当前位置:网站首页>Map and set
Map and set
2022-07-02 12:08:00 【The dishes are not right】

Catalog
🥬Map
Map Use of common methods
1、V put(K key, V value) // Set up key Corresponding value
map.put(1,"hello");
map.put(2,"world");
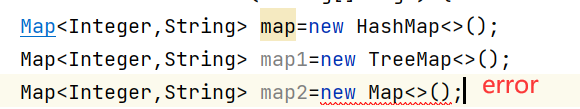
// result :{1=hello, 2=world}2、V get(Object key) // return key Corresponding value
map.get(1);
// result :hello3、V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) // return key Corresponding value,key non-existent , Return default
String str=map.getOrDefault(2,"hi");
String str1=map.getOrDefault(3,"hi");
// result :
//str world
//str1 hi
4、V remove(Object key) // Delete key The corresponding mapping relationship
map.remove(1);
System.out.println(map);
// result :{2=world}
5、Set<K> keySet() Back to all key An unrepeatable set of
map.put(1,"hi");
map.put(2,"thanks");
map.put(2,"what");
map.put(3,"how");
System.out.println(map.keySet());
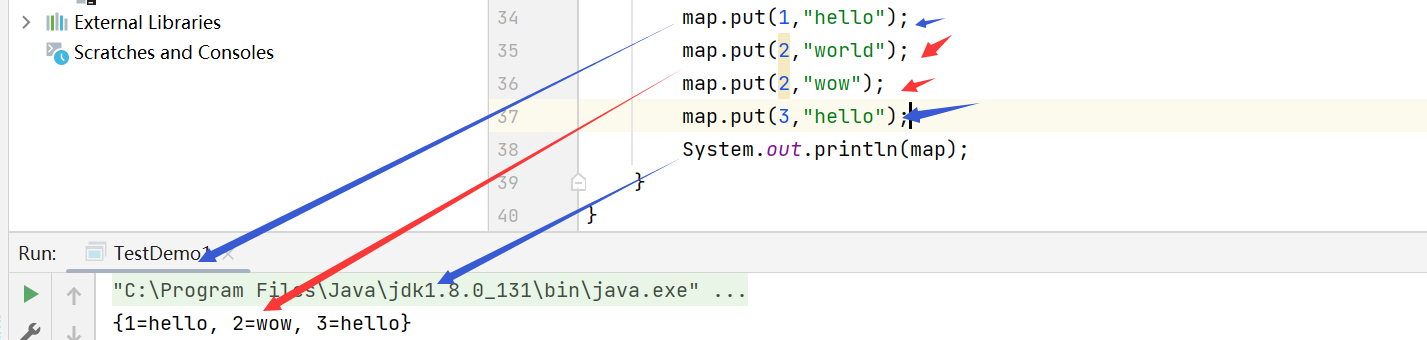
// result :[1, 2, 3]6、Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() // Return all key-value The mapping relationship
map.put(1,"hi");
map.put(2,"thanks");
map.put(3,"how");
for(Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--->" + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
// result :
1--->hi
2--->thanks
3--->how7、boolean containsKey(Object key) // Judge whether it includes key
map.put(1,"hi");
map.put(2,"thanks");
map.put(3,"how");
map.containsKey(1);//true
map.containsKey(5);//false
map.containsValue("hi");//true
map.containsValue("hello");//falseK getKey() // return entry Medium key
V getValue() // return entry Medium value
V setValue(V value) // The key value in the pair value Replace with specified valueBe careful :
2. Map To store key value pairs in Key Is the only one. ,value It can be repeated .


4. Map Medium Key Can be completely separated , Store in Set in To visit ( because Key Can't repeat ).
5. Map Medium value Can be completely separated , Stored in Collection In any subset of (value There may be duplication ).
