当前位置:网站首页>Get started with Aurora 8b/10b IP core in one day (5) -- learn from the official routine of framing interface
Get started with Aurora 8b/10b IP core in one day (5) -- learn from the official routine of framing interface
2022-07-02 03:33:00 【Lonely single knife】
List of articles
1、IP Core customization and generation of official routines
1.1、 Page 1 configuration : Physical layer and link layer information selection
1.2、 Page 2 configuration : Corresponding GT Physical location selection of transceiver
1.3、 Page 3 configuration : Shared logical location
1.4、 Official routine Example Design Generation
2.1、 The composition of official routines
2.2、Support modular (IP Core instantiation core module )
2.3、 Data generation module ( send out )
2.3.2、 Wait for initialization
2.3.4、 The state machine realizes frame sending
2.3.5、 Simulation and analysis
2.4、 Data verification module ( receive )
2.4.4、 Data reprocessing ( decoding )
2.4.6、 Data verification and error flag
Write it at the front
Xilinx Our technology ecology is doing very well , Basically all commonly used IP Nuclear has official routines (example design) For developers to learn , We don't need it for nothing , Today, let's go whoring with him for nothing ---- Start with the official routine and learn how to use this IP nucleus .
Series summary : One day Aurora 8B/10B IP nucleus ---- A summary ( Direct link )
1、IP Core customization and generation of official routines
First, build a new project , This project has nothing but generation Aurora 8B/10B IP Do nothing outside the core .IP The customization process of the core is as follows .
1.1、 Page 1 configuration : Physical layer and link layer information selection
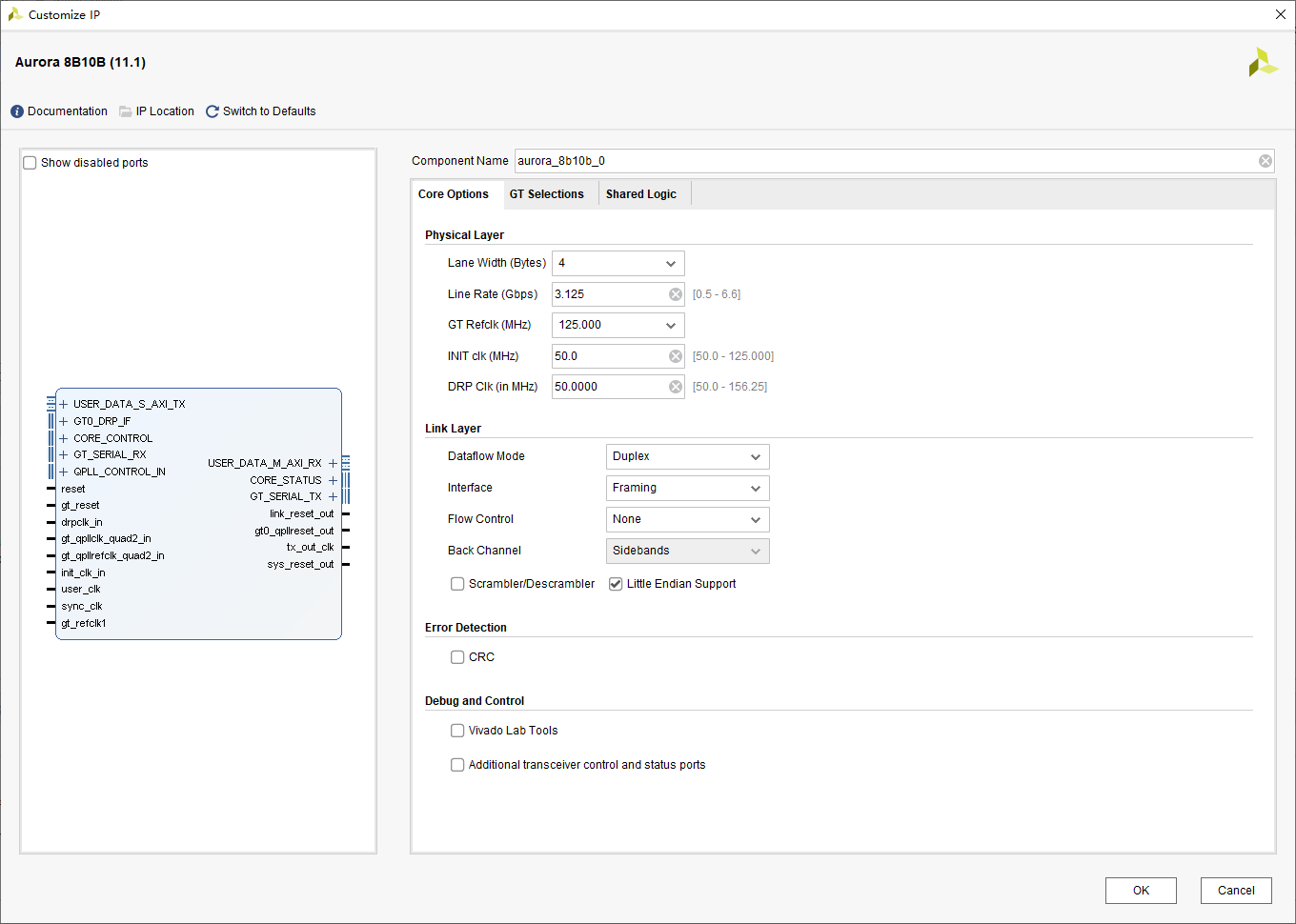
The physical layer Physical Layer:
- Lane Width: Link bit width , optional 2 perhaps 4, Company Bytes( Here, in order to lower the user's clock and facilitate subsequent clock constraints , choice 4bytes)
- Line Rate: Linear rate , Range 0.5~6.25Gbps, This is based on the needs of the project , choice 3.125Gbps
- GT Refclk: Serial transceiver GT The reference clock of , According to the actual situation of the board , We choose 125M
- INIT clk: Initialize the clock , stay GT Reset time ,user_clk It stopped working , recommend INIT CLK The clock frequency is below GT Reference clock , Choose the default 50M
- DRP clk: Dynamically reconfigure the clock , This function is not used much , Press default directly 50M Come on
The link layer Link Layer:
- Dataflow Mode: Data flow mode , Optional full duplex / Only receive / Send only , We choose full duplex mode here
- Interface:Framing/streaming Optional . This paper is about Framing Interface
- Flow Control: Flow control , Not so complicated for the time being , No election
- Back Channel: Only in simplex mode can you select (sidebands/timer Optional )
- Scrambler/Descrambler : Round the code / Unwinding , No choice here
- Little Endian Support : Check the small end mode , The small segment pattern corresponds to [31:0] This writing habit , The big end mode corresponds to [0:31] This writing habit
Commissioning and control ----Debug And Control:
Provides information such as ILA and VIO Etc IO Core and some other status indicator bits IP Monitor the running state of the system , For the convenience of testing , This kind of debugging interface is temporarily not selected .
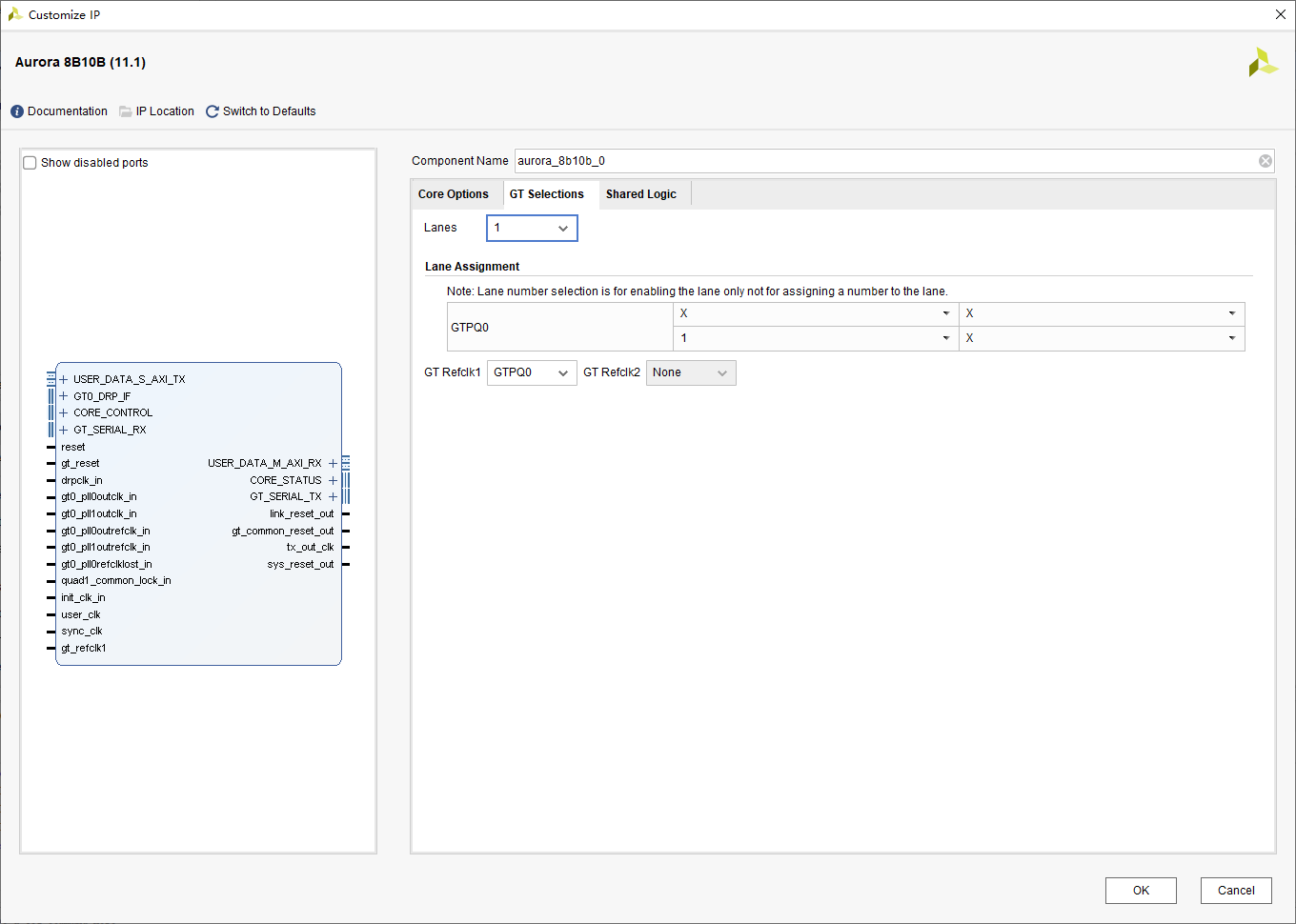
1.2、 Page 2 configuration : Corresponding GT Physical location selection of transceiver
Here according to their own FPGA On the chip GT Just choose according to the actual situation , We only simulate the test , Just choose a random channel :
1.3、 Page 3 configuration : Shared logical location
Such as clock and reset logic , Is it in the core or in the example project ( majority IP nucleus Xilinx Will provide routines for reference ). It is recommended to set the sharing logic in the official routine , So we can follow up on IP The use of the core can be directly based on the official routine with a little modification .

