当前位置:网站首页>PostgreSQL source code (60) transaction system summary
PostgreSQL source code (60) transaction system summary
2022-07-07 07:12:00 【mingjie73】
relevant
《Postgresql Source code (23)Clog The use of Slru Page elimination mechanism 》
《Postgresql Source code (27) Why does the transaction commit pass delayChkpt Blocking checkpoint》
《Postgresql Source code (59) Business ID Summary of value taking and judgment rules 》
To recapitulate PG Transaction management system :
PG The transaction processing in can be divided into two parts according to the functions provided : Basic transaction state management 、 Sub transaction state management .
PG The transaction system of can be summed up in one sentence : User commands trigger state machine functions, resulting in transaction state flow , Call the underlying transaction processing function to work according to the corresponding state during flow .
1 State machine flow system
User commands trigger state machine functions, resulting in transaction state flow , Call the underlying transaction processing function to work according to the corresponding state during flow .
State machine flow function
12 A state machine flow function , It can be divided into three categories .
- Package all single lines SQL Two functions of ( Get into SQL front StartTransactionCommand、SQL After execution CommitTransactionCommand), No matter what you do begin、 still select 1, I will walk through these two functions . It is equivalent to the passive flow of transaction state .
b StartTransactionCommand
b CommitTransactionCommand
- Transaction block processing function , Corresponding to user transaction commands , stay PortalRun It calls , Active circulation transaction status .
// System internal call rollback
b AbortCurrentTransaction
// User execution begin
b BeginTransactionBlock
// User execution commit
b EndTransactionBlock
// User execution rollback、abort
b UserAbortTransactionBlock
- Sub transaction status flow .
b DefineSavepoint
b ReleaseSavepoint
b RollbackToSavepoint
b BeginInternalSubTransaction
b RollbackAndReleaseCurrentSubTransaction
b AbortOutOfAnyTransaction
The underlying transaction processing function
When the state machine flows, it will call the underlying function to work , There are two types of functions
- Basic transaction function
// Called when the transaction is started , Configure transaction status , Apply for resources
StartTransaction
// The normal commit of a transaction is to call
CommitTransaction
// Called when the transaction is rolled back , First tune AbortTransaction, In tune CleanupTransaction
CleanupTransaction
// Called when the transaction is rolled back
AbortTransaction
- Sub transaction function
StartSubTransaction
CommitSubTransaction
AbortSubTransaction
CleanupSubTransaction
2 What does the underlying transaction function do ?
StartTransaction
- Get vxid( from backendid and localid Combination value ) Represents a virtual transaction id( Writing hasn't happened yet , Cannot assign real xid)
- use vxid register MyProc, After registration, you can find vxid lock , Indicates that the transaction started
- The transaction status flows to TRANS_INPROGRESS
StartTransaction
// vxid = {backendId = 3, localTransactionId = 76407}
GetNextLocalTransactionId
VirtualXactLockTableInsert
...
s->state = TRANS_INPROGRESS;
...
CommitTransaction( There are write operations in the transaction )
Assigned transactions ID Scene
- Transaction status flow TRANS_COMMIT
- Open for checkpoint The critical area of :MyProc->delayChkpt = true(《Postgresql Source code (27) Why does the transaction commit pass delayChkpt Blocking checkpoint》)
- Write commit Transaction log for 、 Brush the transaction log
- Write clog( Don't brush )TransactionIdCommitTree
- clear ProcArray Medium xid Information
- Clean up other
- Transaction status flow TRANS_DEFAULT
CommitTransaction
s->state = TRANS_COMMIT
RecordTransactionCommit
[START_CRIT_SECTION]
[[MyProc->delayChkpt = true]]
XactLogCommitRecord
XLogFlush
TransactionIdCommitTree
[[MyProc->delayChkpt = false]]
[END_CRIT_SECTION]
ProcArrayEndTransaction
// Can get the lock and clean it normally , Can't get the lock and add list It's waiting to be cleaned up later
LWLockConditionalAcquire(ProcArrayLock, LW_EXCLUSIVE)
// Normal cleaning : clear MyProc and ProcGlobal It records xid Information
ProcArrayEndTransactionInternal
...
// clear
...
s->state = TRANS_DEFAULT
CommitTransaction( There is no write operation in the transaction )
Unassigned transaction ID
- Transaction status flow TRANS_COMMIT
- clear
- Transaction status flow TRANS_DEFAULT
CommitTransaction
s->state = TRANS_COMMIT
RecordTransactionCommit // do nothing
// clear
s->state = TRANS_DEFAULT
3 Business ID Distribute
Before you really want to write data , Would call GetCurrentTransactionId, such as heap_insert.
