当前位置:网站首页>MySQL transaction log
MySQL transaction log
2022-07-06 10:29:00 【Protect our party a Yao】
Business has 4 Species characteristics : Atomicity 、 Uniformity 、 Isolation and persistence . So what mechanism are the four characteristics of transactions based on ?
- Transaction isolation by Locking mechanism Realization .
- And the atomicity of transactions 、 Consistency and persistence are determined by the nature of the transaction redo Journal and undo Log to ensure .
- REDO LOG be called Redo log , Provides write back operations , Resume the page operation of commit transaction modification , To ensure the durability of the transaction .
- UNDO LOG be called Rollback log , Roll back row records to a specific version , To guarantee the atomicity of transactions 、 Uniformity .
yes , we have DBA You might think UNDO yes REDO The inverse process , It's not .
One . redo journal
1.1. Why REDO journal
aspect , Buffer pools can help us eliminate CPU And disk ,checkpoint The mechanism can ensure the final drop of data , However, due to the checkpoint It doesn't trigger every time you change Of , It is master Threads process at intervals . So the worst-case scenario is after the transaction is committed , Just finished writing buffer pool , The database is down , Then this data is lost , Can't recover .
On the other hand , Transaction contains persistence Characteristics of , That is, for a committed transaction , After the transaction is committed, even if the system crashes , The changes made by this transaction to the database cannot be lost .
So how to ensure this persistence ? A simple approach : Refresh all pages modified by the transaction to disk before the transaction is committed , But this simple and crude approach has some problems .
Another solution : We just want the changes made by the committed transaction to the data in the database to take effect permanently , Even if the system crashes later , This modification can also be restored after restart . Therefore, it is not necessary to refresh all the pages modified in memory of the transaction to disk every time the transaction is committed , Only need to modify What have you learned Make a note of Just fine . such as , A transaction will be in the system table space The first 10 Number The offset in the page is 100 The value of that byte at 1 Change to 2 . We just need to record : Will be the first 0 Table space 10 The offset of page is 100 The value at is updated to 2 .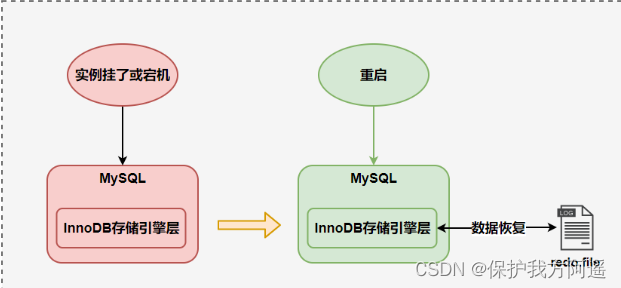
1.2. REDO The benefits of logging 、 characteristic
1.2.1. benefits
- redo The log reduces the disk brushing frequency .
- redo Log space is very small .
1.2.2. characteristic
- redo Logs are written to disk in sequence .
- During transaction execution ,redo log Keep recording .
1.3. redo The composition of
Redo log It can be simply divided into the following two parts :
- Redo log buffer (redo log buffer) , Save in memory , It's volatile .
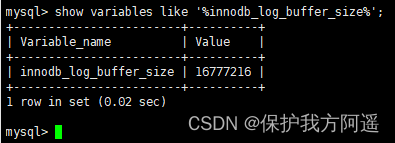
Parameter setting :innodb_log_buffer_size:
redo log buffer size , Default 16M , The maximum is 4096M, The minimum value is 1M.
show variables like '%innodb_log_buffer_size%';
- Redo log file (redo log file) , Save on hard disk , It's persistent .
1.4. redo The overall process of
Take an update transaction as an example ,redo log The flow process , As shown in the figure below :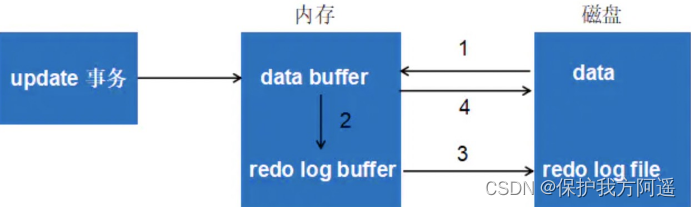
The first 1 Step : First read the original data from the disk into memory , Modify the memory copy of data
The first 2 Step : Generate a redo log and write redo log buffer, What is recorded is the modified value of the data
The first 3 Step : When a transaction commit when , take redo log buffer Refresh the contents of to redo log file, Yes redo log file Use additional
The way of writing
The first 4 Step : Periodically refresh the modified data in memory to disk
experience :Write-Ahead Log( Pre log persistence ): Before persisting a data page , First, persist the corresponding log page in memory .
