当前位置:网站首页>Importance of database security
Importance of database security
2022-07-07 12:44:00 【bisal(Chen Liu)】
Last weekend, , Maybe some friends pay attention to , Someone in the dark net resells at the price of ten bitcoins XX Dozens of institutions T Personal information and data .
Information security 、 The problem of data security , Have been emphasizing , But why does it still appear ? On the one hand, it is the limitation of Technology , On the other hand, it's about management and people . We all know the severity , But it will be repeated .
eygle I have written this article on database information security , In fact, it's not just the database field , In other areas , It can still be used for reference .
P. S. Link to the original text ,https://www.modb.pro/db/19105
Recent data security accidents , It has aroused widespread concern of many enterprises , Many users do find that their databases have been injected , This is an important lesson of data security .
Some enterprises even require to stop using PL/SQL Developer This tool , Although this closes a door from the system , But we know that there are so many similar doors in databases , How to fundamentally improve the security of database management , Reduce the risk of data operation and maintenance ?
I have been in 《 Data security alert 》 A book summarizes various data security risks , Put forward many preventive measures and means , Here are some suggestions for your reference .
In my book, I put forward five dimensions of data security , We can sort out the data security of enterprises based on these five dimensions , Accordingly, corresponding safety protection measures are established .
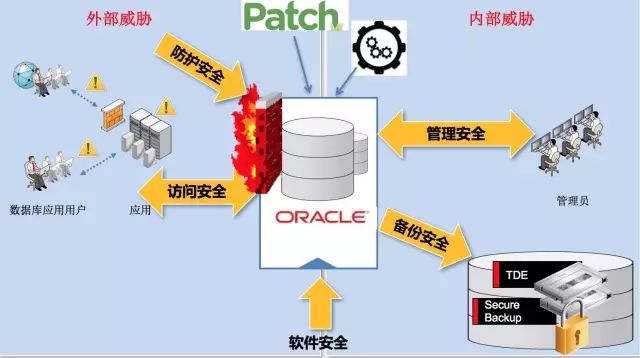
In the context of data security , We divide safety into five aspects , Namely : software security 、 Backup security 、 Access security 、 Protection and safety 、 Manage security .
In enterprise data security , These five aspects complement each other 、 Cross each other 、 Co existing , The following figure is a mind map about safety ,
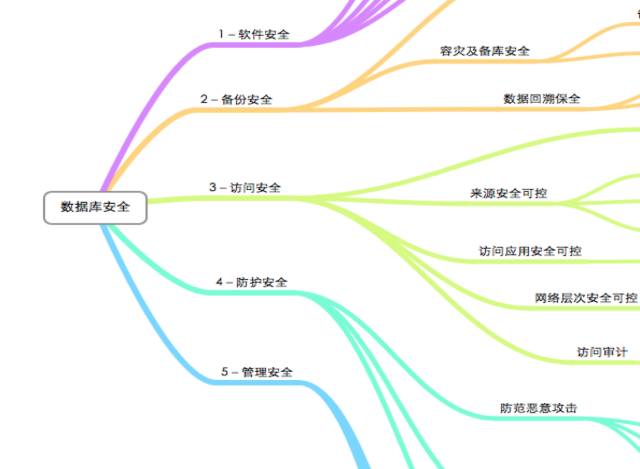
Among these five safety directions , There may be two kinds of security problems , First of all , Data security problems caused by poor internal management ; second , Security problems caused by external malicious attacks and intrusions . Usually, we narrow the security issue to the latter , This is actually one-sided , On the issue of data security , Data loss caused by the former 、 Data corruption , Its incidence and impact are far more than the latter .
Next, we will briefly analyze and discuss the five aspects of data security ,
1. software security It refers to the database product we choose 、 Whether the version is stable and safe ; Patch sets and BUG Whether the correction is timely 、 Whether the basic hardware and operating system are certified . Many users deploy database software , Only the initial release version that is most easily available is selected , Missing patch fixes that may already exist , And it is not able to track software updates in time during operation and maintenance , You can't get BUG Information 、 Patch fixes and security alerts , This makes many hidden risks of the software itself can not be corrected . If software security cannot be guaranteed , The foundation of database security is lost .
2. Backup security It refers to whether user data can be backed up and preserved in a timely and effective manner , Can we get timely recovery and rescue after the failure disaster . During database operation , The most important thing is backup security , If there is no reliable backup , Gathering data can only wait for data disaster , So we will promote backup security to the core , Backup and subsequent disaster recovery security , Are all factors that should be considered in the overall data architecture of the enterprise . Many enterprises are unable to recover after the data disaster due to the lack of effective backup , according to Gartner 2007 A survey report in showed that , In enterprises that have experienced complete data loss leading to system outage , Yes 2/5 Never able to resume operations , The remaining enterprises also have 1/3 Declare bankruptcy within two years , thus it can be seen , The enterprise damage caused by backup security problems may be far greater than hacker attacks .
