当前位置:网站首页>Skills of embedded C language program debugging and macro use
Skills of embedded C language program debugging and macro use
2022-07-07 18:20:00 【Luo Hanxiang】

Link to the original text : The embedded C Language program debugging and macro use skills
1. Debug related macro
stay Linux Use gcc When compiling a program , There are also some special syntax for debugging statements .gcc During compilation , It will generate some macros , You can use these macros to print information about the current source file separately , The main content is the current document 、 The current running function and the current program line .
The specific macro is as follows
__FILE__ Current program source file (char*)
__FUNCTION__ Currently running functions (char*)
__LINE__ The current function line (int): These macros are not defined by program code , It's produced by a compiler . This information is generated dynamically when the compiler processes files .
Test examples :
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("file: %s\n", __FILE__);
printf("function: %s\n", __FUNCTION__);
printf("line: %d\n", __LINE__);
return 0;
}2. # String operators
stay gcc In the compiler system , have access to # Convert the current content to a string .
Program example :
#include <stdio.h>
#define DPRINT(expr) printf("<main>%s = %d\n", #expr, expr);
int main(void)
{
int x = 3;
int y = 5;
DPRINT(x / y);
DPRINT(x + y);
DPRINT(x * y);
return 0;
}Execution results :
[email protected]:~/tmp$ gcc test.c
[email protected]:~/tmp$ ./a.out
<main>x / y = 0
<main>x + y = 8
<main>x * y = 15#expr Indicates that according to the parameters in the macro ( The content of the expression ), Generate a string . The process is also generated by the compiler , When the compiler compiles the source file , If you encounter a macro like this , Automatically according to the content of the expression in the program , Macro that generates a string .
The advantage of this method is that the content of the expression can be printed in a unified way , In the debugging process of the program, you can easily and intuitively see the expression after the conversion string . What is the content of the specific expression , There are compilers that automatically write to programs , This uses the same macro to print the string of all expressions .
// Print character
#define debugc(expr) printf("<char> %s = %c\n", #expr, expr)
// Print floating-point numbers
#define debugf(expr) printf("<float> %s = %f\n", #expr, expr)
// according to 16 Print integers in decimal
#define debugx(expr) printf("<int> %s = 0X%x\n", #expr, expr);because #expr Essentially listing a macro that represents a string , Therefore, it can not be applied in the program %s Print its content , Instead, it can be connected directly to other strings . therefore , The above macro can be equivalent to the following form :
// Print character
#define debugc(expr) printf("<char> #expr = %c\n", expr)
// Print floating-point numbers
#define debugf(expr) printf("<float> #expr = %f\n", expr)
// according to 16 Print integers in decimal
#define debugx(expr) printf("<int> #expr = 0X%x\n", expr);summary :
# yes C String operator in language preprocessing stage , You can convert the contents of a macro to a string .
3. ## Join operators
stay gcc In the compiler system ,## yes C The join operator in language , String concatenation can be implemented in the preprocessing stage of compilation .
Program example :
#include <stdio.h>
#define test(x) test##x
void test1(int a)
{
printf("test1 a = %d\n", a);
}
void test2(char *s)
{
printf("test2 s = %s\n", s);
}
int main(void)
{
test(1)(100);
test(2)("hello world");
return 0;
}In the above procedure ,test(x) A macro is defined as test##x, He said test String and x String connection .
In the debug statement of a program ,## The common way is as follows
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...) printf(fmt, ##args)The way to replace it is to change the two parts of the parameter with ## Connect .## Indicates that the connection variable represents the previous parameter list . In this form, you can pass a macro's argument to an argument .args… Is an argument to a macro , Represents a variable parameter list , Use ##args Pass it on to printf function .
summary :
## yes C The join operator of language preprocessing stage , It can realize the connection of macro parameters .
4. Debug macro first form
A way of defining :
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...) \
{ \
printf("file:%s function: %s line: %d ", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);\
printf(fmt, ##args); \
}
Program example :
#include <stdio.h>
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...) \
{ \
printf("file:%s function: %s line: %d ", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);\
printf(fmt, ##args); \
}
int main(void)
{
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
char *s = "hello world";
DEBUG("a = %d b = %d\n", a, b);
DEBUG("a = %x b = %x\n", a, b);
DEBUG("s = %s\n", s);
return 0;
}
summary :
above DEBUG The way it is defined is a combination of two statements , It is not possible to generate a return value , So you can't use its return value .