🥬Set

Set Use of common methods
1、boolean add(E e) // Additive elements , But duplicate elements will not be added successfully
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
boolean flg=set.add(1);
System.out.println(flg);
System.out.println(set);
// result
//false
//[1, 2, 3]
2、boolean contains(Object o) // Judge o Is in collection
boolean flg=set.contains(1);//true
boolean flg1=set.contains(6);//false3、Iterator<E> iterator() // Return iterator
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
Iterator it= set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next()+" ");
}
// result :1 2 34、boolean remove(Object o) // Delete... From the collection o
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
boolean flg2=set.remove(1);
System.out.println(flg2);//true
System.out.println(set);//[2, 3]5、int size() // return set The number of elements in
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
System.out.println(set.size());//36、boolean isEmpty() // testing set Is it empty , Empty return true, Otherwise return to false
7、Object[] toArray() // take set Convert the elements in to an array and return
Set<Object> set1=new HashSet<>();
Object[] array1=set1.toArray();
Set<Integer> set2=new HashSet<>();// Specify the type
Integer[] array=set2.toArray(new Integer[0]);

5. Realization Set The common classes of interfaces are TreeSet and HashSet, One more LinkedHashSet,LinkedHashSet Is in HashSet The basis of A two-way linked list is maintained on to record the insertion order of elements .
Example
1、 stay 1_0000 Find duplicate data in the data
public static Map<Integer,Integer> func(int[] array){
// Judge array Whether the elements in map in , If it's not there, it's 1, If you add 1
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
for(int x:array){
if(map.get(x)==null){
map.put(x,1);
}else{
int val=map.get(x);
map.put(x,val+1);
}
}
return map;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array=new int[10000];
Random random=new Random();
for(int i=0;i< array.length;i++){
array[i]=random.nextInt(1000);// The generated random number is 0-1000 Between , There must be repeating elements
}
Map<Integer,Integer> map=func(array);
System.out.println(map);
String str="array";
