当前位置:网站首页>[rust notes] 16 input and output (Part 1)
[rust notes] 16 input and output (Part 1)
2022-07-05 06:05:00 【phial03】
16 - Input and output
16.1 - Readers and writers
Rust Standard library features for input and output , It's through
Read、BufReadandWriteSpecial type , And the various types that implement them .- Realization
ReadThe value of is Reader (reader), There is a way to read byte input . - Realization
BufReadThe value of is Buffer reader , SupportReadAll the ways , In addition, it supports the method of reading text lines . - Realization
WriteThe value of is Writer (writer), Both support byte output , Also support UTF-8 Text output .
- Realization
Common readers : Read byte
std::fs::File::open(filename): Used to open a file .std::net::TcpStream: Used to receive data from the network .std::io::stdin(): Used to read data from the standard input stream of the process .std::io::Cursor<&[u8]>value : From the byte array of memory “ Read ” data .
Common writers : Write Bytes
std::fs::File::create(filename): Used to open a file .std::net::TcpStream: Used to send data over the network .std::io::stdout()andstd::io::stderr(): Used to write data to the terminal .std::io::Cursor<&mut [u8]>: Allow any modifiable byte slice to be written as a file .Vec<u8>: It is also a writer , itswriteMethod can append elements to a vector .
be based on
std::io::Readandstd::io::WriteGeneric code for special implementation , It can cover various input and output channels .// From any reader , Copy all bytes to any writer use std::io::{ self, Read, Write, ErrorKind}; const DEFAULT_BUF_SIZE: usize = 8 * 1024; pub fn copy<R: ?Sized, W: ?Sized>(reader: &mut R, writer: &mut W) -> io::Result<u64> where R: Read, W: Write { let mut buf = [0; DEFAULT_BUF_SIZE]; let mut written = 0' loop { let len = match reader.ead(&mut buf) { Ok(0) => return Ok(written), Ok(len) => len, Err(ref e) if e.kind() == ErrorKind::Interrupted => continue, Err(e) => return Err(e), }; writer.write_all(&buf[..len])?; written += len as u64; } }std::io::copy()Is generic , Data can be transferred fromFileCopied to theTcpStream, fromStdinCopied to memoryVec<u8>.
Four commonly used
std::ioSpecial type ofRead、BufRead、WriteandSeekHow to import :Import a dedicated front-end module , They can be included directly :
use std::io::prelude::*;Import
std::ioModule itselfuse std::io::{ self, Read, Write, ErrorKind}; // self Can be io Life is `std::io` Module alias , such std::io::Result and std::io::Error, It can be simply written as io::Result and io::Error.
16.1.1 - Reader
std::io::ReadCommon reader methods , For reading data , They are based on the reader itselfmutReference as parameter :reader.read(&mut buffer): Read some bytes from the data source , Then store it in the givenbufferin .bufferThe type of the parameter is&mut [u8].This method will read
buffer.len()Bytes .The type of return value is
io::Result<u64>, This isResult<y64, io::Error>Alias for type .Read successful , Returns the
u64Number of read bytes of value , The number<= buffer.len().Read error ,
.read()returnErr(err), amongerryesio::Errorvalue ..kind()Method can returnio::ErrorKindError code for type .
reader.read_to_end(&mut byte_vec): Read out all remaining inputs from the reader , And added tobyte_vecin .byte_vecIt's aVec<u8>Type value .- This method returns
io::Result<(usize)>, Indicates the number of bytes read . - This method has no limit on the amount of data added to the vector , Don't use it for untrusted data sources . have access to
.take()Methods to improve security limits .
reader.read_to_string(&mut string): Read out all remaining inputs from the reader , And added tostringin .- If the input stream is not valid UTF-8, Then this method will return
ErrorKind::InvaliDataerror . - except UTF-8 Other character sets besides , It can be through open source
encodingPackage support .
- If the input stream is not valid UTF-8, Then this method will return
read.read_exact(&mut buf): Read just enough data from the reader , Fill to the givenbufferin .- Parameter type is
&[u8]. - If the reader is reading
buf.len()Read the data before bytes , Then this method will returnErrorKind::UnexpectedEoferror .
- Parameter type is
std::io::ReadCommon adapter methods , With reader (reader) As a parameter , Convert it to an iterator or a different reader :reader.bytes(): The iterator that returns the bytes of the input stream .
