当前位置:网站首页>Full stack development of quartz distributed timed task scheduling cluster
Full stack development of quartz distributed timed task scheduling cluster
2022-07-06 09:22:00 【Heartsuit】
background
We have a scheduled task in a single project , Every other hour, it will query and calculate the scores of different users from each business table 、 ranking , It's using Quartz Realized ; This was later expanded horizontally to multi instance cluster deployment , Have a problem : Timed tasks are used in many application instances repeat 了 , Obviously, this is not what we expected , At the same time, it is also a waste of computing resources , What's more serious is the inconsistency of data for a period of time , At this time, it involves the scheduling of tasks in the cluster environment Idempotency problem .
Timing task
About the implementation of timed tasks , It can be done by Spring Of @EnableScheduling , quartz , xxl-job , elastic-job And other solutions . We chose at the beginning Quartz To achieve timing tasks , Here is the main introduction Quartz Construction of distributed cluster service for scheduled tasks .
Distributed cluster task scheduling
How to solve the idempotency problem of distributed task scheduling ? There are generally the following options :
- The configuration file , Switch identification ,flag; Single point
- Distributed lock ,ZooKeeper,Redis; complex
- Timed task decoupling , Independent deployment ; Single point , It should be performed in a load balancing manner
here , We need a simple 、 direct 、 Effective way , Can pass Quartz Cluster solution , No matter how many application instances there are in the cluster , Timed tasks can only be triggered once .
Although single Quartz The instance has good task scheduling ability , But it can't meet the needs of a typical enterprise , Such as scalability 、 High availability . If you need the ability to fail over and run an increasing number of tasks , Quartz Clustering is bound to become a part of your application .
Use Quartz The ability of clustering can better support your business needs , And even if one of the machines crashes at the worst time, it can ensure that all tasks are performed .
Note: Unlike many clusters of application services , independent Quartz The node does not communicate with the other node or the management node . Quartz An application perceives another application through a database table .
Data sheet
Quartz The official provided 11 Data sheets ( Here we use innodb Of SQL file ), Table structure information can be found in IDEA Found in the external dependencies in (Tip: Also available at IDEA Double click directly in Shift, Input tables_mysql_innodb You can quickly locate this SQL file ; You can also copy directly from the end of the article SQL):
.m2\repository\org\quartz-scheduler\quartz\2.3.2\quartz-2.3.2.jar!\org\quartz\impl\jdbcjobstore\tables_mysql_innodb.sql
- 11 Zhang Biaoming
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_PAUSED_TRIGGER_GRPS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_SCHEDULER_STATE;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_LOCKS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_SIMPLE_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_SIMPROP_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_CRON_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_BLOB_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_JOB_DETAILS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_CALENDARS;
- 11 A table shows
| Serial number | Table name | explain |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | QRTZ_CALENDARS | Storage Quartz Calendar information |
| 2 | QRTZ_CRON_TRIGGERS | Deposit Cron Type of Trigger, Include Cron Expressions and time zone information |
| 3 | QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS | Store with triggered Trigger Relevant status information , And connected Job Execution information for |
| 4 | QRTZ_PAUSED_TRIGGER_GRPS | Store paused Trigger Group information |
| 5 | QRTZ_SCHEDULER_STATE | Store a small amount of Scheduler Relevant status information |
| 6 | QRTZ_LOCKS | Store lock information , Provide distributed locks for multiple node scheduling , Realize distributed scheduling , The default is 2 A lock : STATE_ACCESS, TRIGGER_ACCESS |
| 7 | QRTZ_JOB_DETAILS | Store every configured JobDetail Information |
| 8 | QRTZ_SIMPLE_TRIGGERS | Storage Simple Type of Trigger, Including the number of repetitions 、 interval 、 And the number of touches |
| 9 | QRTZ_BLOG_TRIGGERS | With Blob Type stored Trigger |
| 10 | QRTZ_TRIGGERS | Store configured Trigger Basic information of |
| 11 | QRTZ_SIMPROP_TRIGGERS | Storage CalendarIntervalTrigger and DailyTimeIntervalTrigger Two types of triggers |
11 Details of the table , Reference resources :https://blog.csdn.net/xiaoniu_888/article/details/83181078
Note:cron The method needs to use 4 Data sheets :QRTZ_TRIGGERS,QRTZ_CRON_TRIGGERS,QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS,QRTZ_JOB_DETAILS.
The configuration file
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.100.114:3306/quartz_task?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
quartz:
job-store-type: jdbc
properties:
org:
quartz:
jobStore:
class: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.JobStoreTX
clusterCheckinInterval: 10000
driverDelegateClass: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.StdJDBCDelegate
isClustered: true
tablePrefix: QRTZ_
useProperties: false
scheduler:
instanceId: AUTO
instanceName: clusteredScheduler
threadPool:
class: org.quartz.simpl.SimpleThreadPool
threadCount: 10
threadPriority: 5
threadsInheritContextClassLoaderOfInitializingThread: true
Description of main configuration items :
- org.quartz.scheduler.instanceName Property can be any value , Use in JDBC JobStore To uniquely identify the instance , But all cluster nodes must be the same .
- org.quartz.scheduler.instanceId The attribute is AUTO that will do , Generate an instance based on the host name and timestamp ID.
- org.quartz.jobStore.class The attribute is JobStoreTX, Persisting tasks into data . Because nodes in the cluster depend on the database to propagate Scheduler Status of the instance , You can only use JDBC JobStore When the application
Quartzcolony . That means you have to use JobStoreTX or JobStoreCMT As Job Storage ; You cannot use... In a cluster RAMJobStore. - org.quartz.jobStore.isClustered The attribute is true, You told me Scheduler The instance wants it to participate in a cluster . This attribute will run through the whole scheduling framework , Used to modify the default behavior of operations in a cluster environment .