System.out.println(str.toCharArray());
}2、 take 10000 De duplicate data
public static Set<Integer> func(int[] array){
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
for (int x:array) {
set.add(x);
}
return set;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array=new int[10000];
Random random=new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i]=random.nextInt(1000);
}
Set<Integer> set=func(array);
System.out.println(set);
int ret=func1(array);
System.out.println(ret);
}🥬 Binary search tree

lookup
Find a value in the binary search tree key, Just use key Compare with the root node ,key Bigger , Find... In the right subtree ,key smaller , Find in the left subtree .
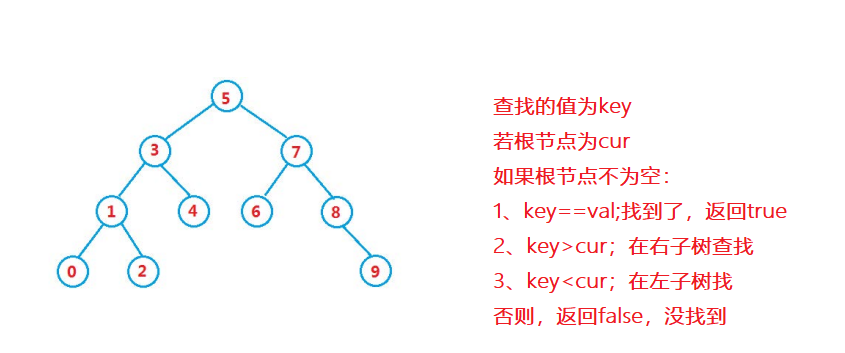
Code example :
public Node search(int key){
Node cur=root;
while(cur!=null){
if(key>cur.val){
cur=cur.right;
}else if(key<cur.val){
cur=cur.left;
}else{
return cur;
}
}
return null;// Did not find
}Insert
Insert a node into the binary search tree , Or destroy its nature , So you have to find the right place to insert , Then insert
public boolean insert(int val){
// Empty tree
if(root==null){
root=new Node(val);
return true;
}
// Find the location to insert
Node cur=root;
Node parent=null;// Record parent
while(cur!=null) {
if (val > cur.val) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur.right;
} else if (val < cur.val) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur.left;
} else {
return false;// Cannot have the same data
}
}
// Insert
Node tmp=new Node(val);
if(val<parent.val){
parent.left=tmp;
}else{
parent.right=tmp;
}
return true;
}Delete
Delete a node in the binary search tree , First find the location to delete , Deleting in progress
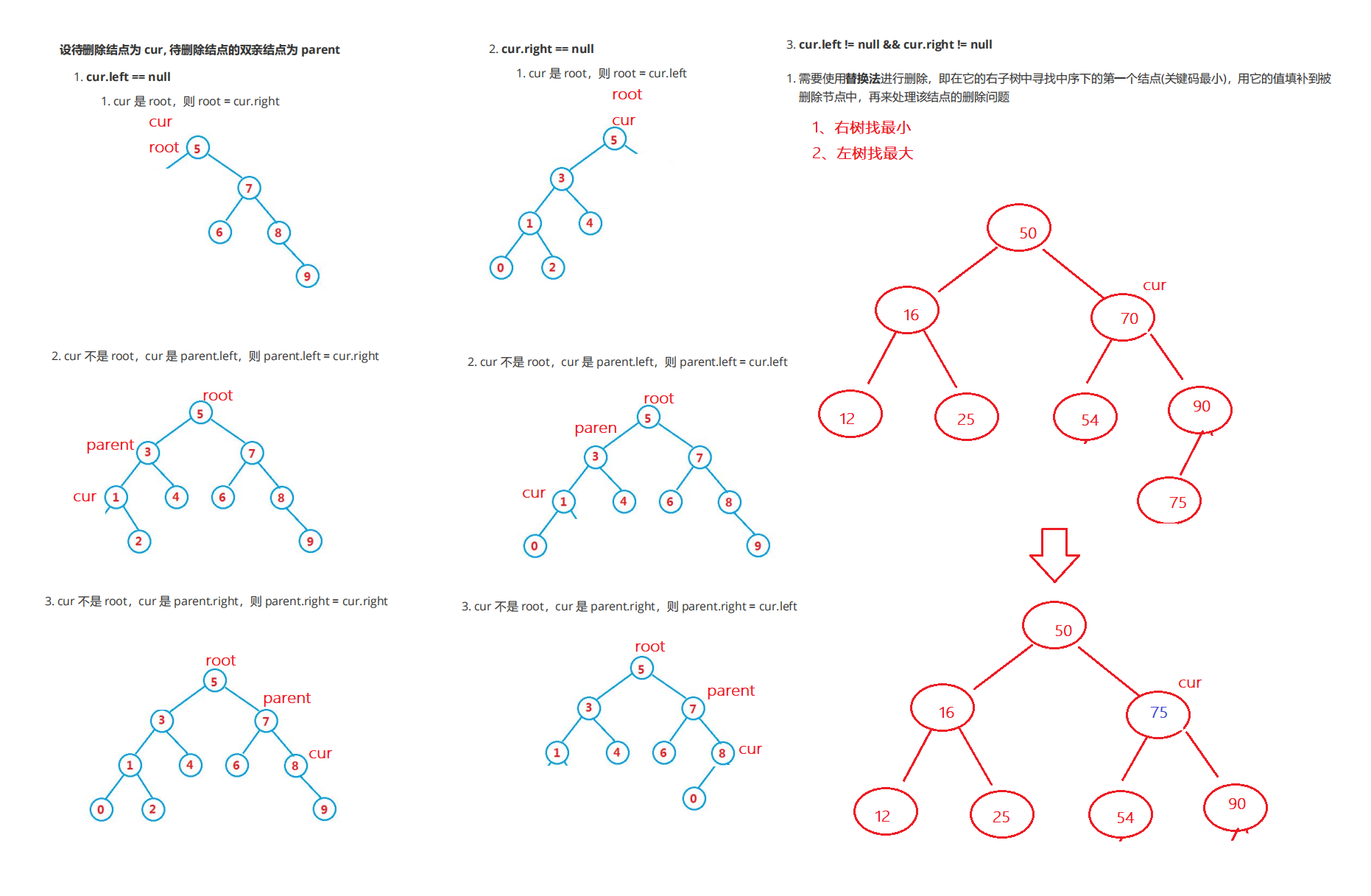
Code example :
public void remove(int key){
Node cur=root;
Node parent=null;
// Find the node location to delete
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
removeNode(cur,parent);
break;
}else if(cur.val<key){
parent=cur;
cur=cur.right;
}else{
parent=cur;
cur=cur.left;
}
}
}
// Delete
public void removeNode(Node cur,Node parent){
if(cur.left==null){
if(cur==root){
root=cur.right;
}else if(cur==parent.left){
parent.left=cur.right;
}else if(cur==parent.right){
