当前位置:网站首页>Deep understanding of C language pointer
Deep understanding of C language pointer
2022-07-05 09:19:00 【Brother Xiao who is not bald】
List of articles
- Preface
- One 、 The concept of pointer
- Two 、 Character pointer
- Two 、 Pointer array
- 3、 ... and 、 Array pointer
- Four 、 Array parameters 、 Pointer parameter
- 5、 ... and 、 A function pointer
- 6、 ... and 、 Function pointer array
- 7、 ... and 、 A pointer to an array of function pointers
- 8、 ... and 、 Callback function
- Conclusion
Preface
Pointer is c The more difficult knowledge points in the language , And very important , Today, let's have a deep understanding of pointers
One 、 The concept of pointer
- A pointer is an address , The address uniquely identifies a piece of memory space .( The pointer often refers to pointer variables )
- The size of the pointer is fixed 4/8 Bytes (32 Bit platform /64 Bit platform ).
- Pointers are typed , The type of pointer determines the type of pointer ± Integer step size , The permission of pointer dereference operation .
- The operation of the pointer : Pointer subtraction is the number of elements between two pointers , The pointer + Integer as pointer
Two 、 Character pointer
Among the pointer types, we know that one pointer type is character pointer char*
In general use :
int main()
{
char ch = 'w';
char *pc = &ch;
*pc = 'w';
return 0;
}
Another way to use it is as follows :
int main()
{
const char* pstr = "hello bit.";// Here is to put a string into pstr Is it in the pointer variable ?
printf("%s\n", pstr);
return 0;
}
Code const char* pstr = "hello bit." It's very easy to think that it's a string hello bit Put it in the character pointer pstr In the , But the essence is to put the string hello bit. The address of the first character is put in pstr in .
There is such an interview question :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char str1[] = "hello bit.";
char str2[] = "hello bit.";
const char *str3 = "hello bit.";
const char *str4 = "hello bit.";
if(str1 ==str2)
printf("str1 and str2 are same\n");
else
printf("str1 and str2 are not same\n");
if(str3 ==str4)
printf("str3 and str4 are same\n");
else
printf("str3 and str4 are not same\n");
return 0;
}
The output is :
here str3 and str4 Points to the same constant string .C/C++ The constant string is stored in a separate memory area , When a few pointers . When pointing to the same string , They actually point to the same block of memory . But initialize with the same constant string
Different arrays will open up different memory blocks . therefore str1 and str2 Different ,str3 and str4 Different .
Two 、 Pointer array
As the name suggests, pointer array is the array that stores pointers
int* arr1[10]; // An array of integer pointers
char *arr2[4]; // An array of first-order character pointers
char **arr3[5];// An array of secondary character pointers
3、 ... and 、 Array pointer
1. Definition of array pointer
Array pointer, as the name suggests, is a pointer to an array
int *p1[10];
int (*p2)[10];
//p1, p2 What are the differences ?
int (*p)[10];
//
//
explain :p The first and * combination , explain p Is a pointer variable , Then point to a size of 10 An array of integers . therefore p It's a pointer , Point to an array , It's called array pointer .
Pay attention here :[] Priority is higher than * The no. , So we have to add () To guarantee p The first and * combination .
2. & Array name and array name
For the following array :
int arr[10];
arr and &arr What's the difference ?
We know arr It's an array name , The array name indicates the address of the first element of the array .
that &arr What is the array name ?
Let's look at a piece of code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
0};
printf("%p\n", arr);
printf("%p\n", &arr);
return 0;
}
The operation results are as follows :
Visible array name and & The address printed by the array name is the same .
Are the two the same ?
Let's take another look at the code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
0 };
printf("arr = %p\n", arr);
printf("&arr= %p\n", &arr);
printf("arr+1 = %p\n", arr+1);
printf("&arr+1= %p\n", &arr+1);
return 0;
}

According to the above code, we find that , Actually &arr and arr, Although the values are the same , But the meaning should be different .
actually : &arr Represents the address of the array , Instead of the address of the first element of the array .
In this case &arr The type is : int(*)[10] , Is an array pointer type
Address of array +1, Skip the size of the entire array , therefore &arr+1 be relative to &arr The difference is 40
3. The use of array pointers
How do you use array pointers ?
Since the array pointer points to an array , The array pointer should store the address of the array .
Look at the code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0};
int (*p)[10] = &arr;// Put the array arr To an array pointer variable p
// But we seldom write code like this
return 0
}
When transferring parameters in a two-dimensional array , You can set the parameter to the form of array pointer
Four 、 Array parameters 、 Pointer parameter
When writing code, it is inevitable to 【 Array 】 perhaps 【 The pointer 】 Pass to function , How to design the parameters of the function ?