1.5. redo log The strategy of disk brushing
redo log The write of is not written directly to the disk ,InnoDB The engine will write redo log When you write redo log buffer, Later on A certain frequency Brush into the real redo log file in . What about a certain frequency here ? This is what we want to say about the disk brushing strategy .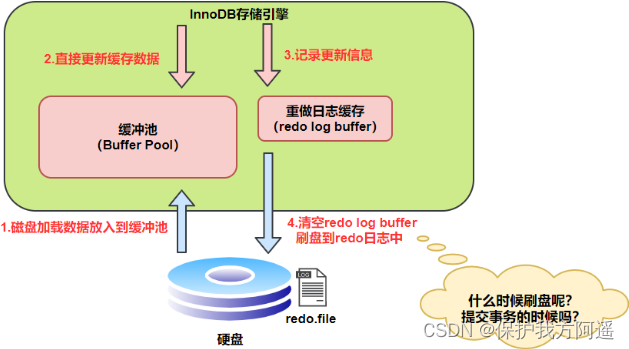
Be careful ,redo log buffer Brush disc to redo log file The process is not really brushing into the disk , Just brush into File system caching
(page cache) In the middle ( This is an optimization made by modern operating systems to improve the efficiency of file writing ), The real write will be left to the system to decide ( such as page cache Big enough ). So for InnoDB There is a problem , If you leave it to the system to synchronize , Similarly, if the system goes down , Then the data is lost ( Although the probability of the whole system downtime is still relatively small ).
In this case ,InnoDB give innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit Parameters , This parameter controls commit When committing a transaction , How to integrate redo log buffer Refresh the log in to redo log file in . It supports three strategies :
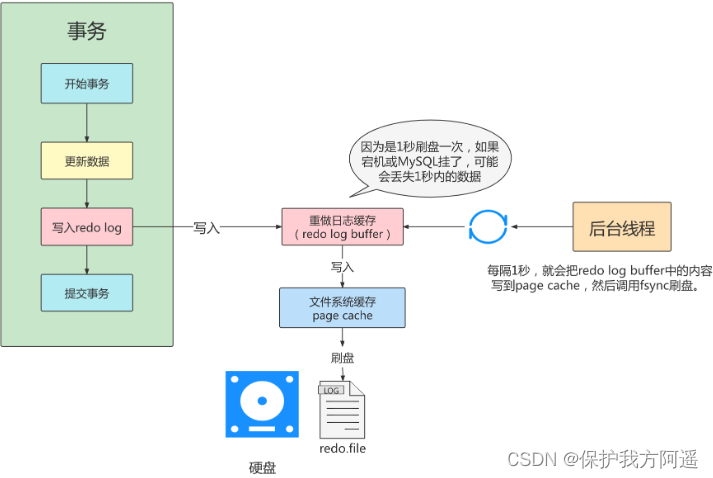
- Set to 0 : Indicates that no disk flushing is performed every time a transaction is committed .( System default master thread every other 1s Perform a synchronization of redo logs ).
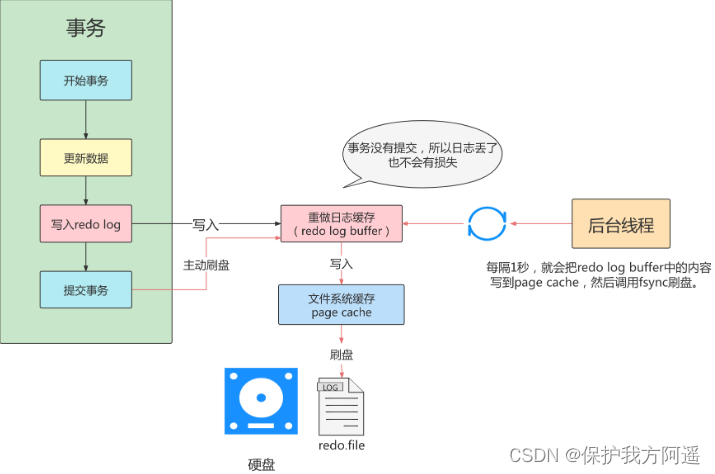
- Set to 1 : Indicates that synchronization will occur every time a transaction is committed , Brush set operation ( The default value is ).