1.4、 Official routine Example Design Generation
take IP After the core is customized and integrated , You can generate official routines Example Design 了 :

2、 Official routine analysis
The analysis of official routines mainly refers to the generated source code and 《PG046:Aurora 8B/10B v11.1 LogiCORE IP Product Guide》. Through the above information , We can master IP How to use the core and understand the general composition of official routines .
2.1、 The composition of official routines
Let's first look at the logical hierarchy of generating routine files :
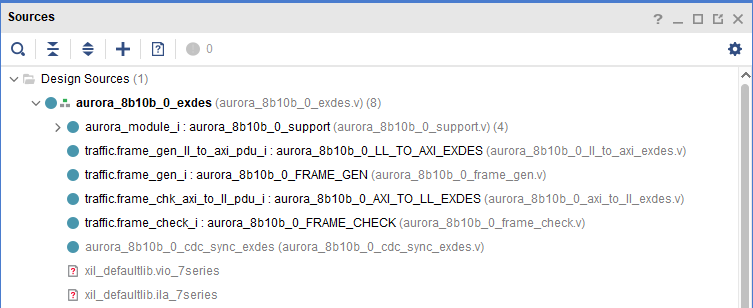
The level of design documents is not obvious , Let's call up the structure diagram and have a look :

In this way, you can basically understand :
- support modular : Core module , Contains the right IP、GT And so on ; In our subsequent applications, this part does not need to be modified
- frame_gen: Data generation module , use LFSR To generate pseudo-random sequences ; Later, in our application, this part can be replaced by our data input module ( It is suggested to join FIFO, This makes the code more reusable )
- frame_check: Data verification module , Check the received data to verify the correctness of transmission ; Later, in our application, this part can be replaced by our data inspection module or deleted
- LL_AXI:LL The bus turns AXI Bus ( It is said that the original interface of this routine is LL Interface , Back Xilinx In order to promote AXI Bus , Therefore, this routine directly adds a bus conversion module on the basis of the original code )
- AXI_LL:AXI The bus turns LL Bus , The reason as above
The content of the simulation part is easy to understand according to the level -- Called the routine twice . according to Xilinx Consistent urination , It's easy to guess that this is a loopback test again . In fact, you can also see one or two from the manual :
- Testbench Instantiated two routines
- routine 1 After the data is generated, it is processed by Aurora Sent to routine 2 Detection module of , And feed the results back to Testbench
- routine 2 After the data is generated, it is processed by Aurora Sent to routine 1 Detection module of , And feed the results back to Testbench

2.2、Support modular (IP Core instantiation core module )
I don't say much nonsense , Let's start with Support The composition of the module :