- org.quartz.jobStore.clusterCheckinInterval Property defines Scheduler How often instances are checked into the database ( Company : millisecond ).Scheduler Check whether other instances are not checked in when they should be ; This points to a failed Scheduler example , And the current Scheduler Will take over any failed and recoverable Job. By checking in ,Scheduler It also updates its own status record .clusterCheckinInterval The smaller it is ,Scheduler Node check failed Scheduler The more frequent the instances are . The default value is 15000( namely 15 second ).
task management
To achieve Quartz Scheduled task distributed cluster service , The core data table and configuration file are enough ; Besides , To facilitate task management , We have also achieved RESTful Style task management interface :
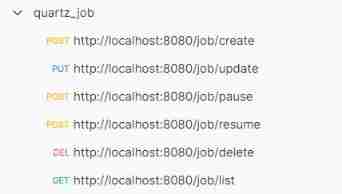
- Add tasks :http://localhost:8080/job/create
- Modify task :http://localhost:8080/job/update
- Suspend task :http://localhost:8080/job/pause
- Recovery task :http://localhost:8080/job/resume
- Delete task :http://localhost:8080/job/delete
- Get task list :http://localhost:8080/job/list
Service layer core code
- Add tasks
/** * add to cron Expression task * * @param info */
public void addCronJob(TaskInfo info) {
String jobName = info.getJobName();
String jobClassName = info.getJobClassName();
String jobGroupName = info.getJobGroupName();
String jobDescription = info.getJobDescription();
String cronExpression = info.getCronExpression();
Date createTime = new Date();
JobDataMap dataMap = new JobDataMap();
if (info.getData() != null) {
dataMap.putAll(info.getData());
}
dataMap.put("createTime", createTime);
try {
if (checkExists(jobName, jobGroupName)) {
throw new CustomException(String.format(" The task already exists , jobName:[%s],jobGroup:[%s]", jobName, jobGroupName));
}
TriggerKey triggerKey = TriggerKey.triggerKey(jobName, jobGroupName);
JobKey jobKey = JobKey.jobKey(jobName, jobGroupName);
CronScheduleBuilder schedBuilder = CronScheduleBuilder
.cronSchedule(cronExpression)
.withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing();
CronTrigger trigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.withIdentity(triggerKey)
.withSchedule(schedBuilder).build();
Class<? extends Job> clazz = (Class<? extends Job>) Class
.forName(jobClassName);
JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(clazz).withIdentity(jobKey)
.withDescription(jobDescription).usingJobData(dataMap).build();
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail, trigger);
log.info(" Mission : {} Add success ", jobName);
} catch (SchedulerException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new CustomException(" Task addition failed ");
}
}
- Modify task
/** * Modify scheduled tasks * * @param info */
public void editCronJob(TaskInfo info) {
String jobName = info.getJobName();
String jobGroupName = info.getJobGroupName();
String jobDescription = info.getJobDescription();
String cronExpression = info.getCronExpression();
JobDataMap dataMap = new JobDataMap();
if (info.getData() != null) {
dataMap.putAll(info.getData());
}
try {
if (!checkExists(jobName, jobGroupName)) {
throw new CustomException(
String.format("Job non-existent , jobName:{%s},jobGroup:{%s}", jobName, jobGroupName));
}
TriggerKey triggerKey = TriggerKey.triggerKey(jobName, jobGroupName);
JobKey jobKey = new JobKey(jobName, jobGroupName);
CronScheduleBuilder cronScheduleBuilder = CronScheduleBuilder
.cronSchedule(cronExpression)
.withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing();
CronTrigger cronTrigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.withIdentity(triggerKey)
.withSchedule(cronScheduleBuilder).build();
JobDetail jobDetail = scheduler.getJobDetail(jobKey);