1. One dimensional array parameters
#include <stdio.h>
void test(int arr[])
{
}
void test(int arr[10])
{
}
void test(int *arr)
{
}
void test2(int *arr[20])
{
}
void test2(int **arr)
{
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
0};
int *arr2[20] = {
0};
test(arr);
test2(arr2);
}
2. Two dimensional array parameters
void test(int arr[3][5])
{
}
void test(int arr[][5])
{
}
void test(int (*arr)[5])
{
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {
0};
test(arr);
}
5、 ... and 、 A function pointer
First look at a piece of code :
#include <stdio.h>
void test()
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
int main()
{
printf("%p\n", test);
printf("%p\n", &test);
return 0;
}
Output result :
The output is two addresses , These two addresses are test Address of function .
The address of our function should be saved , How to keep ?
Let's look at the code :
void test()
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
// below pfun1 and pfun2 Which has the ability to store test Address of function ?
void (*pfun1)();
void *pfun2();
pfun1 It can store .pfun1 The first and * combination , explain pfun1 Is a pointer , The pointer points to a function , The function pointed to has no arguments , The return value type is void.
Read two interesting pieces of code :
// Code 1
(*(void (*)())0)();
// Code 2
void (*signal(int , void(*)(int)))(int);
These two codes come from 《c Pitfalls and pitfalls 》
Code 1:
(void(*)( ) ) stay 0 In front of , The function pointer type is void(*)( ),
Thus we can see that , This is the 0 Cast type to function pointer , And dereference
Code 2:
Put the code 2 Simplify it and it will be clearer
typedef void(*pfun_t)(int);
pfun_t signal(int, pfun_t);
6、 ... and 、 Function pointer array
An array is a storage space for the same type of data , So we've learned about pointer arrays ,
such as :
int *arr[10];
// Each element of the array is int*
Then save the address of the function in an array , This array is called the function pointer array , How to define the array of function pointers ?
int (*parr1[10])();
int *parr2[10]();
int (*)() parr3[10];
The answer is :parr1
parr1 The first and [] combination , explain parr1 It's an array , What is the content of the array ?
yes int (*)() Function pointer of type .
7、 ... and 、 A pointer to an array of function pointers
The pointer to the array of function pointers is a pointer
The pointer points to an array , The elements of the array are function pointers ;
How to define ?
void test(const char* str)
{
printf("%s\n", str);
}
int main()
{
// A function pointer pfun
void (*pfun)(const char*) = test;
// An array of function pointers pfunArr
void (*pfunArr[5])(const char* str);
pfunArr[0] = test;
// Pointer to function array pfunArr The pointer to ppfunArr
void (*(*ppfunArr)[5])(const char*) = &pfunArr;
return 0;
}
8、 ... and 、 Callback function
A callback function is a function called through a function pointer . If you put a pointer to a function ( Address ) Pass as argument to another function , When this pointer is used to call the function it points to , Let's just say this is a callback function . The callback function is not called directly by the function's implementer , It's called by another party when a particular event or condition occurs , Used to respond to the event or condition .
First demonstrate qsort Use of functions :
#include <stdio.h>
//qosrt The user of the function has to implement a comparison function
int int_cmp(const void * p1, const void * p2)
{
return (*( int *)p1 - *(int *) p2);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 2, 4, 6, 8, 0 };
int i = 0;
qsort(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), sizeof (int), int_cmp);
for (i = 0; i< sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); i++)
{
printf( "%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
VC & Delphi , Simulation Implementation qsort( By bubbling ).
#include <stdio.h>
int int_cmp(const void * p1, const void * p2)
{
return (*( int *)p1 - *(int *) p2);
}
void _swap(void *p1, void * p2, int size)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i< size; i++)
{
char tmp = *((char *)p1 + i);
*(( char *)p1 + i) = *((char *) p2 + i);
*(( char *)p2 + i) = tmp;
}
}
void bubble(void *base, int count , int size, int(*cmp )(void *, void *))
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i< count - 1; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j<count-i-1; j++)
{
if (cmp ((char *) base + j*size , (char *)base + (j + 1)*size) > 0)
{
_swap(( char *)base + j*size, (char *)base + (j + 1)*size, size);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 2, 4, 6, 8, 0 };
//char *arr[] = {"aaaa","dddd","cccc","bbbb"};
int i = 0;
bubble(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), sizeof (int), int_cmp);
for (i = 0; i< sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); i++)
{
printf( "%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Conclusion
Today we have a deep understanding of c Some related concepts of language pointer , Next time I will use some topics to deepen my understanding of pointer .