It is not difficult to see from the composition ,Support The main function of the module is instantiation aurora IP Core and turn the clock 、 Reset and other signals are packaged together . So we don't need to be right Support Learn more about the internal structure of the module , Just look at its external interface and you can almost use it .Support Sub module under module :
- clock_module: Clock processing generation module
- support_reset_logic_i: Reset the logic generation module
- gt_common_support: And GT The clock associated with the transceiver generates its other signals
- Aurora IP Nuclear modules
2.3、 Data generation module ( send out )
As mentioned above, as long as we replace the data generation module with our own files, we can realize the secondary creation of official routines , To complete the Aurora IP I've made good use of it . Then we naturally need to explore its source code . The complete code is as follows :
`timescale 1 ns / 1 ps
`define DLY #1
module aurora_8b10b_0_FRAME_GEN
(
// User Interface
TX_D,
TX_REM,
TX_SOF_N,
TX_EOF_N,
TX_SRC_RDY_N,
TX_DST_RDY_N,
// System Interface
USER_CLK,
RESET,
CHANNEL_UP
);
//*****************************Parameter Declarations****************************
//***********************************Port Declarations*******************************
// User Interface
output [0:31] TX_D;
output [0:1] TX_REM;
output TX_SOF_N;
output TX_EOF_N;
output TX_SRC_RDY_N;
input TX_DST_RDY_N;
// System Interface
input USER_CLK;
input RESET;
input CHANNEL_UP;
//***************************External Register Declarations***************************
reg TX_SRC_RDY_N;
reg TX_SOF_N;
reg TX_EOF_N;
//***************************Internal Register Declarations***************************
reg [0:15] data_lfsr_r;
reg [0:7] frame_size_r;
reg [0:7] bytes_sent_r;
reg [0:3] ifg_size_r;
//State registers for one-hot state machine
reg idle_r;
reg single_cycle_frame_r;
reg sof_r;
reg data_cycle_r;
reg eof_r;
wire reset_c;
//*********************************Wire Declarations**********************************
wire ifg_done_c;
//Next state signals for one-hot state machine
wire next_idle_c;
wire next_single_cycle_frame_c;
wire next_sof_c;
wire next_data_cycle_c;
wire next_eof_c;
wire dly_data_xfer;
reg [4:0] channel_up_cnt;
//*********************************Main Body of Code**********************************
always @ (posedge USER_CLK)
begin
if(RESET)
channel_up_cnt <= `DLY 5'd0;
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
if(&channel_up_cnt)
channel_up_cnt <= `DLY channel_up_cnt;
else
channel_up_cnt <= `DLY channel_up_cnt + 1'b1;
else
channel_up_cnt <= `DLY 5'd0;
end
assign dly_data_xfer = (&channel_up_cnt);
//Generate RESET signal when Aurora channel is not ready
assign reset_c = RESET || !dly_data_xfer;
//______________________________ Transmit Data __________________________________
//Generate random data using XNOR feedback LFSR
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
begin
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY 16'hABCD; //random seed value
end
else if(!TX_DST_RDY_N && !idle_r)
begin
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY {!{data_lfsr_r[3]^data_lfsr_r[12]^data_lfsr_r[14]^data_lfsr_r[15]},
data_lfsr_r[0:14]};
end
//Connect TX_D to the DATA LFSR
assign TX_D = {2{data_lfsr_r}};
//Tie DATA LFSR to REM to generate random words
assign TX_REM = data_lfsr_r[0:1];
//Use a counter to determine the size of the next frame to send
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
frame_size_r <= `DLY 8'h00;
else if(single_cycle_frame_r || eof_r)
frame_size_r <= `DLY frame_size_r + 1;
//Use a second counter to determine how many bytes of the frame have already been sent
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
bytes_sent_r <= `DLY 8'h00;
else if(sof_r)
bytes_sent_r <= `DLY 8'h01;
else if(!TX_DST_RDY_N && !idle_r)
bytes_sent_r <= `DLY bytes_sent_r + 1;
//Use a freerunning counter to determine the IFG
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
ifg_size_r <= `DLY 4'h0;
else
ifg_size_r <= `DLY ifg_size_r + 1;
//IFG is done when ifg_size register is 0
assign ifg_done_c = (ifg_size_r == 4'h0);
//_____________________________ Framing State machine______________________________
//Use a state machine to determine whether to start a frame, end a frame, send
//data or send nothing
//State registers for 1-hot state machine
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
begin
idle_r <= `DLY 1'b1;
single_cycle_frame_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
sof_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
data_cycle_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
eof_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
end
else if(!TX_DST_RDY_N)
begin
idle_r <= `DLY next_idle_c;
single_cycle_frame_r <= `DLY next_single_cycle_frame_c;
sof_r <= `DLY next_sof_c;
data_cycle_r <= `DLY next_data_cycle_c;
eof_r <= `DLY next_eof_c;
end
//Nextstate logic for 1-hot state machine
assign next_idle_c = !ifg_done_c &&
(single_cycle_frame_r || eof_r || idle_r);
assign next_single_cycle_frame_c = (ifg_done_c && (frame_size_r == 0)) &&
(idle_r || single_cycle_frame_r || eof_r);
assign next_sof_c = (ifg_done_c && (frame_size_r != 0)) &&
(idle_r || single_cycle_frame_r || eof_r);
assign next_data_cycle_c = (frame_size_r != bytes_sent_r) &&
(sof_r || data_cycle_r);
assign next_eof_c = (frame_size_r == bytes_sent_r) &&
(sof_r || data_cycle_r);
//Output logic for 1-hot state machine
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
begin
TX_SOF_N <= `DLY 1'b1;
TX_EOF_N <= `DLY 1'b1;
TX_SRC_RDY_N <= `DLY 1'b1;
end
else if(!TX_DST_RDY_N)
begin
TX_SOF_N <= `DLY !(sof_r || single_cycle_frame_r);
TX_EOF_N <= `DLY !(eof_r || single_cycle_frame_r);
TX_SRC_RDY_N <= `DLY idle_r;
end
endmoduleNot much code , Let's just dismantle it section by section .
2.3.1、 port
Let's first look at the standards of official documents Framing Interface , Then compare the code .
