当前位置:网站首页>Convolutional neural network (CNN) learning notes (own understanding + own code) - deep learning
Convolutional neural network (CNN) learning notes (own understanding + own code) - deep learning
2022-07-03 10:27:00 【JallinRichel】
Convolutional neural networks (CNN) Learning notes ( My understanding + Write your own code )——Deep Learning
Abstract : The content of the article is that I am learning Deep Learning Understanding in the process , The code is also typed by yourself ( Code ability is not very strong ). If there is something wrong , Welcome to point out , correct .
Why use convolutional neural networks
There are two problems when using a fully connected network to process pictures
- Too many parameters ( Hollow — The first hidden layer ; Solid — Input layer ):

If the input picture is (100x100x3), Then every neuron in the hidden layer to the input layer 30000 Two independent connections , Each connection corresponds to a weight parameter (weight). With the increase of network size , The number of parameters will also rise sharply . This will make the training efficiency of the whole network very low , And it's easy to over fit .
- Locally invariant features : Convolutional neural networks have biological properties Feel the field Mechanism , It can better ensure the local invariance of the image .
at present CNN It is generally composed of convolution (Convolution)、 Pooling layer 【 Some books are also called convergence layer 】(Pooling)、 Fully connected layer (Linear) Cross stacked Feedforward neural networks . The full connection layer is generally CNN Top of .
CNN It has three structural characteristics : Local invariance 、 Weight sharing 、 Converge . These characteristics make CNN It has a certain degree of local invariance , And there are fewer parameters than full connection .
Convolution (Convolution)
One dimensional convolution
Convolution in neural networks is actually well understood , Here's the picture :( The following formula can be expressed in matrix form in two-dimensional processing )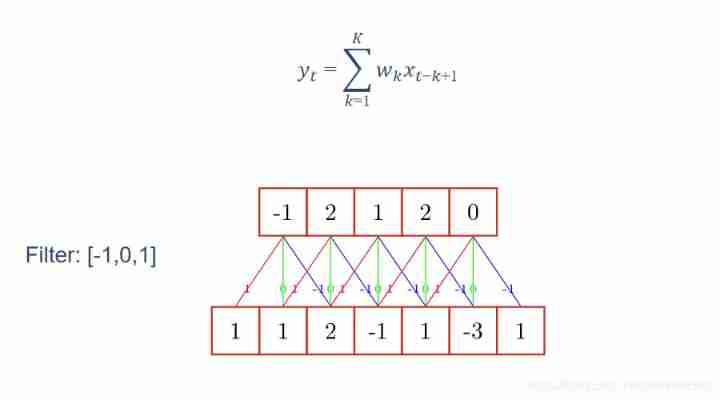
there Filter In signal processing, it is called filter , stay CNN Chinese is what we often use Convolution kernel . The value of convolution kernel [-1,0,1] Is the weight matrix . Given an input sequence ( The next row ) And a convolution kernel , After convolution , You can get an output sequence ( The upper row ).
Different output sequences can be obtained by convoluting input sequences with different convolution kernels , That is to extract different features of the input sequence .
Two dimensional convolution
Because the image is a two-dimensional structure ( Has rows and columns ), So we need to expand convolution ( The following figure shows the two-dimensional convolution operation ):

You can add an offset after the above formula Bias;
Convolution kernel and bias are both learnable parameters .
In machine learning and image processing , The main function of convolution is to slide a convolution kernel on an image , A new set of features is obtained by convolution . Here's the picture :


