当前位置:网站首页>Merge sort
Merge sort
2022-07-05 05:08:00 【ximen502_】
The content and code of this article come from the data structure textbook .
Merge sort (Merging Sort) Is another kind of different sorting method ." Merger " The meaning of will is 2 Or 2 More than ordered tables are combined into 1 New ordered table . Whether it is sequential storage or linked list storage structure , All available O(m+n) In terms of time . The basic idea of merging is as follows :
Suppose the initial sequence contains n A record , We can view it as n Two ordered subsequences , The length of each subsequence is 1, And then they merge , obtain ⌈ n 2 ⌉ \lceil \frac{n}{2} \rceil ⌈2n⌉ A length of 2 or 1 An ordered subsequence of ; And then we merge ,… …, repeat , All the way to a length of zero n The ordered sequence of , This sorting method is called 2- Path merging and sorting . Here's the picture 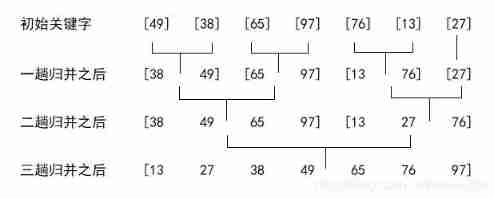
2- The core operation in path merging sorting is to merge two adjacent ordered sequences in a one-dimensional array into an ordered sequence .
java Realization
void merge(int[] sr, int[] tr, int i, int m, int n) {
if (i == n) {
// Processing of the last element of the array
tr[i] = sr[i];
return;
}
int k = 0;
int j = 0;
// take SR[i..m] and SR[m+1..n] Merge into ordered TR[i..n]
for (j = m + 1, k = i; i <= m && j <= n; ++k) {
if (sr[i] <= sr[j]) // take SR From small to large TR
tr[k] = sr[i++];
else
tr[k] = sr[j++];
}
if (i <= m) {
for (int u = i, q = 0; u <= m; u++) {
// Put the rest SR[i...m] Copied to the TR
tr[k + q] = sr[u];
++q;
}
}
if (j <= n) {
for (int u = j, q = 0; u <= n; u++) {
// Put the rest SR[j...n] Copied to the TR
tr[k + q] = sr[u];
++q;
}
}
}
int[] mergSort(int[] arr) {
int[] sr = arr;
int[] tr = new int[arr.length];
int h = 1, len = arr.length;
// It takes several times to merge , With 2 Bottom ,len The logarithm of is rounded up .
int count = (int) Math.ceil(log(len, 2));
for (int x = 0; x < count; x++) {
// In each trip , The number of groups that need to be merged ,len/2h The decimal obtained is rounded up .
int ceil = (int) Math.ceil((float) len / (2 * h));
for (int y = 0; y < ceil; y++) {
int i = y * 2 * h;
int m = i + h - 1;
int n = m + h;
n = n >= len ? n - 1 : n;// Subscript processing of the last element of the array
merge(sr, tr, i, m, n);
}
// Save the result of one sort to the original array
for (int z = 0; z < tr.length; z++) {
arr[z] = tr[z];
}
// Subsequence length modification
h *= 2;
}
return tr;
}
/** * Logarithmic method , This method uses the bottom changing formula in logarithm in mathematics to realize . * because JDK There is no request 2 Method of logarithm of base . * @param value * @param base * @return */
double log(double value, double base) {
return Math.log(value) / Math.log(base);
}
@Test
public void fun1(){
int[] arr = new int[] {
49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27 };
int[] tr = mergSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(tr));
}
The operation of merging and sorting is , call ⌈ n 2 h ⌉ \lceil \frac{n}{2h} \rceil ⌈2hn⌉(n/2h The decimal result after is rounded up , Such as 2.01 Rounded up to 3) Sub algorithm merge take SR[1…n] The middle is adjacent to the front and back and the length is h h h The ordered segments of are merged in pairs , Get adjacent before and after 、 The length is 2 h 2h 2h Ordered segment of , And stored in TR[1…n] in , The whole merging and sorting needs to be done ⌈ log 2 n ⌉ \lceil \log_2n \rceil ⌈log2n⌉ Trip to . so , The realization of merging and sorting requires a number of auxiliary spaces such as records to be arranged , So it's Spatial complexity by O(n), Its Time complexity by O(nlogn).