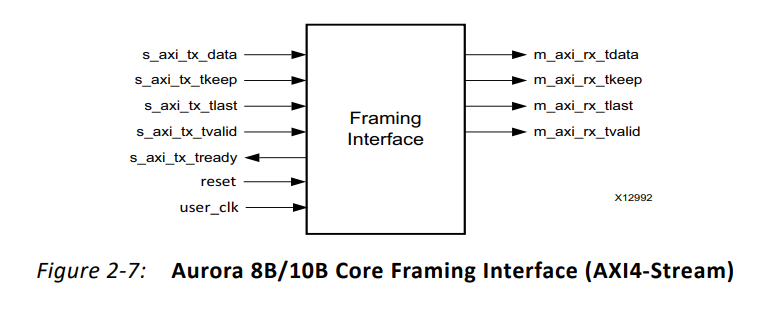
// User Interface
output [0:31] TX_D; // Data to send
output [0:1] TX_REM; // Random words
output TX_SOF_N; // Frame header indication , Low efficiency
output TX_EOF_N; // End of frame indication , Low efficiency
output TX_SRC_RDY_N; //tvalid
input TX_DST_RDY_N; //tready
// System Interface
input USER_CLK; // User clock
input RESET; // Reset
input CHANNEL_UP; // Channel effective signal , Highly effective 2.3.2、 Wait for initialization
//CHANNEL_UP When you get up ,channel_up_cnt Count 16 Clock cycles
always @ (posedge USER_CLK)
begin
if(RESET)
channel_up_cnt <= `DLY 5'd0;
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
if(&channel_up_cnt)
channel_up_cnt <= `DLY channel_up_cnt;
else
channel_up_cnt <= `DLY channel_up_cnt + 1'b1;
else
channel_up_cnt <= `DLY 5'd0;
end
assign dly_data_xfer = (&channel_up_cnt); //channel_up_cnt Count 16 After the clock cycle is full , pull up dly_data_xfer
//Generate RESET signal when Aurora channel is not ready
assign reset_c = RESET || !dly_data_xfer; //If CHANNEL_UP I haven't got up yet , that channel_up_cnt Will be all 0, and dly_data_xfer by 0, So the sentence assign reset_c = RESET || !dly_data_xfer Hang up ,reset_c Constant for the 1, So it has been in the reset state .
When CHANNEL_UP When you get up ,channel_up_cnt It takes some time to count to 5‘b11111, then dly_data_xfer by 1, So at this time assign reset_c = RESET || !dly_data_xfer Equivalent to assign reset_c = RESET, namely RESET control reset_c The signal . and RESET Generally in CHANNEL_UP After getting up, it is in the invalid reset state , So at this time, the channel enters the normal working mode .
2.3.3、LFSR Use
//Generate random data using XNOR feedback LFSR
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
begin
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY 16'hABCD; //random seed value
end
else if(!TX_DST_RDY_N && !idle_r)
begin
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY {!{data_lfsr_r[3]^data_lfsr_r[12]^data_lfsr_r[14]^data_lfsr_r[15]},
data_lfsr_r[0:14]};
end
//Connect TX_D to the DATA LFSR
assign TX_D = {2{data_lfsr_r}};
//Tie DATA LFSR to REM to generate random words
assign TX_REM = data_lfsr_r[0:1];About LFSR May refer to :FPGA Linear feedback shift register LFSR
The seed loaded at this time is 16'hABCD.
2.3.4、 The state machine realizes frame sending
This module uses a state machine to describe the sending process . It should be noted that the writing method of the state machine is different from the three-stage state machine we usually contact , So it looks a little awkward , Like its 5 The states are as follows :
//Use a state machine to determine whether to start a frame, end a frame, send
//data or send nothing
//State registers for 1-hot state machine
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
begin
idle_r <= `DLY 1'b1;
single_cycle_frame_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
sof_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
data_cycle_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
eof_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
end
else if(!TX_DST_RDY_N)
begin
idle_r <= `DLY next_idle_c;
single_cycle_frame_r <= `DLY next_single_cycle_frame_c;
sof_r <= `DLY next_sof_c;
data_cycle_r <= `DLY next_data_cycle_c;
eof_r <= `DLY next_eof_c;Then the state transition conditions are as follows :
//Nextstate logic for 1-hot state machine
assign next_idle_c = !ifg_done_c &&
(single_cycle_frame_r || eof_r || idle_r);
assign next_single_cycle_frame_c = (ifg_done_c && (frame_size_r == 0)) &&
(idle_r || single_cycle_frame_r || eof_r);
assign next_sof_c = (ifg_done_c && (frame_size_r != 0)) &&
(idle_r || single_cycle_frame_r || eof_r);
assign next_data_cycle_c = (frame_size_r != bytes_sent_r) &&
(sof_r || data_cycle_r);
assign next_eof_c = (frame_size_r == bytes_sent_r) &&
(sof_r || data_cycle_r);There are some parameters that need to be understood in order to master the jump of state machine :
(1)ifg_done_c
//Use a freerunning counter to determine the IFG
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
ifg_size_r <= `DLY 4'h0;
else
ifg_size_r <= `DLY ifg_size_r + 1;
//IFG is done when ifg_size register is 0
assign ifg_done_c = (ifg_size_r == 4'h0); Built a 00000~11111 A counter that counts , Whenever the counter value is 0 That is to pull up ifg_done_c
(2) frame_size_r
//Use a counter to determine the size of the next frame to send
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
frame_size_r <= `DLY 8'h00;
else if(single_cycle_frame_r || eof_r)
frame_size_r <= `DLY frame_size_r + 1;frame_size_r Is a counter of the size of a frame of data , The initial value is 0, When the first frame is sent or one frame is sent, it is accumulated 1, After that , The first transmission length is 1 A frame of data , The second time, the transmission length is 2 A frame of data , And so on .
(3)bytes_sent_r
//Use a second counter to determine how many bytes of the frame have already been sent
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
bytes_sent_r <= `DLY 8'h00;
else if(sof_r)
bytes_sent_r <= `DLY 8'h01;
else if(!TX_DST_RDY_N && !idle_r)
bytes_sent_r <= `DLY bytes_sent_r + 1;bytes_sent_r It is used to calculate the current frame data and how many BYTE The data of is sent out .
(4) Output
//Output logic for 1-hot state machine
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
begin
TX_SOF_N <= `DLY 1'b1;
TX_EOF_N <= `DLY 1'b1;
TX_SRC_RDY_N <= `DLY 1'b1;
end
else if(!TX_DST_RDY_N)
begin
TX_SOF_N <= `DLY !(sof_r || single_cycle_frame_r);
TX_EOF_N <= `DLY !(eof_r || single_cycle_frame_r);
TX_SRC_RDY_N <= `DLY idle_r;
end2.3.5、 Simulation and analysis
The state transition diagram is drawn for you :

With these conditions , We can infer how the whole state machine works according to the simulation :
(1) Power on reset
Power on reset , wait for IP Core initialization complete , And continue to delay for a period of time after its initialization .