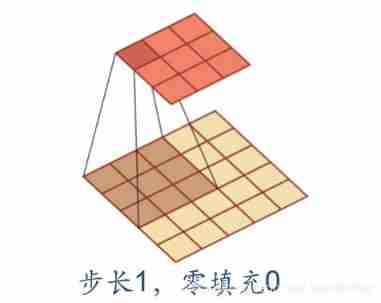
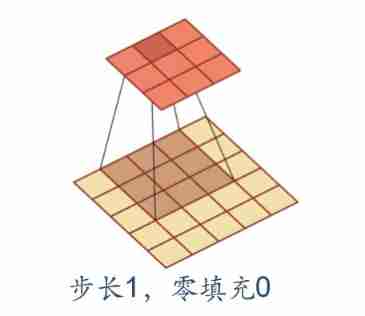
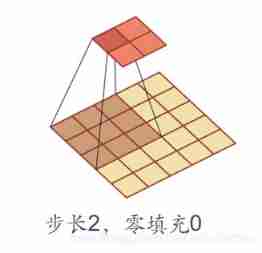
Step size and fill (Stride & padding)
In convolution , We can also introduce convolution kernel Sliding step and Zero fill To increase the diversity of convolution kernels , Feature extraction can be more flexible .
- step : The time interval of convolution kernel in sliding ( Figuratively speaking, it is the span when sliding )
- Zero fill : Fill zero at both ends of the input vector
Here's the picture :



Convolutional neural networks
According to the definition of convolution , Convolution layer has two very important properties :
- Local connection
- Weight sharing
Convolutional neural network is to use convolution layer instead of full connection layer :
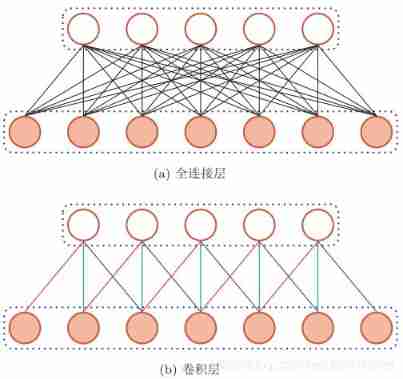
You can see , Because of the convolution layer Local connection Characteristics of , The convolution layer contains much less parameters than the full connection layer .
Weight sharing It can be understood that a convolution kernel only captures a specific local feature in the input data . therefore , If you want to extract multiple features, you need to use multiple different convolution kernels ( You can see clearly in the three-dimensional way behind ). Pictured above , The weight of all connections with the same color is the same .
Because of local connectivity and weight sharing , The convolution layer has only one parameter K The weight of dimensions W(l) And one-dimensional offset b(l) , common K+1 Parameters .
Convolution layer
The function of convolution layer is to extract the features of a local region , Different convolution kernels are equivalent to different feature extractors .
Because the image is a two-dimensional structure , Therefore, in order to make full use of the local information of the image , Neurons are usually organized into three-dimensional neural layers , Size is height M x Width N x depth D, from D individual M x N The feature mapping of size constitutes .
Feature mapping is the feature extracted by convolution of an image , Each feature map can be used as a class of extracted image features .
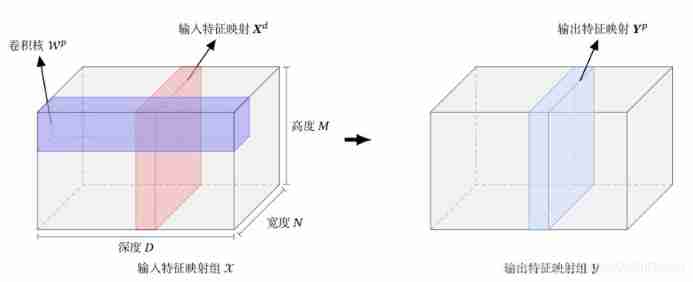

Such as a RGB picture , The depth in the above figure D Is the number of channels in the picture , Height and width correspond to the size of the picture . There are three convolution kernels corresponding to the output of three feature maps Yp .
The calculation of feature mapping is shown in the figure below :

