当前位置:网站首页>Experiment 8 exception handling
Experiment 8 exception handling
2022-07-06 13:55:00 【Wen Wen likes Guo Zia】
Experiment 8 exception handling
The experiment purpose
- Understand the concept of exception and exception handling mechanism
- Master the method of catching exceptions
- Master creating custom exceptions
Experimental hours 2 Class hours
Experimental content
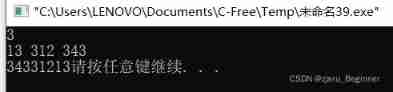
1. Write a program , It is required to input the radius of a circle from the keyboard (double type ), Calculate and output the area of the circle . When no exception handling mechanism is added , The input data is not double Type data ( Such as a string “abc”) What will happen ? After adding the exception handling mechanism , Let the program give an error prompt when entering incorrect type data and ask for re-entry .
package code81;
import java.util.InputMismatchException; // Import input mismatch exception
import java.util.Scanner;
public class code81 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
input:
while(true) { // Loop input
try { // Select the range to catch exceptions
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
double r,area;
System.out.println(" Please enter the radius of the circle :");
r=in.nextDouble();
area=r*r*3.14;
System.out.println(" The area of the circle is :"+area);
}catch(InputMismatchException e) { // Handle input mismatch exceptions
System.out.println(" The input data does not meet the requirements !");
System.out.println(" Please re-enter ");
e.printStackTrace(); // Print the exception information on the command line, the location and cause of the error in the program
continue input; // Keep typing , Make sure the input data is correct
}
}
}
}
2. Analyze the following procedure .
(1) What exceptions will occur when the program runs ? How to catch and handle exceptions ?
(2) Modify the code : No matter whether the program will produce exceptions during execution , Finally, it outputs “ End of program running ”
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExceptionSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[5];
int n,sum=0;
float average;
n=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
sum=sum+a[i];
}
average=(float)sum/n;
System.out.println(average);
}
}
- An input data mismatch exception may occur 、 except 0 abnormal 、 Array out of bounds exception ;
package code82;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.InputMismatchException; // Import input mismatch exception
public class ExceptionSample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[5];
int n,sum=0;
float average;
n=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
try { // Select the range to catch exceptions
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
sum=sum+a[i];
average=(float)sum/n;
System.out.println(average);
}catch(InputMismatchException e) { // Handle input mismatch exceptions
System.out.println(" The input data format does not meet the requirements !");
}catch(ArithmeticException e) { // Processing division 0 abnormal
System.out.println(" except 0 abnormal !");
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { // Handle array out of bounds exception
System.out.println(" Array out of bounds exception !");
}
}
}
}
2. Modify the code : No matter whether the program will produce exceptions during execution , Finally, it outputs “ End of program running ”
package code82;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.InputMismatchException; // Import input mismatch exception
public class ExceptionSample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[5];
int n,sum=0;
int average;
try { // Select the range to catch exceptions
n=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
sum=sum+a[i];
}
average=sum/n;
System.out.println(average);
}catch(InputMismatchException e) { // Handle input mismatch exceptions
System.out.println(" The input data format does not meet the requirements !");
}catch(ArithmeticException e) { // Processing division 0 abnormal
System.out.println(" except 0 abnormal !");
}finally { // Ensure that the final program is output as required
System.out.println(" End of program running !");
}
}
}
3. Design a program , Enter two integers and an arithmetic operator (+、-、*、/), According to the operator , Calculate the result of two integers . Considering that the data entered by the user is illegal , Need to catch exception ( Data format is abnormal 、 Abnormal division by zero 、 Illegal operator exception ).
package code83;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.InputMismatchException; // Import input mismatch exception
public class Calculate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int a,b;
String c;
try { // Select the range to catch exceptions
System.out.println(" Please enter two integers to be calculated :");
a=in.nextInt();
b=in.nextInt();
System.out.println(" Please enter operator :");
c=in.next();
switch(c) {
case "+":
System.out.println(a + c + b +"="+(a+b));
break;
case "-":
System.out.println(a + c + b +"="+(a-b));
break;
case "*":
System.out.println(a + c + b +"="+(a*b));
break;
case "/":
System.out.println(a + c + b +"="+(a/b));
break;
default:
throw new Exception(); // Declare discard exception
}
}catch(InputMismatchException e) { // Handle data mismatch exceptions
System.out.println(" Data format is abnormal !");
}catch(ArithmeticException e) { // Processing division 0 abnormal
System.out.println(" except 0 abnormal !");
}catch(Exception e) { // Handle default Illegal operator exception discarded in statement
System.out.println(" Illegal operator exception !");
}
}
}
4. Design a program , Calculate the area of a triangle according to its three sides . It is required to customize an exception class IllegaException, In the method of finding the area area() Declare to throw this exception type , An exception is thrown when the data of three sides input from the keyboard cannot form a triangle .
package code84;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.InputMismatchException; // Import input mismatch exception
public class Triangle {
public static double area(int a,int b,int c) throws IllegaException { // Construct a method to calculate the area of a triangle
if(a+b<=c || a+c<=b || b+c<=a || a<=0 || b<=0 || c<=0) {
throw new IllegaException(); // The type of exception thrown
}
double s=(a+b+c)/2.0;
double area=Math.sqrt(s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c));
return area; // Find the area of the triangle
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegaException {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int a,b,c;
System.out.println(" Please enter the length of three sides of the triangle :");
try { // Select the range to catch exceptions
a=in.nextInt();
b=in.nextInt();
c=in.nextInt();
System.out.println(" The area of the triangle is :"+area(a,b,c)); // Call the method of finding the area , The value of the output area
}catch(InputMismatchException e) { // Handle input mismatch exceptions
System.out.println(" The input data format does not match !");
}
}
}
package code84;
public class IllegaException extends Exception { // Custom exception classes IllegaException
IllegaException(){ // Construction method
System.out.println(" Such three sides cannot form a triangle !");
}
}
Summary of experiments
- Using exception handling has more advantages than traditional error management techniques ;
- Using exception handling can separate error handling code from normal code ;
- If a method does not know how to handle the exception that occurs , You can declare to discard the exception when declaring the method ;
- Inheritance other than runtime exceptions is from Exception Subclasses of class are collectively referred to as non runtime exceptions , For this kind of exception ,Java The compiler requires that the program must catch or declare to discard exceptions ;
- Capture exception :try...catch...finally;
- Regardless of try Whether there is an exception in the statement block ,finally Statement blocks are executed ;
- If Java The system exception type provided cannot meet the needs of program design , You can design your own exception types .Java Recommend the user's exception type to Exception Is a direct parent class .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
FAQs and answers to the imitation Niuke technology blog project (I)
Canvas foundation 1 - draw a straight line (easy to understand)
强化學習基礎記錄
一段用蜂鸣器编的音乐(成都)
Yugu p1012 spelling +p1019 word Solitaire (string)

