT name FROM sweets WHERE name LIKE 'M%'", connector)output

pd.read_sql("SELECT name FROM sweets WHERE name LIKE 'M_'", connector)output
Screening of complex conditions
Let's take a look at data filtering with multiple conditions , For example, we want the weight to be equal to 300 And the cost price is controlled at 150 The name of dessert , The code is as follows
# Pandas
df_sweets[(df_sweets.cost == 150) & (df_sweets.weight == 300)].name
# SQL
pd.read_sql("SELECT name FROM sweets WHERE cost = '150' AND weight = '300'", connector)output
MikusOr the cost price can be controlled within 200-300 Dessert name between , The code is as follows
# Pandas
df_sweets[df_sweets['cost'].between(200, 300)].name
# SQL
pd.read_sql("SELECT name FROM sweets WHERE cost BETWEEN '200' AND '300'", connector)output
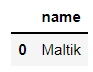
If it comes to sorting , stay SQL It uses ORDER BY sentence , The code is as follows
# SQL
pd.read_sql("SELECT name FROM sweets ORDER BY id DESC", connector)output

And in the Pandas What is called in the module is sort_values() Method , The code is as follows
# Pandas
df_sweets.sort_values(by='id', ascending=False).nameoutput
11 Macus
10 Maltik
9 Sor
8 Co
7 Soviet
6 Soucus
5 Soltic
4 Misa
3 Mi
2 Mivi
1 Mikus
0 Milty
Name: name, dtype: object Select the dessert name with the highest cost price , stay Pandas The code in the module looks like this
df_sweets[df_sweets.cost == df_sweets.cost.max()].nameoutput
11 Macus
Name: name, dtype: objectAnd in the SQL The code in the statement , We need to first screen out which dessert is the most expensive , Then proceed with further processing , The code is as follows
pd.read_sql("SELECT name FROM sweets WHERE cost = (SELECT MAX(cost) FROM sweets)", connector) We want to see which cities are warehousing , stay Pandas The code in the module looks like this , By calling unique() Method
df_storehouses['city'].unique()output
array(['Moscow', 'Saint-petersburg', 'Yekaterinburg'], dtype=object) And in the SQL The corresponding sentence is DISTINCT keyword
pd.read_sql("SELECT DISTINCT city FROM storehouses", connector)
Data grouping Statistics
stay Pandas Group statistics in modules generally call groupby() Method , Then add a statistical function later , For example, it is to calculate the mean value of scores mean() Method , Or summative sum() Methods, etc. , For example, we want to find out the names of desserts produced and processed in more than one city , The code is as follows
df_manufacturers.groupby('name').name.count()[df_manufacturers.groupby('name').name.count() > 1]output
name
Mishan 2
Name: name, dtype: int64 And in the SQL The grouping in the statement is also GROUP BY, If there are other conditions later , It's using HAVING keyword , The code is as follows
pd.read_sql("""
SELECT name, COUNT(name) as 'name_count' FROM manufacturers
GROUP BY name HAVING COUNT(name) > 1
""", connector)
Data merging
When two or more datasets need to be merged , stay Pandas Modules , We can call merge() Method , For example, we will df_sweets Data set and df_sweets_types Merge the two data sets , among df_sweets In the middle of sweets_types_id Is the foreign key of the table
df_sweets.head()output

df_sweets_types.head()output
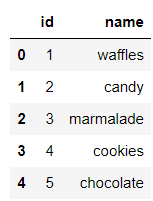
The specific data consolidation code is as follows
df_sweets_1 = df_sweets.merge(df_sweets_types, left_on='sweets_types_id', right_on='id')output
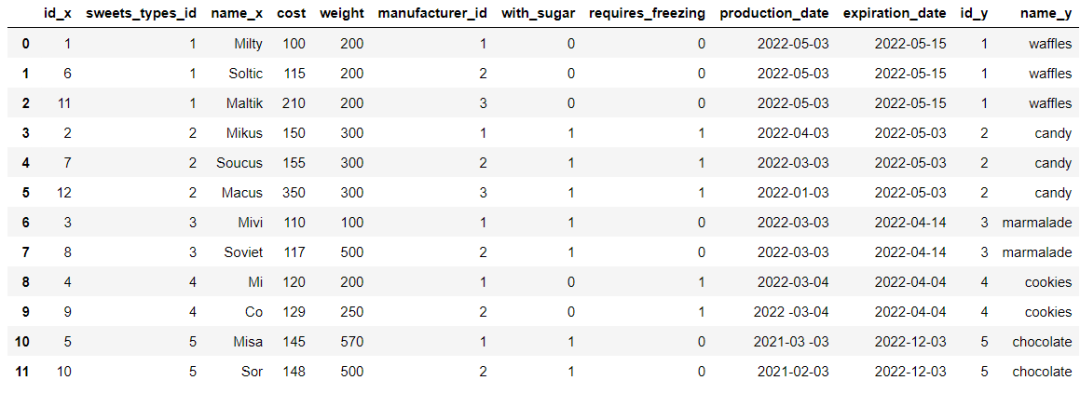
We will further screen out chocolate flavored desserts , The code is as follows
df_sweets_1.query('name_y == "chocolate"').name_xoutput
10 Misa
11 Sor
Name: name_x, dtype: object and SQL The sentence is relatively simple , The code is as follows
# SQL
pd.read_sql("""
SELECT sweets.name FROM sweets
JOIN sweets_types ON sweets.sweets_types_id = sweets_types.id
WHERE sweets_types.name = 'chocolate';
""", connector)output


The structure of the data set
Let's take a look at the structure of the data set , stay Pandas View directly in the module shape Attribute is enough , The code is as follows
df_sweets.shapeoutput
(12, 10) And in the SQL In the sentence , It is
pd.read_sql("SELECT count(*) FROM sweets;", connector)output
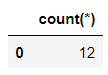

Looking back
It's too voluminous !AI High accuracy of math exam 81%
Python Common encryption algorithms in crawlers !
2D Transformation 3D, Look at NVIDIA's AI“ new ” magic !
How to use Python Realize the security system of the scenic spot ?
Share
Point collection
A little bit of praise
Click to see 边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
全局变量和静态变量的初始化
ROS2——安装ROS2(三)
IPage能正常显示数据,但是total一直等于0
Ros2 - workspace (V)
*P++, (*p) + +, * (p++) differences
. Net core stepping on the pit practice
[OBS] x264 Code: "buffer_size“
Interpretation of the earliest sketches - image translation work sketchygan
Rehabilitation type force deduction brush question notes D3
Xavier CPU & GPU high load power consumption test
PowerManagerService(一)— 初始化
U-Boot初始化及工作流程分析
PHY drive commissioning - phy controller drive (II)
1290_FreeRTOS中prvTaskIsTaskSuspended()接口实现分析
使用paping工具进行tcp端口连通性检测
Vant weapp swippecell set multiple buttons
cgroup_ memcg
SD_CMD_RECEIVE_SHIFT_REGISTER
Executealways of unity is replacing executeineditmode
ROS2——Service服务(九)