Pooling layer ( Convergence layer )
Although the convolution layer can significantly reduce the number of connections in the network , However, the number of neurons in the feature mapping group did not decrease significantly . If followed by a classifier , Its input dimension is still very high , It's easy to get over fitted . Thus, a pool layer is proposed .
The pooling layer is also called sub sampling layer , The function is to select features , Reduce the number of features , So that we can reduce the number of parameters .
Common pooling methods include :
- Maximum pooling (Max pooling): Select the maximum activity value of all neurons in a region as the representation of this region .
- The average pooling (Mean pooling): Take the average value of neuron activity in the region as the representation of this region .
The maximum pooling is shown in the figure below :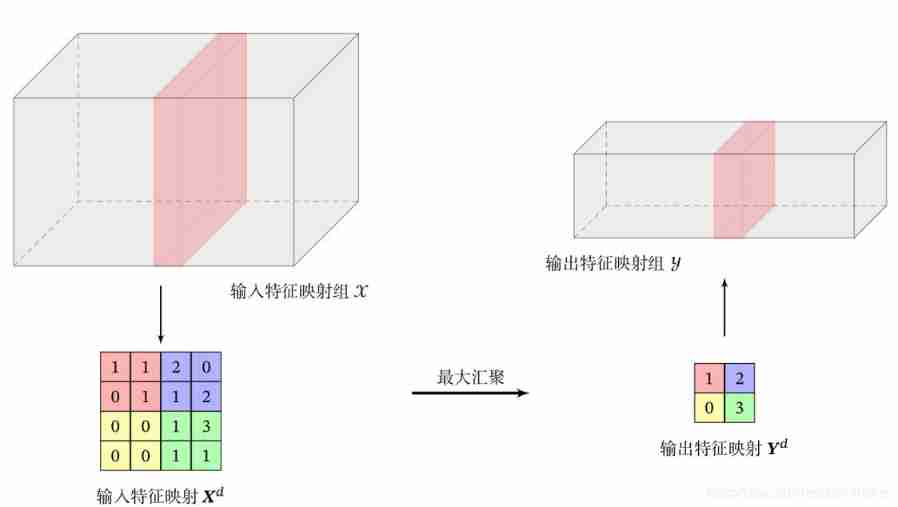
The overall structure of convolution network
The overall structure of the convolution network commonly used at present is shown in the figure below :
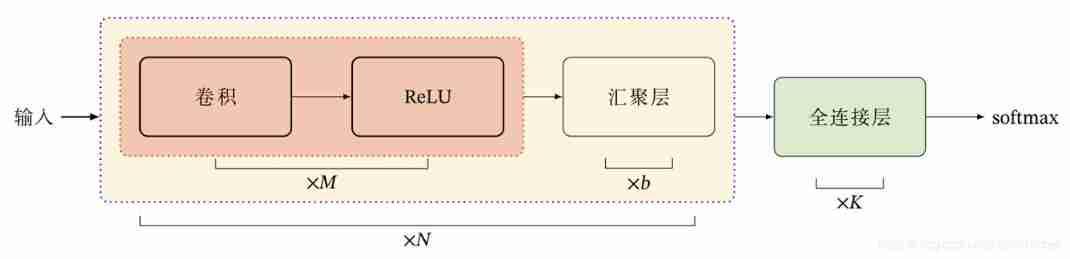
at present , The overall structure of convolution networks tends to use smaller convolution kernels ( The size of convolution kernel is generally odd ) And deeper network structure .
Besides , As the operability of the convolution layer becomes more and more flexible , The role of the pool layer is also getting smaller , Therefore, the current popular convolutional networks tend to be full convolutional Networks .
Residual network (Residual Net)
The residual network increases the propagation efficiency of information by adding direct edges to the nonlinear convolution layer .
- Suppose in a deep network , We expect a nonlinear element ( It can be one or more convolution layers )f(x, y) To approximate an objective function h(x).
- Split the objective function into two parts : Identity function and residual function

Residual unit :

Residual network is a very deep network composed of many residual units in series .
Other convolution methods
Transposition convolution —— Low dimensional features are mapped to high dimensions :


Cavity convolution —— By inserting... Into the convolution kernel “ empty ” To increase its size in disguise :


