当前位置:网站首页>Talk about pseudo sharing
Talk about pseudo sharing
2022-07-07 13:27:00 【Young】
On the weekend , A reader told me , During the interview, I was asked :「 What is pseudo sharing ? How to avoid the problem of pseudo sharing ?」
This is actually an investigation CPU Cache issues , I also mentioned in my previous graphic system .
today , Let me tell you again .
Text
CPU How to read and write data ?
Let's get to know CPU The architecture of , Only understand CPU Of framework , To better understand CPU How to read and write data , For the modern CPU The architecture of is as follows :
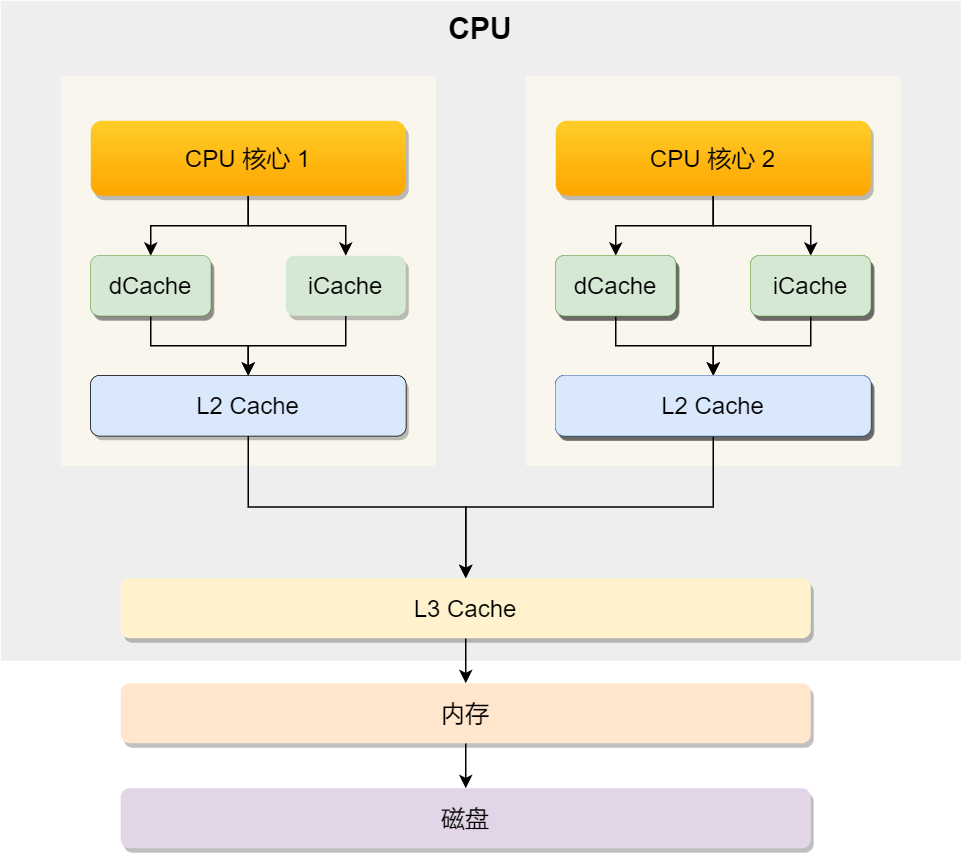
You can see , One CPU There are usually multiple CPU The core , Like the one above 1 Number and 2 Number CPU The core , And each CPU The core has its own L1 Cache and L2 Cache, and L1 Cache Usually divided into dCache( Data caching ) and iCache( Instruction cache ),L3 Cache It's shared by multiple cores , This is it. CPU A typical cache hierarchy .