jobDetail = jobDetail.getJobBuilder().withDescription(jobDescription).usingJobData(dataMap).build();
HashSet<Trigger> triggerSet = new HashSet<>();
triggerSet.add(cronTrigger);
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail, triggerSet, true);
} catch (SchedulerException e) {
throw new CustomException(" Class name does not exist or expression execution error ");
}
}
- Suspend task
/** * Pause scheduled tasks * * @param jobName * @param jobGroup */
public void pauseJob(String jobName, String jobGroup) {
TriggerKey triggerKey = TriggerKey.triggerKey(jobName, jobGroup);
try {
if (checkExists(jobName, jobGroup)) {
scheduler.pauseTrigger(triggerKey);
log.info(" Mission : {} Pause succeeded ", jobName);
} else {
log.warn(" Task not found :{}", jobName);
}
} catch (SchedulerException e) {
throw new CustomException(e.getMessage());
}
}
- Recovery task
/** * Resume suspended tasks * * @param jobName * @param jobGroup */
public void resumeJob(String jobName, String jobGroup) {
TriggerKey triggerKey = TriggerKey.triggerKey(jobName, jobGroup);
try {
if (checkExists(jobName, jobGroup)) {
scheduler.resumeTrigger(triggerKey);
log.info(" Mission : {} Recovery successful ", jobName);
} else {
log.warn(" Task not found :{}", jobName);
}
} catch (SchedulerException e) {
throw new CustomException(e.getMessage());
}
}
- Delete task
/** * Delete scheduled tasks * * @param jobName * @param jobGroup */
public void deleteJob(String jobName, String jobGroup) {
TriggerKey triggerKey = TriggerKey.triggerKey(jobName, jobGroup);
try {
if (checkExists(jobName, jobGroup)) {
scheduler.pauseTrigger(triggerKey);
scheduler.unscheduleJob(triggerKey);
log.info(" Mission : {} Delete successful ", jobName);
} else {
log.warn(" Task not found :{}", jobName);
}
} catch (SchedulerException e) {
throw new CustomException(e.getMessage());
}
}
- Get task list
/** * Get task list * * @return */
public List<TaskInfo> getJobList() {
List<TaskInfo> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
for (String groupJob : getJobGroupNames()) {
for (JobKey jobKey : scheduler.getJobKeys(GroupMatcher.<JobKey>groupEquals(groupJob))) {
List<? extends Trigger> triggers = scheduler.getTriggersOfJob(jobKey);
for (Trigger trigger : triggers) {
Trigger.TriggerState triggerState = scheduler.getTriggerState(trigger.getKey());
JobDetail jobDetail = scheduler.getJobDetail(jobKey);
String cronExpression = "";
Date createTime = null;
long repeatInterval = 0L;
int repeatCount = 0;
Date startDate = null;
Date endDate = null;
if (trigger instanceof CronTrigger) {
CronTrigger cronTrigger = (CronTrigger) trigger;
cronExpression = cronTrigger.getCronExpression();
} else if (trigger instanceof SimpleTrigger) {
SimpleTrigger simpleTrigger = (SimpleTrigger) trigger;
repeatInterval = simpleTrigger.getRepeatInterval();
repeatCount = simpleTrigger.getRepeatCount();
startDate = simpleTrigger.getStartTime();
endDate = simpleTrigger.getEndTime();
}
TaskInfo info = new TaskInfo();
info.setData(jobDetail.getJobDataMap());
info.setJobName(jobKey.getName());
info.setJobTrigger(trigger.getClass().getName());
info.setJobGroupName(jobKey.getGroup());
info.setJobClassName(jobDetail.getJobClass().getName());
info.setJobDescription(jobDetail.getDescription());
info.setJobStatus(triggerState.name());
info.setCronExpression(cronExpression);
info.setCreateTime(createTime);
info.setRepeatInterval(repeatInterval);
info.setRepeatCount(repeatCount);
info.setStartDate(startDate);
info.setEndDate(endDate);
list.add(info);
}
}
}
} catch (SchedulerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
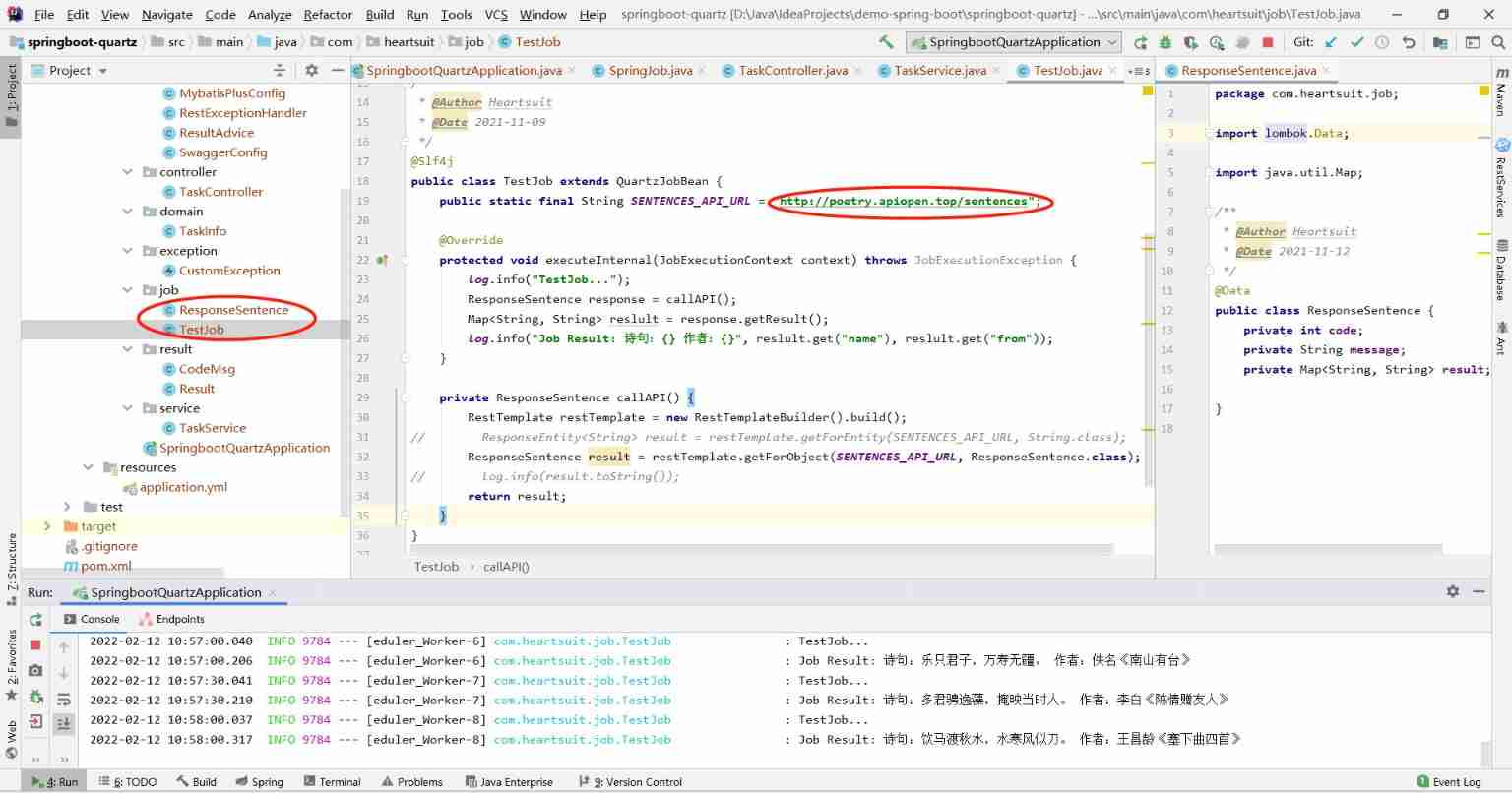
test Job
Here is a test task as an example , timing ( every other 30s) Request a verse to an open interface to demonstrate the execution of timed tasks .
