当前位置:网站首页>[rust notes] 17 concurrent (Part 2)
[rust notes] 17 concurrent (Part 2)
2022-07-05 06:05:00 【phial03】
17.3 - Share modifiable state
17.3.1 - The mutex
The mutex ( Or lock ): Used to force multiple threads to access specific data in turn .
C++ Implementation example of mutual exclusion of :
void FernEngine::JoinWaitingList(PlayerId player) { mutex.Acquire(); // A critical region (critical section): Start waitingList.push_back(player); // If the waiting player meets the conditions, start the game if (waitingList.length() >= GAME_SIZE) { vector<PlayerId> players; waitingList.swap(players); StartGame(players); } mutex.Release(); // A critical region (critical section): end }The role of mutexes :
- Prevent data contention , Avoid multiple threads reading and writing the same block of memory concurrently .
- Prevent the operations of different threads from interleaving .
- Mutexes support invariance (invariant) Programming , The protected data is initialized by the performer , Maintained by each critical zone .
17.3.2-Mutex<T>
Rust The protected data in is stored in
MutexInside :let app = Arc::new(FernEmpireApp { // Create the entire application , Distributed on the heap ... waiting_list: Mutex::new(vec![]), ... });ArcIt is convenient to share data across threads .MutexIt is convenient to share modifiable data across threads .
give an example : Use mutex
impl FernEmpireApp { fn join_waiting_list(&self, player: PlayerId) { let mut guard = self.waiting_list.lock().unwrap(); guard.push(player); if guard.len() == GAME_SIZE { let players = guard.split_off(0); self.start_game(players); } } }The only way to get the data of the mutex is to call
.lock()Method .At the end of the jam ,
guardAfter being cleared , The lock will also be released . But it can also be removed manually :if guard.len() == GAME_SIZE { let players = guard.split_off(0); drop(guard); self.start_game(players); }
17.3.3-mut And Mutex
mut: Means proprietary 、 Exclusive access (exclusive access).- Not
mut: Means shared access (shared access). MutexThe mutex , Provide proprietary access to datamutAccess right , Even if many threads are rightMutexOwn sharing ( Notmut) Access right .- Rust Compiler at compile time , Proprietary access can be dynamically controlled through the type system .
17.3.4 - The problem of mutex
- Only rely on “ Parallel bifurcation — Merge ” The procedure is deterministic , It's impossible to deadlock .
- Procedures that specifically use channels to achieve pipeline operations are also deterministic , Although the time of message transmission may be different , But it will not affect the output .
- Data contention : Concurrent reading of the same block of memory by multiple threads leads to meaningless results . Safe Rust Code does not trigger data contention .
- There may be a problem with mutexes :
- Effective Rust There will be no data contention in the program , But there may still be race conditions (race condition), That is, the program behavior depends on the execution time of the thread , Therefore, the results of each run may be different . Using mutexes in an unstructured way can lead to race conditions .
- Shared modifiable state will affect program design . Channels can be used as abstract boundaries in code . Mutexes encourage the addition of a method to solve the problem , May cause code entanglement , Difficult to peel off .
- The implementation of mutex is more complex .
- Use structured programming whenever possible , Use mutexes when necessary
Mutex.
17.3.5 - Deadlock
Threads may cause deadlocks when trying to read locks they already hold .
let mut guard1 = self.waiting_list.lock().unwrap(); let mut guard2 = self.waiting_list.lock().unwrap(); // DeadlockUsing channels can also lead to deadlocks . For example, two threads block each other , Each waits to receive a message from the other .
17.3.6 - Poisoned mutex
If the thread is holding
MutexI was surprised , that Rust Will
MutexMark as poisoned .
- Later, I want to lock the contaminated
MutexAll attempts will get a wrong result . .unwrap()Call to tell Rust In this case, be surprised , Propagate the surprise of other threads to the current thread .- Surprised threads ensure that the rest of the program is in a safe state .
- Later, I want to lock the contaminated
Rust Poison this mutex to prevent other threads from inadvertently doing the same .
- In the case of complete mutual exclusion , It can lock the poisoned mutex , Access the data in it at the same time .
- See
PoisonError::into_inner().