All of the above are CPU Inside Cache, If you look outside , There will also be memory and hard disk , These storage devices together constitute the pyramid storage hierarchy . As shown in the figure below :
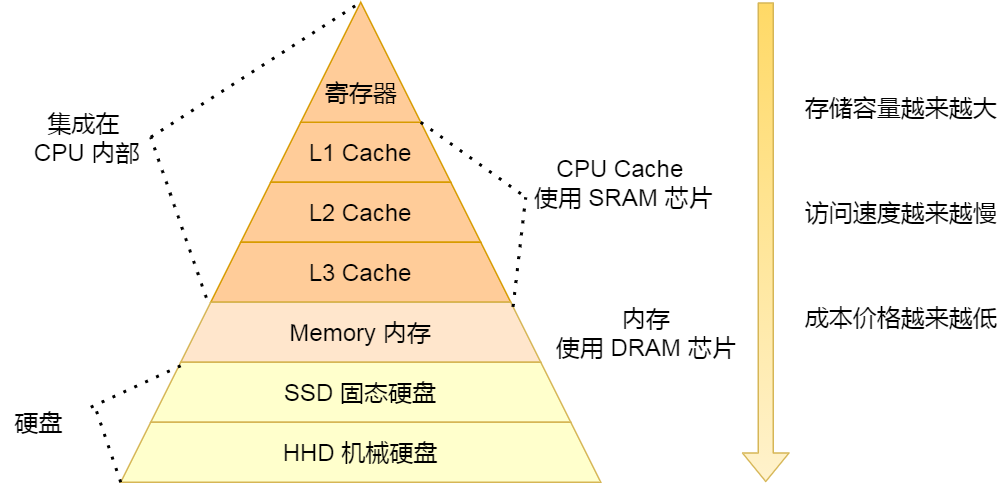
As you can see from the picture above , From the top down , The larger the capacity of the storage device , And the slower the access speed . As for the access delay of each storage device , You can see the chart below :
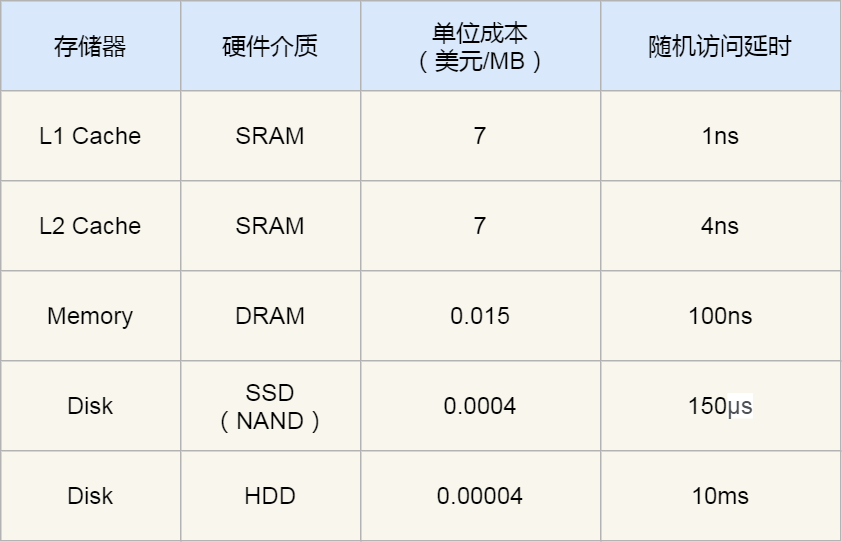
You can see , CPU visit L1 Cache Faster than accessing memory 100 times , That's why CPU There will be L1~L3 Cache Why , The purpose is to put Cache As CPU Cache layer between and memory , To reduce the frequency of memory access .
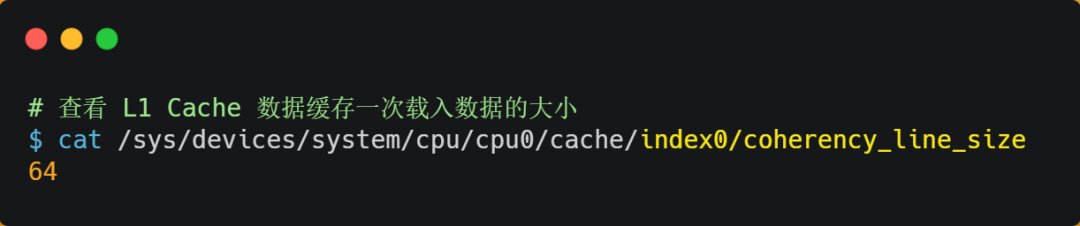
CPU Read data from memory to Cache When , It's not a byte by byte read , It's block by block , This piece of data is called CPU Line( Cache line ), therefore CPU Line yes CPU Read data from memory to Cache The unit of .
as for CPU Line size , stay Linux The system can view , You can see my server's L1 Cache Line Size is 64 byte , That means L1 Cache The size of the data loaded at a time is 64 byte .
So loading arrays , CPU It will load multiple consecutive data in the array to Cache in , Therefore, we should access the elements in the order of physical memory address distribution , When accessing array elements like this ,Cache The hit rate will be high , So you can reduce the frequency of reading data from memory , This can improve the performance of the program .
however , We don't use arrays , But when you use separate variables , Will have a Cache The problem of pseudo sharing ,Cache Pseudo sharing is a performance killer , We should avoid it .