5. The second way to define a debug macro
The second way to define a debug macro
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...) \
printf("file:%s function: %s line: %d "fmt, \
__FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, ##args)
Program example
#include <stdio.h>
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...) \
printf("file:%s function: %s line: %d "fmt, \
__FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, ##args)
int main(void)
{
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
char *s = "hello world";
DEBUG("a = %d b = %d\n", a, b);
DEBUG("a = %x b = %x\n", a, b);
DEBUG("s = %s\n", s);
return 0;
}
summary :
fmt Must be a string , You can't use a pointer , Only in this way can we realize the function of string .
6. Review debugging statements in different levels
Even if the macro for debugging is defined , When the project is big enough , It also causes a lot of information in the terminal when the macro switch is turned on . And there's no way to tell what's useful . At this time, it is necessary to add a hierarchical inspection mechanism , You can define different debugging levels , In this way, different important programs and different modules can be distinguished , You can open the debug level of that module by debugging it .
Generally, you can use the configuration file to display , Actually Linux The kernel does the same thing , It divides the level of debugging into 7 Different levels of importance , Only set a certain level to display , The corresponding debugging information will be printed to the terminal .
You can write out the configuration file
[debug]
debug_level=XXX_MODULE
Parsing the configuration file uses standard string manipulation library functions to get XXX_MODULE The numerical .
int show_debug(int level)
{
if (level == XXX_MODULE)
{
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...) \
printf("file:%s function: %s line: %d "fmt, \
__FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, ##args)
}
else if (...)
{
....
}
}
7. Conditional compilation debugging statements
In actual development , Two kinds of source programs are generally maintained , One is a debug version program with debug statements , The other is a release program without debugging statements . Then compile the options according to different conditions , Compile different debug and release versions of the program .
In the process of implementation , You can use a debug macro to control the switch of debugging statements .
#ifdef USE_DEBUG
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...) \
printf("file:%s function: %s line: %d "fmt, \
__FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, ##args)
#else
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...)
#endif
If USE_DEBUG Defined , So there's debugging information , otherwise DEBUG It's empty .
If you need debugging information , Just change one line in the program .
#define USE_DEBUG
#undef USE_DEBUG
Define how conditional compilation works using a macro with values
#if USE_DEBUG
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...) \
printf("file:%s function: %s line: %d "fmt, \
__FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, ##args)
#else
#define DEBUG(fmt, args...)
#endif
Conditional compilation can be done in the following ways
#ifndef USE_DEBUG
#define USE_DEBUG 0
#endif
8. Use do…while The macro definition of
Using macro definition can encapsulate some shorter functions , Easy to use . The form of a macro is similar to a function , But it can save the cost of function jump . How to encapsulate a statement into a macro , It is often used in programs do…while(0) In the form of .
#define HELLO(str) do { \
printf("hello: %s\n", str); \
}while(0)
Program example :
int cond = 1;
if (cond)
HELLO("true");
else
HELLO("false");
9. Code analysis
For larger programs , You can use some tools to clean up the points that need to be optimized first . Next, let's take a look at the tools for getting data and analyzing it during program execution : Code parser .
The test program :
#include <stdio.h>
#define T 100000
void call_one()
{
int count = T * 1000;
while(count--);
}
void call_two()
{
int count = T * 50;
while(count--);
}
void call_three()
{
int count = T * 20;
while(count--);
}
int main(void)
{
int time = 10;
while(time--)
{
call_one();
call_two();
call_three();
}
return 0;
}
When compiling, add -pg Options :
[email protected]:~/tmp$ gcc -pg test.c -o test
After execution , A... Is generated in the current file gmon.out file .
[email protected]:~/tmp$ ./test
[email protected]:~/tmp$ ls
gmon.out test test.c
[email protected]:~/tmp$
Use gprof Dissect the main program :
[email protected]:~/tmp$ gprof test
Flat profile:
Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds.
% cumulative self self total
time seconds seconds calls ms/call ms/call name
95.64 1.61 1.61 10 160.68 160.68 call_one
3.63 1.67 0.06 10 6.10 6.10 call_two
2.42 1.71 0.04 10 4.07 4.07 call_three
There are two main messages , One is the percentage of execution time of each function in the total program time , The other is the number of times a function is called . Through this information , Can optimize the implementation of the core program to improve efficiency .
Of course, this parser has some limitations due to its own characteristics , It is more suitable for programs that run for a long time , Because the statistical time is based on the interval counting mechanism , So we also need to consider the relative time of function execution , If the program execution time is too short , The information we get is of no reference significance .
