当前位置:网站首页>Browser reflow and redraw
Browser reflow and redraw
2022-07-06 00:24:00 【Zhouxiaofeng】
1. Rendering in the browser
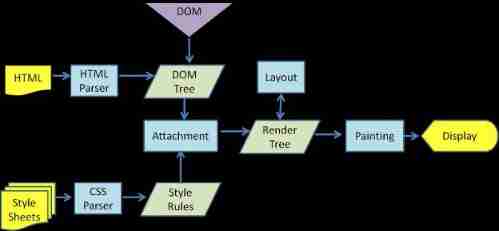
From the top , We can see , The browser rendering process is as follows :
- analysis HTML, Generate DOM Trees , analysis CSS, Generate CSSOM Trees
- take DOM Trees and CSSOM Tree combined with , Generate render tree (Render Tree)
- Layout( backflow ): According to the generated render tree , To return (Layout), Get the geometric information of the node ( Location , size )
- Painting( Repaint ): Geometric information from the render tree and backflow , Gets the absolute pixels of the node
- Display: Send pixels to GPU, Displayed on the page .
1.1 Generate render tree

To build the render tree , The browser does the following :
- from DOM The root node of the tree begins traversing each visible node .
- For each of the visible nodes , find CSSOM The corresponding rule in the tree , And apply them .
- According to each visible node and its corresponding style , Composition generates the render tree .
Invisible nodes include :
- Some nodes that do not render output , such as script、meta、link etc. .
- Some of the css Hidden nodes . such as display:none.
Be careful :
- utilize visibility and opacity Hidden node , It will still be on the render tree . Only display:none Is not displayed on the render tree .
- The render tree contains only visible nodes
1.2 backflow
When rendering trees (render Tree) Part of ( Or all ) Because of the size of the element , Layout , Changes such as hiding need to be rebuilt . This process is called reflow (reflow), That is to rearrange (relayout).
1.3 Repaint
When render tree Some of the elements in the , These attributes only affect the appearance of the element , style , It doesn't affect the layout , such as background-color . It's called redrawing .
2. When reflux repainting occurs
In the reflow stage, it is necessary to calculate the position and geometric information of nodes , When page layout and geometric information changes , You need to go back .
- Add or remove visible DOM Elements
- The position of the element changes
- The size of the element changes ( Including margins 、 Within the frame 、 The frame size 、 Height and width, etc )
- Content changes , Such as text changes or an image being replaced by another image of a different size .
- When the page starts to render ( It can't be avoided )
- The window size of the browser changes ( Because the backflow is based on the size of the viewport to calculate the location and size of the element )
Backflow must redraw , Repainting does not necessarily cause backflow . Redraw and backflow occur frequently when we set the node style , It can also significantly affect performance . The cost of backflow is much higher , Changing the children in the parent node is likely to cause a series of backflows to the parent node . Depending on the scope and extent of the change , More or less some nodes in the rendering tree need to be recalculated , Some changes will also trigger the rearrangement of the entire page .
3. Browser optimization mechanism
Each rearrangement results in additional computational overhead , Therefore, most browsers optimize the rearrangement process by queueing changes and executing them in batches . The browser queues up the changes , Until some time has passed or the operation has reached a threshold , Before emptying the queue . however ! When you get the operation of the layout information , A queue refresh is forced , Such as when you access the following properties or use the following methods :
- offsetTop、offsetLeft、offsetWidth、offsetHeight
- scrollTop、scrollLeft、scrollWidth、scrollHeight
- clientTop、clientLeft、clientWidth、clientHeight
- getComputedStyle()
- getBoundingClientRect
Both the above properties and methods need to return the latest layout information , So the browser has to clear the queue , Triggers a backflow redraw to return the correct value . therefore , While we're modifying the style , It is best to avoid using the properties listed above , They all refresh the render queue .
4. Reduce backflow and redraw
4.1 Minimize redrawing and rearranging
Avoid frequent operation styles , Merge multiple pairs of DOM And style modification .
- One time rewrite style attribute
- Use cssText Instead of modifying the style many times
- Define the style as class, One-time modification class attribute
4.2 Batch modification without document flow DOM
When we need to be right DOM When you make a series of changes , You can reduce the number of backflow redraws by following these steps :
- Detach the element from the document stream
- Make several changes to it
- Brings the element back into the document .
The first and third steps of the process may cause reflux , But after the first step , Yes DOM None of the changes to the will cause backflow , Because it's not rendering trees anymore .
There are three ways to do this DOM Off stream :
- Hidden elements , Application of modified , To display , This will show and hide nodes , Produce two redraws .