Next , Take a look at Cache What is pseudo sharing ? And how to avoid this problem ?
Now suppose you have a dual core CPU, these two items. CPU The core runs two different threads in parallel , They read two different data from memory at the same time , They are of type long The variable of A and B, The addresses of these two data are in physical memory continuity Of , If Cahce Line Its size is 64 byte , And variable A stay Cahce Line At the beginning of , So these two data are located in The same Cache Line in , Again because CPU Line yes CPU Read data from memory to Cache The unit of , So these two data will be read into two at the same time CPU Each in the core Cache in .
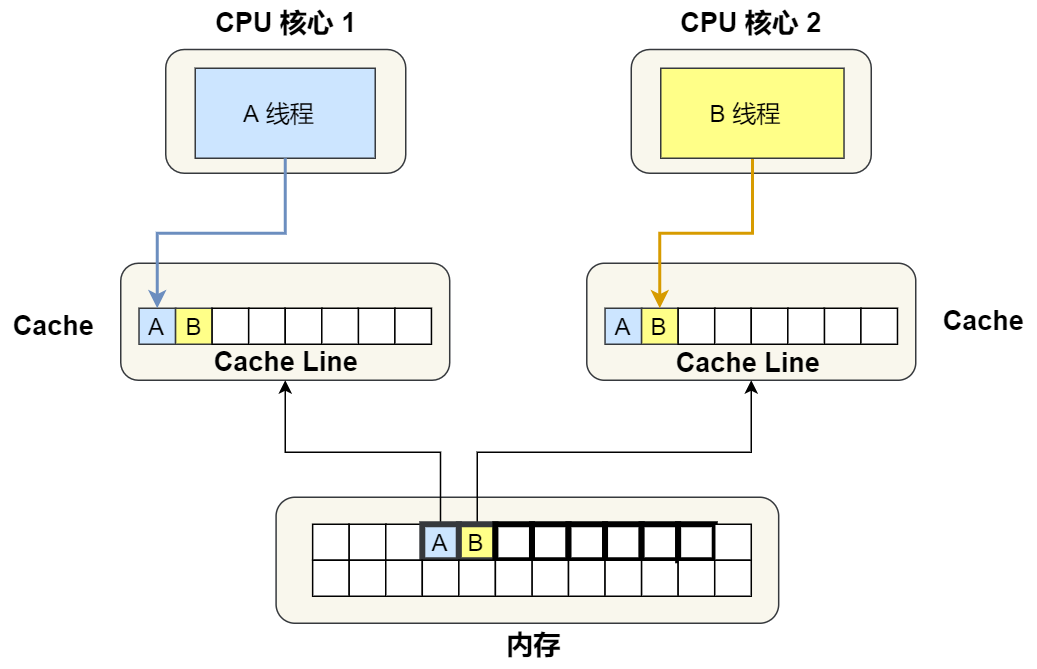
Let's think about a problem , If these two threads with different cores modify different data , such as 1 Number CPU The core thread only modified Variable A, or 2 Number CPU The thread of the core thread only modifies the variables B, What will happen ?
Analyze the problem of pseudo sharing
Now let's combine to ensure the consistency of multi-core cache MESI agreement , To illustrate the whole process , If you don't know MESI agreement , You can read my article 「10 A picture opens CPU The door to cache consistency 」.