- The type of iterator item is
io::Result<u8>, Every byte needs error checking . - This method will be called once for each byte
reader.read(), It is inefficient for readers without buffer .
- The type of iterator item is
reader.chars(): The reader is UTF-8, And returns an iterator whose item is a character . invalid UTF-8 It can lead toInvalidDataerror .reader1.chain(reader2): Return to a new reader , containreader1andreader2All of the inputs .reader.take(n): From andreaderThe same data source reads the input , But only readnbyte , Return to a new reader .
Both reader and write will be realized
DropSpecial type , It will close automatically after the operation is completed .
16.1.2 - Buffer reader
buffer : Allocate a block of memory to the reader and writer as a buffer , Temporarily save the input and output data . Buffering can reduce system calls .
The buffer reader implements
ReadandBufReadTwo special types .BufReadTypical common reader methods :
reader.read_line(&mut line): Read a line of text and append to
line.
lineIt's aStringType value .- Line break at end of line
'\n'or"\r\n"It will also be included inlinein . - The return value is
io::Result<usize>, Represents the number of bytes read , Including line terminators . - If the read is at the end of the input , be
lineunchanged , And return toOk(0).
reader.lines(): Returns the iterator of the input line .
- The iteration item type is
io::Result<String>. - Line breaks are not included in the string .
- The iteration item type is
reader.read_until(stop_byte, &mut byte_vec)andreader.split(stop_byte): And.read_line()and.lines()similar . But in bytes , produceVec<u8>value .stop_byteIndicates the delimiter ..fill_buf()and.consume(n): It can be used to directly access the buffer inside the reader .
16.1.3 - Read text lines
Unix Of
grepCommand analysis :- Search for multiline text , And used in combination with pipes , To find the specified writer .
use std::io; use std::io::prelude:: *; fn grep(target: &str) -> io::Result<()> { let stdin = io::stdin(); for line_result in stdin.lock().lines() { let line = line_result?; if line.contains(target) { println!("{}", line); } } Ok(()) }Further expansion , Add the function of searching files on disk , Improved to generic function :
fn grep<R>(target: &str, reader: R) -> io::Result<()> where R: BufRead { for line_result in reader.lines() { let ine = line_result?; if line.contains(target) { println!("{}", line); } } Ok(()) }adopt
StdinLockOr bufferFilecall .let stdin = io::stdin() grep(&target, stdin.lock())?; let f = File::open(file)?; grep(&target, BufReader::new(f))
FileandBufReaderThere are two different library features , Because sometimes you need unbuffered files , Sometimes you need non file buffers .FileNo automatic buffering , But throughBufReader::new(reader)establish .- If you want to set the arrival of the buffer , You can use
BufReader::with_capacity(size, reader).
Unix Of
grepCommand complete program :// grep: Search for stdin Or lines in some files that match the specified string use std::error::Error; use std::io::{ self, BufReader}; use std::io::prelude:: *; use std::fs::File; use std::path::PathBuf; fn grep<R>(target: &str, reader: R) -> io::Result<()> where R: BufRead { for line_result in reader.lines() { let line = line_result?; if line.contains(target) { println!("{}", line); } } Ok(()) } fn grep_main() -> Result<(), Box<Error>> { // Get command line parameters . The first parameter is the string to search , The other parameters are file names let mut args = std::env::args().skip(1); let target = match args.next() { Some(s) => s, None = Err("usage: grep PATTERN FILE...")? }; let files: Vec<PathBuf> = args.map(PathBuf::from).collect(); if files.is_empty() { let stdin = io::stdin(); grep(&target, stdin.local())?; } else { for file in files { let f = File::open(file)?; grep(&target, BufReader::new(f))?; } } Ok(()) } fn main() { let result = grep_main(); if let Err(err) = result { let _ = writelen!(io::stderr(), "{}, err"); } }
16.1.4 - Collection line
- The reader method will return
ResultValue iterator . .collect()You can collect rows .
let lines = reader.lines().collect::<io::Result<Vec<String>>>()?;
// io::Result<Vec<String>> It's a collection type , therefore .collect() Method can create and fill in values of this type .
