当前位置:网站首页>In depth understanding of USB communication protocol
In depth understanding of USB communication protocol
2022-07-07 17:49:00 【A mouthful of Linux】
0. Basic concepts
One 【 transmission 】( control 、 Batch 、 interrupt 、 Isochronous ): By multiple 【 Business 】 form ;
One 【 Business 】(IN、OUT、SETUP): By one or more 【Packet】 form .
USB The data is in 【 Host software 】 And 【USB Device specific endpoint 】 Transmitted between .【 Host software 】 And 【USB Device specific endpoint 】 The relationship between them is called 【pipes】. One USB Equipment can have multiple pipes (pipes).
1. package (Packet)
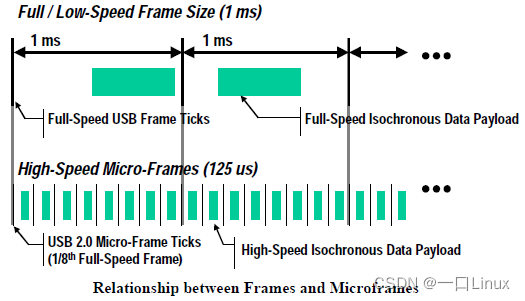
package (Packet) yes USB The basic unit of information transmission in a system , All data is packaged and transferred on the bus . The data is in USB Transmission on the bus is in packets , Packets can only be transmitted within frames . High speed USB The frame period of the bus is 125us, Full speed and low speed USB The frame period of the bus is 1ms. The frame starts with a specific packet (SOF package ) Express , End of frame EOF.EOF It's not a bag , It is a level state ,EOF Data transmission is not allowed during .
Be careful : Although high speed USB Bus and full speed / low speed USB The frame period of the bus is different , however SOF The increase rate of frame number in the package is the same , Because on the highway USB In the system ,SOF The frame number in the packet is actually the high of the counter 11 position , The lowest three digits are not used as the microframe number , Therefore, the increase period of its frame number is 1mS
- USB What is the situation on the bus ?
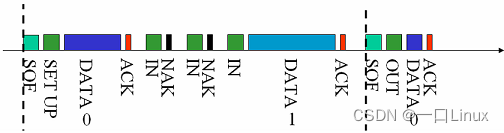
Bag is USB The smallest unit of data transmission on the bus , Cannot be interrupted or disturbed , Otherwise, it will lead to mistakes . Several packets form a transaction transmission , A transaction transmission cannot be interrupted , Several packets belonging to a transaction transmission must be continuous , It cannot be completed across frames . A transfer consists of one to many transaction transfers , It can be completed across frames .
USB The package consists of five parts , Synchronization field (SYNC)、 Package identifier field (PID)、 Data field 、 Cyclic redundancy check fields (CRC) And package end fields (EOP), The basic format of the package is shown in the following figure :
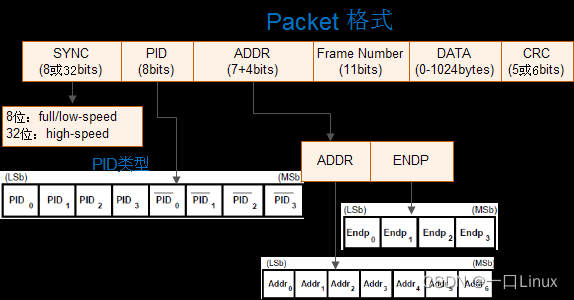
1.1 PID type ( Package type )
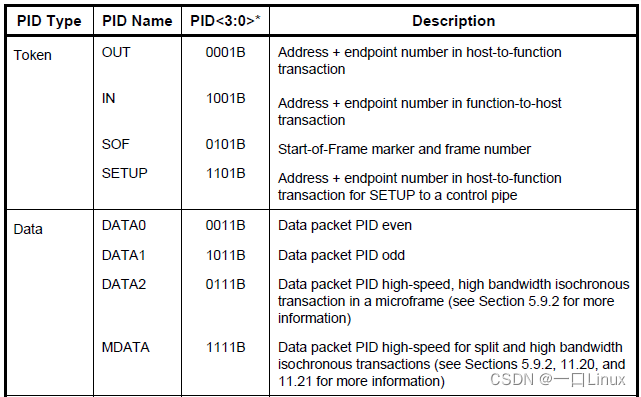
1.2 Token Packets
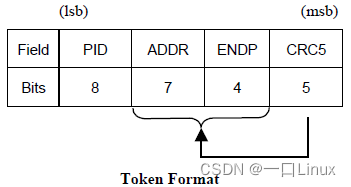
This format applies to IN、OUT、SETUP、PING.
