当前位置:网站首页>[risc-v] external interrupt
[risc-v] external interrupt
2022-07-06 03:13:00 【Mr. Jiada】
It is divided into interrupt and exception , The main record here is RISC-V Interrupt of instruction set .
List of articles
One 、CPU block diagram
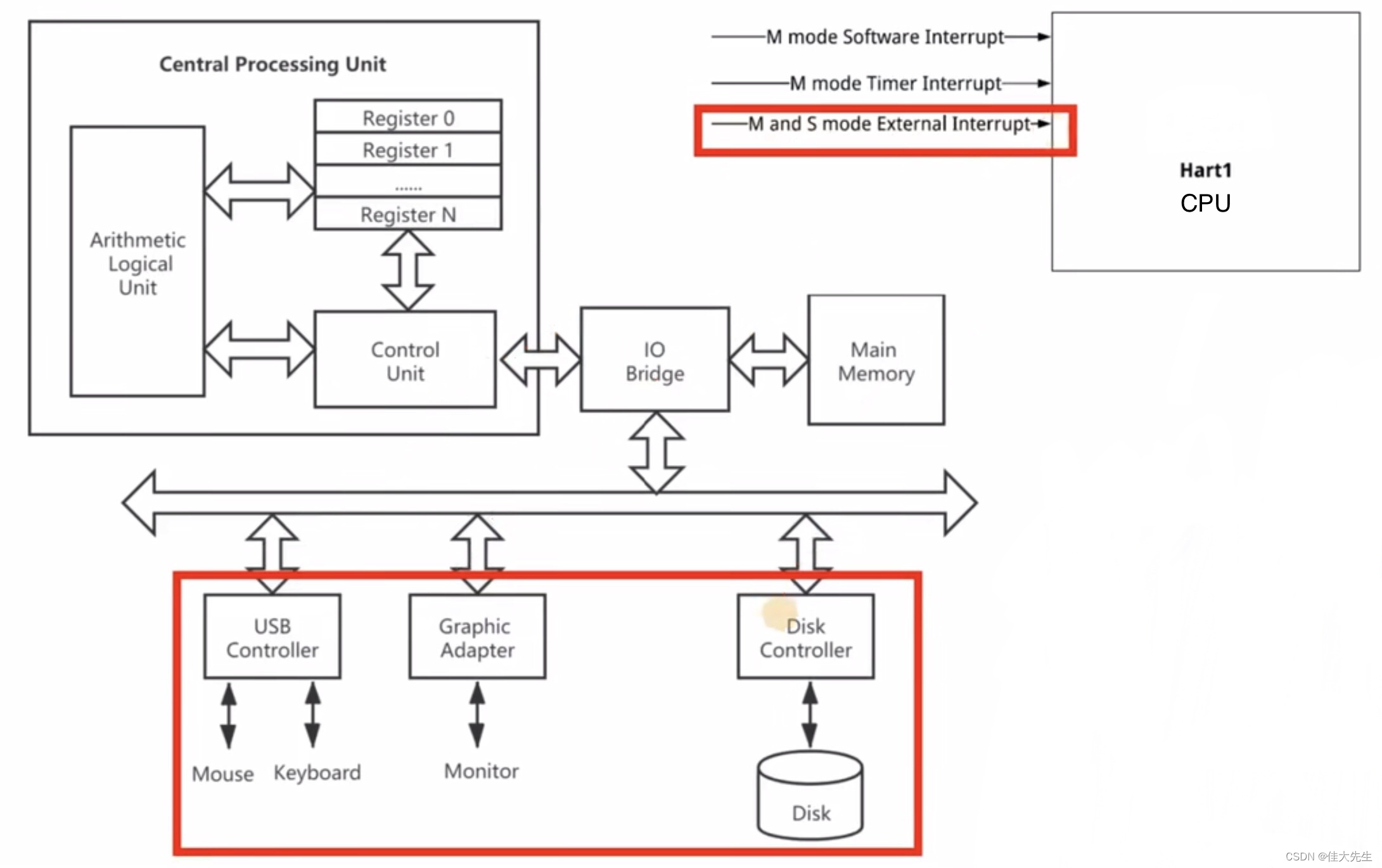
Two 、RISC-V Classification of interruptions
- Local interrupt (Local interrupt)
- software interrupt
- timer interrupt
- Global interrupt (Global interrupt)
- externel interrupt
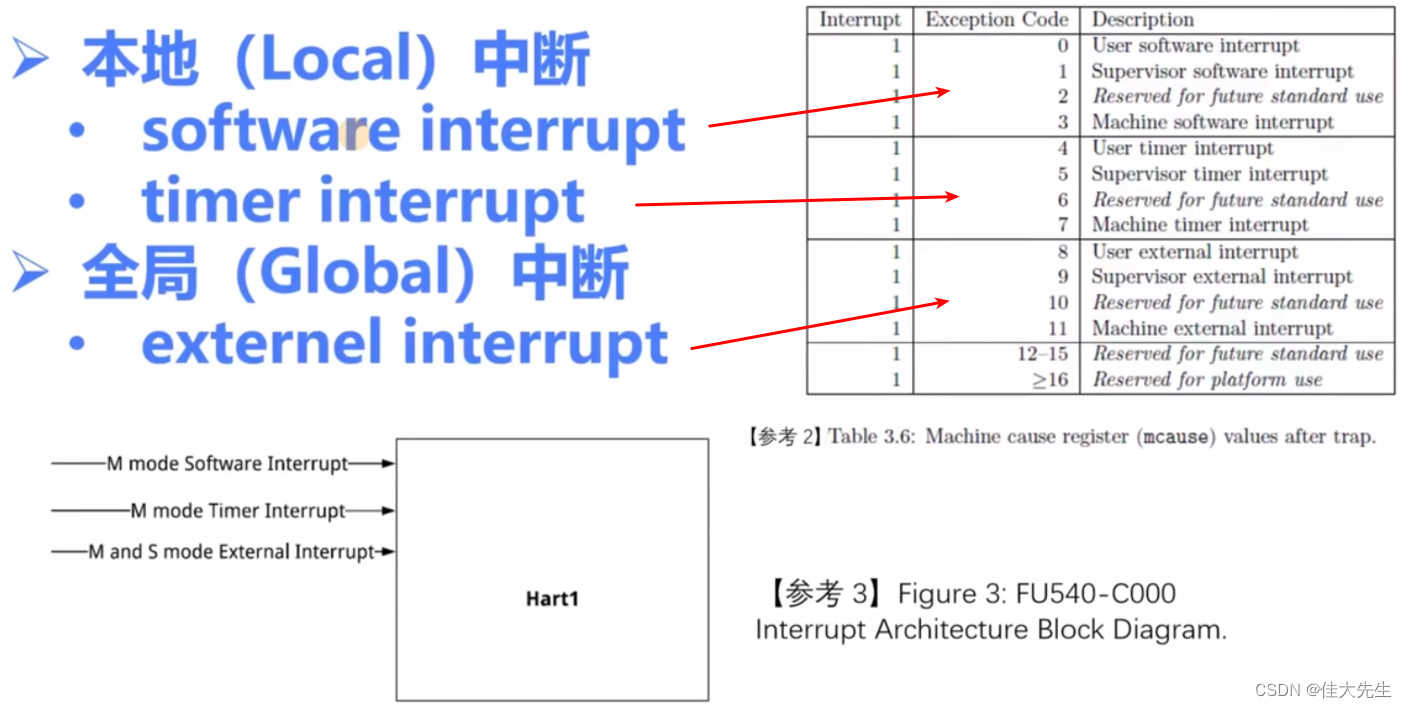
- externel interrupt
3、 ... and 、 Interrupt related registers (mie/mip)
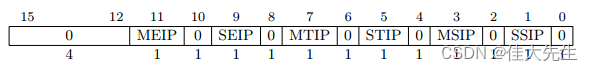
mstatus The register of MIE The flag bit is the global interrupt switch bit , Equivalent to level 1 interrupt flag .
mie (Machine interrupt Enable)
Used for setting up M/S/U Corresponding in mode External/Timer/Software interrupt .(M/S/U The privilege mode below says )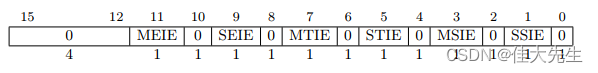
stay RISCV Next , Will interrupt (interrupt) It is subdivided into three types : Timed interrupt (timer)、 Internuclear interruption (soft)、 Interrupt Controller Interrupt (external). Timed interrupts can be used to generate tick, Internuclear interrupts are used for different cpu Nuclear communication , The interrupt controller is responsible for all peripheral interrupts . This design and arm It's a little different , stay arm Multi core , Timer interrupt in architecture 、 Inter core interrupt and peripheral interrupt are managed by interrupt controller , And in the RISCV Timer and inter core interrupt are separated in , These two interrupts are called CLINT(Core Local Interrupt), The interrupt controller that manages other peripheral interrupts is called PLIC(Platform-Level Interrupt Controller).
mip (Machine Interrupt Pending): Get current M/S/U Corresponding in mode External/Timer/Software Whether the interruption occurs .
Four 、 Privilege mode