And Quick sort and Heap sort comparison , The biggest feature of merging and sorting is , It is a stable sorting method . Looks like Java JDK in Collections.sort(List); The method is to merge and sort or an improved version .
this 2 Mathematical library functions for calculating logarithms and rounding up are used in both language versions , By Math Classes and math.h The header file provides .
When calculating logarithms, there is an implementation method of using the bottom exchange formula of logarithms , The original mathematical formula is as follows :
about a , c ∈ ( 0 , 1 ) ∪ ( 1 , + ∞ ) a,c\in(0,1) \cup (1,+\infin) a,c∈(0,1)∪(1,+∞) And b ∈ ( 0 , + ∞ ) b\in(0,+\infin) b∈(0,+∞), Yes
log a b = log c b log c a \log_ab=\frac{\log_cb}{\log_ca} logab=logcalogcb
Here is C/C++ Implementation version of .
/* * Merge sort * data structure (C Language version ) YanWeiMin Wei-min wu * */
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
/** * Logarithmic method * @param value * @param base * @return */
double logPlus(double value, double base) {
return log(value) / log(base);
}
void merge(int sr[], int tr[], int i, int m, int n) {
if (i == n) {
// Processing of the last element of the array
tr[i] = sr[i];
return;
}
int k = 0;
int j = 0;
// System.out.println(i+","+m+","+n);
for (j = m + 1, k = i; i <= m && j <= n; ++k) {
if (sr[i] <= sr[j]) {
tr[k] = sr[i++];
} else {
tr[k] = sr[j++];
}
}
if (i <= m) {
// Put the rest SR[i...m] Copied to the TR
for (int u = i, q = 0; u <= m; u++) {
tr[k + q] = sr[u];
++q;
}
}
if (j <= n) {
// Put the rest SR[j...n] Copied to the TR
for (int u = j, q = 0; u <= n; u++) {
tr[k + q] = sr[u];
++q;
}
}
}
int* mergSort(int arr[], int arrLength) {
int* sr = arr;
int* tr = new int[arrLength];// Allocate memory for array pointers , Otherwise, a segment error will be reported, and the core has been dumped
int h = 1, len = arrLength;
// It takes several times to merge , With 2 Bottom ,len The logarithm of is rounded up .
int count = (int) ceil(logPlus(len, 2));
for (int x = 0; x < count; x++) {
// In each trip , The number of groups that need to be merged ,len/2h The decimal obtained is rounded up .
int _ceil = (int) ceil((float) len / (2 * h));
for (int y = 0; y < _ceil; y++) {
int i = y * 2 * h;
int m = i + h - 1;
int n = m + h;
n = n >= len ? n - 1 : n;// Subscript processing of the last element of the array
merge(sr, tr, i, m, n);
}
// Save the result of one sort to the original array
for (int z = 0; z < arrLength; z++) {
arr[z] = tr[z];
}
// Subsequence length modification
h *= 2;
}
return tr;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int arr[] = {
49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27 };
int* tr = mergSort(arr, 7);
for(int i=0;i<7;i++){
cout<<tr[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
Finally, there is a version of recursive implementation
The original pseudo code is as follows :
void MSort(RcdType SR[], RcdType &TR1[], int s, int t){
// take SR[s..t] The order of merging is TR1[s..t].
if(s == t) TR1[s]=SR[s];
else{
m = (s+t)/2;
MSort(SR, TR2,s,m);
MSort(SR, TR2,m+1,t);
Merge(TR2, TR1, s, m, t);
}
}// MSort
void MergeSort(SqList &L){
// For the sequence table L Merge and sort
MSortt(L.r, L.r, 1, L.length);
}//MergeSort
The above pseudocode has never been converted successfully , So I rewritten a version . This pseudo code means to split the array until there is 1 Individual elements , Then continue to merge in pairs , Keep going forward and backward , Until the final array is ordered . This recursive process is like the preorder traversal of a binary tree , Finally, return to , Form an ordered array , However, it this TR1,TR2 I really don't know what to say .