Learn a little every day , Time is long. , A rookie can also become a great God
边栏推荐
- Multiple solutions to one problem, asp Net core application startup initialization n schemes [Part 1]
- LeetCode 556. 下一个更大元素 III
- Blue Bridge Cup provincial match simulation question 9 (MST)
- Alibaba's ten-year test brings you into the world of APP testing
- STM32简易多级菜单(数组查表法)
- Codeforces round 684 (Div. 2) e - green shopping (line segment tree)
- OpenGL - Coordinate Systems
- OpenGL - Lighting
- Applet data attribute method
- 一文详解图对比学习(GNN+CL)的一般流程和最新研究趋势
猜你喜欢
Introduction Guide to stereo vision (1): coordinate system and camera parameters

The research trend of map based comparative learning (gnn+cl) in the top paper
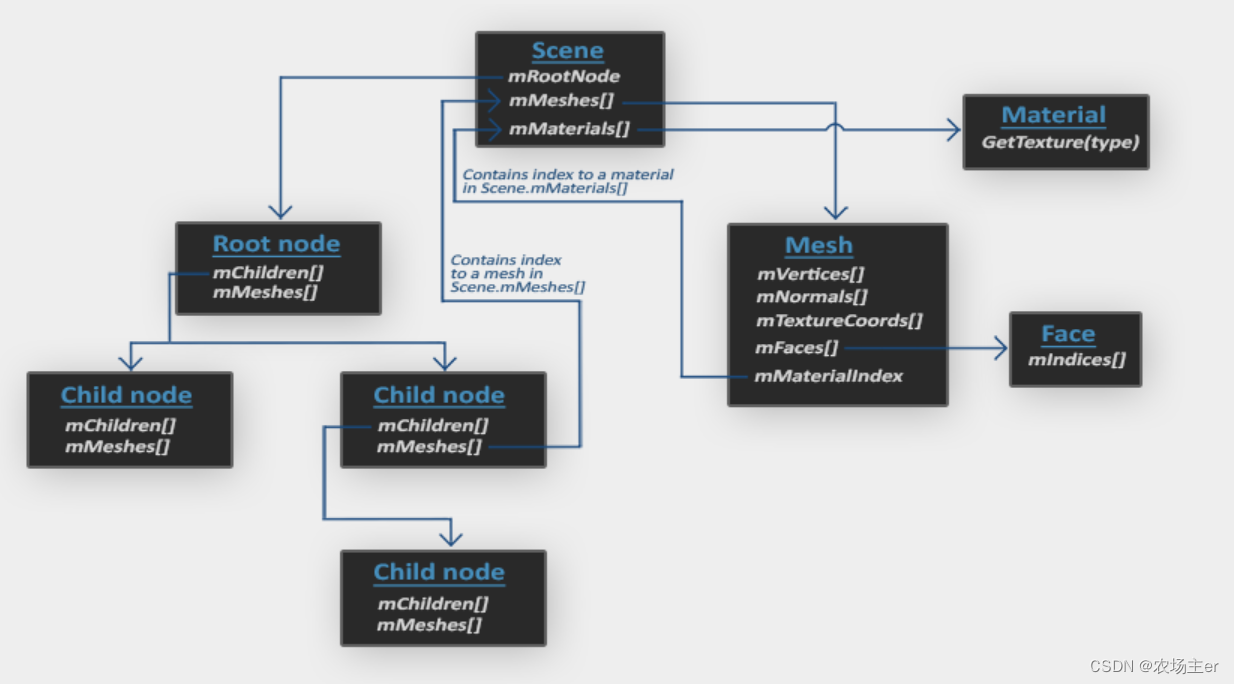
OpenGL - Model Loading
An article takes you into the world of cookies, sessions, and tokens
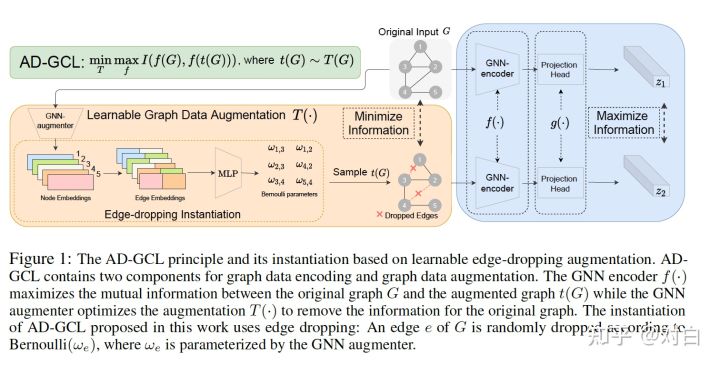
NIPS2021 | 超越GraphCL,GNN+对比学习的节点分类新SOTA
【阅读笔记】图对比学习 GNN+CL

OpenGL - Model Loading
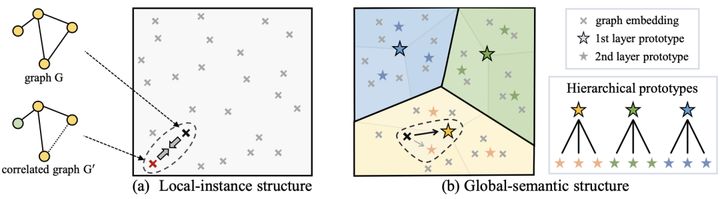
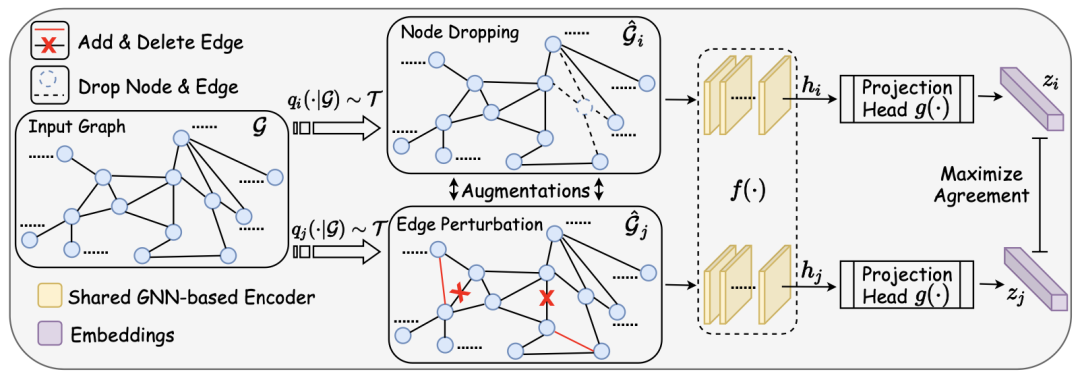
Figure neural network + comparative learning, where to go next?
![[beauty of algebra] singular value decomposition (SVD) and its application to linear least squares solution ax=b](/img/ee/8e07e2dd89bed63ff44400fe1864a9.jpg)