Non business processing
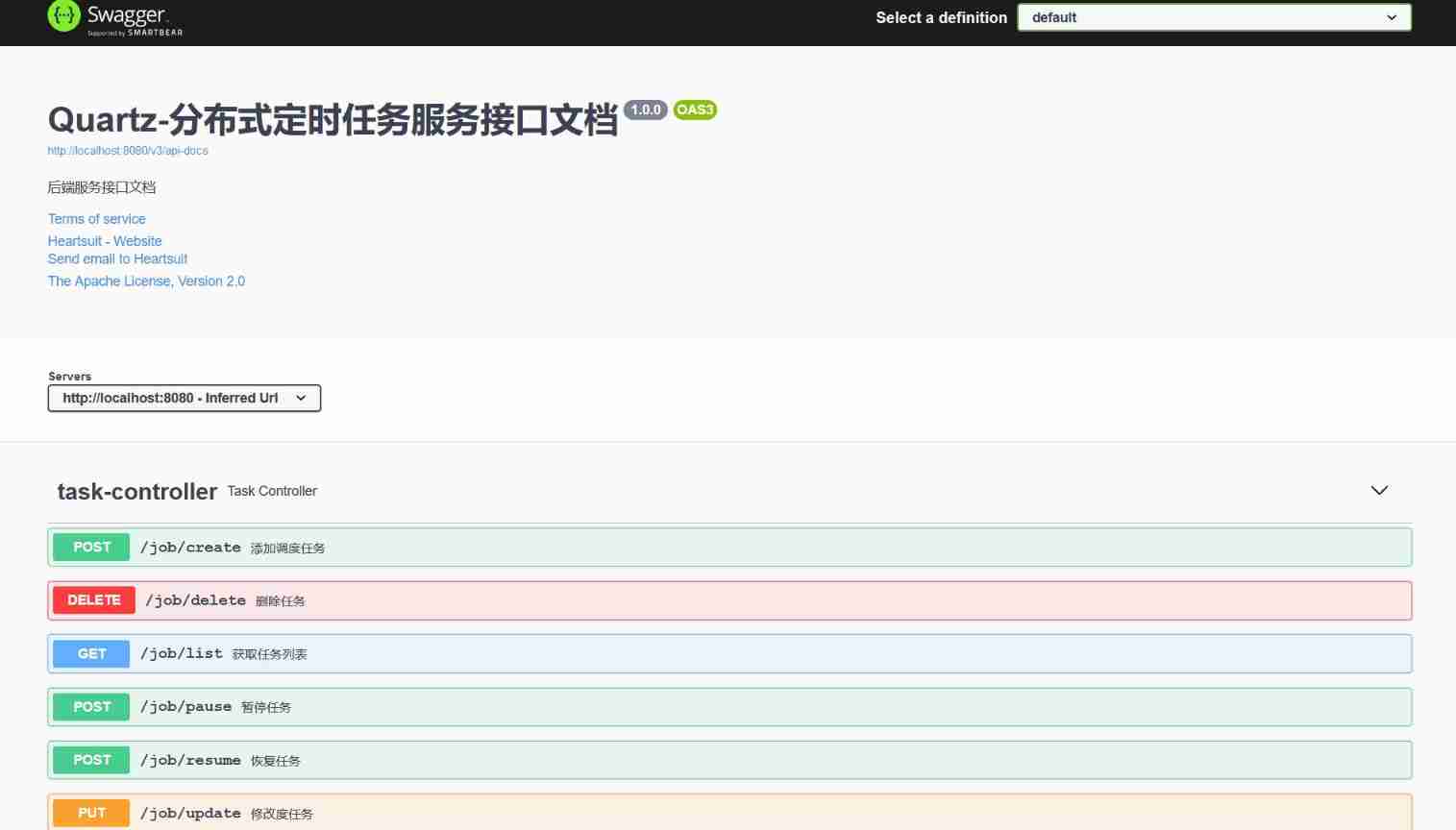
The following non business functions : Unified response encapsulation , Global exception interception , Paging query , Swagger3 Interface document .
Task scheduling effect display
Realized Quartz After the scheduled task cluster service , We need to verify whether it can achieve : No matter how many application instances there are in the cluster , Timed tasks can only be triggered once This effect .
Here I use three service examples ( Local development environment 1 Service number A, Each of the two servers on the virtual machine 1 A service , Number separately B、C) To verify .
- Compile the package :mvn clean package
- Will be compiled jar Upload the package to the virtual machine
- Start this separately 3 An example :java -jar springboot-quartz-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
3 After all instances are started , The main changes of data in database tables are qrtz_scheduler_state This table : With 3 Running service instances , Other tables can be observed by yourself , Don't put the picture ..
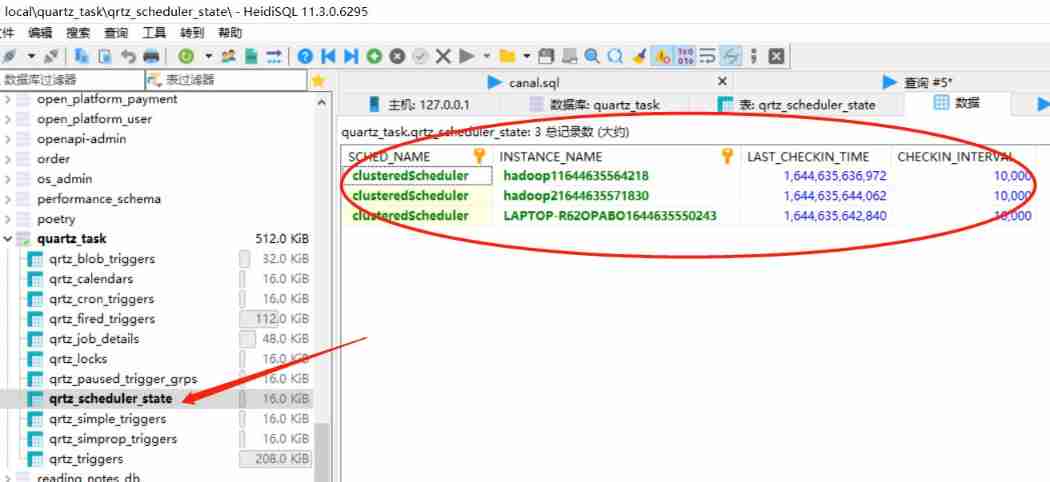
- start-up 3 An example
start-up 3 After an example , We found that , Quartz The implementation of the cluster does not balance the load between different instances in the cluster like other middleware , But on one of them ( example A) The above continues . Then when a service hangs up , How to achieve failover ? Don't worry. , Now let's try to hang up a service .