17.3.7 - Multi consumer channels using mutexes
There is only one channel
Receiver.No thread pool can have multiple threads using one
mpscChannel sharing succeeded .An exceptional way to bypass this limitation : It can be for
ReceiverAdd oneMutex, Then share .pub mod shared_channel { use std::sync::{ Arc, Mutex}; use std::sync::mpsc::{ channel, Sender, Receiver}; /// Yes Receiver Thread safe encapsulation #[derive(Clone)] pub struct SharedReceiver<T>(Arc<Mutex<Receiver<T>>>); // Arc<Mutex<Receiver<T>>> Is a nested generic impl <T> Iterator for SharedReceiver<T> { type Item = T; /// Get the next item from the encapsulated recipient fn next(&mut self) -> Option<T> { let guard = self.0.lock().unwrap(); guard.recv().ok() } } /// Create a new channel , Its recipients can share across threads . /// Return a sender and a receiver , And stdlib Of channel() similar . /// Sometimes it can be used directly instead of it . pub fn shared_channel<T>() -> (Sender<T>, SharedReceiver<T>) { let (sender, receiver) = channel(); (sender, SharedReceiver(Arc::new(Mutex::new(receiver)))) } }
17.3.8 - Read write lock and RwLock<T>
Mutex uses
lockMethod to read and write data .The read-write lock uses
readandwriteThere are two ways to read and write data .RwLock::writeMethod : AndMutex::locksimilar , Are waiting to get proprietary information about protected datamutvisit .RwLock::readMethod provides nonmutvisit , There's almost no need to wait , Because multiple threads can read data safely at the same time .
The difference between mutex and read-write lock :
- At any given moment , Protected data can only have one reader or writer .
- When a read-write lock is used , There can be one writer or multiple readers , Be similar to Rust quote .
- It is preferred to use read-write lock , Not mutexes .
Optimize the above
FernEmpireAppProgram :Create a structure to save configuration information , And by the
RwLockProtect .use std::sync::RwLock; struct FernEmpireApp { ... config: RwLock<AppConfig>, ... }The method of reading this configuration can use
RwLock::read():fn mushrooms_enabled(&self) -> bool { let config_guard = self.config.read().unwrap(); config_guard.mushrooms_enabled }How to reload this configuration , Then use
RwLock::write():fn reload_config(&self) -> io::Result<()> { let new_config = AppConfig::load()?; let mut config_guard = self.config.write().unwrap(); *config_guard = new_config; Ok(()) }self.config.read()Return to a guard , Can provide forAppConfigNon -mut( Sharing ) visit ;self.config.write()Return a different type of guard , Can providemut( Proprietary ) visit .
17.3.9 - Condition variables, (Condvar)
A thread often needs to wait for a condition to become
true:
- During server shutdown , The main thread may need to wait for all other threads to exit completely .
- When the worker thread is idle , You need to wait for the data to be processed .
- Threads that implement distributed consensus protocols , You need to wait for enough peer threads to respond .
For conditions that require waiting , There will be convenient blockage API, without , Then you can use conditional variables (condition variable) To build your own API.
std::sync::CondvarType implements conditional variables .- its
.wait()Method can block some threads to call its.notify_all().
MutexAndCondvarThere is a direct connection : The conditional variable always represents by someMutexProtected data or true or false conditions .
17.3.10 - Type of atom
std::sync::atomioThe module contains the atomic types used in lock free concurrent programming .
AtomicIsizeandAtomicUsize: Is a shared integer type , Corresponding to single threadisizeandusizetype .AtomicBool: It's a sharedboolvalue .AtomicPtr<T>: Is an unsafe pointer type*mut TShared value of .
The simplest application of atoms is to cancel operations . Suppose there is a thread performing some time-consuming computation of any , Such as rendering video , We hope to cancel this operation asynchronously . Then you can use a shared
AtomicBoolTo achieve . Render every pixel , Threads will call.load()Method to check the value of the cancel flag .Atomic operations never use system calls . Loading and storage will be compiled into a CPU Instructions .
atom 、
Mutex、RwLockYou can useselfThe shared reference of is a parameter . They can also be used as simple global variables .
17.3.11 - Global variables
- For global variables : Thread safety must be guaranteed in some way . Static variables must be both
Sync, Right and wrong againmut. - Static initializers cannot call functions . have access to
lazy_staicPackage to achieve .
