当前位置:网站首页>Huge number (C language)
Huge number (C language)
2022-07-04 10:27:00 【Lol only plays Timo】
What is a huge number ? seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , Huge numbers are especially large numbers , As big as C Language is no longer recognizable , For example, thousands of trillions of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division ,C Linguistic int, And long int Obviously, it can't be expressed , Because they are all four byte complements , The range of integer numbers that can be represented is -2,147,483,648 ~ 2,147,483,647, namely -2^32 ~ 2^32-1.
So how to solve this problem ?
First , according to int We can use Ten thousand system , Similar to decimal , It's just that the decimal is 4 One by one , The decimal system is a group of digits . Speaking of this, some people may be confused , Why is it ten thousand decimal , Not 100000 , Or thousands , Choose a decimal . Because if we are doing multiplication , Everyone is at most 9999 The multiplication of the two will not exceed int Representation range of , It's not true int The representation range of causes too much waste .
Now let's solve the problem of digital storage :
We can save the numbers into the file in advance , Transfer directly from the file , This is convenient for our testing , And it is convenient for us to modify , After the data is transferred from the file, the next step is to convert these a lot of strings into hexadecimal and store them in a int In an array of types .
Here's a tip , It's the opposite , In other words, the low order of a huge number is stored in the front of the array , The higher the bit, the lower the stored subscript , The advantage of doing this is that it is very consistent with our computing habits when performing operations, starting from the low order , And it is also subscripted from the array 0 Start with the number of . Then let's take a look at the code :
void storeInfor(HUGE_NUM *NUM, char *temp) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
int flag = 1;
if (temp[0] == '-') {
NUM->sign = 1;
for (i = 0; i < NUM->count-1; i++) {
temp[i] = temp[i+1];
}
NUM->count--;
} else {
NUM->sign = 0;
}
for (j = NUM->count-1, i = 0; j >= NUM->count%4 + 3; i++) {
NUM->value[i] = ((int)temp[j]-48) + ((int)temp[j-1] - 48) * 10 + ((int)temp[j-2] - 48)* 100 + ((int)temp[j-3] - 48)* 1000;
j = j-4;
}
for (k = NUM->count%4-1,flag = 1; k >= 0; k--) {
if (k == NUM->count%4-1) {
NUM->value[i] = ((int)temp[k]-48) * flag;
} else {
NUM->value[i] += ((int)temp[k]-48) * flag;
}
flag = flag * 10;
}
printInfor(NUM);
}
It doesn't matter if you can't understand some of the code here , Finally, I will attach all the complete code , For your reference .
At this point, we have saved all the figures , Let's first look at the basic operations - Addition and subtraction .
Of course, the addition operation is very simple , Here you can first try how to realize the addition operation of decimal .
Compared with addition , Subtraction is much harder to achieve , Because of carry, we can easily add one to him , But excuse me , If there is continuous borrowing, it will be a big test for us , What's going on ?