(2) The initial state
After power on and reset successfully , The state machine is in state idle_r, At this time, the frame size frame_size_r by 0, Counter ifg_size_r by 0, therefore ifg_done_c by 1, The status will jump to single_cycle_frame_r

(3) Send a frame of data ( Single data )
Frame size frame_size_r+1, At this time, no conditions are met , Stay in this state ; At this time, send single frame data
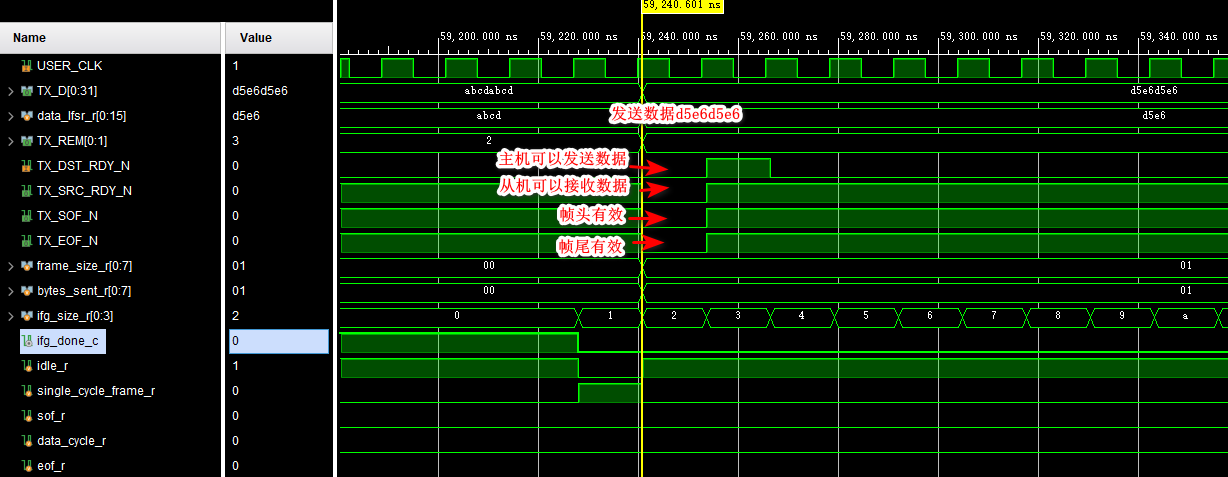
(4) Send a frame of data ( Multiple data )
Counter ifg_size_r Count to 11111 Then jump to 00000,ifg_done_c by 1, And the frame size frame_size_r by 1( Not 0), So the state will jump to sof
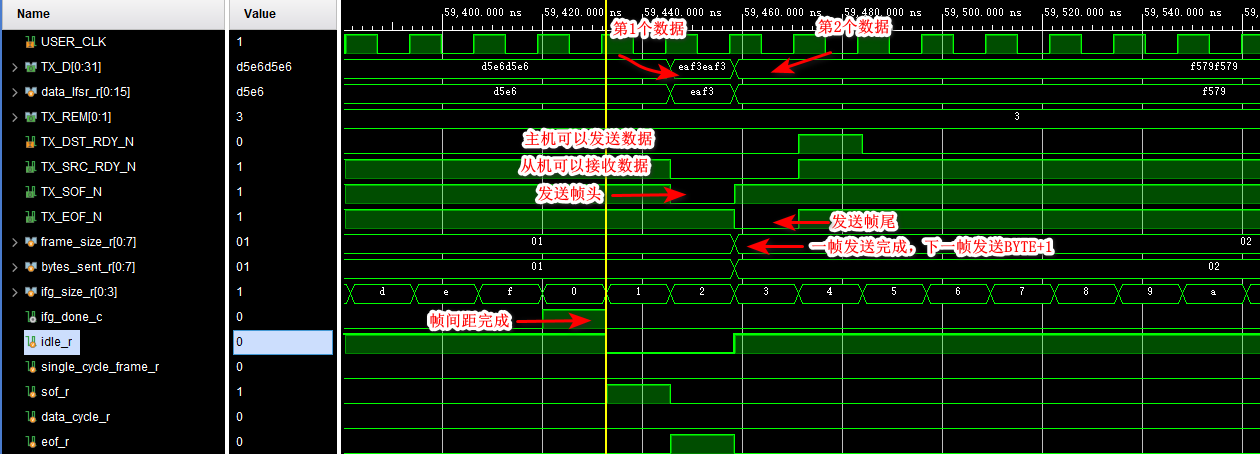
(5) Send a frame of data ( Multiple data )
thereafter , Each frame of data sent will be smaller than the previous frame 1 individual BYTE, Until the end of the simulation .
(6) summary
therefore , The function of the sending module is actually : Send... First 1 individual BYTE A frame of data , Send after an interval 2 individual BYTE A frame of data , It will happen after a period of time 3 individual BYTE A frame of data , And so on ······ The data sent is using LFSR To generate a pseudo-random sequence .
2.4、 Data verification module ( receive )
Since there is a sending module , There must also be reception ( check ) Module , Otherwise, how can I know whether you sent it correctly ?
`timescale 1 ns / 1 ps
`define DLY #1
module aurora_8b10b_0_FRAME_CHECK
(
// User Interface
RX_D,
RX_REM,
RX_SOF_N,
RX_EOF_N,
RX_SRC_RDY_N,
// System Interface
USER_CLK,
RESET,
CHANNEL_UP,
ERR_COUNT
);
//***********************************Port Declarations*******************************
// User Interface
input [0:31] RX_D;
input [0:1] RX_REM;
input RX_SOF_N;
input RX_EOF_N;
input RX_SRC_RDY_N;
// System Interface
input USER_CLK;
input RESET;
input CHANNEL_UP;
output [0:7] ERR_COUNT;
//***************************Internal Register Declarations***************************
// Slack registers
reg [0:31] RX_D_SLACK;
reg [0:1] RX_REM_1SLACK;
reg [0:1] RX_REM_2SLACK;
reg RX_SOF_N_SLACK;
reg RX_EOF_N_SLACK;
reg RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK;
reg [0:8] err_count_r = 9'd0;
reg data_in_frame_r;
reg data_valid_r;
reg [0:31] RX_D_R;
reg [0:31] pdu_cmp_data_r;
// RX Data registers
reg [0:15] data_lfsr_r;
//*********************************Wire Declarations**********************************
wire reset_c;
wire [0:31] data_lfsr_concat_w;
wire data_valid_c;
wire data_in_frame_c;
wire data_err_detected_c;
reg data_err_detected_r;
//*********************************Main Body of Code**********************************
//Generate RESET signal when Aurora channel is not ready
assign reset_c = RESET;
// SLACK registers
always @ (posedge USER_CLK)
begin
RX_D_SLACK <= `DLY RX_D;
RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK <= `DLY RX_SRC_RDY_N;
RX_REM_1SLACK <= `DLY RX_REM;
RX_REM_2SLACK <= `DLY RX_REM;
RX_SOF_N_SLACK <= `DLY RX_SOF_N;
RX_EOF_N_SLACK <= `DLY RX_EOF_N;
end
//______________________________ Capture incoming data ___________________________
//Data is valid when RX_SRC_RDY_N is asserted and data is arriving within a frame
assign data_valid_c = data_in_frame_c && !RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK;
//Data is in a frame if it is a single cycle frame or a multi_cycle frame has started
assign data_in_frame_c = data_in_frame_r || (!RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK && !RX_SOF_N_SLACK);
//RX Data in the pdu_cmp_data_r register is valid
//only if it was valid when captured and had no error
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
data_valid_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
data_valid_r <= `DLY data_valid_c && !data_err_detected_c;
else
data_valid_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
//Start a multicycle frame when a frame starts without ending on the same cycle. End
//the frame when an EOF is detected
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
data_in_frame_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
begin
if(!data_in_frame_r && !RX_SOF_N_SLACK && !RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK && RX_EOF_N_SLACK) //1 Frame start
data_in_frame_r <= `DLY 1'b1;
else if(data_in_frame_r && !RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK && !RX_EOF_N_SLACK) //1 End of the frame
data_in_frame_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
end
//Register and decode the RX_D data with RX_REM bus
always @ (posedge USER_CLK)
begin
if((!RX_EOF_N_SLACK) && (!RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK))
begin
case(RX_REM_1SLACK)
2'd0 : RX_D_R <= `DLY {RX_D_SLACK[0:7], 24'b0};
2'd1 : RX_D_R <= `DLY {RX_D_SLACK[0:15], 16'b0};
2'd2 : RX_D_R <= `DLY {RX_D_SLACK[0:23], 8'b0};
2'd3 : RX_D_R <= `DLY RX_D_SLACK;
default : RX_D_R <= `DLY RX_D_SLACK;
endcase
end
else if(!RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK)
RX_D_R <= `DLY RX_D_SLACK;
end
//Calculate the expected frame data
always @ (posedge USER_CLK)
begin
if(reset_c)
pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY {2{16'hD5E6}};
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
begin
if(data_valid_c && !RX_EOF_N_SLACK)
begin
case(RX_REM_2SLACK)
2'd0 : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY {data_lfsr_concat_w[0:7], 24'b0};
2'd1 : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY {data_lfsr_concat_w[0:15], 16'b0};
2'd2 : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY {data_lfsr_concat_w[0:23], 8'b0};
2'd3 : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY data_lfsr_concat_w;
default : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY data_lfsr_concat_w;
endcase
end
else if(data_valid_c)
pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY data_lfsr_concat_w;
end
end
//generate expected RX_D using LFSR
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
begin
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY 16'hD5E6; //random seed value
end
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
begin
if(data_valid_c)
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY {!{data_lfsr_r[3]^data_lfsr_r[12]^data_lfsr_r[14]^data_lfsr_r[15]},
data_lfsr_r[0:14]};
end
else
begin
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY 16'hD5E6; //random seed value
end
assign data_lfsr_concat_w = {2{data_lfsr_r}};
//___________________________ Check incoming data for errors __________________________
//An error is detected when LFSR generated RX data from the pdu_cmp_data_r register,
//does not match valid data from the RX_D port
assign data_err_detected_c = (data_valid_r && (RX_D_R != pdu_cmp_data_r));
//We register the data_err_detected_c signal for use with the error counter logic