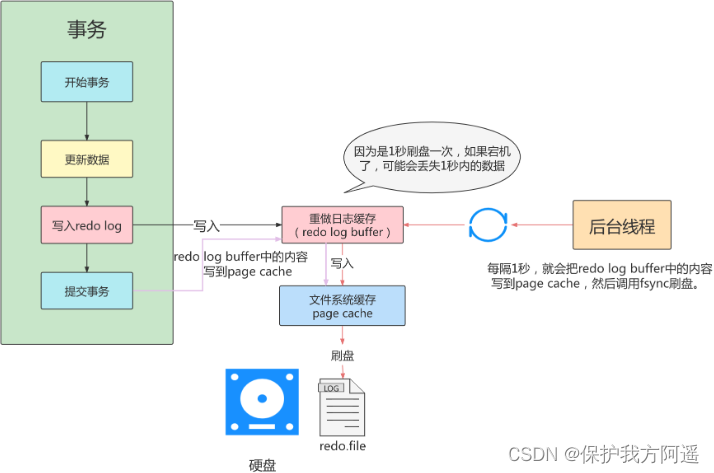
- Set to 2 : It means that only redo log buffer Content write page cache, Out of sync . from os Decide when to synchronize to disk files .
1.6. Demonstration of different disk brushing strategies
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1;
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=2;
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=0
1.7. write in redo log buffer The process
1.7.1. Add concept :Mini-Transaction
A transaction can contain several statements , Each statement is actually composed of several mtr form , every last mtr It can also contain several
redo journal , Draw a diagram to show their relationship. That's it :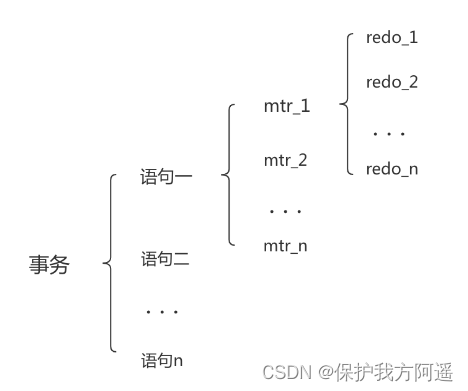
1.7.2. redo Log write log buffer
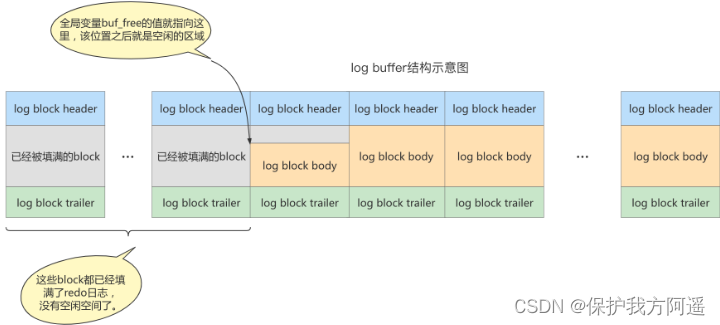
Every mtr There will be a group of redo journal , Use a diagram to describe these mtr Log generated :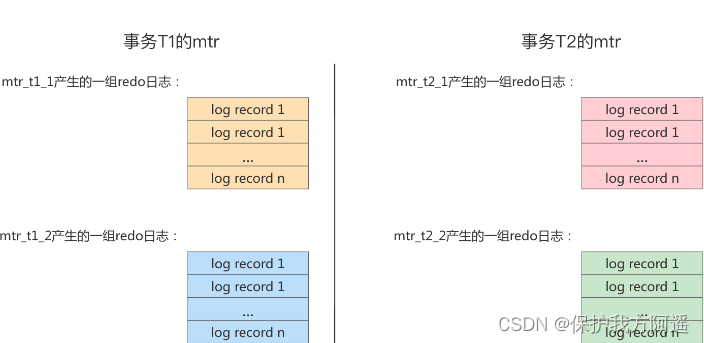
Different transactions may be Concurrent Executive , therefore T1 、 T2 Between mtr May be Alternate execution Of .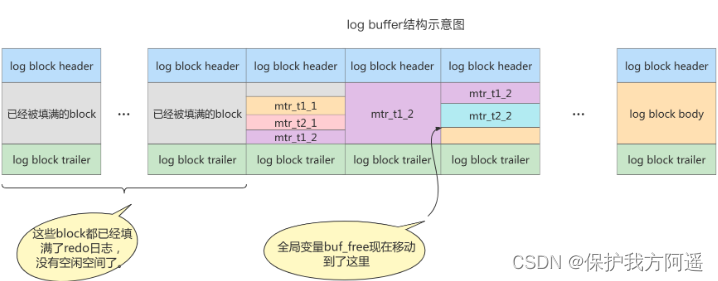
