当前位置:网站首页>用列錶初始化你的vector&&initializer_list簡介
用列錶初始化你的vector&&initializer_list簡介
2022-07-05 23:44:00 【月半木斤】
目錄
2. 用initializer_list來實現列錶構造vector
用列錶初始化就是用"{}"來初始化你的vector等自定義實現的容器。我們可以看到STL庫中給出的vector,list,map等等容器都是可以用"{}"的方式來初始化的,例如:
vector<int> v{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
list<int> l={ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
map<int, int> m = { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 }, { 3, 3 } };那麼它是如何實現的呢?其實它具體的實現方式並沒有你現象中的那麼高大上,他是用一個initializer_list的容器來接收"{}"中的元素然後通過給出一個以initializer_list為參數列錶的構造函數然後實現通過"{}"來構造容器。
1. initializer_list
先來介紹一下initializer_list:

可以看到他是C++11中才有的,那麼也就說明之前C++98是不支持用列錶構造對象的。它只有三個方法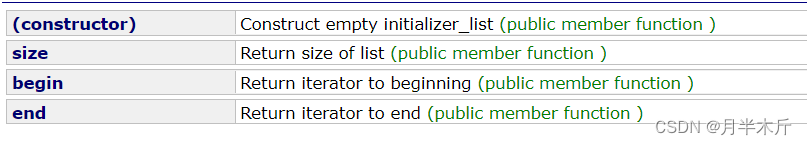
我們來測試一下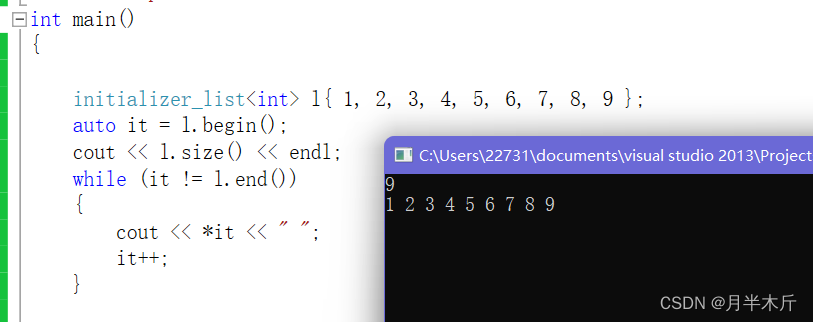
2. 用initializer_list來實現列錶構造vector
這裏我將vector模擬實現的全部代碼給出以免遭有些讀者對於vector當中的具體實現細節不明白而不明白如何用列錶來實現vector的構造:我還會將用initializer_list部分代碼單獨拿出來說明。(這裏如果對vector模擬實現的代碼有疑問可以看我對vector模擬實現的博客的詳細解析:http://t.csdn.cn/vDdJ9 http://t.csdn.cn/vDdJ9)
http://t.csdn.cn/vDdJ9)
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<vector>
#include<initializer_list>
using namespace std;
namespace wbx
{
template<class T>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
/構造和析構
vector()
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, end_of_storage(nullptr)
{}
//用列錶構造vector:
vector(initializer_list<T> l)
{
_start = new T[l.size()];
_finish = _start;
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
*_finish = *it;
_finish++;
it++;
}
end_of_storage = _finish;
}
//用列錶賦值vector:
vector<T>& operator=(initializer_list<T> l)
{
reserve(l.size());
_finish = _start;
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
*_finish = *it;
_finish++;
it++;
}
return *this;
}
vector(size_t n, const T &val = T())//構造n個T類型的val值
:_start(nullptr)//指針要初始化這是一個良好的編程習慣
,_finish(nullptr)
,end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
_start = new T[n*sizeof(T)];
_finish = _start+n;
end_of_storage = _finish;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_start[i] = val;
}
}
vector(int n,const T &val = T())//構造n個T類型的val值,這裏的val必須要用const修飾不然當傳入參數時是編譯通過不了的
:_start(nullptr)//指針要初始化這是一個良好的編程習慣
, _finish(nullptr)
, end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
_start = new T[n*sizeof(T)];
_finish = _start + n;
end_of_storage = _finish;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_start[i] = val;
}
}
vector(const vector<T> &v)//拷貝構造
:_start(nullptr),
_finish(nullptr),
end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
//vector temp(v.begin(), v.end());//這裏不可以調用普通類型的返回迭代器的指針,
vector<T> temp(v.cbegin(), v.cend());//因為const對象只能調用const類型的成員函數
this->swap(temp);
}
template<class Iterator>//這裏要再定義一個迭代器類的模板,因為這裏假設我們vector中存放的不同類型對象
//所返回的迭代器類型也是不同的,所以我們這裏重新設置一個模板類對於多種不同
//類型具有普遍的適用性
vector(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
size_t n = last - first; //這裏獲取frist和last之間的距離應當寫一個distance函數來
//獲取他們之間的距離,這裏這樣寫是因為簡單模擬實現
_start = new T[n];
_finish = _start;
end_of_storage = _start + n;
while (first != last)
{
*_finish = *first;
_finish++;
first++;
}
}
~vector()
{
if (_start)
{
delete[] _start;
_start = nullptr;
_finish = nullptr;
end_of_storage = nullptr;
}
}
運算符重載:
vector <T>operator=(vector<T> v)
{
this->swap(v);
return *this;
}
T& operator[](size_t index)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= size())
{
assert(false);
}
return *(_start + index) ;
}
///容量相關
size_t size()
{
int a = 0;
return a=_finish - _start;
}
size_t capacity()
{
return end_of_storage - _start;
}
bool empty()
{
if (_start == _finish)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void resize(size_t n, T val = T())