- The standard library is
ResultRealizedFromIteratorSpecial type :
impl<T, E, C> FromIterator<Result<T, E>> for Result<C, E> where C: FromIterator<T> {
...
}
- If the type can be
TThe item , Collected typeC(where C: FromIterator<T>) The collection of , Then you can typeResult<T, E>The item collection of is of typeResult<C, E>(FromIterator<Result<T, E>> for Result<C, E>).
16.1.5 - Writer
Output to the standard output stream , have access to
println!()andprint!()macro . They will only be surprised when they fail to write .Output to writer , You can use
writeln!()andwrite!()macro .- They contain two parameters , The first parameter is the writer .
- Their return value is
Result. When use , It is suggested that?The end of the operator , Used to handle errors .
WriteSpecial method :writer.write(&buf): SlicebufSome bytes in are written to the underlying stream . returnio::Result<usize>, Include the number of bytes written when successful , It may be less thanbuf.len(). This method has low safety limits , Try not to use .writer.write_all(&buf): SlicebufAll bytes in are written , returnResult<()>.writer.flush(): Write all buffered data to the underlying stream , returnResult<()>.
Similar to readers , The writer will also close automatically when it is cleared . All remaining buffered data will be written to the underlying writer , An error occurred during writing , Errors will be ignored . To ensure that the application can find all output errors , Should be cleared before , Manual use
.flush()Method to clean up the buffer writer .BufWriter::new(writer)Any writer can be buffered .BufReader::new(reader)A buffer can be added to any reader .let file = File::create("tmp.txt")?; let writer = BufWriter::new(file);To set the buffer size of the reader , have access to
BufWriter::with_capacity(size, writer).
16.1.6 - file
How to open a file :
File::open(filename): Open an existing file for reading . Return to oneio::Result<File>, If the file does not exist, an error will be returned .File::create(finename): Create a new file for writing . If the file with the specified name already exists , Then the document will be abridged .Use
OpenOptionsSpecify the behavior of opening filesuse std::fs::OpenOptions; let log = OpenOptions::new() .append(true) // If the file exists , Then add content at the end .open("server.lgo")?; let file = OpenOptions::new() .write(true) .create_new(true) // If the file exists, it fails .open("new_file.txt")?;.append()、.write()、.create_new()And so on can be called by concatenation , Because they all returnself. This mode of method concatenation calls , stay Rust The species is called Builder (builder).
FileType in file system modulestd::fsin .FileAfter opening , It can be used like other readers or writers . You can add buffers as needed .FileIt will also turn off automatically when it is cleared .
16.1.7 - Search for
File Realized Seek Special type : Support jump reading in the file , Instead of reading or writing from beginning to end at once .
pub trait Seek {
fn seek(&mut self, pos: SeekFrom) -> io::Result<u64>;
}
pub enum SeekFrom {
Start(u64),
End(i64),
Current(i64)
}
file.seek(SeekFrom::Start(0))It means to jump to the starting position .file.seek(SeekFrom::Current(-8))Back off 8 byte .- Whether it's mechanical hard disk or SSD Solid state disk , A search can only read a few megabytes of data .
16.1.8 - Other reader and writer types
io::stdin(): Reader that returns the standard input stream , The type isio::Stdin.It is shared by all threads , Each read is designed to obtain and release mutexes .
StdinOf.lock()Method , Used to obtain mutex , And return aio::StdinLockBuffer reader , The mutex will be held before it is cleared , Avoid mutex overhead .and
io::stdin().lock()Cannot apply to mutexes , Because it will save rightStdinThe value of the reference , requirementStdinValues must be stored in a place with a long lifetime . But it can be used in collecting rows .let stdin = io::stdin(); let lines = stdin.lock().lines();
io::stdout(): The writer that returns the standard output stream . Have mutexes and.lock()Method .io::stderr(): The writer that returns the standard error stream . Have mutexes and.lock()Method .Vec<u8>RealizedWrite.- Can write
Vec<u8>, Expand the vector with new data . StringIt didn't come trueWrite. To useWriteBuild string , First you need to write aVec<u8>in , And then useString::from_utf8(vec)Convert the limit to a string .