- Take a new one xid
- Configuration to MyProc->xid
- Configuration to ProcGlobal->xids[MyProc->pgxactoff]
- xid Lock XactLockTableInsert
TransactionId
GetCurrentTransactionId(void)
{
TransactionState s = CurrentTransactionState;
if (!FullTransactionIdIsValid(s->fullTransactionId))
AssignTransactionId(s);
return XidFromFullTransactionId(s->fullTransactionId);
}
If not assigned , perform AssignTransactionId Take a new one xid Assigned to TransactionState. Refer to this article (《Postgresql Source code (59) Business ID Summary of value taking and judgment rules 》)
AssignTransactionId
...
GetNewTransactionId
...
MyProc->xid = xid;
ProcGlobal->xids[MyProc->pgxactoff] = xid;
...
XactLockTableInsert
...
4 Sub transaction system
Example :
drop table t1;
create table t1 (c1 int, c2 int);
begin;
insert into t1 values (1,1);
savepoint a;
insert into t1 values (2,1);
savepoint b;
insert into t1 values (3,1);
Here are some differences with ordinary affairs :
State of affairs : Sub transactions will make CurrentTransactionState It has a multi-layer structure , Used between parent Connect .
p *CurrentTransactionState
$39 = {fullTransactionId = {value = 4000071}, subTransactionId = 3, name = 0x199ca60 "b", savepointLevel = 0,
state = TRANS_INPROGRESS, blockState = TBLOCK_SUBINPROGRESS, nestingLevel = 3, gucNestLevel = 3,
curTransactionContext = 0x19de090, curTransactionOwner = 0x192a458, childXids = 0x0, nChildXids = 0, maxChildXids = 0,
prevUser = 10, prevSecContext = 0, prevXactReadOnly = false, startedInRecovery = false, didLogXid = false,
parallelModeLevel = 0, chain = false, assigned = false, parent = 0x199c558}
p *CurrentTransactionState->parent
$40 = {fullTransactionId = {value = 4000070}, subTransactionId = 2, name = 0x199c6c0 "a", savepointLevel = 0,
state = TRANS_INPROGRESS, blockState = TBLOCK_SUBINPROGRESS, nestingLevel = 2, gucNestLevel = 2,
curTransactionContext = 0x19d7200, curTransactionOwner = 0x19164c8, childXids = 0x0, nChildXids = 0, maxChildXids = 0,
prevUser = 10, prevSecContext = 0, prevXactReadOnly = false, startedInRecovery = false, didLogXid = true, parallelModeLevel = 0,
chain = false, assigned = false, parent = 0xe6a940 <TopTransactionStateData>}
p *CurrentTransactionState->parent->parent
$41 = {fullTransactionId = {value = 4000069}, subTransactionId = 1, name = 0x0, savepointLevel = 0, state = TRANS_INPROGRESS,
blockState = TBLOCK_INPROGRESS, nestingLevel = 1, gucNestLevel = 1, curTransactionContext = 0x199c400,
curTransactionOwner = 0x191e3e8, childXids = 0x0, nChildXids = 0, maxChildXids = 0, prevUser = 10, prevSecContext = 0,
prevXactReadOnly = false, startedInRecovery = false, didLogXid = true, parallelModeLevel = 0, chain = false, assigned = false,
parent = 0x0}
Allocating transactions ID when , Each sub transaction will get its own XID.
AssignTransactionId
...
SubTransSetParent(XidFromFullTransactionId(s->fullTransactionId),
XidFromFullTransactionId(s->parent->fullTransactionId));
And put yourself on a higher level xid It was recorded that subtrans in (SLRU Page and CLOG The same mechanism is used , This article is part of 《Postgresql Source code (23)Clog The use of Slru Page elimination mechanism 》).