PID Data transmission direction
IN Device->Host
OUT Host->Device
SETUP Host->Device
PING Device->Host
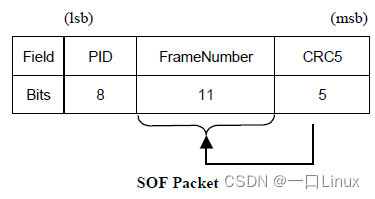
1.3 Start-of-Frame(SOF) Packets
SOF By Host Send to Device.
- about full-speed Bus , every other 1.00 ms ±0.0005 ms Send it once ;
- about high-speed Bus , every other 125 μs ±0.0625 μs Send it once ;
SOF The package composition is shown in the following figure
1.4 Data Packets
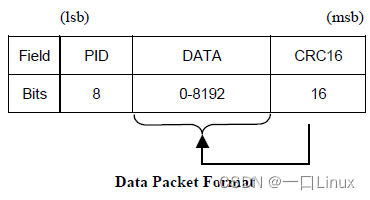
There are four types of packets :DATA0, DATA1, DATA2,and MDATA, And by the PID To distinguish between .DATA0 and DATA1 It is defined to support data switching and synchronization (data toggle synchronization).
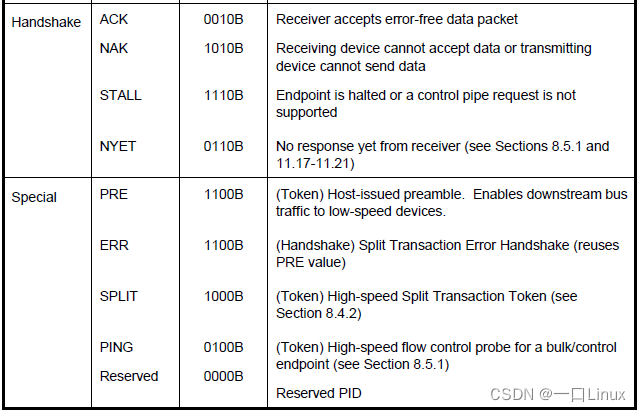
1.5 Handshake Packets
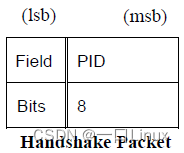
- ACK: about IN Business , It will be host issue ; about OUT、SETUP and PING Business , It will be device issue .
- NAK: In the data phase , about IN Business , It will be device issue ; In the handshake phase , about OUT and PING Business , It will also be device issue ;host Never send NAK package .
2. Business (Transaction)
stay USB The process of receiving or sending data information on a is called transaction processing (Transaction) namely :The delivery of service to an endpoint. A transaction consists of a system packet form , By which packet form , It depends on the specific transaction . It may consist of the following packages :
- One token packet
- Optional data pcket
- Optional handshake packet
- Optional special packet
2.1 Input (IN) Transaction processing
Enter transaction : Express USB The host is from a... On the bus USB The process of a device receiving a packet .
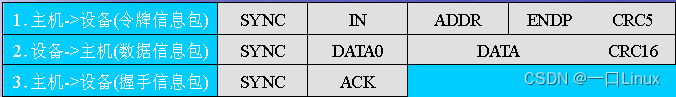
- 【 normal 】 Input transactions for
- 【 The device is busy 】 Input transactions at

- 【 Device error 】 Input transactions at
2.2. Output (OUT) Transaction processing
Output transactions : Express USB The host outputs a packet to a point on the bus USB The process of equipment receiving .