3. Access security It refers to whether the access source and access method of the user database are safe and controllable . Usually, the database system is in IT The core of the system , Its security architecture involves the host 、 System 、 Storage 、 Network and many other aspects , If there is no explicit access control , Lack of sufficient access analysis and management , Then the security of the database will be chaotic and uncontrollable . When the application software uses and accesses the database , Set permissions correctly , Control reliable access sources , Ensure database access security , Only by ensuring access security can we ensure that data is not used beyond Authority 、 Not damaged by misoperation , Generally, the most basic access security is to realize program control 、 Network isolation 、 Source constraints, etc .
4. Safety precautions It refers to communicating with the database through active security means 、 Transmission, etc 、 monitor 、 protective 、 Shield or block , Such as data encryption 、 Audit 、 Data firewall and other technologies are in this category . We have to realize that , stay IT Today, technology is highly developed , Risk is everywhere 、 One after another , Maybe we have never thought about safety , It is emerging every day , So take active protection in the database environment , It can help us monitor, analyze and shield many unknown risks , There are many mature products and technologies that can be used for security .
5. Manage security It refers to the daily management and maintenance of enterprise data , Whether the data security and high availability of services can be fully guaranteed . Such as DBA The maintenance of the 、 Document management 、 Changes in parameters or data structures may introduce data risks , Managing safety requires us to pass the specification 、 Systems and technical means to ensure the safety of maintenance and management ; in addition , Hardware based 、 The failure of basic platforms such as power may affect the high availability of database services , In the management, we should use monitoring means to give early warning in time , By clustering 、 Standby database switching and service sharing ensure the continuity of services .
For the recent outbreak of safety accidents , I extract ideas from the book , Summarize the ways to improve database security "16 Rules " For your reference , Many friends ask us , How to prevent such risks completely , I think you can find the answer from the following suggestions ,
Backup is more important than everything
I was summarizing DBA The first of the four codes points out ,『 Backup is more important than everything 』, With effective backup , Even in case of disaster , You can take it easy , For important production environments , Properly establish a backup database for data protection , Query sharing , It will also reduce the risk of production warehouse .
The only thing that will make DBA What people wake up from their dreams is : No backup ! So for database operation and maintenance , The first important thing is to do a good backup ! Nothing can happen unless you are prepared !
Strictly control authority
Over authorization is to bury security risks for the database , When authorizing users, we must follow the principle of minimum permission granting , Avoid security risks due to over Authorization . This safety risk , If the user only has the minimum permission , If not DDL jurisdiction , Then there will be no risk .
Define user responsibilities
It should clarify the scope of work that different database users can use , Should use ordinary user identity , You should never use DBA The user identity of , Only the authority is commensurate , To avoid mistakes , Reduce risk . Even users with administrator responsibilities , We should also follow the habit of performing different tasks in different identities , for example SYS and SYSTEM The use of users should be distinguished and defined .
Password strategy enhancement
without doubt , Database users should use strong password rules , Ensure the security risks caused by weak passwords , Many data leakage problems come from weak password attacks and right raising .
Restrict login tools
Clearly limit the use scenarios of different tools , Specify the exact source of the tool , Or restrict database access through fortress machines . Clear rules and restrictions can also be made for tools , If the restriction can only be passed SQL Developer Access production ,PL/SQL Developer The tool can only access the test environment , To reduce the safety risk and even the risk of misoperation .
Remote control is prohibited DDL
Can restrict DDL Operations can only be performed locally on the database server , Prohibit remote connection execution DDL operation , This method is strictly implemented in many companies .
Use bound variables
In the development process , Strictly use bound variables , Binding variables can prevent SQL Injection attack , Reduce database security risks ; This safety accident , Many users began to guess that SQL Inject , Took many detours in analysis .
Monitor the monitoring log
The listening log records the source of database access 、 Program and other information , Including malicious scanning , Password attempt, etc , We must pay attention to the role of monitoring logs , And analyze and monitor it , Access the map with a clear exchange database ;
Data network isolation
The network environment of the database should always be hidden at the end , Avoid placing databases under direct access connections , This can reduce the risk of database access .
Test and production isolation
Interworking means that you can access at the same time , It may also bring many unexpected security risks , Enterprises should deploy the test environment and production environment in a non interoperable , Or in a network environment that cannot be accessed at the same time , Avoid database disasters caused by incorrect connections . On the one hand, separate deployment can reduce the possibility of misoperation , You can also block some irrelevant accesses , So as to ensure data security from the network link .