{
size_t oldsize = size();
if (n >capacity())
{
reserve(n - capacity());
}
for (int i = oldsize; i < n; i++)
{
_start[i] = val;
}
_finish = _start + n;//如果新的size小於老的size這裏直接訪問不到了
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n>capacity())
{
T *temp = new T[n];
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++)
{
temp[i] = _start[i];//這裏必須要用=來進行拷貝如果用其他如memcpy的話就會發生淺拷貝的情况
}
size_t oldsize = size();
if (_start)
{
delete[] _start;
}
_start = temp;
_finish = _start + oldsize;
end_of_storage = _start + n;
}
}
迭代器
iterator begin()
{
return _start;
}
iterator end()
{
return _finish;
}
const_iterator cbegin()const
{
return _start;
}
const_iterator cend()const
{
return _finish;
}
/插入函數
void push_back(T val)
{
if (_finish == end_of_storage)
{
reserve(2 * capacity());
}
*_finish = val;
_finish++;
}
void pop_back()
{
if (empty())
{
assert(false);
}
_finish--;
}
iterator insert(iterator pos,T val)
{
if (empty()||pos==_finish)
{
push_back(val);
return pos;
}
if (_finish == end_of_storage)
{
reserve(capacity() + 1);
}
iterator temp = _finish-1;
while (temp >= pos)
{
*(temp + 1) = *temp;
temp--;
}
*pos = val;
_finish++;
return pos;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
if (pos < _start || pos >= _finish)
{
assert(false);
}
iterator ret = pos;
while (pos != _finish - 1)
{
*pos = *(pos + 1);
pos++;
}
_finish--;
return ret + 1;
}
T & front()
{
return *(_start);
}
T &back()
{
return *(_finish-1);
}
交換函數
void swap(vector <T> &v)
{
std::swap(v._start, _start);
std:: swap(v._finish, _finish);
std::swap(v.end_of_storage, end_of_storage);
}
private:
iterator _start;
iterator _finish;
iterator end_of_storage;
};
}
using namespace std;
wbx::vector<int> static v4(5, 4);
void test1()
{
wbx::vector<int> v1{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
cout << "v1: ";
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
wbx::vector<int> v2;
v2 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
cout << "v2: ";
for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++)
{
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
wbx::vector<int> v3(11);
v3 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
cout << "v3: ";
for (int i = 0; i < v3.size(); i++)
{
cout << v3[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << v1.size() << endl;
cout << v2.size() << endl;
cout << v3.size() << endl;
cout << v1.capacity() << endl;
cout << v2.capacity() << endl;
cout << v3.capacity() << endl;
}關於initializer_list部分代碼:可以看到實現是十分簡單的,就是用initializer_list內部的元素對vector空間循環賦值。
//用列錶構造vector:
vector(initializer_list<T> l)
{
_start = new T[l.size()];//這裏的start是vector底層管理數組空間的指針起始地址
_finish = _start;
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
*_finish = *it;//finish是vector底層數組的結束比特置
_finish++;
it++;
}
end_of_storage = _finish;//end_of_storage是vector所開辟空間的結束比特置
}
//用列錶賦值vector:
vector<T>& operator=(initializer_list<T> l)
{
reserve(l.size());
_finish = _start;
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
*_finish = *it;
_finish++;
it++;
}
return *this;
}边栏推荐
- orgchart. JS organization chart, presenting structural data in an elegant way
- C file and folder operation
- 2022.6.20-6.26 AI行业周刊(第103期):新的小生命
- How to rotate the synchronized / refreshed icon (EL icon refresh)
- 带外和带内的区别
- Spire.PDF for NET 8.7.2
- STM32__06—单通道ADC
- Spreadjs 15.1 CN and spreadjs 15.1 en
- LeetCode——Add Binary
- Spécifications techniques et lignes directrices pour la sélection des tubes TVS et ESD - Recommandation de jialichuang
猜你喜欢
Spire Office 7.5.4 for NET
Rasa 3. X learning series -rasa 3.2.1 new release