Shorten the appeal process :
#include <stdio.h>
#define T 100
void call_one()
{
int count = T * 1000;
while(count--);
}
void call_two()
{
int count = T * 50;
while(count--);
}
void call_three()
{
int count = T * 20;
while(count--);
}
int main(void)
{
int time = 10;
while(time--)
{
call_one();
call_two();
call_three();
}
return 0;
}
The analysis results are as follows :
[email protected]:~/tmp$ gcc -pg test.c -o test
[email protected]:~/tmp$ ./test
[email protected]:~/tmp$ gprof test
Flat profile:
Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds.
no time accumulated
% cumulative self self total
time seconds seconds calls Ts/call Ts/call name
0.00 0.00 0.00 10 0.00 0.00 call_one
0.00 0.00 0.00 10 0.00 0.00 call_three
0.00 0.00 0.00 10 0.00 0.00 call_two
So the more complex the profiling program is for 、 Functions that take longer to execute also apply .
So the longer the absolute time each function takes to execute , The longer it takes to dissect and show ? Here's another example
#include <stdio.h>
#define T 100
void call_one()
{
int count = T * 1000;
while(count--);
}
void call_two()
{
int count = T * 100000;
while(count--);
}
void call_three()
{
int count = T * 20;
while(count--);
}
int main(void)
{
int time = 10;
while(time--)
{
call_one();
call_two();
call_three();
}
return 0;
}
The analysis results are as follows :
[email protected]:~/tmp$ gcc -pg test.c -o test
[email protected]:~/tmp$ ./test
[email protected]:~/tmp$ gprof test
Flat profile:
Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds.
% cumulative self self total
time seconds seconds calls ms/call ms/call name
101.69 0.15 0.15 10 15.25 15.25 call_two
0.00 0.15 0.00 10 0.00 0.00 call_one
0.00 0.15 0.00 10 0.00 0.00 call_three
summary :
In the use of gprof When it comes to tools , For a function gprof Analysis of the way , Time in essence refers to the exception of library function calls and system calls , The running time of the actual code developed by the pure application part .
in other words ,time The time value of a description does not include library functions printf、 system call system Wait for the running time . Although the programs of these utility library functions are running , It will take more time than the original program , But it doesn't affect parsing functions .
边栏推荐
- 数学分析_笔记_第11章:Fourier级数