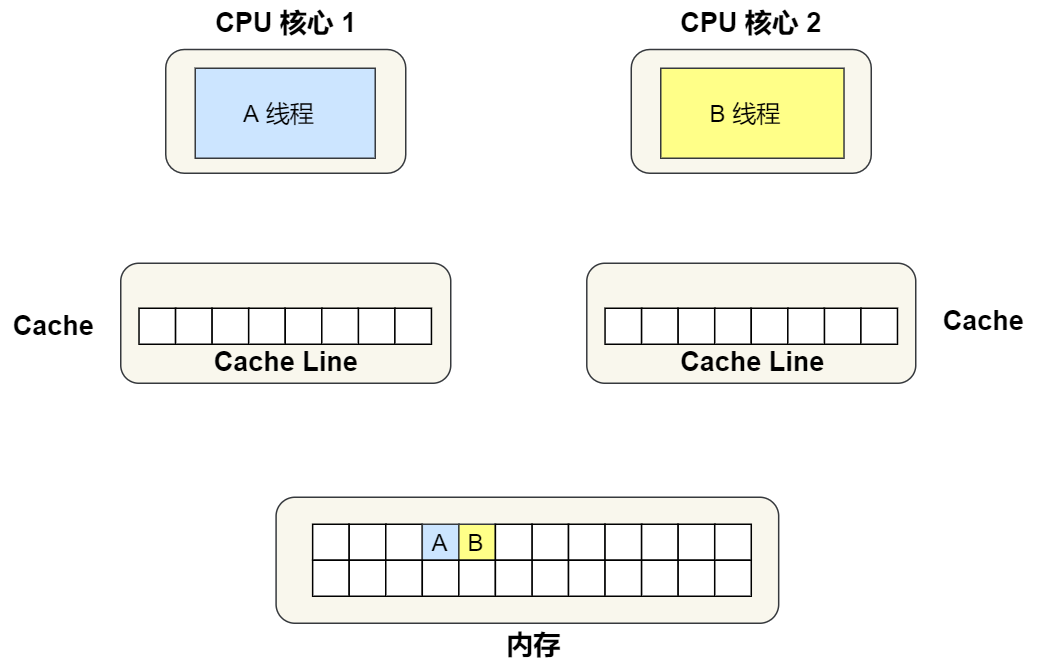
①. First variable A and B Not yet Cache Inside , hypothesis 1 Core No. 1 binds threads A,2 Core No. 1 binds threads B, Threads A Only read and write variables A, Threads B Only read and write variables B.
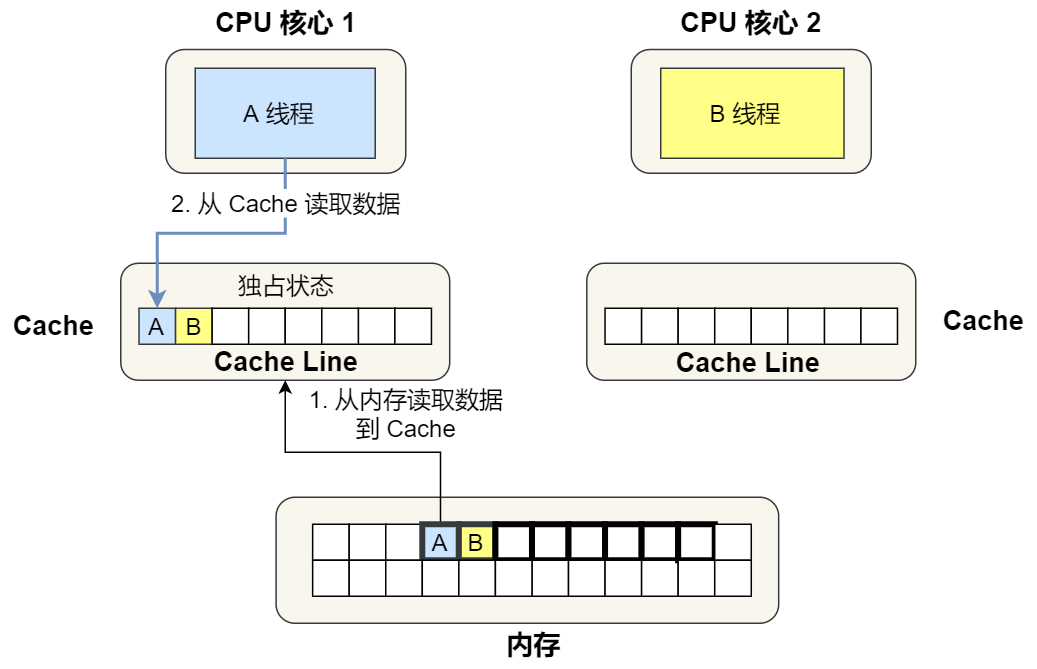
②. 1 Core read variables A, because CPU Read data from memory to Cache Its unit is Cache Line, It's just the variable A and Variable B The data belongs to the same Cache Line, therefore A and B The data will be loaded into Cache, And Cache Line Marked as 「 Monopoly 」 state .