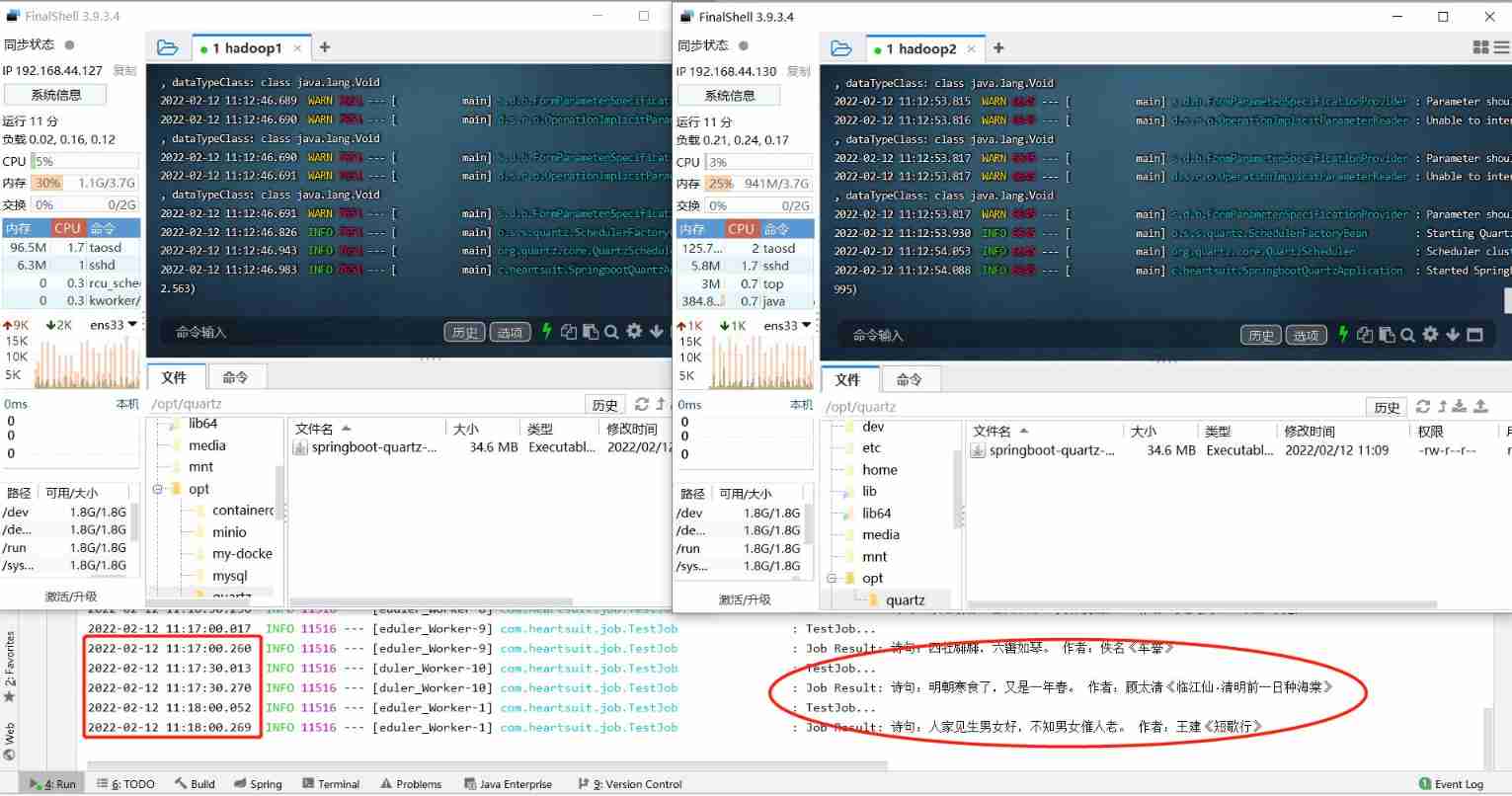
- Close the service instance that executes the task
Close the service instance that executes the task ( Here is an example in the development environment A) after , adopt Quartz Cluster scheduling , We found that one of the remaining two instances ( example C) A hung instance was detected , The log is as follows , Then the task switches to the instance C Continue on .
2022-02-12 11:19:54.322 INFO 6645 --- [_ClusterManager] o.s.s.quartz.LocalDataSourceJobStore : ClusterManager: detected 1 failed or restarted instances.
2022-02-12 11:19:54.322 INFO 6645 --- [_ClusterManager] o.s.s.quartz.LocalDataSourceJobStore : ClusterManager: Scanning for instance "LAPTOP-R62OPABO1644635550243"'s failed in-progress jobs.
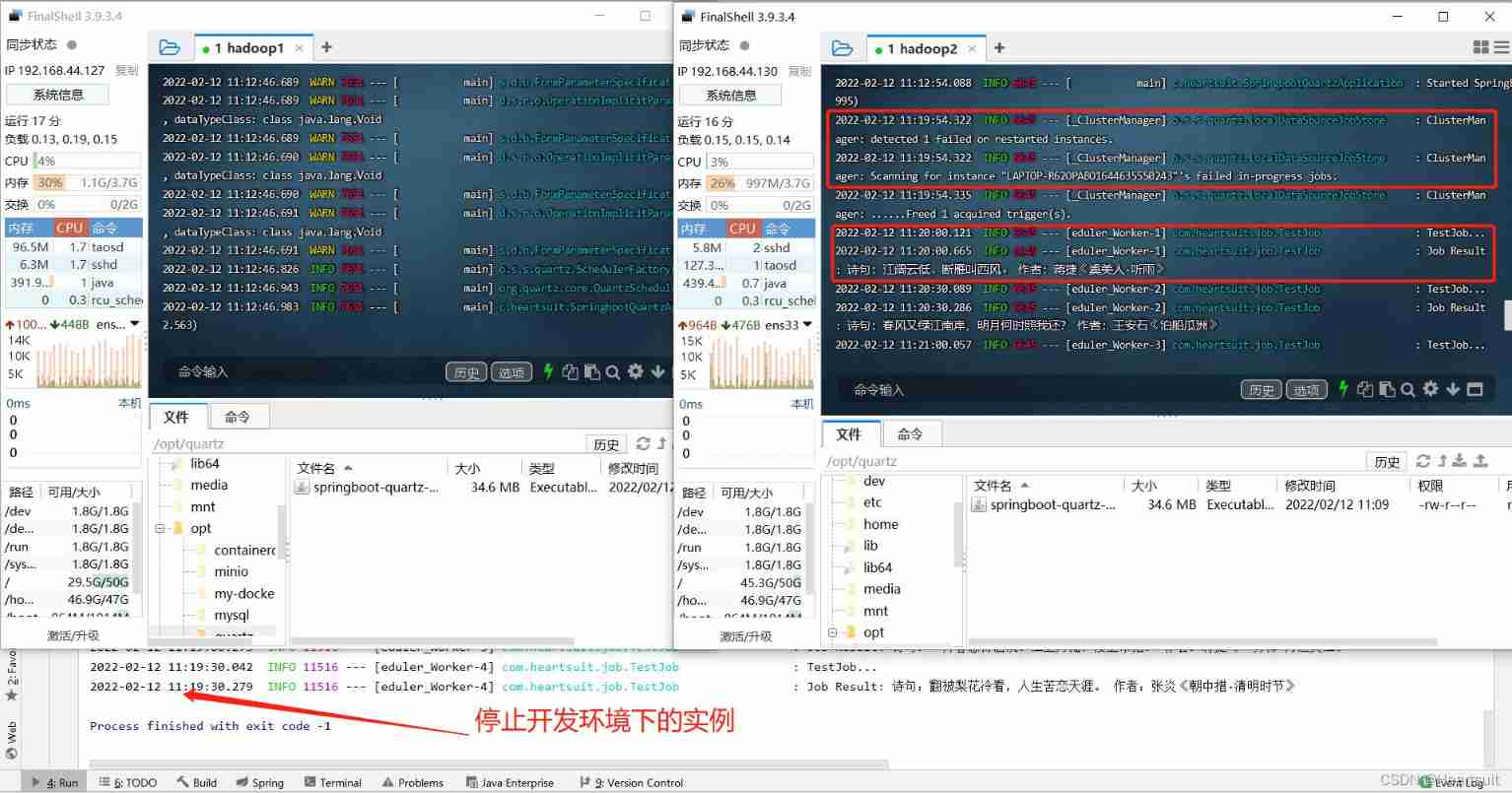
- Close the service instance executing the task again