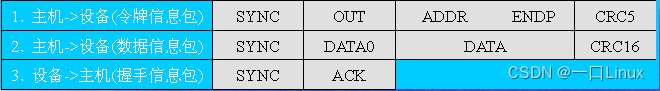
- 【 normal 】 Output transactions of

- 【 Device busy 】 Output transactions of
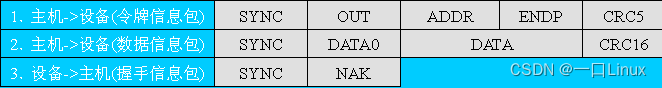
- 【 Device error 】 Output transactions of

2.3 Set up (SETUP) Transaction processing
- 【 normal 】 Set transactions
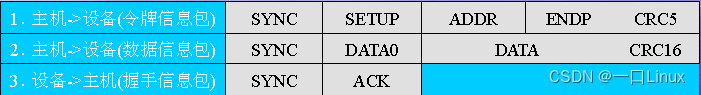
- 【 Device busy 】 Set transactions
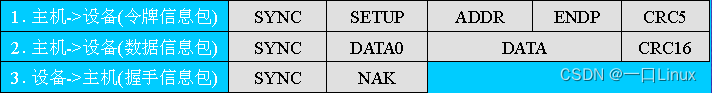
- 【 Device error 】 Set transactions
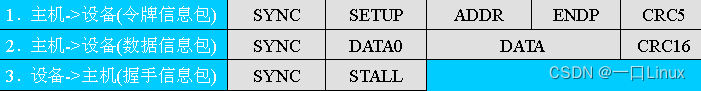
3. USB Transfer type
stay USB In transit , Defined 4 Types of transmission :
- Control transmission (Control Transfer)
- Interrupt transmission (Interrupt Transfer)
- Bulk transfer (Bulk Transfer)
- Synchronous transmission (Isochronous)
3.1 Control transmission (Control Transfer)
The control transmission is controlled by 2~3 There are three stages :
- The establishment phase (Setup)
- Data phase ( No data control, no such stage )(DATA)
- State phase (Status)
Each stage consists of one or more ( Data phase ) The transaction transmission consists of (Transaction).
The control data is controlled by USB The system software is used to configure the equipment ( When enumerating ), Other driver software can be used control transfer To achieve specific functions , Data transmission cannot be lost .
3.1.1 The establishment phase
Host from USB The device obtains configuration information , And set the configuration value of the device . The data exchange in the establishment phase includes SETUP Token packet 、 Next to it DATA0 Data packets and ACK Handshake packet . Its function is to execute a setting ( Vague concept ) Data exchange of , And define the content of this control transmission ( namely : stay Data Stage in IN or OUT Of data Number of packages , And sending direction , stay Setup Stage Has been set ).
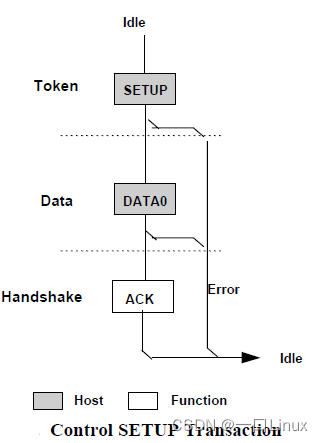
3.1.2 Data phase
According to the direction of data transmission in the data stage , Control transmission can be divided into 3 Types :
- Control reading ( Read USB The descriptor )
- Control write ( To configure USB equipment )
- No data control
Data transmission phase : It is used to transmit data between the host and the device .
- Control reading
It is to read data from the device to the host , Read data USB Device descriptor . The process is shown in the figure below 【Control Read】 Shown . For every data packet , First , The host will send a IN Token packet , It means to read data in . then , The device passes data through DATA1/DATA0 Data packets are sent back to the host . Last , The host will respond in the following way : When the data has been received correctly , The host sends ACK Token packet ; When the host is busy , issue NAK Handshake packet ; When an error occurs , The host sends out STALL Handshake packet .
- Control write
It is to transfer data from the host to the device , The data transmitted is right USB Configuration information of the device , The process is shown in the following figure 【Control Wirte】 Shown . For every data packet , The host will send a OUT Token packet , It means that the data should be sent out . Then , The host passes data through DATA1/DATA0 Data packets are passed to the device . Last , The equipment will respond in the following ways : When the data has been received correctly , The equipment sends ACK Token packet ; When the device is busy , Equipment issue NAK Handshake packet ; When an error occurs , Equipment issue STALL Handshake packet .