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
data_err_detected_r <= `DLY data_err_detected_c;
//Compare the incoming data with calculated expected data.
//Increment the ERROR COUNTER if mismatch occurs.
//Stop the ERROR COUNTER once it reaches its max value (i.e. 255)
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(CHANNEL_UP)
begin
if(&err_count_r)
err_count_r <= `DLY err_count_r;
else if(data_err_detected_r)
err_count_r <= `DLY err_count_r + 1;
end
else
begin
err_count_r <= `DLY 9'd0;
end
//Here we connect the lower 8 bits of the count (the MSbit is used only to check when the counter reaches
//max value) to the module output
assign ERR_COUNT = err_count_r[1:8];
endmodule 2.4.1、 Port and deposit
// User Interface
input [0:31] RX_D;
input [0:1] RX_REM;
input RX_SOF_N;
input RX_EOF_N;
input RX_SRC_RDY_N;
// System Interface
input USER_CLK;
input RESET;
input CHANNEL_UP;
output [0:7] ERR_COUNT;
// SLACK registers
always @ (posedge USER_CLK)
begin
RX_D_SLACK <= `DLY RX_D;
RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK <= `DLY RX_SRC_RDY_N;
RX_REM_1SLACK <= `DLY RX_REM;
RX_REM_2SLACK <= `DLY RX_REM;
RX_SOF_N_SLACK <= `DLY RX_SOF_N;
RX_EOF_N_SLACK <= `DLY RX_EOF_N;
endThe port signal basically corresponds to the sending module one by one , Only one more error count output . Then all the input signals are stored for a beat , To improve timing .
2.4.2、 Reset
//Generate RESET signal when Aurora channel is not ready
assign reset_c = RESET;Reset and use it directly , There is no problem of unstable initialization . Because when the sender can send data normally , It indicates that the data link has been successfully established .
2.4.3、 Data validity judgment
//Data is valid when RX_SRC_RDY_N is asserted and data is arriving within a frame
assign data_valid_c = data_in_frame_c && !RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK;
//Data is in a frame if it is a single cycle frame or a multi_cycle frame has started
assign data_in_frame_c = data_in_frame_r || (!RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK && !RX_SOF_N_SLACK);
//RX Data in the pdu_cmp_data_r register is valid
//only if it was valid when captured and had no error
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
data_valid_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
data_valid_r <= `DLY data_valid_c && !data_err_detected_c;
else
data_valid_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
//Start a multicycle frame when a frame starts without ending on the same cycle. End
//the frame when an EOF is detected
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
data_in_frame_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
begin
if(!data_in_frame_r && !RX_SOF_N_SLACK && !RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK && RX_EOF_N_SLACK) //1 Frame start
data_in_frame_r <= `DLY 1'b1;
else if(data_in_frame_r && !RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK && !RX_EOF_N_SLACK) //1 End of the frame
data_in_frame_r <= `DLY 1'b0;
endAccording to frame header 、 The end of frame signal is used to construct a signal that represents the validity of a frame data .
2.4.4、 Data reprocessing ( decoding )
//Register and decode the RX_D data with RX_REM bus
always @ (posedge USER_CLK)
begin
if((!RX_EOF_N_SLACK) && (!RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK))
begin
case(RX_REM_1SLACK)
2'd0 : RX_D_R <= `DLY {RX_D_SLACK[0:7], 24'b0};
2'd1 : RX_D_R <= `DLY {RX_D_SLACK[0:15], 16'b0};
2'd2 : RX_D_R <= `DLY {RX_D_SLACK[0:23], 8'b0};
2'd3 : RX_D_R <= `DLY RX_D_SLACK;
default : RX_D_R <= `DLY RX_D_SLACK;
endcase
end
else if(!RX_SRC_RDY_N_SLACK)
RX_D_R <= `DLY RX_D_SLACK;
endaccording to RX_REM_1SLACK The signal reprocesses the received data ( Similar to the decoding process ), It can improve the randomness of data .RX_REM_1SLACK The signal is RX_REM The signal after being deposited , and RX_REM The signal is sent by a sender 2bit random number .
2.4.5、LFSR The data generated
//Calculate the expected frame data
always @ (posedge USER_CLK)
begin
if(reset_c)
pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY {2{16'hD5E6}};
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
begin
if(data_valid_c && !RX_EOF_N_SLACK)
begin
case(RX_REM_2SLACK)
2'd0 : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY {data_lfsr_concat_w[0:7], 24'b0};
2'd1 : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY {data_lfsr_concat_w[0:15], 16'b0};
2'd2 : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY {data_lfsr_concat_w[0:23], 8'b0};
2'd3 : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY data_lfsr_concat_w;
default : pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY data_lfsr_concat_w;
endcase
end
else if(data_valid_c)
pdu_cmp_data_r <= `DLY data_lfsr_concat_w;
end
end
//generate expected RX_D using LFSR
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(reset_c)
begin
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY 16'hD5E6; //random seed value
end
else if(CHANNEL_UP)
begin
if(data_valid_c)
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY {!{data_lfsr_r[3]^data_lfsr_r[12]^data_lfsr_r[14]^data_lfsr_r[15]},
data_lfsr_r[0:14]};
end
else
begin
data_lfsr_r <= `DLY 16'hD5E6; //random seed value
end
assign data_lfsr_concat_w = {2{data_lfsr_r}};The data at the sending end is LFSR Generated , Of course, the verifier should use the same method to generate data , Easy to compare , To judge the sending -- Whether the receiving process is normal .
2.4.6、 Data verification and error flag
//An error is detected when LFSR generated RX data from the pdu_cmp_data_r register,
//does not match valid data from the RX_D port
assign data_err_detected_c = (data_valid_r && (RX_D_R != pdu_cmp_data_r));
//We register the data_err_detected_c signal for use with the error counter logic
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
data_err_detected_r <= `DLY data_err_detected_c;
//Compare the incoming data with calculated expected data.
//Increment the ERROR COUNTER if mismatch occurs.
//Stop the ERROR COUNTER once it reaches its max value (i.e. 255)
always @(posedge USER_CLK)
if(CHANNEL_UP)
begin
if(&err_count_r)
err_count_r <= `DLY err_count_r;
else if(data_err_detected_r)
err_count_r <= `DLY err_count_r + 1;
end
else
begin
err_count_r <= `DLY 9'd0;
end
//Here we connect the lower 8 bits of the count (the MSbit is used only to check when the counter reaches
//max value) to the module output
assign ERR_COUNT = err_count_r[1:8];Compare the received signal with the standard signal , At the same time, the error counter flag signal is output according to the number of errors .
2.4.7、 Simulation results
The previous initialization process is skipped , Select only one reception in the reception process to explain :