We close the service instance that executes the task again ( Here's an example C) after , adopt Quartz Cluster scheduling , We found that the task will automatically switch to the remaining 1 An example B Continue on .
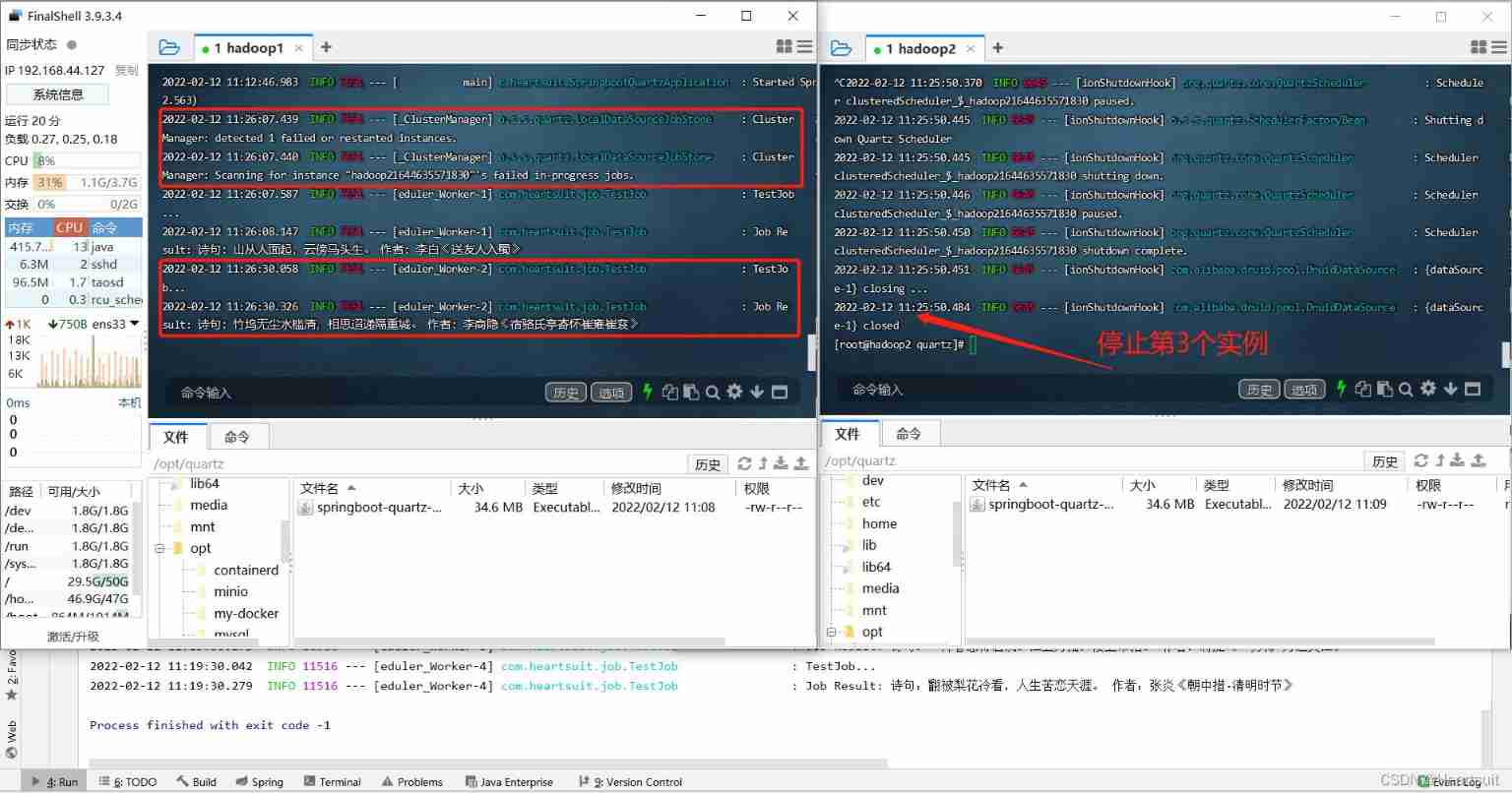
thus , We can come to a conclusion :
QuartzScheduled task cluster service scheduling , Unlike other middleware, it does not balance the load between different instances in the cluster , But on one of them ;- Once it is detected that a service instance stops running , The task will switch to the normally running service instance to continue execution , That's it No matter how many application instances there are in the cluster , Timed tasks can only be triggered once This effect , At the same time, we have a Fail over Distributed task scheduling cluster .