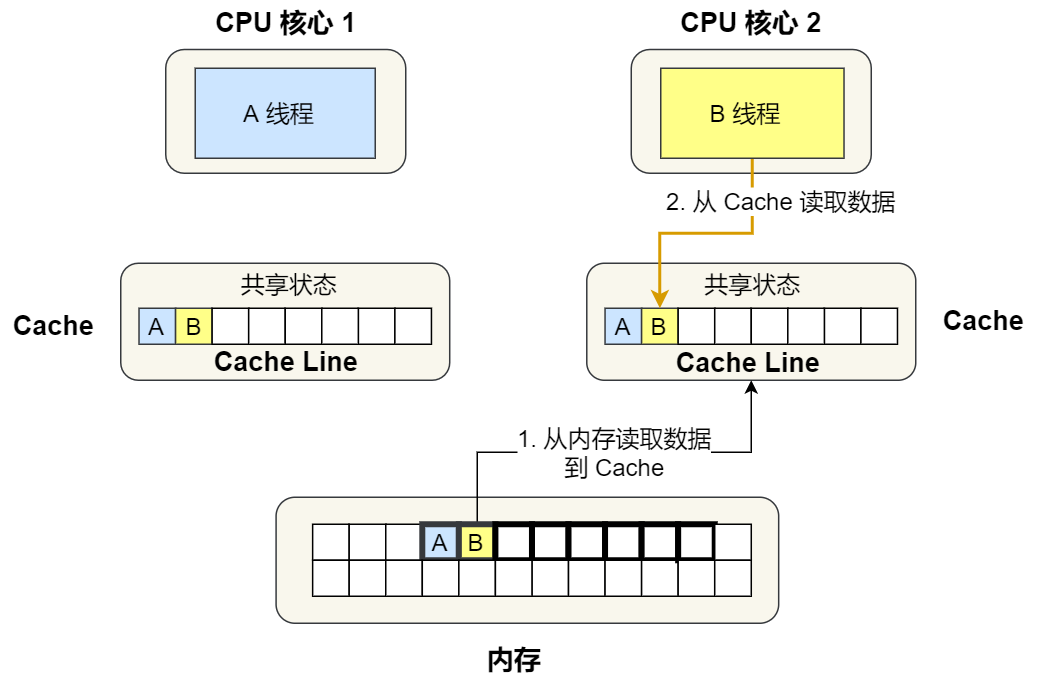
③. next ,2 The core starts to read variables from memory B, It's also about reading Cache Line The size of the data to Cache in , this Cache Line The data in also contains variables A and Variable B, here 1 Number and 2 No. 1 core Cache Line The status changes to 「 share 」 state .
④. 1 Core No. 2 needs to modify variables A, Found this Cache Line The state of is 「 share 」 state , So we need to send a message to 2 Number one core , notice 2 No. 1 core handle Cache Corresponding Cache Line Marked as 「 Has lapsed 」 state , then 1 The core of No Cache Line The state becomes 「 The modified 」 state , And modify the variable A.
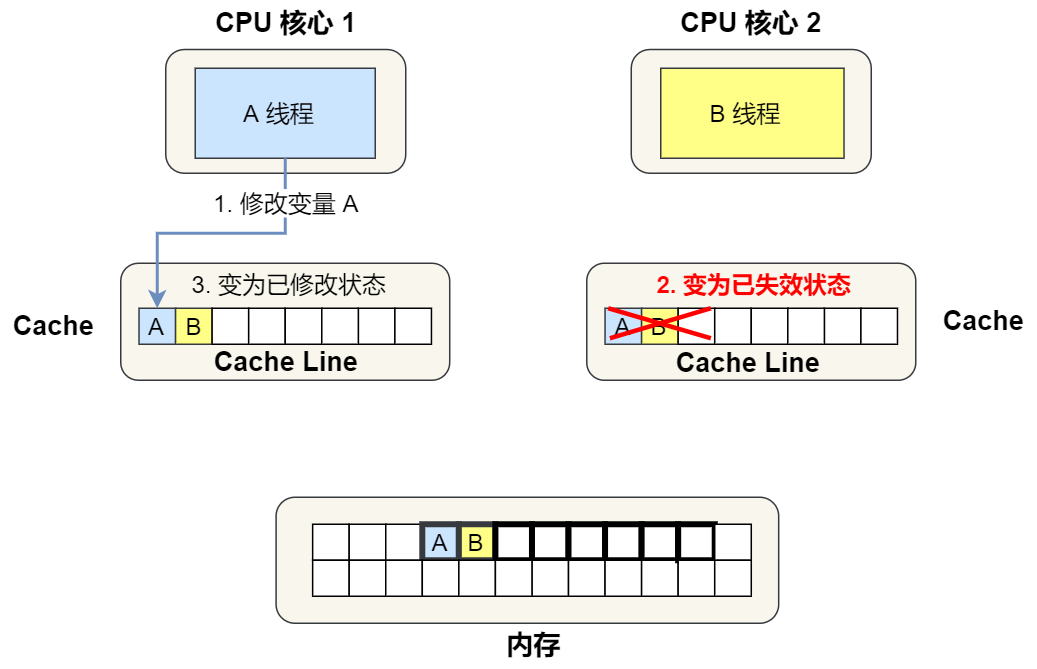
⑤. after ,2 Core No. 2 needs to modify variables B, here 2 No. 1 core Cache Corresponding Cache Line It's a failed state , In addition, due to 1 No. 1 core Cache There's the same data , And the state is 「 The modified 」 state , So we need to 1 No. 1 core Cache Corresponding Cache Line Write back to memory , then 2 And then read it from memory Cache Line The size of the data to Cache in , Finally, put the variable B Modify to 2 No. 1 core Cache in , And mark the status as 「 The modified 」 state .