1. First knowledge of C language (1)

Thoroughly understand LRU algorithm - explain 146 questions in detail and eliminate LRU cache in redis
canvas基础2 - arc - 画弧线

仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(二)
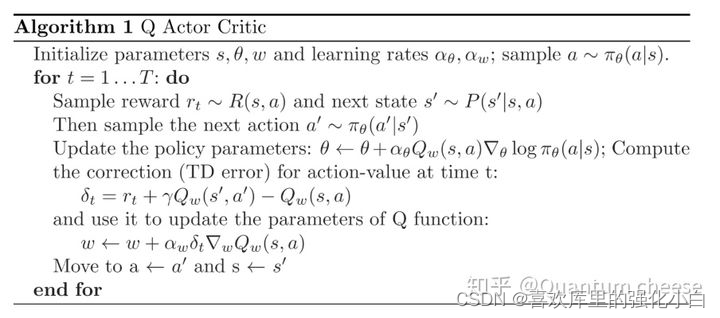
强化学习基础记录
随机推荐
【Numpy和Pytorch的数据处理】
Mortal immortal cultivation pointer-2
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2020 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
Strengthen basic learning records
Caching mechanism of leveldb
Service ability of Hongmeng harmonyos learning notes to realize cross end communication
A piece of music composed by buzzer (Chengdu)
Read only error handling
7-3 构造散列表(PTA程序设计)
7-5 走楼梯升级版(PTA程序设计)
1. First knowledge of C language (1)
A comprehensive summary of MySQL transactions and implementation principles, and no longer have to worry about interviews
[MySQL table structure and integrity constraint modification (Alter)]
[data processing of numpy and pytoch]
[面試時]——我如何講清楚TCP實現可靠傳輸的機制
强化学习基础记录
附加简化版示例数据库到SqlServer数据库实例中
Reinforcement learning series (I): basic principles and concepts
记一次猫舍由外到内的渗透撞库操作提取-flag
Redis的两种持久化机制RDB和AOF的原理和优缺点