当前位置:网站首页>Discriminant model: a discriminant model creation framework log linear model
Discriminant model: a discriminant model creation framework log linear model
2022-07-06 10:30:00 【HadesZ~】
Log-Linear Model It is a framework for creating discriminant model algorithm , It does not refer to a particular model 、 It refers to a kind of model .
1. Definition
Let the model predict and consider J J J Species characteristics , j = 1 , 2 , ⋯ , J j=1,2, \cdots, J j=1,2,⋯,J; w j w_j wj Indicates that the model is right j j j Parameters of kinds of features , Its value is estimated in the process of model training ; F j ( X , y ) F_j(X, y) Fj(X,y) Represents the second part of the model j j j Characteristic function of kinds of characteristics (feature function), It expresses characteristics X X X And labels y y y Some of the relationships between , The dependent variable is the... Used for model prediction j j j Features ; Z ( X , W ) Z(X,W) Z(X,W) The normalization coefficient representing the predicted value of model characteristics , It is called normalization term or partion function. Under these conditions , The objective function of the model can be expressed as follows :
P ( y ∣ X ; W ) = e x p [ ∑ j = 1 J w j F j ( X , y ) ] Z ( X , W ) (1) P(y|\ X;W) = \frac{exp[\sum_{j=1}^{J} w_jF_j(X, y)]}{Z(X,W)} \tag{1} P(y∣ X;W)=Z(X,W)exp[∑j=1JwjFj(X,y)](1)
In the model , The characteristic function of each feature (feature function) Set manually , Given different characteristic functions, different kinds of models can be derived , establish feature function It is a process of Feature Engineering . When given manually feature function when , It's a machine learning process , When given by automatic feature mechanism feature function when , It's a deep learning process .
Z ( X , W ) Z(X,W) Z(X,W) Equal to the sum of the numerators of all possible categories of the label , namely Z ( X , W ) = ∑ i = 1 C e x p [ ∑ j = 1 J w j F j ( X , y = c i ) ] Z(X,W) = \sum_{i=1}^{C}exp[\sum_{j=1}^{J} w_jF_j(X, y = c_i)] Z(X,W)=∑i=1Cexp[∑j=1JwjFj(X,y=ci)], Its function is to normalize the molecular term , Let the fractional result satisfy the conditional probability property .
2. Derivative logistic regression model
Let the set of all possible tags be C = { c 1 , c 2 , ⋯ , c N } C = \{c_1, c_2, \cdots, c_N\} C={ c1,c2,⋯,cN}、 Input characteristics X X X Is a length of J J J Vector X = ( x 1 , x 2 , ⋯ , x d ) X=(x_1, x_2, \cdots, x_d) X=(x1,x2,⋯,xd). So given F j ( X , y ) = x j ⋅ I ( y = c i ) F_j(X, y) = x_j \cdot I(y=c_i) Fj(X,y)=xj⋅I(y=ci), I ( y = c i ) I(y=c_i) I(y=ci) yes indicator function, When y = c i y=c_i y=ci when indicator function The value of is 1, Otherwise 0. therefore , The objective function of the model is :