- Can write
Cursor::new(buf): Create a newCursor, It's abufBuffer reader reading data in .- Used to create read
StringReader . - Parameters
bufIt can be implementationAsRef<[u8]>Any type of , Therefore, it can also be transferred&[u8]、&strorVec<u8>. CursorInternal onlybufItself and an integer . This integer is used to indicate thatbufOffset in , The initial value is 0.CursorRealizedRead、BufReadandSeekSpecial type .- If
bufThe type is&mut [u8]orVec<u8>, Then supportWriteSpecial type .Cursor<&mut [u8]>andCursor<Vec<u8>>It has also been realized.std::io::preludeAll of the 4 A special type .
- Used to create read
std::net::TcpStream: Express TCP network connections .- It's a reader , It is also a writer , To support the TCP Two-way communication .
TcpStream::connect(("hostname", PORT))Static methods : Try to connect to the server , returnio::Result<TcpStream>.
std::process::Command: Support the creation of a child process , Import data into its standard input .use std::process::{ Command, Stdio}; let mut child = Command::new("grep") .arg("-e") .arg("a.*e.*i.*o.*u") .stdin(Stdio::piped()) .spawn()?; let mut to_child = child.stdin.take().unwrap(); for word in my_words { writelen!(to_child, "{}", word)?; } drop(to_child); // close grep Of stdin child.wait()?;child.stdinThe type isOption<std::process::ChildStdin>.CommandAlso have.stdout()and.stderr()Method .
std::iomodular : Some functions are provided , To return simple readers and writers .io::sink(): No operation writer . All write methods return Ok, But the data will be discarded .io::empty(): No operation reader . Reading is always successful , But the return input terminates .io::repeat(byte): The returned reader will repeatedly give the specified bytes .
16.1.9 - binary data 、 Compression and serialization —— Open source package std::io Expand
byteorderpackage : ProvidesReadBytesExtandWriteBytesExtSpecial type , Provide methods for readers and writers of all binary inputs and outputs .flate2package : For reading 、 WritegzipCompressed data provides additional adapter methods .serdepackage : For serialization and deserialization , Can achieve Rust Conversion between data structures and bytes .serde::SerializeSpecialserializeMethod : Serve all types that support serialization , Such as a string 、 character 、 Tuples 、 Vector andHashMap.serdeIt also supports derived features , To serve custom types :#[derive(Serialize, Deserialize)] struct Player { location: String, items: Vec<String>, health: u32 }
See 《Rust Programming 》( Jim - Brandy 、 Jason, - By orendov , Translated by lisongfeng ) Chapter 18
Original address
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
数据可视化图表总结(一)

【云原生】微服务之Feign自定义配置的记录
Sword finger offer 53 - I. find the number I in the sorted array
1.13 - RISC/CISC
SQLMAP使用教程(一)
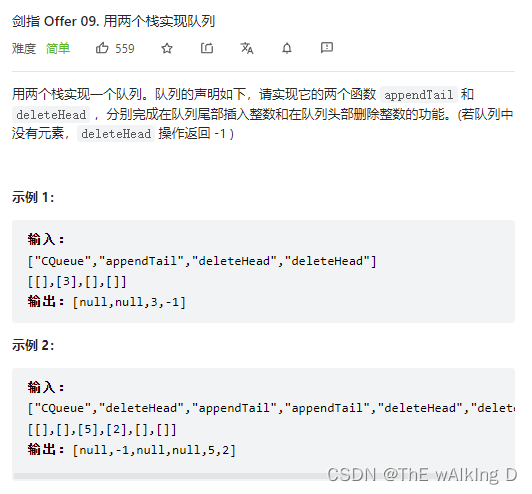
Sword finger offer 09 Implementing queues with two stacks
![[jailhouse article] jailhouse hypervisor](/img/f4/4809b236067d3007fa5835bbfe5f48.png)
[jailhouse article] jailhouse hypervisor

【实战技能】如何做好技术培训?