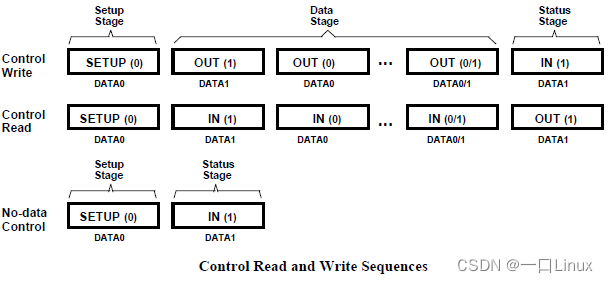
3.1.3 State phase
State phase : Used to indicate that the whole transmission process has completely ended .
The direction of state phase transmission must be opposite to that of data phase , It turns out to be IN Token packet , This stage should be OUT Token packet ; conversely , Turned out to be OUT Token packet , This stage should be IN Token packet .
about 【 Control reading 】 for , The host will send OUT Token packet , Then follow 0 Of length DATA1 Packet . And then , The equipment will also make corresponding actions , send ACK Handshake packet 、NAK Handshake packets or STALL Handshake packet .
Relatively speaking, for 【 Control write 】 transmission , The host will send IN Token packet , Then, the device sends out the 0 Of length DATA1 Packet , The host makes corresponding actions again : send ACK Handshake packet 、NAK Handshake packets or STALL Handshake packet .
3.2 Bulk transfer (Bulk Transfer)
Used to transmit large amounts of data , Request that the transmission cannot fail , But there is no requirement for time , Suitable for printers 、 Storage devices, etc .
Batch transmission is a reliable transmission , A handshake packet is required to indicate the result of the transmission . If the amount of data is large , Multiple batch transaction transfers will be used to complete the transmission of all data , Of packets during transmission PID according to DATA0-DATA1-DATA0-… Flip... In a way , To ensure the synchronization between the sender and the receiver .
USB Allow continuous 3 Less than transmission errors , The transfer will be retried , If successful, reset the error count , Otherwise, the counter is accumulated . After more than three times ,HOST It is considered that the endpoint function is wrong (STALL), Abandon the transmission task of the endpoint .
One batch transmission (Transfer) from 1 One to more batch transaction transfers (Transaction) form .
Flip synchronization : The sending end follows DATA0-DATA1-DATA0-… Send packets in order , Only a successful transaction transfer will result in PID Flip , That is to say, the sender only receives ACK And then flip PID, Send next packet , Otherwise, this transaction transfer will be retried . Again , If it is found at the receiving end that the received packets are not flipped in this order , For example, two consecutive DATA0, Then the receiving end considers the second DATA0 It was the previous one DATA0 The retransmission .
It is implemented at the hardware level “ Error detection ” and “ Retransmission ” To make sure that host And device Between “ Accurate ” Transmit data more efficiently , Can rely on transmission . It consists of three kinds of bags ( namely IN Business or OUT Business ):
- token
- data
- handshake
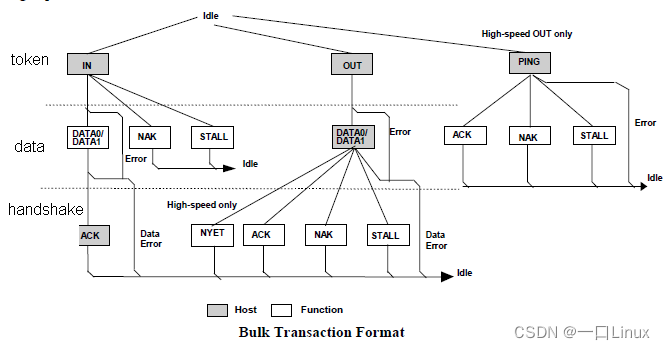
- For IN Token ( namely :IN Transaction)
- ACK: Express host Receive data correctly
- NAK: Indicates that the device is temporarily unable to return or receive data ( Such as : The device is busy )
- STALL: Indicates that the device will stop forever , need host Software intervention ( Such as : Device error )
- For OUT Token ( namely :OUT Transaction)
If the received packet is incorrect , Such as :CRC error ,Device Don't send any handshake package
- ACK: Device The packet has been received correctly , And notify Host You can send the next packet in sequence
- NAK: Device The packet has been received correctly , And notify Host Retransmission data , because Device Temporary situation ( Such as buffer full )
- STALL: instructions Device endpoint Has stopped , And notify Host No retransmission
- Bulk Read write sequence
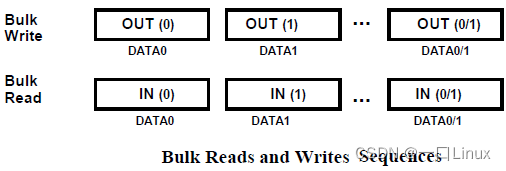
That is, by a system IN Business or OUT Transaction composition .