P ( y = c i ∣ X ; W ) = e x p [ ∑ j = 1 + d ( i − 1 ) d + d ( i − 1 ) w j x j − d ( i − 1 ) ] ∑ i = 1 C e x p [ ∑ j = 1 + d ( i − 1 ) d + d ( i − 1 ) w j x j − d ( i − 1 ) ] (2) P(y=c_i|\ X;W) = \frac{ exp \begin{bmatrix} \sum_{j=1 + d(i-1)}^{d+d(i-1)} w_jx_{j-d(i-1)} \end{bmatrix} }{ \sum_{i=1}^{C} exp \begin{bmatrix} \sum_{j=1 + d(i-1)}^{d+d(i-1)} w_jx_{j-d(i-1)} \end{bmatrix} } \tag{2} P(y=ci∣ X;W)=∑i=1Cexp[∑j=1+d(i−1)d+d(i−1)wjxj−d(i−1)]exp[∑j=1+d(i−1)d+d(i−1)wjxj−d(i−1)](2)
Where the model parameters w j ∈ R 3 d wj \in R^{3d} wj∈R3d, Parameter vector W = ( w 1 , w 2 , ⋯ , w d , w d + 1 , ⋯ , w 2 d , ⋯ , w 1 + d ( C − 1 ) , ⋯ , w d + d ( C − 1 ) ) W = (w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_d, w_{d+1}, \cdots, w_{2d}, \cdots,w_{1+d(C-1), \cdots, w_{d+ d(C-1)}}) W=(w1,w2,⋯,wd,wd+1,⋯,w2d,⋯,w1+d(C−1),⋯,wd+d(C−1)); Let's take the sub vectors in the parameter vector ( w 1 + d ( i − 1 ) , ⋯ , w d + d ( i − 1 ) ) (w_{1 + d(i-1)}, \cdots, w_{d + d(i-1)}) (w1+d(i−1),⋯,wd+d(i−1)) Write it down as W i W_{i} Wi, So the parameter vector can be rewritten as W = ( W 1 , W 2 , ⋯ , W C ) W=(W_{1}, W_{2}, \cdots, W_{C}) W=(W1,W2,⋯,WC), Bring it into type ( 2 ) type (2) type (2) The objective function of the model can be abbreviated as :
P ( y = c i ∣ X ; W ) = e x p [ W i T ⋅ X ] ∑ i = 1 C e x p [ W i T ⋅ X ] (3) P(y=c_i|\ X;W) = \frac{ exp [W_{i}^T \cdot X] }{ \sum_{i=1}^{C} exp [W_{i}^T \cdot X] } \tag{3} P(y=ci∣ X;W)=∑i=1Cexp[WiT⋅X]exp[WiT⋅X](3)
obviously , type ( 3 ) type (3) type (3) Equivalent to P ( y ∣ X ; W ) = S o f t m a x ( W T X ) P(y|\ X;W) = Softmax(W^TX) P(y∣ X;W)=Softmax(WTX); thus , We have Log-Linear Model A multi classification logistic regression model is derived (Multinomial Logistic Regression).
3. derivative CRF Model
Empathy , set up X ˉ \bar{X} Xˉ Is a length of T T T Observable feature sequence of , y ˉ \bar{y} yˉ Is its corresponding tag sequence , If given F j ( X , y ) = ∑ t = 2 T f t ( y t − 1 , y t , X ˉ , t ) F_j(X, y) = \sum_{t=2}^{T} f_t(y_{t-1}, y_t, \bar{X}, t) Fj(X,y)=∑t=2Tft(yt−1,yt,Xˉ,t) , Then you can get Linera CRF The objective function of the model :
P ( y ˉ ∣ X ˉ ; W ) = 1 Z ( X , W ) e x p [ ∑ t = 2 T f t ( y t − 1 , y t , X ˉ , t ) ] (4) P(\bar{y}|\ \bar{X};W) = \frac{1}{Z(X,W)}exp \begin{bmatrix} \sum_{t=2}^{T} f_t(y_{t-1}, y_t, \bar{X}, t) \end{bmatrix} \tag{4} P(yˉ∣ Xˉ;W)=Z(X,W)1exp[∑t=2Tft(yt−1,yt,Xˉ,t)](4)
边栏推荐
- MySQL27-索引優化與查詢優化
- 第一篇博客
- MySQL实战优化高手07 生产经验:如何对生产环境中的数据库进行360度无死角压测?
- 该不会还有人不懂用C语言写扫雷游戏吧
- Implement context manager through with
- Windchill配置远程Oracle数据库连接
- Solution to the problem of cross domain inaccessibility of Chrome browser
- pytorch的Dataset的使用
- [paper reading notes] - cryptographic analysis of short RSA secret exponents
- How to build an interface automation testing framework?