成为程序员的你,后悔了吗?

Go language introduction detailed tutorial (I): go language in the era
el-cascader的使用以及报错解决

开关电源Buck电路CCM及DCM工作模式
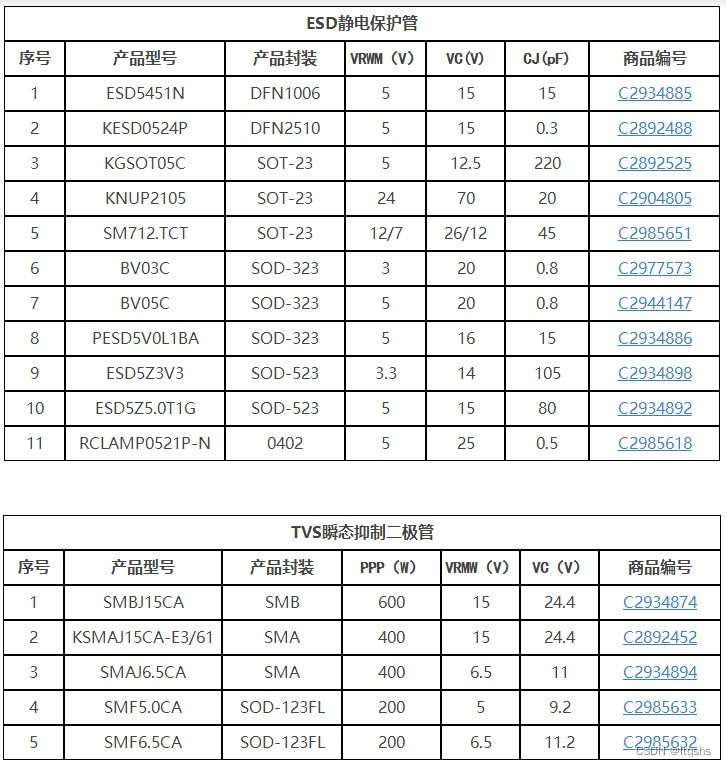
TVS管和ESD管的技術指標和選型指南-嘉立創推薦

Rasa 3. X learning series -rasa x Community Edition (Free Edition) changes
21.PWM应用编程

21. PWM application programming
随机推荐
Breadth first search open turntable lock
Rasa 3.x 学习系列-Rasa X 社区版(免费版) 更改
The PostgreSQL column reference 'ID' is ambiguous - PostgreSQL column reference'id'is ambiguous
poj 2762 Going from u to v or from v to u? (推断它是否是一个薄弱环节图)
Huawei simulator ENSP - hcip - MPLS experiment
PADS ROUTER 使用技巧小记
JVM的简介
14 MySQL-视图
[original] what is the core of programmer team management?
VS2010 writes DLL and unit test of dynamic link library, and transfers the correctness of DLL test
Go language implementation principle -- map implementation principle
C# Linq Demo
Code farmers to improve productivity
帶外和帶內的區別
Use CAS instead of synchronized
Design and implementation of secsha system
Rasa 3.x 学习系列-Rasa 3.2.1 新版本发布
动态规划 之 打家劫舍
芯源&立创EDA训练营——无刷电机驱动
Biased sample variance, unbiased sample variance