1.7.3. redo log block Structure diagram
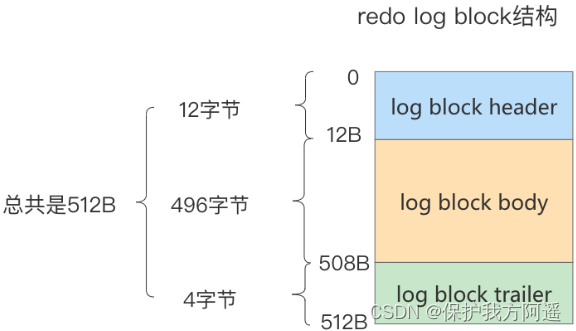
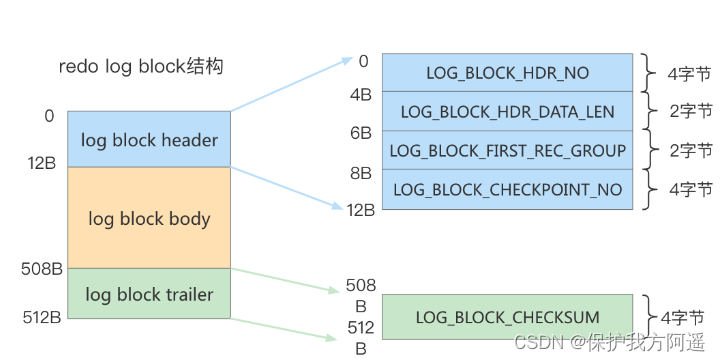
1.8. redo log file
1.8.1. Related parameter settings
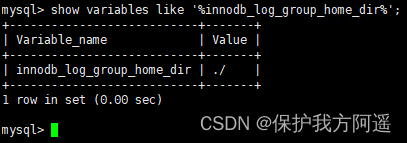
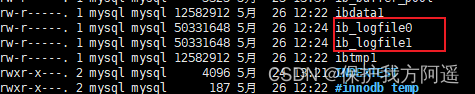
innodb_log_group_home_dir : Appoint redo log The path where the filegroup is located , The default value is ./ , In the database data directory .MySQL The default data directory for ( var/lib/mysql ) By default, there are two named ib_logfile0 and ib_logfile1 The file of ,log buffer The logs in are refreshed to these two disk files by default . this redo The log file location can also be modified .
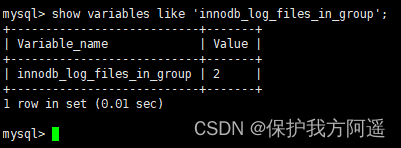
innodb_log_files_in_group: To specify redo log file The number of , Name it in the following way :ib_logfile0,iblogfile1…iblogfilen. Default 2 individual , Maximum 100 individual .
cd /var/lib/mysql
- innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit: control redo log Refresh to disk policy , The default is 1.