- Easy to understand [linear regression of machine learning]
- Backup Alibaba cloud instance OSS browser
- Mobile pixel bird game JS play code
- Deep learning machine learning various data sets summary address
- More than 10000 units were offline within ten days of listing, and the strength of Auchan Z6 products was highly praised
- AI 击败了人类,设计了更好的经济机制
- “解密”华为机器视觉军团:华为向上,产业向前
- [answer] if the app is in the foreground, the activity will not be recycled?
- Deep learning - make your own dataset
猜你喜欢

A few simple steps to teach you how to see the K-line diagram
In depth understanding of USB communication protocol
![[论文分享] Where’s Crypto?](/img/27/9b47bfcdff8307e63f2699d6a4e1b4.png)
[论文分享] Where’s Crypto?
Chapter 3 business function development (to remember account and password)
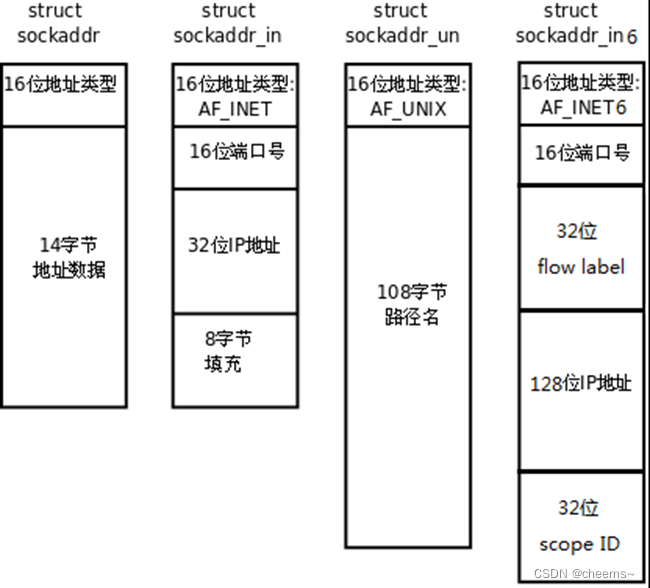
socket編程之常用api介紹與socket、select、poll、epoll高並發服務器模型代碼實現

The report of the state of world food security and nutrition was released: the number of hungry people in the world increased to 828million in 2021
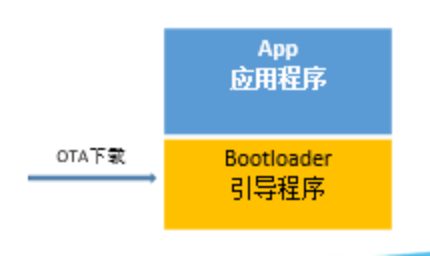
物联网OTA技术介绍
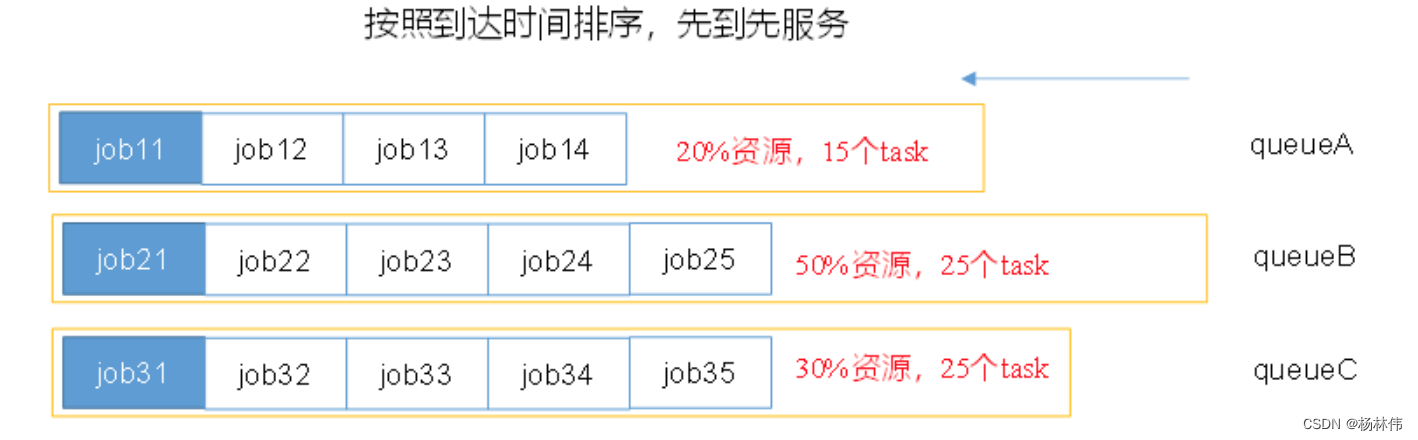
Yarn capacity scheduler (ultra detailed interpretation)

Introduction to OTA technology of Internet of things
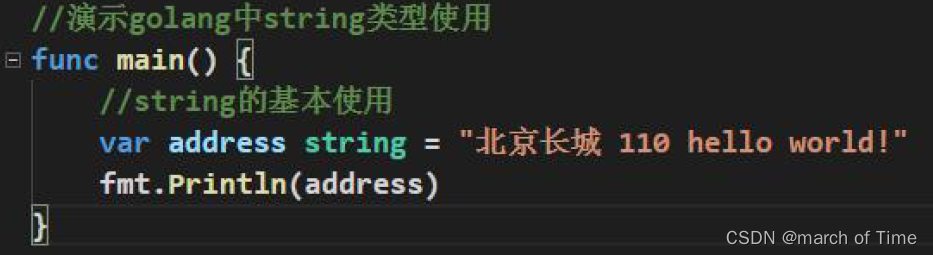
go语言的字符串类型、常量类型和容器类型
随机推荐
More than 10000 units were offline within ten days of listing, and the strength of Auchan Z6 products was highly praised
Disk storage chain B-tree and b+ tree
Understanding of 12 methods of enterprise management
zdog. JS rocket turn animation JS special effects
Chapter 3 business function development (user login)
List selection JS effect with animation
Improve application security through nonce field of play integrity API
PIP related commands
财富证券证券怎么开户?通过链接办理股票开户安全吗
nest. Database for getting started with JS
Do you really understand sticky bag and half bag? 3 minutes to understand it
你真的理解粘包与半包吗?3分钟搞懂它
< code random recording two brushes> linked list
Use onedns to perfectly solve the optimization problem of office network
直播软件搭建,canvas文字加粗
A few simple steps to teach you how to see the K-line diagram
上市十天就下线过万台,欧尚Z6产品实力备受点赞
Introduction of common API for socket programming and code implementation of socket, select, poll, epoll high concurrency server model
用存储过程、定时器、触发器来解决数据分析问题
通过 Play Integrity API 的 nonce 字段提高应用安全性