See 《Rust Programming 》( Jim - Brandy 、 Jason, - By orendov , Translated by lisongfeng ) Chapter 19
Original address
边栏推荐
- Codeforces round 712 (Div. 2) d. 3-coloring (construction)
- Daily question 2013 Detect square
- 个人开发的渗透测试工具Satania v1.2更新
- 1040 Longest Symmetric String
- 【Rust 笔记】15-字符串与文本(上)
- Introduction et expérience de wazuh open source host Security Solution
- In this indifferent world, light crying
- CF1634E Fair Share
- The connection and solution between the shortest Hamilton path and the traveling salesman problem
- Scope of inline symbol
猜你喜欢
![R language [import and export of dataset]](/img/5e/a15ab692a6f049f846024c98820fbb.png)
R language [import and export of dataset]
![[jailhouse article] jailhouse hypervisor](/img/f4/4809b236067d3007fa5835bbfe5f48.png)
[jailhouse article] jailhouse hypervisor
Graduation project of game mall
![[practical skills] how to do a good job in technical training?](/img/a3/7a1564cd9eb564abfd716fef08a9e7.jpg)
[practical skills] how to do a good job in technical training?
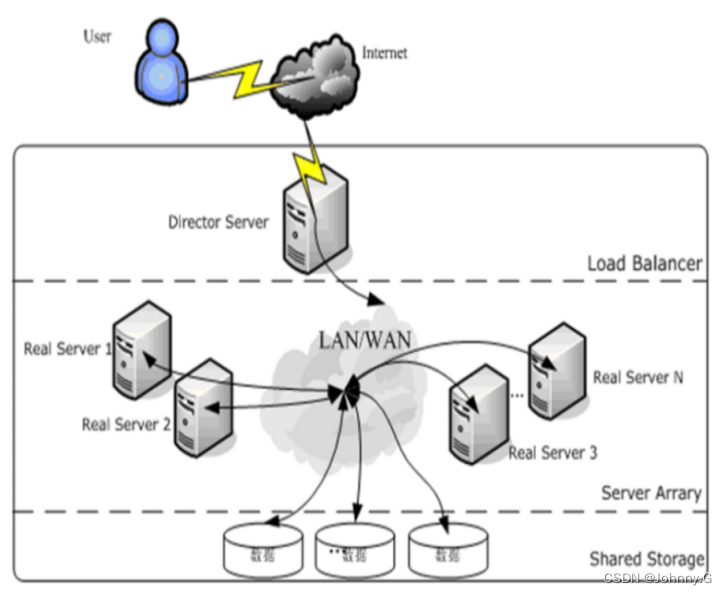
LVS简介【暂未完成(半成品)】

Data visualization chart summary (II)
