当前位置:网站首页>2022-5-the fourth week daily
2022-5-the fourth week daily
2022-07-05 06:23:00 【mentalps】
0 2022/5/23
1 Provably Secure Federated Learning against Malicious Clients Code reappearance
1.1 aggregator.py
import numpy as np
class FedAvg:
def __init__(self, global_model, different_client_values, client_count):
global_weights = np.array(global_model.getWeights())
for i in range(len(different_client_values)):
global_weights -= different_client_values[i] / client_count
global_model.setWeights(global_weights)
1.2 model.py
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Activation,Flatten
from keras.models import model_from_json
import tensorflow as tf
class Model:
def __init__(self):
self.model = Sequential()
self.model.add(Flatten())
self.model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
self.model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
self.model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
def saveModel(self, name):
model_json = self.model.to_json()
with open("model/model_%s.json" % name, "w") as json_file:
json_file.write(model_json)
# serialize weights to HDF5
self.model.save_weights("model/model_%s.h5" % name)
print("Saved model to disk")
def loadModel(self, name):
json_file = open('model/model_%s.json' % name, 'r')
loaded_model_json = json_file.read()
json_file.close()
loaded_model = model_from_json(loaded_model_json)
# load weights into new model
loaded_model.load_weights("model/model_%s.h5" % name)
print("Loaded model from disk")
loaded_model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True), metrics=['accuracy'])
return loaded_model
def run(self, X, Y, load=True):
if (load):
self.model = self.loadModel('sever_model')
self.model.fit(X, Y, epochs=2)
def evaluate(self, X, Y, verbose=2):
return self.model.evaluate(X, Y, verbose=verbose)
def loss(self, X, Y):
return self.model.evaluate(X, Y)[0]
def predict(self, X):
return self.model.predict(X)
def getWeights(self):
return self.model.get_weights()
def setWeights(self, weight):
self.model.set_weights(weight)
1.3 data.py
from tensorflow.python.keras.datasets import cifar10, mnist, fashion_mnist
import numpy as np
def Mnist_data():
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 28 * 28) / 255
x_test = x_test.reshape(-1, 28 * 28) / 255
return x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test
def generate_client_data(num_clients=10):
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 28 * 28) / 255
x_test = x_test.reshape(-1, 28 * 28) / 255
data = list(zip(x_train, y_train))
size = len(data) // num_clients
shards = [data[i:i+size] for i in range(0, size * num_clients, size)]
return data, shards, x_test, y_test
def generate_malice_data(data):
x, y = zip(*data)
x = np.array(x)
y = np.array(y)
for i in range(len(y)):
if y[i] == 1:
y[i] = 2
return list(zip(x, y))
#
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# data, shards, x_test, y_test = generate_client_data(4)
# x_1, y_1 = zip(*shards[0])
#
# print(type(x_test))
1.4 main.py
import numpy as np
import data
import model
import aggregator
ClientNum = 5
EPOCH = 5
if __name__ == '__main__':
data1, shards, x_test, y_test = data.generate_client_data(ClientNum)
model_client = []
for i in range(ClientNum):
model_client.append(model.Model())
global_model = model.Model()
shards[0] = data.generate_malice_data(shards[0])
shards[1] = data.generate_malice_data(shards[1])
x_all = []
y_all = []
for i in range(ClientNum):
xx, yy = zip(*shards[i])
xx = np.array(xx)
yy = np.array(yy)
x_all.append(xx)
y_all.append(yy)
a_0 = np.argmax(global_model.predict(x_all[0][0:784]))
global_model.saveModel('sever_model')
for i in range(ClientNum):
np.argmax(model_client[i].predict(x_all[0][0:784]))
for i in range(EPOCH):
client_difference_value = []
for j in range(ClientNum):
model_client[j].setWeights(global_model.getWeights())
for j in range(ClientNum):
model_client[j].run(x_all[j], y_all[j])
for j in range(ClientNum):
client_difference_value.append(np.array(global_model.getWeights()) - np.array(model_client[j].getWeights()))
fedavg = aggregator.FedAvg(global_model, client_difference_value, 3)
global_model.saveModel('sever_model')
x = []
y = []
for i in range(len(x_test)):
if y_test[i] == 1:
x.append(x_test[i])
y.append(y_test[i])
test_loss, test_acc = global_model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=2)
print('\nTest accuracy:', test_acc)
0 2022/5/24
1 The group will discuss
1.1 Provably Secure Federated Learning against Malicious Clients
- Integrated learning ;
- 1000 A client ,20 Attacked ;
- from 1000 Clients randomly choose 5 Aggregate , choice 10 Time , There is 10 Such an aggregation model ;
- forecast : An unknown sample is here 10 Each model is labeled , Decide the label of the sample according to the vote ;
- Give each prediction sample a safety level ;
- By changing the number of attacked clients , Then predict the same sample , Get the probability that the sample is predicted to be different tag values , The critical number of attacked clients that make the tag value reverse is taken as the security level of the sample .