- innodb_log_file_size: Single redo log File set size , The default value is 48M . The maximum value is 512G, Note that the maximum refers to the whole of redo log The sum of a series of documents , namely (innodb_log_files_in_group * innodb_log_file_size ) Can't be greater than the maximum 512G.
show variables like '%innodb_log_file_size%';
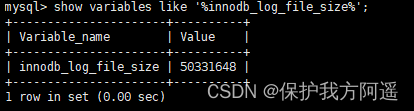
Modify its size according to the business , To accommodate larger transactions . edit my.cnf File and restart the database to take effect , As shown below :
vim /etc/my.cnf
innodb_log_file_size=200M
1.8.2. Log file group
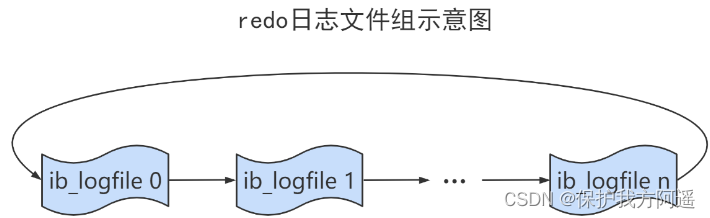 Total redo The log file size is actually : innodb_log_file_size × innodb_log_files_in_group .
Total redo The log file size is actually : innodb_log_file_size × innodb_log_files_in_group .
Use recycling to redo If you write data in the log file group , Will cause post write redo The log overwrites the previous write redo journal ? Of course ! therefore InnoDB The designer proposed checkpoint The concept of .
1.8.3. checkpoint
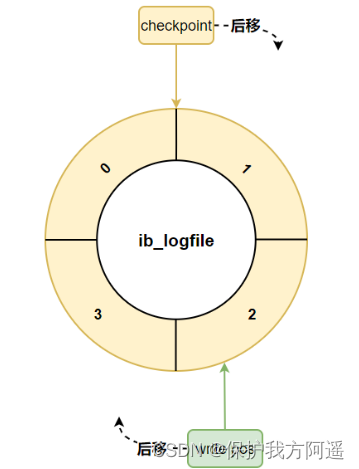
If write pos Catch up checkpoint , Indicates that the log file group is full , No new... Can be written at this time redo log Record ,MySQL We have to stop , Clear some records , hold checkpoint Push on .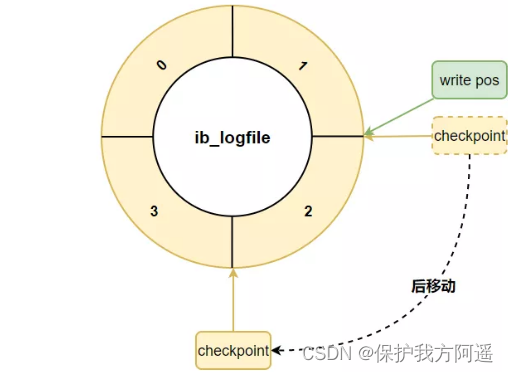
Two . Undo journal
redo log It is the guarantee of transaction persistence ,undo log Is the guarantee of transaction atomicity . In business Update data Of Front operation In fact, you have to write a undo log .
2.1. How to understand Undo journal
Affairs need to be guaranteed Atomicity , That is, all operations in the transaction are either completed , Or do nothing . But sometimes things happen in the middle of a transaction , such as :
- Situation 1 : Various errors may be encountered during transaction execution , such as The error of the server itself , Operating system error , Even suddenly power failure The resulting error .
- Situation two : Programmers can manually enter during transaction execution ROLLBACK Statement ends the execution of the current transaction .
The above situation occurs , We need to change the data back to the original , This process is called Roll back , This can create an illusion : This business seems to have done nothing , So in line with Atomicity requirement .
2.2. Undo The role of logs
- effect 1: Undo Data .
- effect 2:MVCC.
2.3. undo Storage structure of
2.3.1. Rollback segments and undo page
InnoDB Yes undo log The management of the system is in the form of segments , That is to say Rollback segment (rollback segment) . Each rollback segment records 1024 individual undo log segment , And in each undo log segment In paragraph undo page Application for .
- stay InnoDB1.1 Before the release ( barring 1.1 edition ), only one rollback segment, Therefore, transactions that support simultaneous online are limited to 1024 . Although it is enough for most applications .
- from 1.1 Version start InnoDB Maximum support 128 individual rollback segment , Therefore, the transaction limit of supporting simultaneous online has been raised to 128*1024 .
show variables like 'innodb_undo_logs';
2.3.2. Rollback segment and transaction
- Only one rollback segment is used per transaction , A rollback segment may serve multiple transactions at the same time .
- When a transaction begins , A rollback segment will be made , In the course of the transaction , When the data is modified , The original data will be copied to the rollback segment .