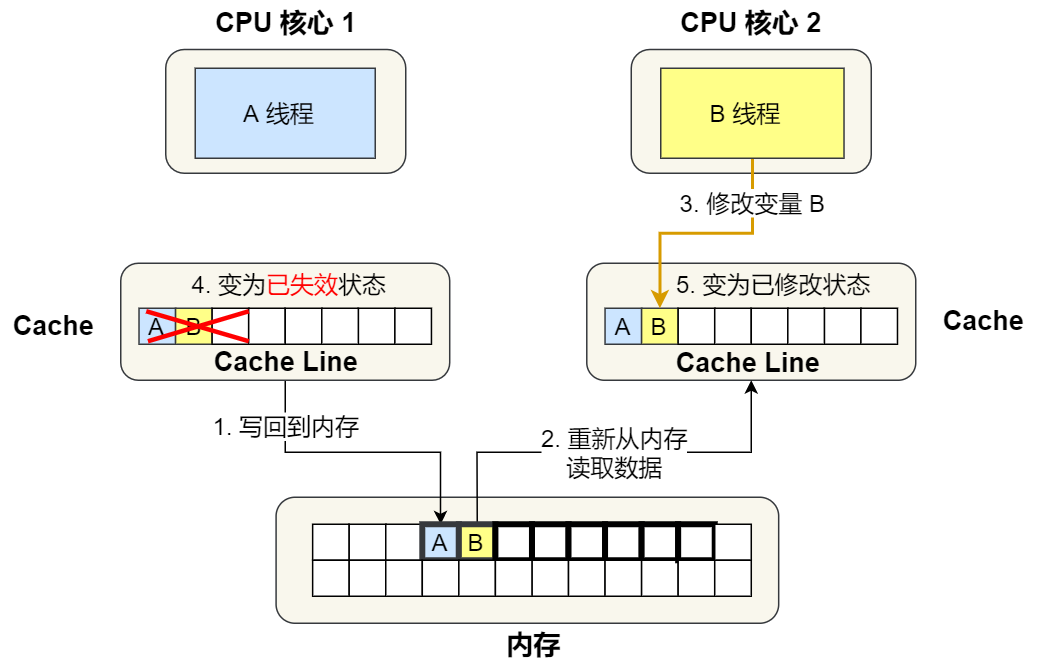
therefore , You can see if 1 Number and 2 Number CPU In this way, the core continuously alternates the variables A and B, Will repeat ④ and ⑤ These two steps ,Cache It doesn't work as a cache , Although variable A and B There is no relationship between them , But because it belongs to one at the same time Cache Line , This Cache Line After any data in has been modified , Will affect each other , So that ④ and ⑤ These two steps .
therefore , This is because multiple threads read and write the same Cache Line Different variables of , And lead to CPU Cache The phenomenon of failure is called False sharing (*False Sharing*).
How to avoid pseudo sharing
therefore , For hot data shared by multiple threads , Data that is often modified , It should be avoided that these data happen to be in the same Cache Line in , Otherwise, there will be the problem of pseudo sharing .
Next , Let's see how to avoid the problem of pseudo sharing in the actual project .
stay Linux There is... In the kernel __cacheline_aligned_in_smp Macro definition , Is used to solve the problem of pseudo sharing .