Add
(1) We can go through :
- Increase the size of the convolution kernel
- Increase the number of layers
- The convergence operation is performed before convolution
To increase the receptive field of the output unit
Code
Environmental preparation :
- numpy
- anaconda
- Pycharm
One dimensional convolution
def Convolution_1d(input, kernel, padding=False, stride=1):
input = np.array(input)
kernel = np.array(kernel)
kernel_size = kernel.shape[0]
output = np.zeros((len(input) - kernel_size) // stride + 1)
if padding:
paddings = 1
input_shape = len(input) + 2*paddings
output = np.zeros((input_shape - kernel_size) // stride + 1)
for i in range(len(output)):
output[i] = np.dot(input[i:i+kernel_size], kernel)
return output
Input :
input = [2,5,9,6,3,5,7,8,5,4,5,2,5,6,3,5,8,7,1,0,5,0,10,20,60]
print('input_len: ', len(input))
kernel = [1,-1,1]
print('kernel_len: ', len(kernel))
output = Convolution_1d(input=input, kernel=kernel)
print('output_len: ', len(output))
print('output: ',output)
Output results :
Two dimensional convolution
def Convolution_2d(input, kernel, padding=False, stride=1):
input = np.array(input)
kernel = np.array(kernel)
stride = stride
input_row = input.shape[0]
input_col = input.shape[1]
kernel_size = kernel.shape[0]
output_row = (input_row - kernel_size) // stride + 1
output_col = (input_col - kernel_size) // stride + 1
output = np.zeros((output_row, output_col))
if padding:
padding=1
input_row = input.shape[0]+2*padding
input_col = input.shape[1]+2*padding
output_row = (input_row-kernel_size) // stride + 1
output_col = (input_col-kernel_size) // stride + 1
output = np.zeros((output_row, output_col))
for i in range(output_row):
for j in range(output_col):
output[i,j] = np.sum(input[i:i+kernel_size,j:j+kernel_size] * kernel)
return output
Input :
input = np.array([[2,7,3],[2,5,4],[9,4,2]])
kernel = np.array([[-1,1],[1,-1]])
output = Convolution_2d(input,kernel)
print('\n',output)
Output results :
Two dimensional convolution can also be realized by one-dimensional convolution , Just make some modifications to the one-dimensional convolution .
High dimensional convolution can be achieved by modifying two-dimensional convolution .
The code is a little fragmented , Forgive me , Forgive me
边栏推荐
- 20220606数学:分数到小数
- 20220607 others: sum of two integers
- LeetCode - 919. Full binary tree inserter (array)
- 20220610 other: Task Scheduler
- Training effects of different data sets (yolov5)
- CV learning notes - clustering
- 2312. Selling wood blocks | things about the interviewer and crazy Zhang San (leetcode, with mind map + all solutions)
- Policy gradient Method of Deep Reinforcement learning (Part One)
- 20220608其他:逆波兰表达式求值
- LeetCode - 900. RLE iterator
猜你喜欢

Leetcode-106:根据中后序遍历序列构造二叉树

Handwritten digit recognition: CNN alexnet
Leetcode bit operation
![[LZY learning notes dive into deep learning] 3.1-3.3 principle and implementation of linear regression](/img/ce/8c2ede768c45ae6a3ceeab05e68e54.jpg)
[LZY learning notes dive into deep learning] 3.1-3.3 principle and implementation of linear regression

Raspberry pie 4B deploys lnmp+tor and builds a website on dark web

Leetcode - the k-th element in 703 data flow (design priority queue)
Leetcode - 1670 conception de la file d'attente avant, moyenne et arrière (conception - deux files d'attente à double extrémité)

Label Semantic Aware Pre-training for Few-shot Text Classification

2312. Selling wood blocks | things about the interviewer and crazy Zhang San (leetcode, with mind map + all solutions)

openCV+dlib实现给蒙娜丽莎换脸
随机推荐
CV learning notes alexnet
Leetcode-106: construct a binary tree according to the sequence of middle and later traversal
Synchronous vs asynchronous
Several problems encountered in installing MySQL under MAC system
Leetcode - 705 design hash set (Design)
一步教你溯源【钓鱼邮件】的IP地址
Configure opencv in QT Creator
High imitation Netease cloud music
One click generate traffic password (exaggerated advertisement title)
Leetcode interview question 17.20 Continuous median (large top pile + small top pile)
CV learning notes - deep learning
Powshell's set location: unable to find a solution to the problem of accepting actual parameters
Anaconda安装包 报错packagesNotFoundError: The following packages are not available from current channels:
Training effects of different data sets (yolov5)
[LZY learning notes dive into deep learning] 3.4 3.6 3.7 softmax principle and Implementation
Leetcode-513:找树的左下角值
Hands on deep learning pytorch version exercise solution - 2.4 calculus
CV learning notes - clustering
LeetCode - 705 设计哈希集合(设计)
LeetCode - 900. RLE iterator