The receiving process is actually quite simple , To increase the randomness of data , Some treatment has been done , Including taking more beats of several signals in order to align the timing , It seems that there will be more signals .
3、 Overall simulation
As mentioned above, the overall simulation is composed of two loop modules : The first module sends + The second module determines whether the first loop is correct ; The second module sends + The first module determines whether the second loop is correct .
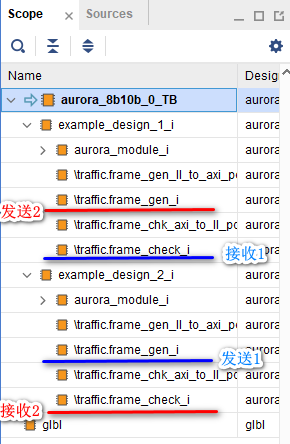
( One ) Simulation results of the first loop , Too many signals , Let's delete some , Only some key signals are retained :
The data sent by the sender :
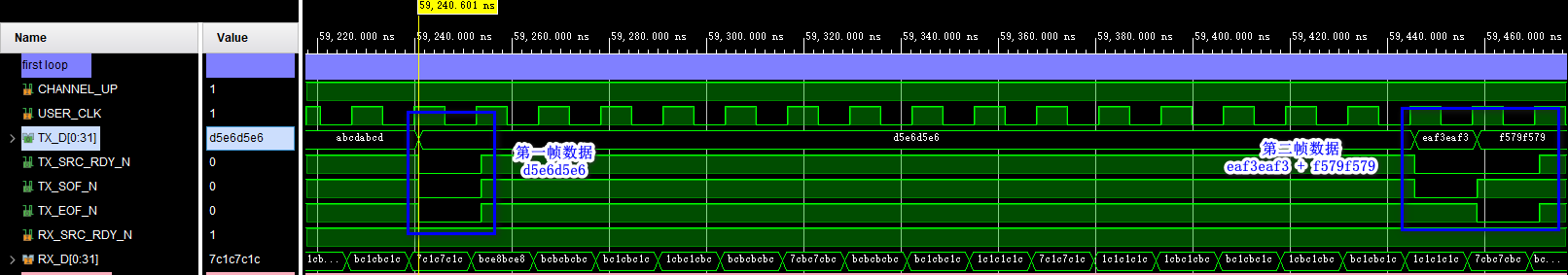
Data received by the receiving end :
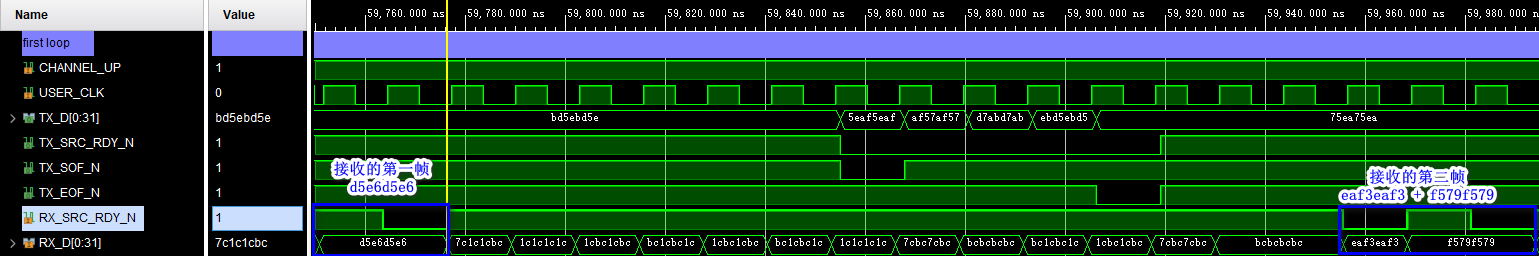
Sending and receiving are consistent , Loopback simulation is no problem .
( Two ) Simulation results of the second loop :
The data sent by the sender :
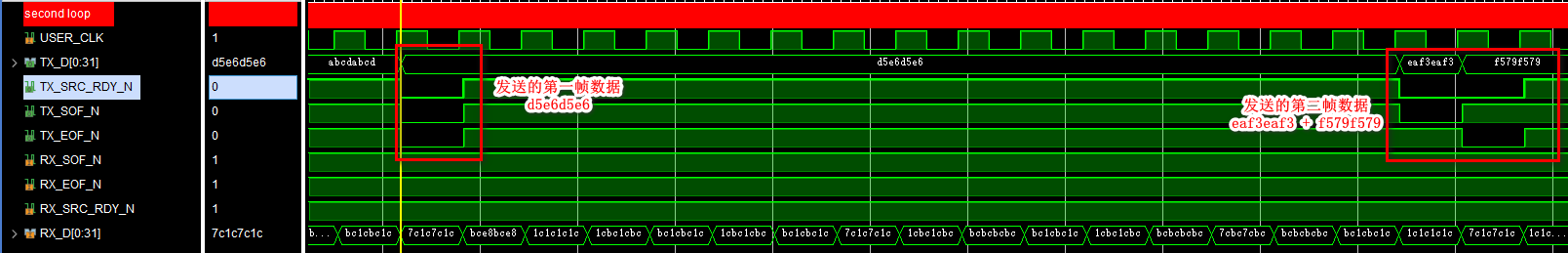
Data received by the receiving end :