The official data sheet structure is attached
#
# In your Quartz properties file, you'll need to set
# org.quartz.jobStore.driverDelegateClass = org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.StdJDBCDelegate
#
#
# By: Ron Cordell - roncordell
# I didn't see this anywhere, so I thought I'd post it here. This is the script from Quartz to create the tables in a MySQL database, modified to use INNODB instead of MYISAM.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_PAUSED_TRIGGER_GRPS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_SCHEDULER_STATE;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_LOCKS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_SIMPLE_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_SIMPROP_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_CRON_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_BLOB_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_TRIGGERS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_JOB_DETAILS;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS QRTZ_CALENDARS;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_JOB_DETAILS(
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
JOB_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
JOB_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
DESCRIPTION VARCHAR(250) NULL,
JOB_CLASS_NAME VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL,
IS_DURABLE VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL,
IS_NONCONCURRENT VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL,
IS_UPDATE_DATA VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL,
REQUESTS_RECOVERY VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL,
JOB_DATA BLOB NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,JOB_NAME,JOB_GROUP))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_TRIGGERS (
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
JOB_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
JOB_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
DESCRIPTION VARCHAR(250) NULL,
NEXT_FIRE_TIME BIGINT(13) NULL,
PREV_FIRE_TIME BIGINT(13) NULL,
PRIORITY INTEGER NULL,
TRIGGER_STATE VARCHAR(16) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_TYPE VARCHAR(8) NOT NULL,
START_TIME BIGINT(13) NOT NULL,
END_TIME BIGINT(13) NULL,
CALENDAR_NAME VARCHAR(190) NULL,
MISFIRE_INSTR SMALLINT(2) NULL,
JOB_DATA BLOB NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP),
FOREIGN KEY (SCHED_NAME,JOB_NAME,JOB_GROUP)
REFERENCES QRTZ_JOB_DETAILS(SCHED_NAME,JOB_NAME,JOB_GROUP))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_SIMPLE_TRIGGERS (
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
REPEAT_COUNT BIGINT(7) NOT NULL,
REPEAT_INTERVAL BIGINT(12) NOT NULL,
TIMES_TRIGGERED BIGINT(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP),
FOREIGN KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP)
REFERENCES QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_CRON_TRIGGERS (
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
CRON_EXPRESSION VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
TIME_ZONE_ID VARCHAR(80),
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP),
FOREIGN KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP)
REFERENCES QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_SIMPROP_TRIGGERS
(
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
STR_PROP_1 VARCHAR(512) NULL,
STR_PROP_2 VARCHAR(512) NULL,
STR_PROP_3 VARCHAR(512) NULL,
INT_PROP_1 INT NULL,
INT_PROP_2 INT NULL,
LONG_PROP_1 BIGINT NULL,
LONG_PROP_2 BIGINT NULL,
DEC_PROP_1 NUMERIC(13,4) NULL,
DEC_PROP_2 NUMERIC(13,4) NULL,
BOOL_PROP_1 VARCHAR(1) NULL,
BOOL_PROP_2 VARCHAR(1) NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP),
FOREIGN KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP)
REFERENCES QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_BLOB_TRIGGERS (
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
BLOB_DATA BLOB NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP),
INDEX (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME, TRIGGER_GROUP),
FOREIGN KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP)
REFERENCES QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_CALENDARS (
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
CALENDAR_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
CALENDAR BLOB NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,CALENDAR_NAME))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_PAUSED_TRIGGER_GRPS (
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS (
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
ENTRY_ID VARCHAR(95) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
TRIGGER_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
INSTANCE_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
FIRED_TIME BIGINT(13) NOT NULL,
SCHED_TIME BIGINT(13) NOT NULL,
PRIORITY INTEGER NOT NULL,
STATE VARCHAR(16) NOT NULL,
JOB_NAME VARCHAR(190) NULL,
JOB_GROUP VARCHAR(190) NULL,
IS_NONCONCURRENT VARCHAR(1) NULL,
REQUESTS_RECOVERY VARCHAR(1) NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,ENTRY_ID))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_SCHEDULER_STATE (
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
INSTANCE_NAME VARCHAR(190) NOT NULL,
LAST_CHECKIN_TIME BIGINT(13) NOT NULL,
CHECKIN_INTERVAL BIGINT(13) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,INSTANCE_NAME))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE QRTZ_LOCKS (
SCHED_NAME VARCHAR(120) NOT NULL,
LOCK_NAME VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCHED_NAME,LOCK_NAME))
ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_J_REQ_RECOVERY ON QRTZ_JOB_DETAILS(SCHED_NAME,REQUESTS_RECOVERY);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_J_GRP ON QRTZ_JOB_DETAILS(SCHED_NAME,JOB_GROUP);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_J ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,JOB_NAME,JOB_GROUP);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_JG ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,JOB_GROUP);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_C ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,CALENDAR_NAME);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_G ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_STATE ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_STATE);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_N_STATE ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP,TRIGGER_STATE);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_N_G_STATE ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP,TRIGGER_STATE);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_NEXT_FIRE_TIME ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,NEXT_FIRE_TIME);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_NFT_ST ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_STATE,NEXT_FIRE_TIME);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_NFT_MISFIRE ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,MISFIRE_INSTR,NEXT_FIRE_TIME);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_NFT_ST_MISFIRE ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,MISFIRE_INSTR,NEXT_FIRE_TIME,TRIGGER_STATE);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_T_NFT_ST_MISFIRE_GRP ON QRTZ_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,MISFIRE_INSTR,NEXT_FIRE_TIME,TRIGGER_GROUP,TRIGGER_STATE);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_FT_TRIG_INST_NAME ON QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,INSTANCE_NAME);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_FT_INST_JOB_REQ_RCVRY ON QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,INSTANCE_NAME,REQUESTS_RECOVERY);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_FT_J_G ON QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,JOB_NAME,JOB_GROUP);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_FT_JG ON QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,JOB_GROUP);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_FT_T_G ON QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP);
CREATE INDEX IDX_QRTZ_FT_TG ON QRTZ_FIRED_TRIGGERS(SCHED_NAME,TRIGGER_GROUP);
commit;
If you have any questions or any bugs are found, please feel free to contact me.