[beauty of algebra] singular value decomposition (SVD) and its application to linear least squares solution ax=b
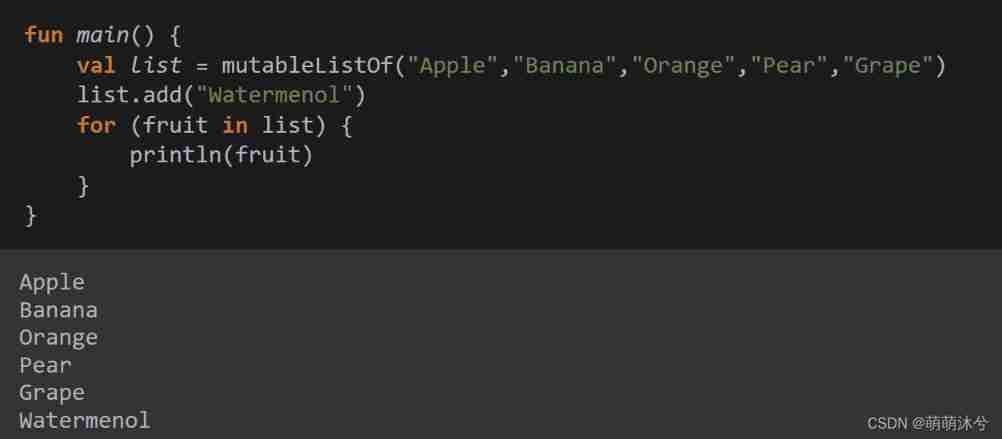
Kotlin introductory notes (VIII) collection and traversal
随机推荐
【PyTorch Bug】RuntimeError: Boolean value of Tensor with more than one value is ambiguous
.NET服务治理之限流中间件-FireflySoft.RateLimit
. Net service governance flow limiting middleware -fireflysoft RateLimit
scipy. misc. imread()
Kotlin introductory notes (III) kotlin program logic control (if, when)
Solution to the problems of the 17th Zhejiang University City College Program Design Competition (synchronized competition)
优先级队列(堆)
迁移学习和域自适应
Introduction Guide to stereo vision (7): stereo matching
C语言-从键盘输入数组二维数组a,将a中3×5矩阵中第3列的元素左移到第0列,第3列以后的每列元素行依次左移,原来左边的各列依次绕到右边
[code practice] [stereo matching series] Classic ad census: (6) multi step parallax optimization
Hi Fun Summer, play SQL planner with starrocks!
np.allclose
It's too difficult to use. Long articles plus pictures and texts will only be written in short articles in the future
阿里云发送短信验证码
nodejs_ fs. writeFile
Return of missing persons
c语言指针深入理解
Applet (use of NPM package)
Composition of applet code