parent.right=cur.right;
}
}else if(cur.right==null){
if(cur==root){
root=root.left;
}else if(cur==parent.left){
parent.left=cur.left;
}else if(cur==parent.right){
parent.right=cur.left;
}
}else{
// Find the minimum value of the right number , Find the maximum value of the left number
Node targetParent=cur;
Node target=cur.right;
while(target.left!=null){
targetParent=target;
target=target.left;
}
// Found the minimum value of the right tree
cur.val=target.val;
if(target==targetParent.left){
targetParent.left=target.right;
}else{
targetParent.right=target.left;
}
}
}🥬 Hashtable
This is called hash ( hash ) Method , The conversion function used in the hash method is called hash ( hash ) function , The constructed structure is called a hash table (HashTable)( Or a hash table ).
Hash Collisions
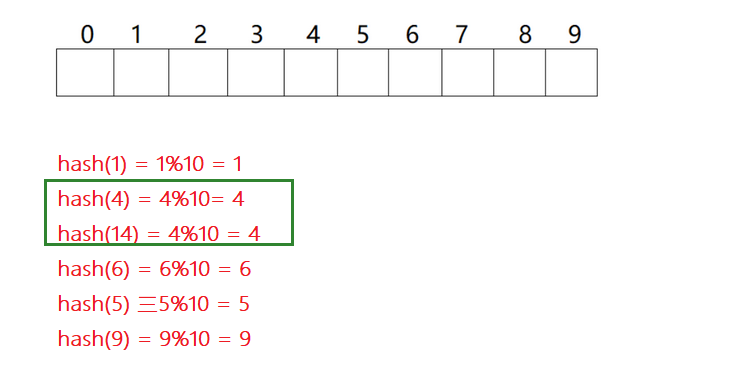
We can see 4 and 14 The same location is found through the same hash function , There was a conflict .
At this time, different keywords may find the same location through the same hash function . The situation at this time is called : Hash Collisions / Hash collision .
To avoid conflict
The load factor of the hash table is defined as : a = The number of elements in the table / The length of the hash table .
a It is a marker factor of hash table fullness . Since the meter length is a fixed value ,a And “ The number of elements in the table ” In direct proportion to , therefore ,a The bigger it is , Indicates that the more elements to fill in the table , The more likely there is to be a conflict . conversely ,a The smaller it is , Indicate that the fewer elements to fill in the table , The less likely there is a conflict . actually , The average lookup length of the hash table is the load factor a Function of , It's just that different methods of dealing with conflicts have different functions . For open addressing , The load factor is a particularly important factor , It should be strictly limited to 0. 7-0.8 following . exceed 0.8, Look up the table CPU Cache miss ( cachemissing) Follow the exponential curve . therefore , Some use open addressing hash library , Such as Java The system library limits the load factor to 0.75, Exceeding this value will resize Hash table .