Sub transaction commit
- In addition to the above (CommitTransaction( There are write operations in the transaction )) The steps mentioned
- Writing CLOG when , It is different from the case without sub transactions
- If there are no sub transactions , direct writing CLOG that will do
- When there are sub transactions
- Writing CLOG First of all, the sub business XID To configure SUB_COMMITTED State to CLOG in
- And then the father XID Configure the submission status of
- And then we can deal with the sub business XID The state of the from SUB_COMMITTED Become submitted ( Similar to a two-stage submission )
CommitTransaction
RecordTransactionCommit
TransactionIdCommitTree
TransactionIdSetTreeStatus
// One CLOG The page is all done
TransactionIdSetPageStatus
TransactionIdSetPageStatusInternal
// every last subxid All configured TRANSACTION_STATUS_SUB_COMMITTED
for
TransactionIdSetStatusBit
// Configure
TransactionIdSetStatusBit
// Then configure the submission of sub transactions
for
TransactionIdSetStatusBit
边栏推荐
- libcurl返回curlcode说明
- Pass child component to parent component
- MySQL binlog related commands
- 什么情况下考虑分库分表
- jdbc数据库连接池使用问题
- Academic report series (VI) - autonomous driving on the journey to full autonomy
- Tumor immunotherapy research prosci Lag3 antibody solution
- 【JDBC以及内部类的讲解】
- readonly 只读
- How Oracle backs up indexes
猜你喜欢