Password difference settings
Some test environments or non product environments are recovered by using the product environment ,DBA After establishing the test environment , The login password of the database user has not been modified ; Often ,DBA Also used to setting common passwords in all environments ; These habits bring a lot of risks and uncertainties to the system . We recommend that users use different password settings in different environments , This is because, on the one hand, the access users faced by the product environment and the test environment are different , The same password setting means that the security of the product environment is not guaranteed ; On the other hand ,DBA Login to different databases requires different passwords , This further reduces DBA The possibility of executing commands in the wrong environment .
Important data encryption
A lot of important data , Need encrypted storage , The most typical is user and password information , A large number of leaks are essentially due to the lack of the most basic encryption prevention , Implement certain security protection and encryption for important data , It is one of the safety aspects that should be considered in due course .
Timely software upgrade
The software here refers to database software , Especially when Oracle A security patch has been released , Known security vulnerabilities have been exploited by hackers , It is more likely to cause fatal damage to the database .
Guard against internal risks
Undeniable? , The vast majority of security issues come from within the enterprise , From the closest 、 The easiest contact and access , Personnel changes in the enterprise , Post change , May lead to data security problems , Relying on the trust of the administrator is not enough to ensure data security , Regulations must be passed 、 System and regulation Fan's constraints can avoid security risks .
Many enterprises abandon norms for convenience 、 Regulations or safety restrictions are not worth the loss . Security precautions should start from the inside , Start by restricting yourself , When the most closely related visits comply with the code , Then the security of the system can be greatly improved .
Establish a sense of safety
The biggest enemy of security is luck , Many enterprises believe that the probability of safety problems is extremely low , Will not fall into their own environment , So do not make necessary investment in safety , Caused safety negligence . So the biggest enemy of security is ourselves , Security needs to be strengthened bit by bit , Gradually improve .
Start safety audit
With Oracle Database, for example , Database has provided many means and methods of security protection , We recommend users to take appropriate safety precautions , Start some task audits , Analyze database risks on a regular basis , Thus gradually improve database security .
Data security , We should start from our daily work bit by bit .
Recently updated articles :
《CentOS 7.9 install Oracle 21c Adventure 》
《Linux Of 10 Great danger orders 》
《 You know, Oracle Is there an upper limit on the size of the data file ?》
《Oracle and JSON The combination of 》
《 How to " grace " avoid MySQL Login tips 》
Recent hot articles :
《" Red Alert " Game open source code brings us a shock 》
Article classification and indexing :
边栏推荐
- Processing strategy of message queue message loss and repeated message sending
- BGP third experiment report
- SQL Lab (36~40) includes stack injection, MySQL_ real_ escape_ The difference between string and addslashes (continuous update after)
- Sorting, dichotomy
- Epp+dis learning path (1) -- Hello world!
- Attack and defense world ----- summary of web knowledge points
- SQL Lab (41~45) (continuous update later)
- (to be deleted later) yyds, paid academic resources, please keep a low profile!
- 【从 0 开始学微服务】【03】初探微服务架构
- SQL head injection -- injection principle and essence
猜你喜欢
![[statistical learning method] learning notes - support vector machine (Part 2)](/img/bc/bb4f809ff434fabc10f8e97f592fa7.png)
[statistical learning method] learning notes - support vector machine (Part 2)
Cookie

ES底层原理之倒排索引
Vxlan 静态集中网关
![[statistical learning method] learning notes - logistic regression and maximum entropy model](/img/f7/857d053cc2cee81c24919aafab3c6e.png)
[statistical learning method] learning notes - logistic regression and maximum entropy model
![[statistical learning methods] learning notes - Chapter 5: Decision Tree](/img/0e/c60e04ab4a7ae4728cc76eff1c028a.png)
[statistical learning methods] learning notes - Chapter 5: Decision Tree
基于NeRF的三维内容生成
Day-19 IO stream

Aike AI frontier promotion (7.7)
NPM instal reports agent or network problems
随机推荐
Object. Simple implementation of assign()
Minimalist movie website
Routing strategy of multi-point republication [Huawei]
ACL 2022 | 序列标注的小样本NER:融合标签语义的双塔BERT模型
leetcode刷题:二叉树23(二叉搜索树中的众数)
密码学系列之:在线证书状态协议OCSP详解
leetcode刷题:二叉树25(二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先)
Solutions to cross domain problems
2022-07-07日报:GAN发明者Ian Goodfellow正式加入DeepMind
opencv的四个函数
Tutorial on the principle and application of database system (011) -- relational database
Processing strategy of message queue message loss and repeated message sending
Day-14 common APIs
Apache installation problem: configure: error: APR not found Please read the documentation
Solve server returns invalid timezone Go to ‘Advanced’ tab and set ‘serverTimezone’ property manually
2022广东省安全员A证第三批(主要负责人)考试练习题及模拟考试
Learning and using vscode
The left-hand side of an assignment expression may not be an optional property access. ts(2779)
Realize a simple version of array by yourself from
利用棧來實現二進制轉化為十進制