1.2 Our thoughts
- Yes 100 Cluster clients , Number of clusters as super parameter , Suppose we get together 10 class ;
- Each class has a different number of clients , The number of clients is the weight of the later integration model ;
- 10 Class training out 10 An aggregation model ;
- Each virtual center is compared with the last update , If a threshold is exceeded , These clients are still attacked , Abandon it .
- Predict the label of an unknown sample = The weight * The prediction results of each benign aggregation model .
0 2022/5/25
1 Ideas for improvement
1. Calculate the similarity between all client updates , Aggregate clients whose similarity is higher than a certain threshold into a model ;
2. The number of clients contained in each model is used as the weight of the following set ;
3. At the same time, take the median in the model update ;
4. After that, before each round of aggregation , Compare the update with the median of the previous round , If the threshold is exceeded, discard ;
5. Predict the label of an unknown sample = The weight * Prediction results of each aggregation model .
2 Comparison scheme
- Krum
- Trimmed mean
- Median
0 2022/5/26
1 krum
Algorithm steps :
- The server s Put the parameters of the global model W W W Distribute to all clients ;
- Per client c i c_{i} ci Use local data to train the model to get the gradient d i d_{i} di, Then send it to the server ;
- After the server receives the gradient from the client , Calculate the distance between two gradients d i , j d_{i,j} di,j;
- For each gradient g i g_{i} gi, Choose the one closest to him n − f − 1 n-f-1 n−f−1 Distance , Add it up to get the gradient d i d_{i} di Score of ;
- After calculating all gradient scores , Find the gradient with the lowest score g i ∗ g_{i^{*}} gi∗;
- to update W = W − l r ⋅ g i ∗ W=W-lr\sdot g_{i^{*}} W=W−lr⋅gi∗;
- repeat 1-6, Until the model converges .
2 Trimmed mean
Algorithm steps :
- The server s Put the parameters of the global model W W W Distribute to all clients ;
- Per client c i c_{i} ci Use local data to train the model to get the gradient W i W_{i} Wi, Then send it to the server ;
- After the server receives the parameters from the client , Start aggregating ;
w j ′ = m β ( w j 1 , w j 2 , . . . , w j n ) . w_{j}^{'}=m_{\beta}(w_{j}^{1},w_{j}^{2},...,w_{j}^{n}). wj′=mβ(wj1,wj2,...,wjn). - The weight after aggregation is W ′ = ( w 1 ′ , w 2 ′ , . . . , w p ′ ) W^{'}=(w_{1}^{'},w_{2}^{'},...,w_{p}^{'}) W′=(w1′,w2′,...,wp′), The server sends the new parameters to the client ;
- repeat 1-4, Until the model converges .
3 Median
Algorithm steps :
- The server s Put the parameters of the global model W W W Distribute to all clients ;
- Per client c i c_{i} ci Use local data to train the model to get the gradient W i W_{i} Wi, Then send it to the server ;
- After the server receives the parameters from the client , Start aggregating ;
w j ′ = m e d ( w j 1 , w j 2 , . . . , w j n ) . w_{j}^{'}=med(w_{j}^{1},w_{j}^{2},...,w_{j}^{n}). wj′=med(wj1,wj2,...,wjn).
m e d med med It means taking the median . - The weight after aggregation is W ′ = ( w 1 ′ , w 2 ′ , . . . , w p ′ ) W^{'}=(w_{1}^{'},w_{2}^{'},...,w_{p}^{'}) W′=(w1′,w2′,...,wp′), The server sends the new parameters to the client ;
- repeat 1-4, Until the model converges .