3.3 Interrupt transmission (Interrupt Transfer)
Interrupt transmission by IN or OUT Transaction composition .
Interrupt transmission is not supported in the process PING outside , Others are the same as batch transmission . The only difference between them is that the endpoint of transaction transmission is different 、 The maximum package length supported is different 、 Different priorities and other things that are transparent to users .
When the host schedules an interrupt transmission task , The interrupt transmission will be initiated according to the query interval specified in the corresponding interrupt endpoint descriptor . Interrupt transmission has a higher priority , Second only to synchronous transmission .
Similarly, interrupt transmission also adopts PID Flip mechanism to ensure data synchronization at the receiving and transmitting ends . The following figure shows the flow chart of interrupt transmission .
Interrupt transmission mode is always used to query the equipment , To determine whether there is data to be transmitted . Therefore, the direction of interrupt transmission is always from USB Device to host .

DATA0 or DATA1 Contains interrupt information , Instead of interrupting data .
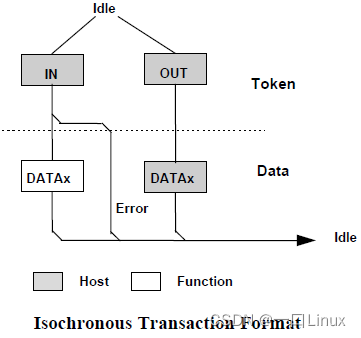
3.4 Synchronous transmission (Isochronous Transfer)
- It consists of two packages :
- token
- data
Synchronous transmission is not supported “handshake” and “ Retransmission capability ”, So it is unreliable transmission .
Synchronous transmission is an unreliable transmission , So it doesn't have a handshake bag , Nor does it support PID Flip . When the host schedules a transaction transfer , Synchronous transmission has the highest priority .
Synchronous transmission applies when you must arrive at a fixed rate or at a specified time , Can tolerate occasional wrong data . Real time transmission is generally used for wheat Kefeng 、 horn 、UVC Camera Other equipment . Real time transmission only requires two packet stages, token and data , No handshake bag , Therefore, the data will not be retransmitted when it is wrong .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Devops' operational and commercial benefits Guide

Functions and usage of viewflipper
Create dialog style windows with popupwindow
【网络攻防原理与技术】第5章:拒绝服务攻击
Supplementary instructions to relevant rules of online competition
2021-06-28

《世界粮食安全和营养状况》报告发布:2021年全球饥饿人口增至8.28亿
自动化测试:Robot FrameWork框架大家都想知道的实用技巧

viewflipper的功能和用法
swiper左右切换滑块插件
随机推荐
第2章搭建CRM项目开发环境(数据库设计)
Threshold segmentation based on RGB image and threshold adjustment by sliding
zdog.js火箭转向动画js特效
本周小贴士131:特殊成员函数和`= default`
本周小贴士#134:make_unique与私有构造函数
第3章业务功能开发(安全退出)
cf:C. Factorials and Powers of Two【dp + 排序 + 选不选板子 + 选若干个数等于已知和的最少数】
TabHOST 选项卡的功能和用法
企业经营12法的领悟
【TPM2.0原理及应用指南】 12、13、14章
Devops' operational and commercial benefits Guide
Yarn capacity scheduler (ultra detailed interpretation)
YARN Capacity Scheduler容量调度器(超详细解读)
Robot engineering lifelong learning and work plan-2022-
L1-028 判断素数(Lua)
<代码随想录二刷>链表
LeetCode 497(C#)
跟奥巴马一起画方块(Lua)
actionBar 导航栏学习
第3章业务功能开发(实现记住账号密码)