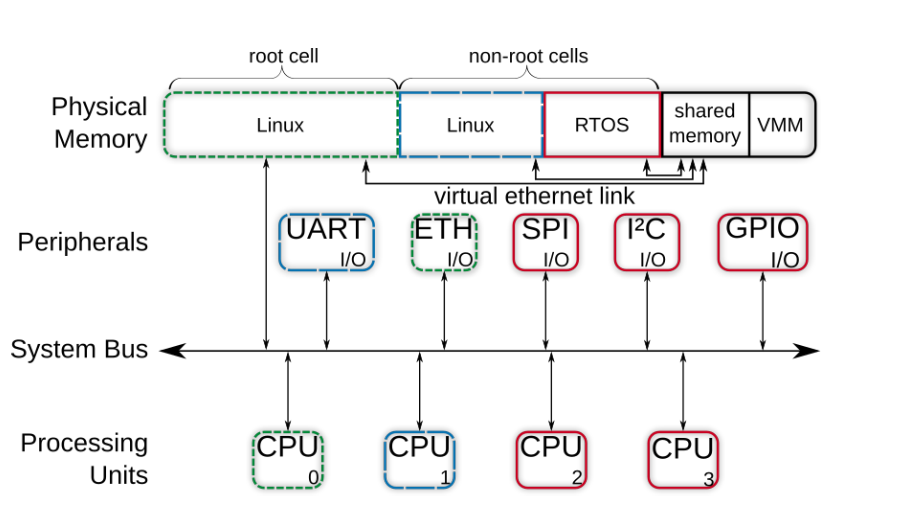
【Jailhouse 文章】Look Mum, no VM Exits

1.15 - 输入输出系统
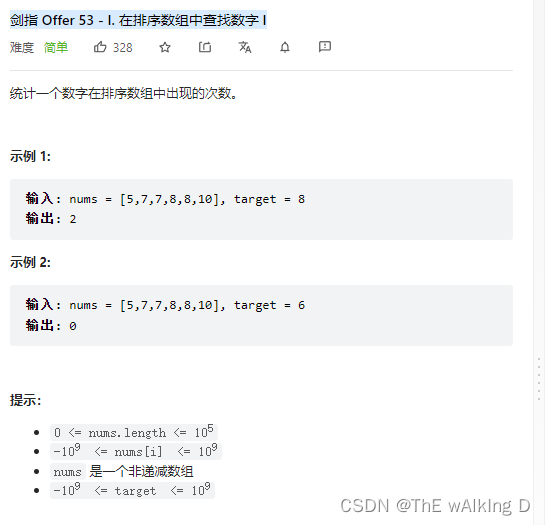
Sword finger offer 53 - ii Missing numbers from 0 to n-1
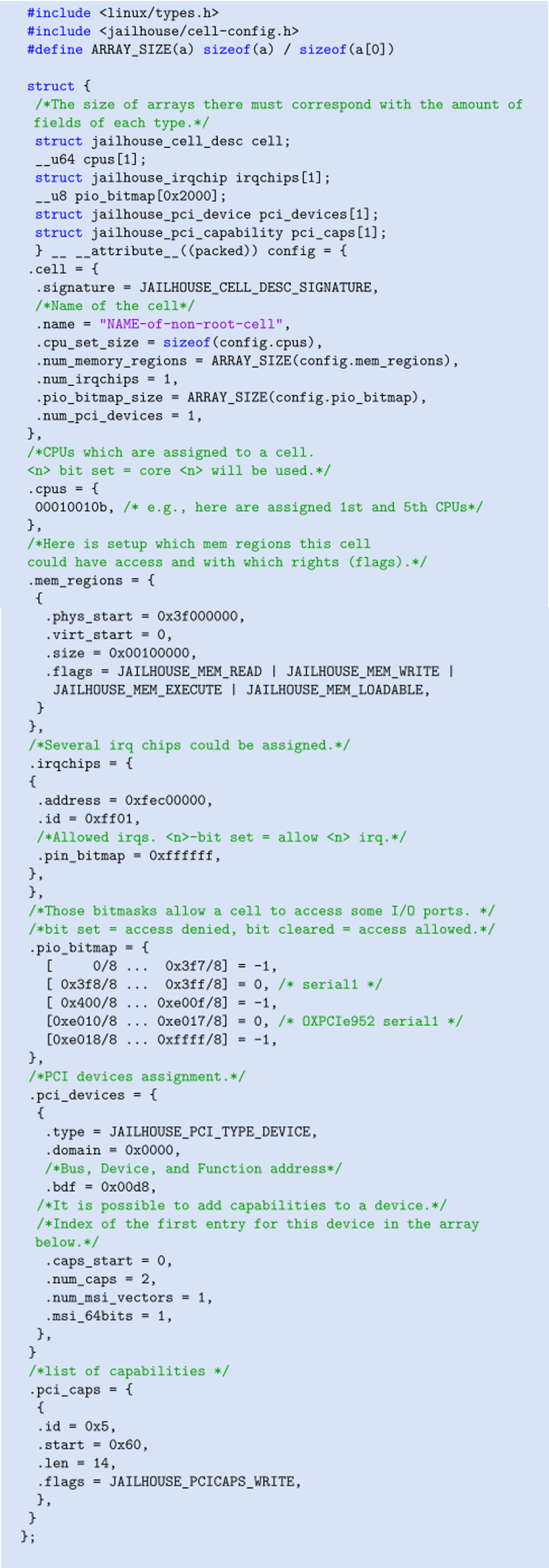
【Jailhouse 文章】Jailhouse Hypervisor
随机推荐
网络工程师考核的一些常见的问题:WLAN、BGP、交换机
[jailhouse article] jailhouse hypervisor
liunx启动redis
SQLMAP使用教程(一)
Codeforces Round #716 (Div. 2) D. Cut and Stick
Graduation project of game mall
Dichotomy, discretization, etc
Implement a fixed capacity stack
redis发布订阅命令行实现
[jailhouse article] look mum, no VM exits
Analysis of backdoor vulnerability in remote code execution penetration test / / phpstudy of national game title of national secondary vocational network security B module
对for(var i = 0;i < 5;i++) {setTimeout(() => console.log(i),1000)}的深入分析
Dynamic planning solution ideas and summary (30000 words)
Individual game 12
F - Two Exam(AtCoder Beginner Contest 238)
API related to TCP connection
MIT-6874-Deep Learning in the Life Sciences Week 7
RGB LED infinite mirror controlled by Arduino
Sword finger offer 53 - ii Missing numbers from 0 to n-1
Time of process