边栏推荐
- What's wrong with this paragraph that doesn't work? (unresolved)
- 4.Oracle-重做日志文件管理
- Bash exercise 17 writing scripts to install the server side of FRP reverse proxy software
- 栈 AcWing 3302. 表达式求值
- Leetcode heap correlation
- 4. 对象映射 - Mapping.Mapster
- Leetcode-22: bracket generation
- [rust notes] 14 set (Part 1)
- Traversal of leetcode tree
- TCP's understanding of three handshakes and four waves
猜你喜欢
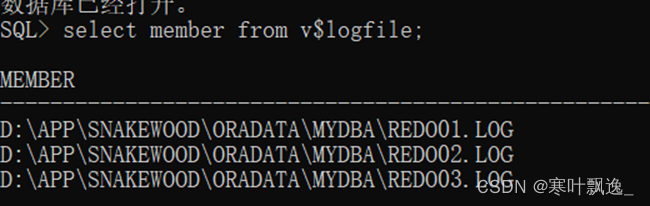
3.Oracle-控制文件的管理
![[moviepy] unable to find a solution for exe](/img/0a/4841f53cedc1333654b9443e406f4c.jpg)
[moviepy] unable to find a solution for exe
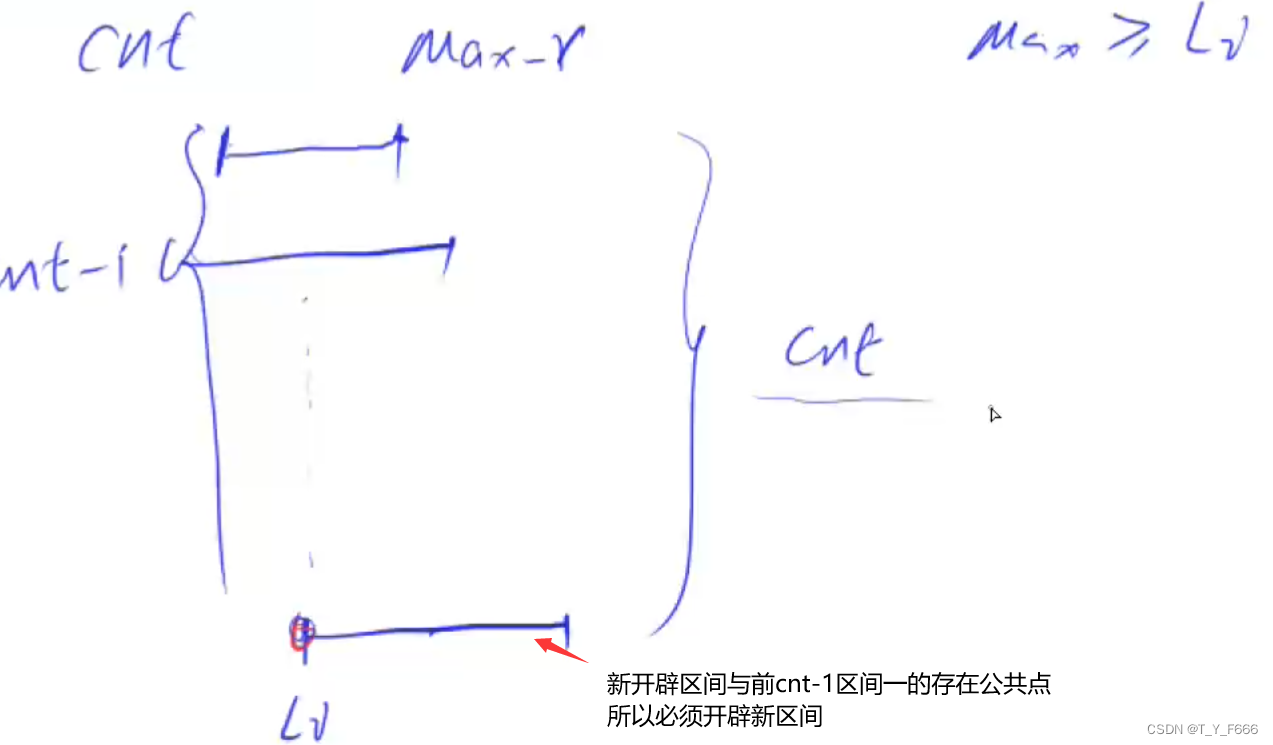
区间问题 AcWing 906. 区间分组

Sorting out the latest Android interview points in 2022 to help you easily win the offer - attached is the summary of Android intermediate and advanced interview questions in 2022
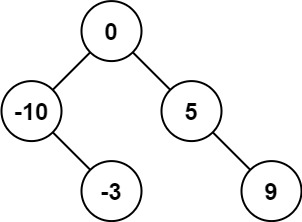
LeetCode 0108. Convert an ordered array into a binary search tree - the median of the array is the root, and the left and right of the median are the left and right subtrees respectively
4. Object mapping Mapster
Single chip computer engineering experience - layered idea
SQLMAP使用教程(一)
Matrixdb V4.5.0 was launched with a new mars2 storage engine!
Redis publish subscribe command line implementation
随机推荐
5.Oracle-表空间
博弈论 AcWing 894. 拆分-Nim游戏
2.Oracle-数据文件的添加及管理
开源存储这么香,为何我们还要坚持自研?
[2021]IBRNet: Learning Multi-View Image-Based Rendering Qianqian
LeetCode 0107. Sequence traversal of binary tree II - another method
5. Oracle TABLESPACE
FFmpeg build下载(包含old version)
MatrixDB v4.5.0 重磅发布,全新推出 MARS2 存储引擎!
Data visualization chart summary (I)
Regulations for network security events of vocational group in 2022 Guizhou Vocational College skill competition
1.13 - RISC/CISC
Daily question 1189 Maximum number of "balloons"
4. 对象映射 - Mapping.Mapster
Nested method, calculation attribute is not applicable, use methods
Gauss Cancellation acwing 884. Solution d'un système d'équations Xor linéaires par élimination gaussienne
AE tutorial - path growth animation
[leetcode] day94 reshape matrix
Currently clicked button and current mouse coordinates in QT judgment interface
Error ora-28547 or ora-03135 when Navicat connects to Oracle Database