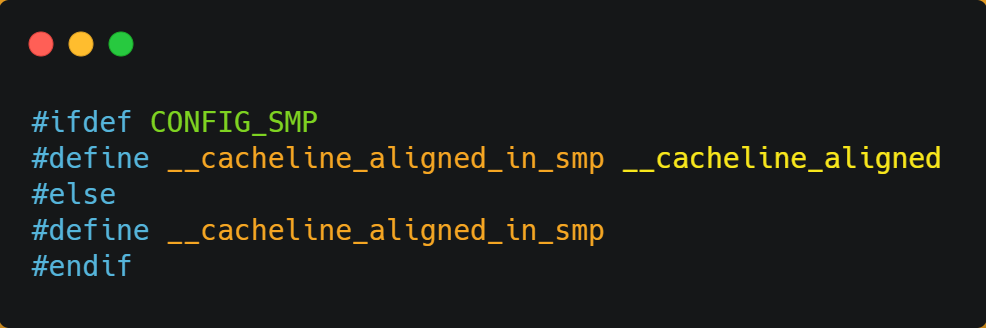
From the above macro definition , We can see :
- If it's multi-core (MP) In the system , The macro definition is
__cacheline_aligned, That is to say Cache Line Size ; - And if you're in a single core system , The macro definition is empty ;
therefore , For the same Cache Line Shared data in , If there is serious competition between multiple cores , In order to prevent the occurrence of pseudo sharing , You can use the macro definition above to make the variable in Cache Line It's aligned inside .
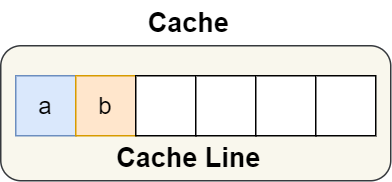
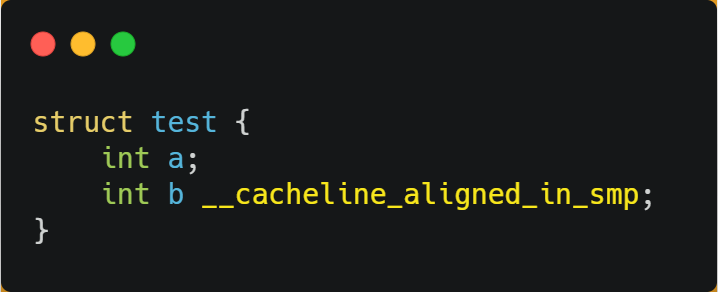
for instance , There's this structure :

Two member variables in a structure a and b Continuous in physical memory address , So they might be in the same place Cache Line in , Here's the picture :
therefore , In order to prevent the above mentioned Cache Pseudo sharing problem , We can use the macro definition described above , take b The address of is set to Cache Line Align address , as follows :
such a and b Variables will not be in the same Cache Line It's in , Here's the picture :
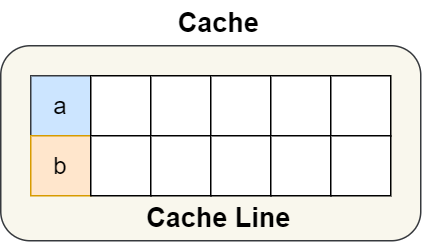
therefore , avoid Cache Pseudo sharing is actually the idea of exchanging space for time , Waste a part of Cache Space , In exchange for performance improvement .
Disruptor
Let's look at an application level circumvention scheme , There is one Java Concurrent framework Disruptor Use 「 Byte padding + Inherit 」 The way , To avoid the problem of pseudo sharing .