Here I would like to introduce a way studied by my teacher Zhu Hong - Wechat complement , According to the underlying principle knowledge , Inferential , We all know that computer subtraction is realized by complement , My teacher's method is the same . Next, let's take a look at this hand of God :

Now these main knowledge and technologies have been told to you , Let's take a look at my code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
typedef struct HUGE_NUM {
int sign;
int *value;
int count;
}HUGE_NUM;
void storeInfor(HUGE_NUM *NUM, char *temp);
void addNum(HUGE_NUM *NUM1, HUGE_NUM *NUM2, HUGE_NUM *NUM3, char *temp1, char *temp2);
void printInfor(HUGE_NUM *NUM);
void printInfor(HUGE_NUM *NUM) {
int i;
int count = (NUM->count+3) / 4 - 1;
if (NUM->sign == 1) {
printf("-:");
} else {
printf("+:");
}
if(NUM->value[(NUM->count+3) / 4 - 1] == 0) {
count = (NUM->count+3) / 4 - 2;
}
for (i = count; i >= 0; i--) {
if (i == count) {
printf("%d ",NUM->value[i]);
} else {
printf("%04d ",NUM->value[i]);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
void addNum(HUGE_NUM *NUM1, HUGE_NUM *NUM2, HUGE_NUM *NUM3, char *temp1, char *temp2) {
int sign;
int *caculate1;
int *caculate2;
int count;
int i;
if (NUM1->count >= NUM2->count) {
count = (NUM1->count + 3) / 4 + 1;
caculate1 = (int *) calloc(sizeof(int),count);
caculate2 = (int *) calloc(sizeof(int),count);
} else {
count = (NUM2->count + 3) / 4 + 1;
caculate1 = (int *) calloc(sizeof(int),count);
caculate2 = (int *) calloc(sizeof(int),count);
}
for (i = 0; i < (NUM1->count+3)/4; i++) {
caculate1[i] = NUM1->value[i];
}
for (i = 0; i < (NUM2->count+3)/4; i++) {
caculate2[i] = NUM2->value[i];
}
if (NUM1->sign == NUM2->sign) {
if(NUM1->sign == 0) {
NUM3->sign = 0;
} else {
NUM3->sign = 1;
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
NUM3->value[i] = (caculate1[i]+caculate2[i])%10000;
} else {
NUM3->value[i] = (caculate1[i]+caculate2[i])%10000 + (caculate1[i-1]+caculate2[i-1])/10000;
if(NUM3->value[i-1] == 10000) {
NUM3->value[i]++;
NUM3->value[i-1] = 0;
}
}
}
if(NUM3->value[count-1] >= 10000) {
NUM3->value[count-1] -= 10000;
NUM3->value[count]++;
}
} else {
if (NUM1->sign == 1) {
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
caculate1[i] = 9999 - caculate1[i];
}
}
if (NUM2->sign == 1) {
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
caculate2[i] = 9999 - caculate2[i];
}
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
NUM3->value[i] = (caculate1[i]+caculate2[i])%10000;
} else {
NUM3->value[i] = (caculate1[i]+caculate2[i])%10000 + (caculate1[i-1]+caculate2[i-1])/10000;
if(NUM3->value[i-1] == 10000) {
NUM3->value[i]++;
NUM3->value[i-1] = 0;
}
}
}
if(NUM3->value[count-1] >= 10000) {
NUM3->value[count-1] -= 10000;
NUM3->value[count]++;
}
if (NUM3->value[count] == 1) {
NUM3->value[0] += 1;
NUM3->sign = 0;
}
if (NUM3->value[count] == 0) {
NUM3->sign = 1;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
NUM3->value[i] = 9999 - NUM3->value[i];
}
}
}
}
void storeInfor(HUGE_NUM *NUM, char *temp) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
int flag = 1;
if (temp[0] == '-') {
NUM->sign = 1;
for (i = 0; i < NUM->count-1; i++) {
temp[i] = temp[i+1];
}
NUM->count--;
} else {
NUM->sign = 0;
}
for (j = NUM->count-1, i = 0; j >= NUM->count%4 + 3; i++) {
NUM->value[i] = ((int)temp[j]-48) + ((int)temp[j-1] - 48) * 10 + ((int)temp[j-2] - 48)* 100 + ((int)temp[j-3] - 48)* 1000;
j = j-4;
}
for (k = NUM->count%4-1,flag = 1; k >= 0; k--) {
if (k == NUM->count%4-1) {
NUM->value[i] = ((int)temp[k]-48) * flag;
} else {
NUM->value[i] += ((int)temp[k]-48) * flag;
}
flag = flag * 10;
}
printInfor(NUM);
}
int main () {
FILE *fp1;
FILE *fp2;
char temp1[10000];
char temp2[10000];
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
int flag = 1;
HUGE_NUM NUM1;
HUGE_NUM NUM2;
HUGE_NUM NUM3;
fp1 = fopen("testdata1.txt","r");
fp2 = fopen("testdata2.txt","r");
fseek(fp1,0,SEEK_END);
NUM1.count = ftell(fp1);
fseek(fp2,0,SEEK_END);
NUM2.count = ftell(fp2);
if (NUM1.count >= NUM2.count) {
NUM3.count = NUM1.count + 1;
} else {
NUM3.count = NUM2.count + 1;
}
NUM1.value = (int *) calloc(sizeof(int), ((NUM1.count+3) / 4));
NUM2.value = (int *) calloc(sizeof(int), ((NUM2.count+3) / 4));
NUM3.value = (int *) calloc(sizeof(int), ((NUM3.count+3) / 4));
fseek(fp1,0,SEEK_SET);
fseek(fp2,0,SEEK_SET);
fgets(temp1,1000,fp1);
fgets(temp2,1000,fp2);
storeInfor(&NUM1,temp1);
storeInfor(&NUM2,temp2);
addNum(&NUM1, &NUM2, &NUM3, temp1, temp2);
printInfor(&NUM3);
fclose(fp1);
fclose(fp2);
return 0;
}
It's not very good , You can point out any problems , Welcome to leave a message below , The multiplication program will be updated later .