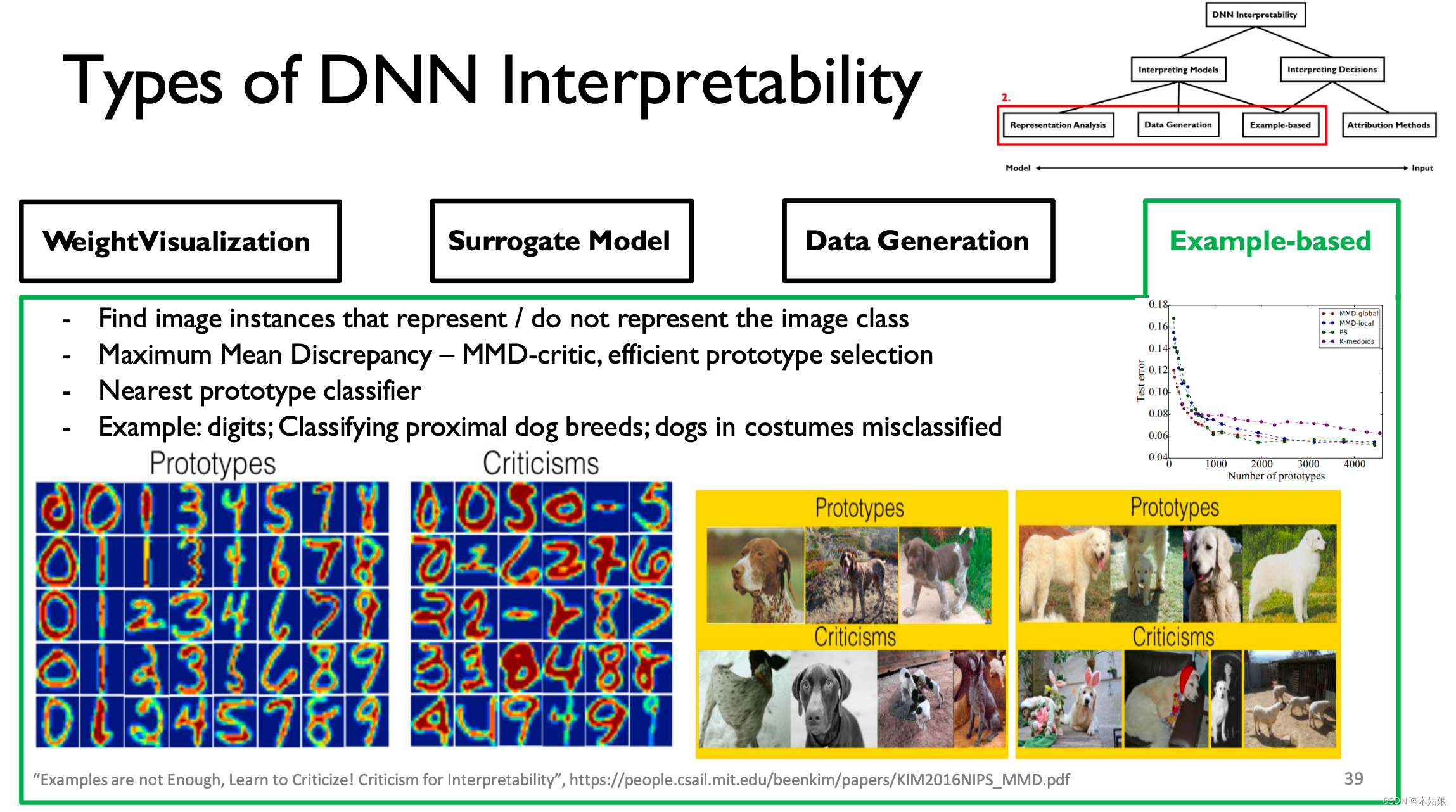
MIT-6874-Deep Learning in the Life Sciences Week 7

Educational Codeforces Round 116 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Arena
随机推荐
927. 三等分 模拟
leetcode-6110:网格图中递增路径的数目
Appium automation test foundation - Summary of appium test environment construction
PC register
Codeforces Round #715 (Div. 2) D. Binary Literature
【Rust 笔记】17-并发(下)
【Jailhouse 文章】Jailhouse Hypervisor
Graduation project of game mall
leetcode-1200:最小绝对差
SQLMAP使用教程(一)
RGB LED infinite mirror controlled by Arduino
leetcode-6109:知道秘密的人数
Appium基础 — 使用Appium的第一个Demo
CF1634 F. Fibonacci Additions
可变电阻器概述——结构、工作和不同应用
Introduction and experience of wazuh open source host security solution
Sword finger offer 05 Replace spaces
shared_ Repeated release heap object of PTR hidden danger
1041 Be Unique
Daily question 2013 Detect square