Rewrite as follows :
void mergeV2(int[] sr, int[] tr, int i, int m, int n) {
int k = 0;
int j = 0;
// take SR[i..m] and SR[m+1..n] Merge into ordered TR[i..n]
for (j = m + 1, k = i; i <= m && j <= n; ++k) {
if (sr[i] <= sr[j]) // take SR From small to large TR
tr[k] = sr[i++];
else
tr[k] = sr[j++];
}
if (i <= m) {
for (int u = i, q = 0; u <= m; u++) {
// Put the rest SR[i...m] Copied to the TR
tr[k + q] = sr[u];
++q;
}
}
if (j <= n) {
for (int u = j, q = 0; u <= n; u++) {
// Put the rest SR[j...n] Copied to the TR
tr[k + q] = sr[u];
++q;
}
}
}
// Recursive implementation , complete . It is slightly different from pseudo code
void MSortV2(int[] sr, int[] tr1, int s, int t) {
if (s == t) {
tr1[s] = sr[t];
} else {
int m = (s + t) / 2;
MSortV2(sr, tr1, s, m);
MSortV2(sr, tr1, m + 1, t);
mergeV2(sr, tr1, s, m, t);
for (int i = s; i <= t; i++) {
sr[i] = tr1[i];
}
}
}
@Test
public void fun3() {
int[] arr = new int[] {
49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27 };
int[] tr1 = new int[7];
MSortV2(arr, tr1, 0, arr.length - 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(tr1));
}
边栏推荐
- Basic knowledge points
- Out and ref functions of unity
- Pause and resume of cocos2dx Lua scenario
- AutoCAD - isometric annotation
- 《动手学深度学习》学习笔记
- 用 Jmeter 工具做个小型压力测试
- Generate filled text and pictures
- Unity writes timetables (without UI)
- UE4/UE5 虚幻引擎,材质篇(三),不同距离的材质优化
- 2022 thinking of mathematical modeling C problem of American college students / analysis of 2022 American competition C problem
猜你喜欢

Leetcode word search (backtracking method)
UE fantasy engine, project structure

2022 U.S. college students' mathematical modeling e problem ideas / 2022 U.S. game e problem analysis
Create a pyGame window with a blue background

Django reports an error when connecting to the database. What is the reason

JVM call not used once in ten years
UE4/UE5 虚幻引擎,材质篇,纹理,Compression and Memory压缩和内存
![Rip notes [rip three timers, the role of horizontal segmentation, rip automatic summary, and the role of network]](/img/e7/f699ee982ea325b8d04f8bd467a559.jpg)
Rip notes [rip three timers, the role of horizontal segmentation, rip automatic summary, and the role of network]
BUUCTF MISC
![[paper notes] multi goal reinforcement learning: challenging robotics environments and request for research](/img/17/db8614b177f33ee4f67b7d65a8430f.png)
[paper notes] multi goal reinforcement learning: challenging robotics environments and request for research
随机推荐
2022/7/2 question summary
Rip notes [rip three timers, the role of horizontal segmentation, rip automatic summary, and the role of network]
MD5 bypass
The difference between heap and stack
Understand encodefloatrgba and decodefloatrgba
用 Jmeter 工具做个小型压力测试
mysql审计日志归档
cocos_ Lua loads the file generated by bmfont fnt
小程序直播+電商,想做新零售電商就用它吧!
Vs2015 secret key
AutoCAD - Center zoom
【Leetcode】1352. Product of the last K numbers
[leetcode] integer inversion [7]
Unity and database
3dsmax scanning function point connection drawing connection line
Judge the position of the monster in the role under unity3d
Forecast report on research and investment prospects of Chinese wormwood industry (2022 Edition)
GameObject class and transform class of unity
Sixth note
使用命令符关闭笔记本自带键盘命令