边栏推荐
- AUTOSAR从入门到精通100讲(106)-域控制器中的SOA
- Differences among opencv versions
- Three schemes of ZK double machine room
- Development guidance document of CMDB
- Es entry series - 6 document relevance and sorting
- Latex insert picture, insert formula
- [200 opencv routines] 218 Multi line italic text watermark
- Linked list operation can never change without its roots
- Use the data to tell you where is the most difficult province for the college entrance examination!
- Debug:==42==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-buffer-overflow on address
猜你喜欢
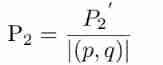
Latex error: missing delimiter (. Inserted) {\xi \left( {p,{p_q}} \right)} \right|}}
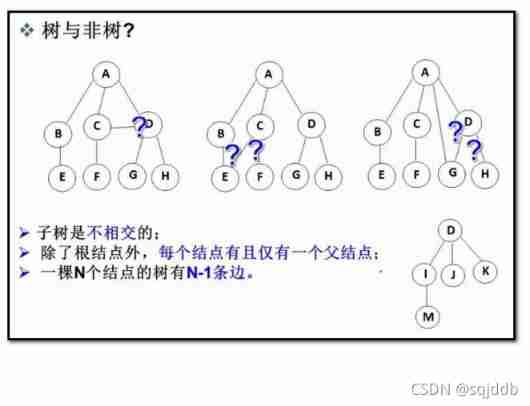
Introduction to tree and binary tree
When I forget how to write SQL, I
PHP代码审计3—系统重装漏洞
基于线性函数近似的安全强化学习 Safe RL with Linear Function Approximation 翻译 1
【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks
Reasons and solutions for the 8-hour difference in mongodb data date display
Vs201 solution to failure to open source file HPP (or link library file)
【FAQ】华为帐号服务报错 907135701的常见原因总结和解决方法
Idea SSH channel configuration
随机推荐
leetcode842. Split the array into Fibonacci sequences
Rhcsa - day 13
【OpenCV 例程200篇】218. 多行倾斜文字水印
Servlet基本原理与常见API方法的应用
Hands on deep learning (III) -- Torch Operation (sorting out documents in detail)
For programmers, if it hurts the most...
VLAN part of switching technology
Exercise 9-1 time conversion (15 points)
Rhcsa day 9
leetcode1-3
Reprint: summation formula of proportional series and its derivation process
Dynamic memory management
From programmers to large-scale distributed architects, where are you (I)
Remove linked list elements
Devop basic command
Press the button wizard to learn how to fight monsters - identify the map, run the map, enter the gang and identify NPC
System. Currenttimemillis() and system Nanotime (), which is faster? Don't use it wrong!
Knapsack problem and 0-1 knapsack problem
Sword finger offer 05 (implemented in C language)
DML statement of MySQL Foundation