- In the rollback segment , Transactions keep filling the extents , Until the transaction ends or all space is used up . If the current extent is not enough , The transaction will request to expand the next extent in the segment , If all allocated extents are used up , The transaction will overwrite the original extent or expand the new extent to use if the rollback segment allows .
- Rollback segment exists in undo Tablespace , There can be more than one in the database undo Table space , But only one... Can be used at a time undo Table space .
- When the transaction commits ,InnoDB The storage engine does the following two things :1. take undo log Put it in the list , For later purge operation 2. Judge undo log Whether the page can be reused , If it can be assigned to the next transaction .
2.3.3. Data classification in rollback segment
- Uncommitted rollback data (uncommitted undo information).
- Rollback data submitted but not expired (committed undo information).
- Data that the transaction has committed and expired (expired undo information).
2.4. undo The type of
stay InnoDB In the storage engine ,undo log It is divided into :
- insert undo log
- update undo log
2.5. undo log Life cycle of
2.5.1. Brief generation process
Only Buffer Pool The process of :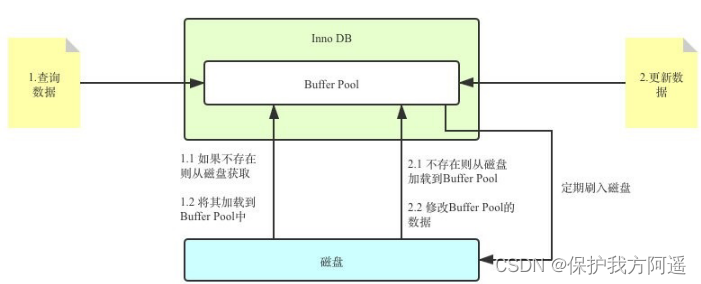
With Redo Log and Undo Log after :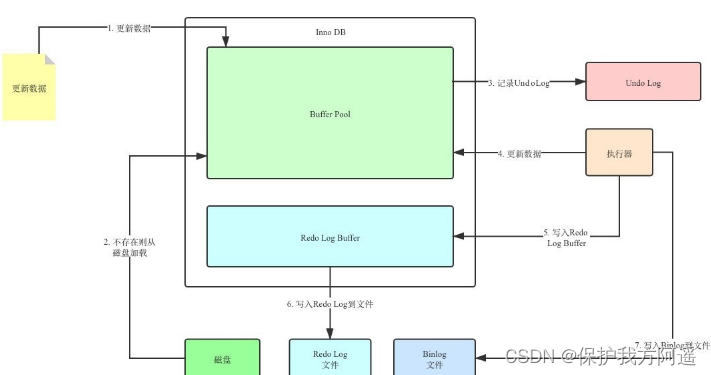
2.5.2. Detailed generation process

When we execute INSERT when :
begin;
INSERT INTO user (name) VALUES ("tom");
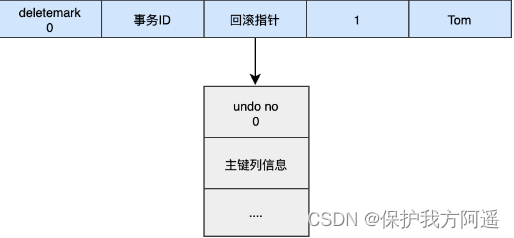
When we execute UPDATE when :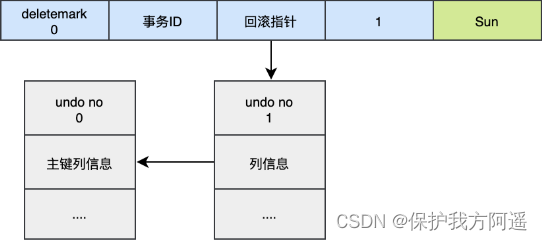
UPDATE user SET id=2 WHERE id=1;
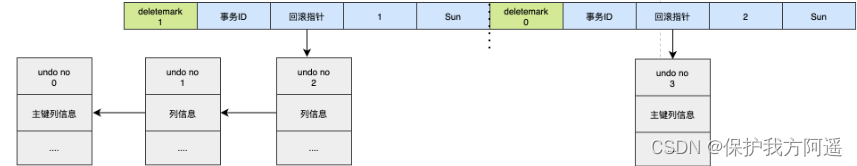
2.5.3. undo log How to rollback
Take the example above , Hypothetical execution rollback, Then the corresponding process should be like this :
- adopt undo no=3 My log put id=2 Data deletion .