Sending and receiving are consistent , Loopback simulation is no problem .
4、 summary
- You can see Aurora 8B/10B IP nucleus It's still easier to get started .
- Based on the official routine , Slightly modify the sending and receiving module , You can almost take it directly for simple use .
- Blog home page :wuzhikai.blog.csdn.net
- This paper is written by Lonely single blade original , First appeared in CSDN platform
- Do you have any questions , You can communicate with me in the comment area !
- It's not easy to create , Your support is the biggest driving force for me to continuously update ! If this article helps you , Please give me more praise 、 Reviews and collections !
边栏推荐
- Global and Chinese market of X-ray detectors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Kotlin basic learning 16
- Uniapp uses canvas to generate posters and save them locally
- Basic syntax of unity script (7) - member variables and instantiation
- ORA-01547、ORA-01194、ORA-01110
- Kotlin基础学习 14
- How to establish its own NFT market platform in 2022
- Kotlin基础学习 17
- Intersection vengraph
- 高性能 低功耗Cortex-A53核心板 | i.MX8M Mini
猜你喜欢

One of the future trends of SAP ui5: embrace typescript
Sentry experience and architecture, a fledgling monitoring product with a market value of $100million

MySQL index, transaction and storage engine

In the era of programmers' introspection, five-year-old programmers are afraid to go out for interviews

Basic syntax of unity script (6) - specific folder

Review materials of project management PMP high frequency examination sites (8-1)
SAML2.0 notes (I)
![[C Advanced] brother Peng takes you to play with strings and memory functions](/img/95/ab1bb0b3fa0b99e32233a5ca5d42a4.jpg)
[C Advanced] brother Peng takes you to play with strings and memory functions
![[yolo3d]: real time detection of end-to-end 3D point cloud input](/img/5e/f17960d302f663db75ad82ae0fd70f.jpg)
[yolo3d]: real time detection of end-to-end 3D point cloud input

MSI announced that its motherboard products will cancel all paper accessories
随机推荐
Basic syntax of unity script (6) - specific folder
Use blocking or non blocking for streamline
aaaaaaaaaaaaa
Global and Chinese market of autotransfusion bags 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Detailed explanation of ThreadLocal
Xlwings drawing
uniapp 使用canvas 生成海报并保存到本地
Unity脚本的基础语法(8)-协同程序与销毁方法
Kotlin基础学习 15
【DesignMode】原型模式(prototype pattern)
Custom classloader that breaks parental delegation
[yolo3d]: real time detection of end-to-end 3D point cloud input
Docker安装canal、mysql进行简单测试与实现redis和mysql缓存一致性
[HCIA continuous update] working principle of OSPF Protocol
JS generate random numbers
焱融看 | 混合云时代下,如何制定多云策略
Discrimination between sap Hana, s/4hana and SAP BTP
[HCIA continuous update] overview of dynamic routing protocol
[designmode] builder model
Pointer array & array pointer