Disruptor There is one of them. RingBuffer Classes are often used by multiple threads , The code is as follows :
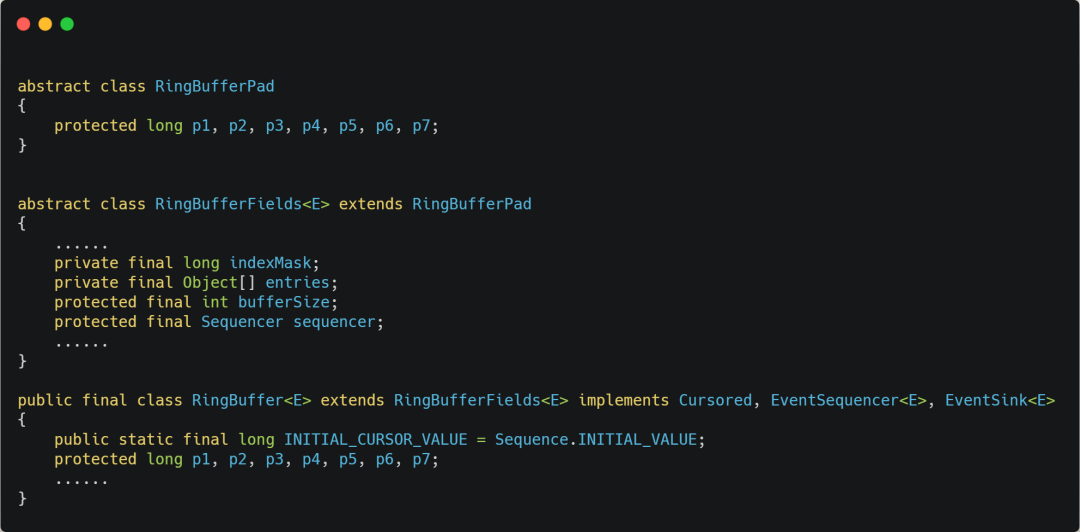
You might think RingBufferPad In class 7 individual long The name of the type is strange , But in fact , They don't seem to work , But it plays a crucial role in improving the performance .
We all know ,CPU Cache The unit of reading data from memory is CPU Line, commonly 64 position CPU Of CPU Line Its size is 64 Bytes , One long The type of data is 8 Bytes , therefore CPU It will load later 8 individual long Data of type .
according to JVM Object inheritance relationship in the parent class members and child class members , Memory addresses are arranged sequentially , therefore RingBufferPad Medium 7 individual long Type data as Cache Line Prepopulation , and RingBuffer Medium 7 individual long Type data is used as Cache Line Post fill , this 14 individual long Variables have no practical use , And they don't read and write them .
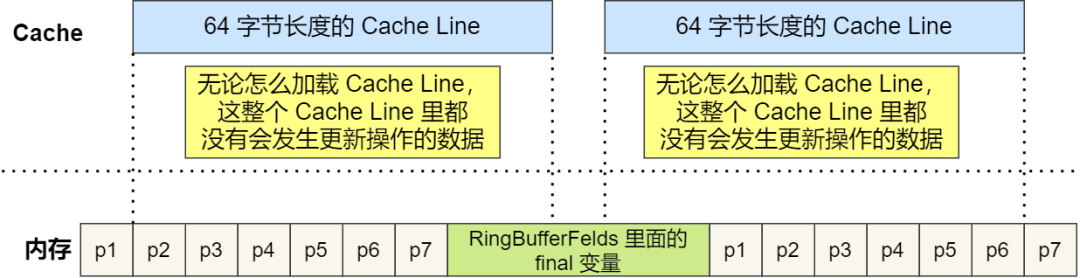
in addition ,RingBufferFelds The variables defined in it are final Embellished , It means that it will not be modified after the first load , also because 「 Before and after 」 Each is filled with 7 One that can't be read or written long Type variable , So no matter how you load Cache Line, This whole Cache Line There is no data in the database that will be updated , So as long as the data is read and accessed frequently , Naturally, no data is swapped out Cache The possibility of , Therefore, there will be no pseudo sharing problem .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
DETR介绍
DHCP 动态主机设置协议 分析

Cinnamon 任务栏网速
Write it down once Net a new energy system thread surge analysis

飞桨EasyDL实操范例:工业零件划痕自动识别
ESP32构解工程添加组件
JS slow motion animation principle teaching (super detail)
xshell连接服务器把密钥登陆改为密码登陆
OSI 七层模型
Cloud detection 2020: self attention generation countermeasure network for cloud detection in high-resolution remote sensing images
随机推荐
【Presto Profile系列】Timeline使用
飞桨EasyDL实操范例:工业零件划痕自动识别
学习突围2 - 关于高效学习的方法
MongoDB 分片总结
Storage principle inside mongodb
MySQL入门尝鲜
共创软硬件协同生态:Graphcore IPU与百度飞桨的“联合提交”亮相MLPerf
MongoDB 遇见 spark(进行整合)
Analysis of DHCP dynamic host setting protocol
Test next summary
Vscode编辑器ESP32头文件波浪线不跳转彻底解决
信号强度(RSSI)知识整理
Milkdown 控件图标
QQ medicine, Tencent ticket
一文读懂数仓中的pg_stat
OSI seven layer model
LeetCode_二分搜索_中等_153.寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值
详细介绍六种开源协议(程序员须知)
Scrapy教程经典实战【新概念英语】
Mongodb slice summary