As the load factor increases , The conflict rate is also increasing , So when the conflict rate is unbearable , We need to reduce the conflict rate by reducing the load factor . It is known that the number of existing keywords in the hash table is immutable , Then all we can adjust is the size of the array in the hash table .
Closed hash
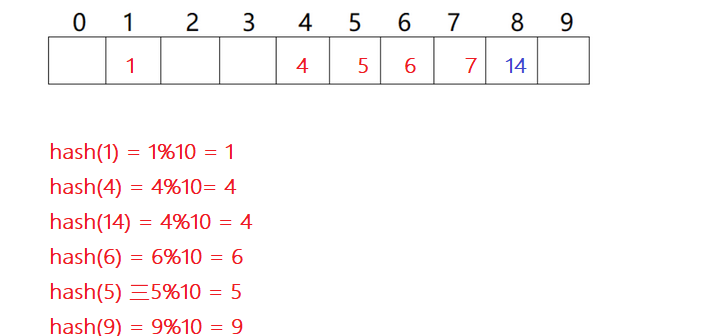
But there is one bad thing about linear detection , it Sequential backward detection , Until we find the next empty position , If the empty positions are continuous, the conflicting elements are put together .
Hash
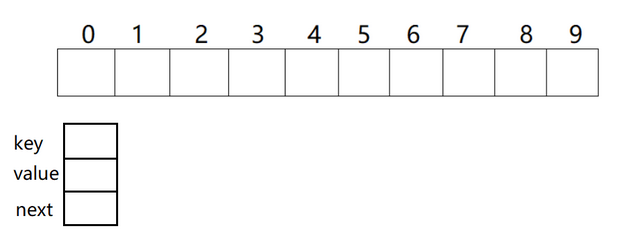
Realization
public class HashBuck {
static class Node{
public int key;
public int val;
Node next;
public Node(int key,int val){
this.key=key;
this.val=val;
}
}
public Node[] array;
public int usedSize;
public static final double DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75;// Load factor
public HashBuck(){
this.array=new Node[10];
}
/**
* put function
* @param key
* @param val
*/
public void put(int key,int val){
//1、 confirm key The position of
int index=key% array.length;
Node cur=array[index];
//2、 Traverse the linked list of this subscript , See if there are the same key, Update if any val value
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key==key){
cur.val=val;
return;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
//3、 No, key This element , Insert... By head insertion
Node node=new Node(key,val);
node.next=array[index];
array[index]=node;
this.usedSize++;
//4、 After the element is successfully inserted , Check the load factor of the current hash table
if(loadFactor()>=DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR){
resize();// Capacity expansion
}
}
private void resize(){
Node[] newArray=new Node[array.length*2];
for(int i=0;i< newArray.length;i++){
Node cur=newArray[i];
while(cur!=null){
int index= cur.key% newArray.length;// Get new subscript
// Is to put cur This node , In the form of head insertion Insert into the linked list corresponding to the subscript of the new array
Node curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=newArray[index];
newArray[index]=cur;
cur=curNext;
}
}
array=newArray;
}
private double loadFactor() {
return 1.0*usedSize/ array.length;
}
/**
* according to key get val value
* @param key
* @return
*/
public int get(int key){
//1、 confirm key The position of
int index=key% array.length;
Node cur=array[index];
//2、 Traverse the linked list of this subscript , find key, Returns the current val value
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key==key){
return cur.val;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return -1;
}
}class Person{
public String ID;
public Person(String ID){
this.ID=ID;
}
// rewrite
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return Objects.equals(ID, person.ID);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(ID);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"ID='" + ID + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class HashBuck2<K,V> {
static class Node<K,V>{
public K key;
public V val;
public Node<K,V> next;
public Node(K key,V val){
this.key=key;
this.val=val;
}
}
public Node<K,V>[] array=( Node<K,V>[])new Node[10];
int usedSize;
/**
* put function
* @param key
* @param val
*/
public void put(K key,V val){
int hash=key.hashCode();
int index=hash% array.length;
Node<K,V> cur=array[index];
while(cur!=null){
// utilize equals Make equality comparison
if(cur.key.equals(key)){
cur.val=val;
return;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
Node<K,V> node=new Node<>(key,val);
node.next=array[index];
array[index]=node;
this.usedSize++;
}
/**
* according to key get val value
* @param key
* @return
*/
public V get(K key){
int hash=key.hashCode();
int index=hash% array.length;
Node<K,V> cur=array[index];
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key.equals(key)){
return cur.val;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return null;
}common problem :( Look at the source code )