- Using document fragments (document fragment) At present DOM Build a subtree outside , Application of modified , Copy it back into the document .
- Copies the original element to a node that is detached from the document , After modifying the node , Replace the original element .
4.3 Avoid backflow caused by frequent reads / Redrawn properties
When we access some attributes of the element , Causes the browser to force the queue to be emptied , Do a forced synchronous layout . Attributes that need to be used multiple times , Use variables to cache , Avoid direct reading .
4.4 For complex animation elements, use absolute positioning to separate them from the document flow
For complex animation effects , This often causes backflow redrawing , therefore , We can use absolute positioning , Detach it from the document stream . This causes frequent backflow of parent and subsequent elements .
4.5 CSS3 Hardware acceleration (GPU Speed up )
Use css3 Hardware acceleration , It can make transform、opacity、filters These animations do not cause backflow redraw . But for other properties of animation , such as background-color these , It still causes backflow to redraw , But it can still improve the performance of these animations .
Common trigger for hardware acceleration css attribute :
- transform
- opacity
- filter
- Will-change
css3 Disadvantages of hardware acceleration
- If you use too many elements css3 Hardware acceleration , This results in a large memory footprint , There will be performance issues .
- stay GPU Rendering fonts will cause anti-aliasing to be ineffective . This is because GPU and CPU The algorithm is different . So if you don't turn off hardware acceleration at the end of the animation , It will create font blur .
4.6 Other details
- Use CSS Instead of directly modifying the position or size of elements, animation .
- Use visibility Replace display: none , Because the former only causes a redraw , The latter causes backflow ( Changed the layout )
- Avoid modifying element styles in batches in loops .
- Avoid using table Layout , Maybe a small change will make the whole thing table relayout .
- JS Used in animation requestAnimationFrame replace setTimeout and setInterval.
- CSS The selector matches from right to left , Avoid excessive node hierarchy
- Set nodes that are frequently redrawn or backdrawn to layers , The layer prevents the rendering behavior of this node from affecting other nodes . such as video、canvas label , The browser will automatically turn the node into a layer
- As far as possible DOM The end of the tree changes class.
- Avoid multiple inline styles .
- Apply animation effects to position The attribute is absolute or fixed Elements on .
- Avoid using CSS expression ( for example :calc()).
requestAnimationFrame Compared with setTimeout、setInterval There are two main advantages of :
- requestAnimationFrame Will put all the DOM Operations together , Done in one redraw or reflow , And the interval between redraws or reflows closely follows the refresh rate of the browser , Generally speaking , This frequency is per second 60 frame .
- In hidden or invisible elements ,requestAnimationFrame Will not redraw or reflow , Which of course means less cpu,gpu And memory usage .
stop it requestAnimationFrame
Is there something like clearTimeout and clearInterval A similar approach like this ? Yes .cancelAnimationFrame() Receive a parameter requestAnimationFrame The default is to return a id,cancelAnimationFrame Just pass in this id You can stop .
边栏推荐
- 多线程与高并发(8)—— 从CountDownLatch总结AQS共享锁(三周年打卡)
- Choose to pay tribute to the spirit behind continuous struggle -- Dialogue will values [Issue 4]
- There is no network after configuring the agent by capturing packets with Fiddler mobile phones
- Power query data format conversion, Split Merge extraction, delete duplicates, delete errors, transpose and reverse, perspective and reverse perspective
- Spark获取DataFrame中列的方式--col,$,column,apply
- Ffmpeg captures RTSP images for image analysis
- Huawei equipment configuration ospf-bgp linkage
- Single source shortest path exercise (I)
- 【EI会议分享】2022年第三届智能制造与自动化前沿国际会议(CFIMA 2022)
- QT -- thread
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Opencv classic 100 questions
MySql——CRUD
Go learning --- structure to map[string]interface{}
Search (DFS and BFS)
Analysis of the combination of small program technology advantages and industrial Internet
如何利用Flutter框架开发运行小程序
Atcoder beginer contest 258 [competition record]
Detailed explanation of APP functions of door-to-door appointment service
如何解决ecology9.0执行导入流程流程产生的问题
Yunna | what are the main operating processes of the fixed assets management system
剖面测量之提取剖面数据
Transport layer protocol ----- UDP protocol
Spark DF增加一列
MySql——CRUD
How to solve the problems caused by the import process of ecology9.0
Key structure of ffmpeg - avframe
7.5 decorator
There is no network after configuring the agent by capturing packets with Fiddler mobile phones
An understanding of & array names
[designmode] adapter pattern

![[designmode] Decorator Pattern](/img/65/457e0287383d0ca9a28703a63b4e1a.png)