Sword finger offer high quality code
FPGA course: application scenario of jesd204b (dry goods sharing)
Prime partner of Huawei machine test questions
![[noi simulation] regional division (conclusion, structure)](/img/7d/4c66cd0a30e52ccd167b6138fcb4df.png)
[noi simulation] regional division (conclusion, structure)

How can brand e-commerce grow against the trend? See the future here!
Comment les entreprises gèrent - elles les données? Partager les leçons tirées des quatre aspects de la gouvernance des données
sql中对集合进行非空校验
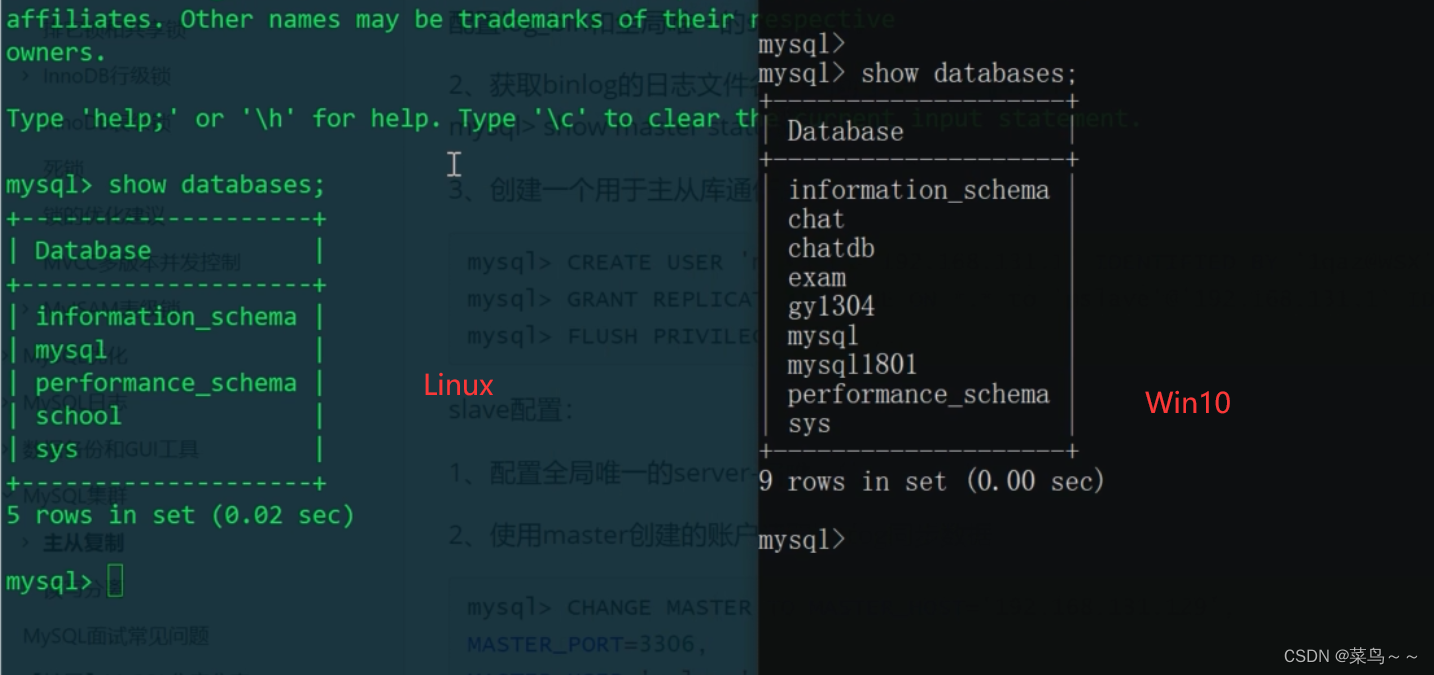
MySQL的主从复制原理
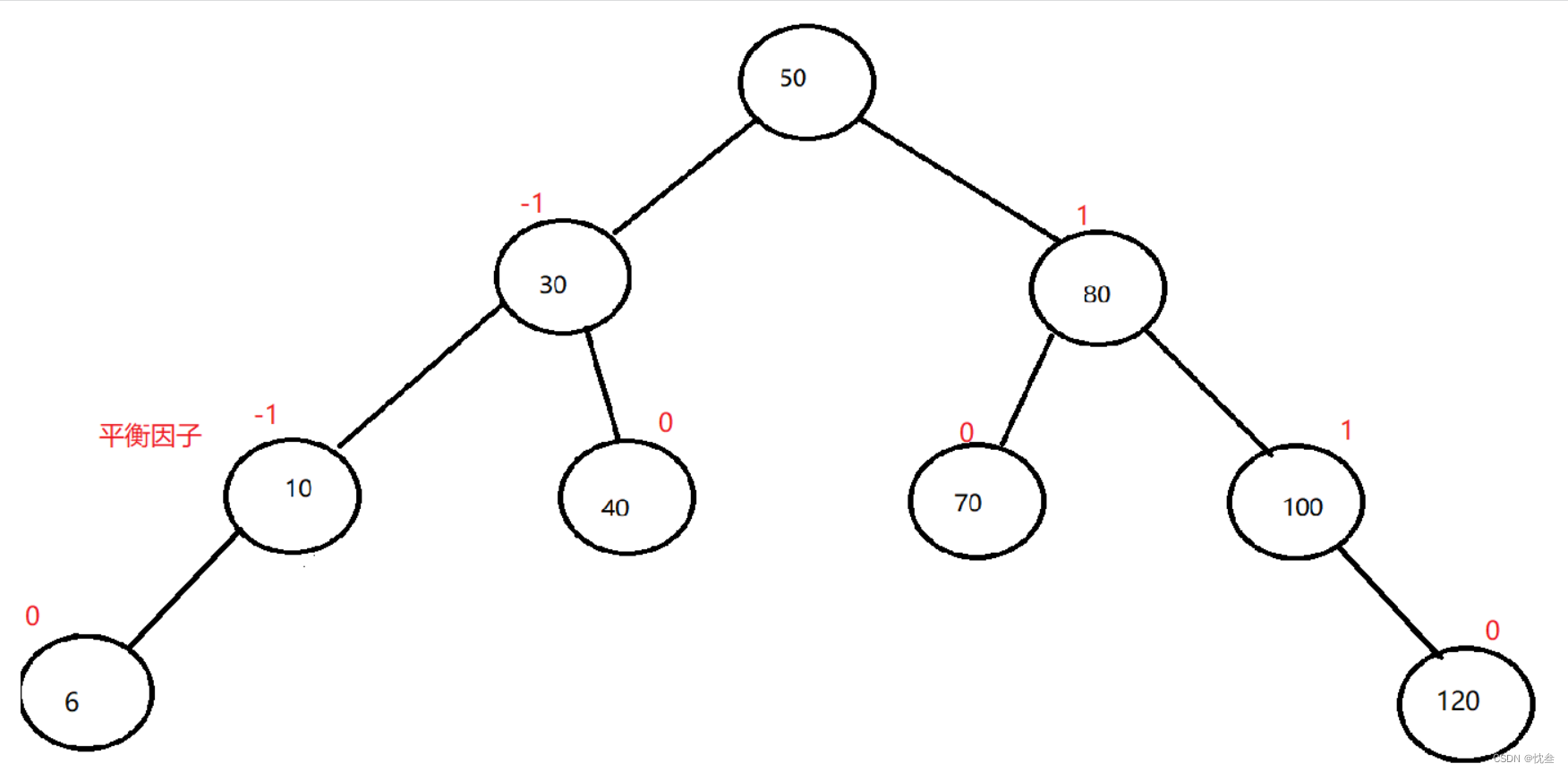
AVL树的实现
How to do sports training in venues?
随机推荐
Matlab tips (30) nonlinear fitting lsqcurefit
子组件传递给父组件
How can brand e-commerce grow against the trend? See the future here!
2022年全国所有A级景区数据(13604条)
Master-slave replication principle of MySQL
Unity C function notes
oracle如何备份索引
Precise space-time travel flow regulation system - ultra-high precision positioning system based on UWB
Network foundation - header, encapsulation and unpacking
Composition API premise
$refs:组件中获取元素对象或者子组件实例:
异步组件和Suspense(真实开发中)
SQLMAP使用教程(四)实战技巧三之绕过防火墙
Bus消息总线
Complete process of MySQL SQL
数据资产管理与数据安全国内外最新趋势
Test of transform parameters of impdp
The startup of MySQL installed in RPM mode of Linux system failed
LC 面试题 02.07. 链表相交 & LC142. 环形链表II
transform-origin属性详解