1. If new HashMap(19), bucket How big is the array ?
>=19 && Nearest 19 One of the 2 The next power --32
2. HashMap When to open up bucket Array takes up memory ?
for the first time put When --16
3. hashMap When to expand ?
Capacity expansion when the load factor is exceeded , And is 2 Double capacity
4. When two objects hashcode What will happen in the same way ?
Conflict
5. If you have two keys hashcode identical , How do you get value objects ?
Traversal and hashCode Linked list when values are equal , Until it's equal (equals) perhaps null( Can't find )
6. You know how to readjust HashMap Is there any problem with size ?
Re hash the original elements into the new linked list
🥬 Summary
That's what we have today , If you have any questions, you can leave a message in the comment area

边栏推荐
- Yygh-10-wechat payment
- (C language) input a line of characters and count the number of English letters, spaces, numbers and other characters.
- File operation (detailed!)
- 深入理解PyTorch中的nn.Embedding
- PgSQL string is converted to array and associated with other tables, which are displayed in the original order after matching and splicing
- [geek challenge 2019] upload
- SVO2系列之深度滤波DepthFilter
- QT meter custom control
- (C语言)输入一行字符,分别统计出其中英文字母、空格、数字和其它字符的个数。
- JZ63 股票的最大利润
猜你喜欢

PyTorch nn. Full analysis of RNN parameters

HOW TO CREATE A BEAUTIFUL INTERACTIVE HEATMAP IN R
![[QT] Qt development environment installation (QT version 5.14.2 | QT download | QT installation)](/img/18/f0c9ef6250a717f8e66c95da4de08c.jpg)
[QT] Qt development environment installation (QT version 5.14.2 | QT download | QT installation)
Yygh-9-make an appointment to place an order

测试左移和右移
![[visual studio 2019] create MFC desktop program (install MFC development components | create MFC application | edit MFC application window | add click event for button | Modify button text | open appl](/img/6a/111da81436659c7502648907ec1367.jpg)
[visual studio 2019] create MFC desktop program (install MFC development components | create MFC application | edit MFC application window | add click event for button | Modify button text | open appl
YYGH-BUG-04
How to Add P-Values onto Horizontal GGPLOTS
CDH存在隐患 : 该角色的进程使用的交换内存为xx兆字节。警告阈值:200字节
Thesis translation: 2022_ PACDNN: A phase-aware composite deep neural network for speech enhancement
随机推荐
字符串回文hash 模板题 O(1)判字符串是否回文
排序---
File operation (detailed!)
甜心教主:王心凌
Uniapp uni list item @click, uniapp uni list item jump with parameters
【C语言】十进制数转换成二进制数
Leetcode topic [array] -540- single element in an ordered array
【2022 ACTF-wp】
[geek challenge 2019] upload
Those logs in MySQL
Data analysis - Matplotlib sample code
Le tutoriel F - String le plus facile à comprendre de l'histoire.
b格高且好看的代码片段分享图片生成
深入理解PyTorch中的nn.Embedding
SCM power supply
Find the factorial of a positive integer within 16, that is, the class of n (0= < n < =16). Enter 1111 to exit.
Jenkins voucher management
测试左移和右移
HOW TO EASILY CREATE BARPLOTS WITH ERROR BARS IN R
Orb-slam2 data sharing and transmission between different threads