Your comments and suggestions are welcome!
边栏推荐
- Selenium+pytest automated test framework practice (Part 2)
- BMINF的后训练量化实现
- go-redis之初始化连接
- Leetcode: Jianzhi offer 04 Search in two-dimensional array
- IDS cache preheating, avalanche, penetration
- 在QWidget上实现窗口阻塞
- Advanced Computer Network Review(3)——BBR
- [oc]- < getting started with UI> -- common controls - prompt dialog box and wait for the prompt (circle)
- Redis之主从复制
- What is MySQL? What is the learning path of MySQL
猜你喜欢
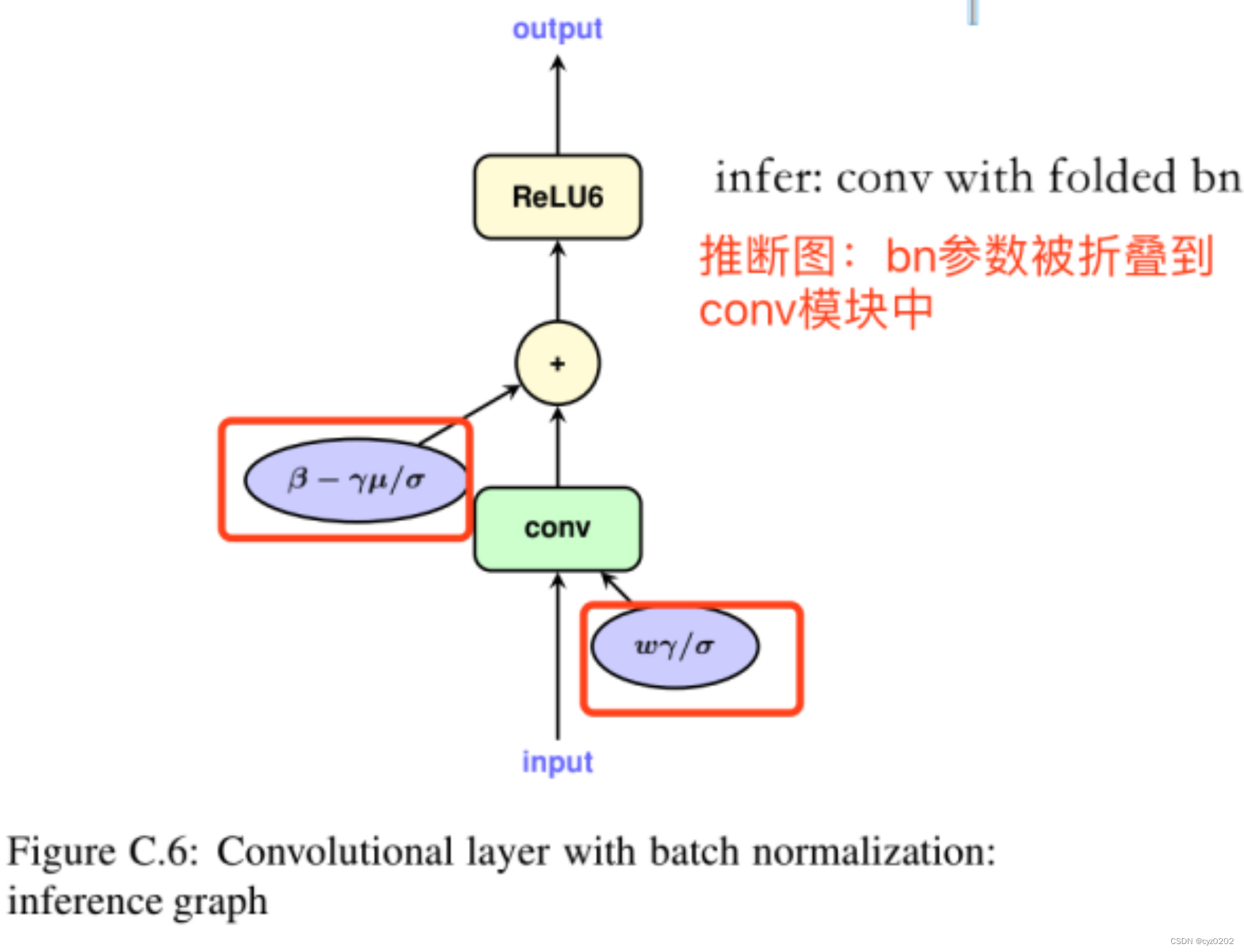
BN folding and its quantification
Redis之Lua脚本
CUDA implementation of self defined convolution attention operator
How to intercept the string correctly (for example, intercepting the stock in operation by applying the error information)

IDS' deletion policy

Different data-driven code executes the same test scenario

Redis之连接redis服务命令
甘肃旅游产品预订增四倍:“绿马”走红,甘肃博物馆周边民宿一房难求
Redis之持久化实操(Linux版)

Pytest之收集用例规则与运行指定用例
随机推荐
Global and Chinese market for annunciator panels 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
[oc]- < getting started with UI> -- learning common controls
Kratos战神微服务框架(三)
Pytest之收集用例规则与运行指定用例
运维,放过监控-也放过自己吧
The carousel component of ant design calls prev and next methods in TS (typescript) environment
[three storage methods of graph] just use adjacency matrix to go out
【文本生成】论文合集推荐丨 斯坦福研究者引入时间控制方法 长文本生成更流畅
Advance Computer Network Review(1)——FatTree
Redis之核心配置
[oc]- < getting started with UI> -- common controls uibutton
Advanced Computer Network Review(5)——COPE
Kratos战神微服务框架(二)
BMINF的后训练量化实现
Redis之哨兵模式
Basic usage of xargs command
Sentinel mode of redis
注意力机制的一种卷积替代方式
QML type: overlay
Redis之cluster集群