猜你喜欢
MySQL 29 other database tuning strategies
South China Technology stack cnn+bilstm+attention
基于Pytorch的LSTM实战160万条评论情感分类
Installation of pagoda and deployment of flask project

Sichuan cloud education and double teacher model
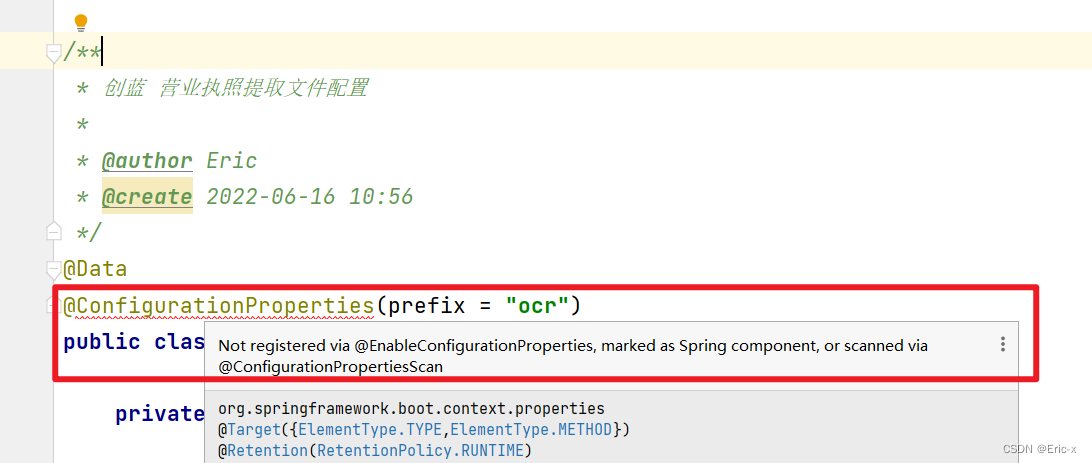
Not registered via @EnableConfigurationProperties, marked(@ConfigurationProperties的使用)
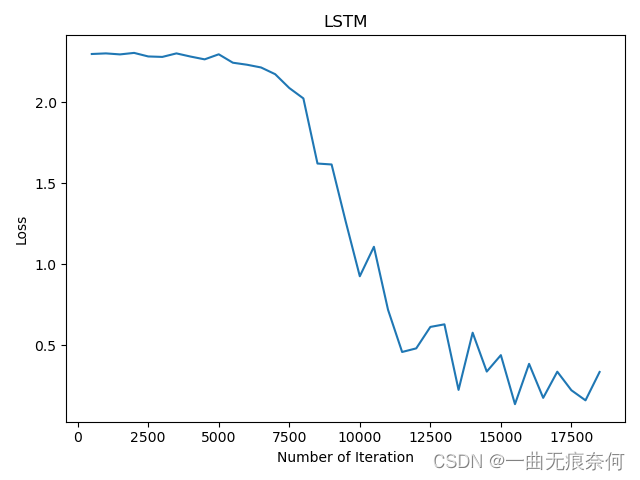
Pytoch LSTM implementation process (visual version)

寶塔的安裝和flask項目部署
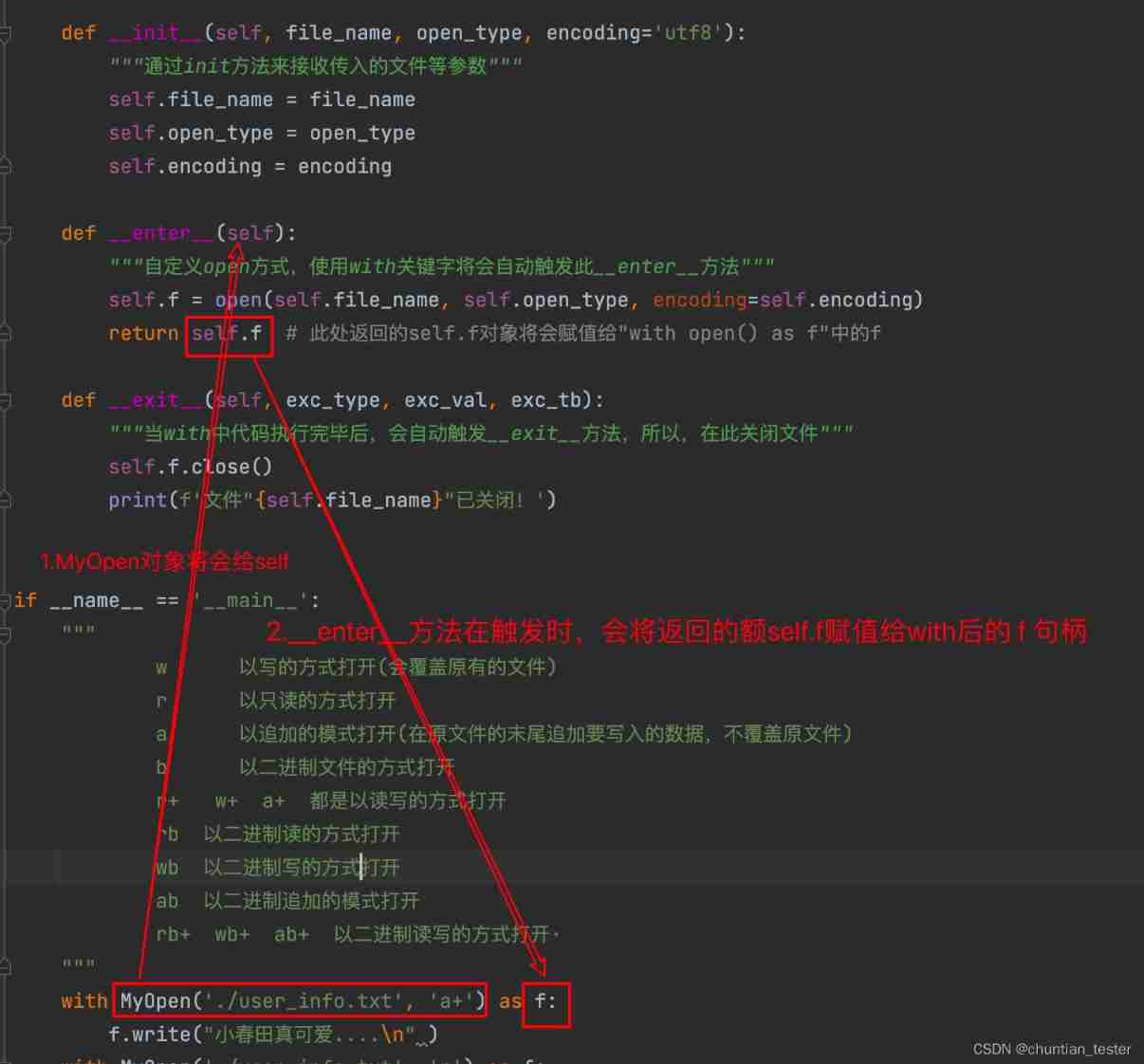
Implement context manager through with
Mysql30 transaction Basics
随机推荐
MySQL底层的逻辑架构
[programmers' English growth path] English learning serial one (verb general tense)
Implement context manager through with
Installation de la pagode et déploiement du projet flask
安装OpenCV时遇到的几种错误
寶塔的安裝和flask項目部署
Routes and resources of AI
14 医疗挂号系统_【阿里云OSS、用户认证与就诊人】
MySQL combat optimization expert 10 production experience: how to deploy visual reporting system for database monitoring system?
MySQL ERROR 1040: Too many connections
MySQL实战优化高手07 生产经验:如何对生产环境中的数据库进行360度无死角压测?
Download and installation of QT Creator
C miscellaneous lecture continued
Set shell script execution error to exit automatically
Mysql27 - Optimisation des index et des requêtes
Technology | diverse substrate formats
软件测试工程师必备之软技能:结构化思维
Export virtual machines from esxi 6.7 using OVF tool
基于Pytorch肺部感染识别案例(采用ResNet网络结构)
The appearance is popular. Two JSON visualization tools are recommended for use with swagger. It's really fragrant