- adopt undo no=2 My log put id=1 Data. deletemark restore 0.
- adopt undo no=1 My log put id=1 Data. name restore Tom.
- adopt undo no=0 My log put id=1 Data deletion .
2.5.4. undo log The deletion of
- Aim at insert undo log
because insert Records of operations , Visible only to the transaction itself , Not visible to other things . Therefore, we should undo log You can delete... Directly after the transaction is committed , There is no need for purge operation . - Aim at update undo log
The undo log May need to provide MVCC Mechanism , So you can't delete a transaction when it's committed . Submit with undo log Linked list , wait for purge Thread for final deletion .
2.6. Summary
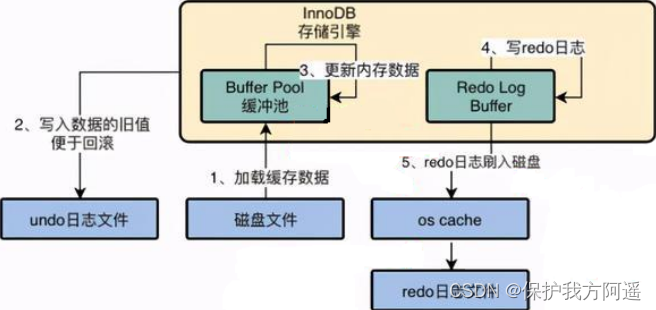
undo log It's a logical log , When rolling back a transaction , Just logically restore the database to its original state .
redo log It's a physical log , It records physical changes to the data page ,undo log No redo log The inverse process .
边栏推荐
- Mysql32 lock
- ByteTrack: Multi-Object Tracking by Associating Every Detection Box 论文阅读笔记()
- MySQL combat optimization expert 02 in order to execute SQL statements, do you know what kind of architectural design MySQL uses?
- A new understanding of RMAN retention policy recovery window
- Complete web login process through filter
- Not registered via @EnableConfigurationProperties, marked(@ConfigurationProperties的使用)
- Solve the problem of remote connection to MySQL under Linux in Windows
- Mysql36 database backup and recovery
- MySQL实战优化高手07 生产经验:如何对生产环境中的数据库进行360度无死角压测?
- text 文本数据增强方法 data argumentation
猜你喜欢
寶塔的安裝和flask項目部署

Use xtrabackup for MySQL database physical backup
AI的路线和资源
MySQL34-其他数据库日志
PyTorch RNN 实战案例_MNIST手写字体识别
Mexican SQL manual injection vulnerability test (mongodb database) problem solution
![[C language] deeply analyze the underlying principle of data storage](/img/d6/1c0cd38c75da0d0cc1df7f36938cfb.png)
[C language] deeply analyze the underlying principle of data storage
Security design verification of API interface: ticket, signature, timestamp
![16 medical registration system_ [order by appointment]](/img/7f/d94ac2b3398bf123bc97d44499bb42.png)
16 medical registration system_ [order by appointment]
Pytoch LSTM implementation process (visual version)
随机推荐
Southwest University: Hu hang - Analysis on learning behavior and learning effect
Export virtual machines from esxi 6.7 using OVF tool
16 medical registration system_ [order by appointment]
MySQL实战优化高手02 为了执行SQL语句,你知道MySQL用了什么样的架构设计吗?
text 文本数据增强方法 data argumentation
AI的路线和资源
寶塔的安裝和flask項目部署
[after reading the series of must know] one of how to realize app automation without programming (preparation)
MySQL实战优化高手04 借着更新语句在InnoDB存储引擎中的执行流程,聊聊binlog是什么?
数据库中间件_Mycat总结
The underlying logical architecture of MySQL
Nanny hand-in-hand teaches you to write Gobang in C language
Solve the problem of remote connection to MySQL under Linux in Windows
15 医疗挂号系统_【预约挂号】
Vscode common instructions
The programming ranking list came out in February. Is the result as you expected?
MySQL combat optimization expert 04 uses the execution process of update statements in the InnoDB storage engine to talk about what binlog is?
[unity] simulate jelly effect (with collision) -- tutorial on using jellysprites plug-in
基于Pytorch的LSTM实战160万条评论情感分类
Implement sending post request with form data parameter