RISCV There are three privilege levels under the architecture , Namely Machine、Supervisor and User, abbreviation M Pattern 、S Patterns and U Pattern .M Mode permission is the highest , Programs at this level can access all hardware and execute all privileged instructions ;S Mode is generally used to run the operating system , You can set MMU Use a virtual address ;U Patterns are generally used by ordinary applications , Minimum authority .
M Mode uses physical addresses for access , Not pass MMU, But there are similar arm Next cortex-m Medium MPU function ;S The mode can be set MMU To access memory using virtual addresses , So it's like Linux This kind of operating system runs on S In mode . So someone has to ask , Why? RISCV The architecture privilege pattern is designed like this , Put... Directly M Patterns and S Can't the two modes be integrated ? This has to come from RISCV From the background of the birth of architecture ,RISCV Architecture was born in 2010 About years ago , At this time, whether it is x86 still arm The architecture is relatively mature , therefore RISCV When designing the architecture, it is targeted that this architecture can be used from microcontrollers to large supercomputers . Used on microcontrollers RISCV The architecture is generally only M Pattern , Or use M and U Two modes , Be similar to cortex-m Positioning of architecture ; And in the belt MMU On the chip ,RISCV Architecture is generally used M、S and U Three models , This way “ Building blocks ” Can make RISCV The architecture is applicable to various scenarios .
5、 ... and 、PLIC (Platform-Level Interrupt Controller)
RISC-V The interrupt controller inside , amount to ARM Medium GIC, Mainly deal with external interrupts according to priority
Interrupt source -> Interrupt number -> Interrupt vector -> Interrupt service routine (ISR)-> Interrupt return
Interrupt source ID Range :1 ~ 53(0x35),0 Retain 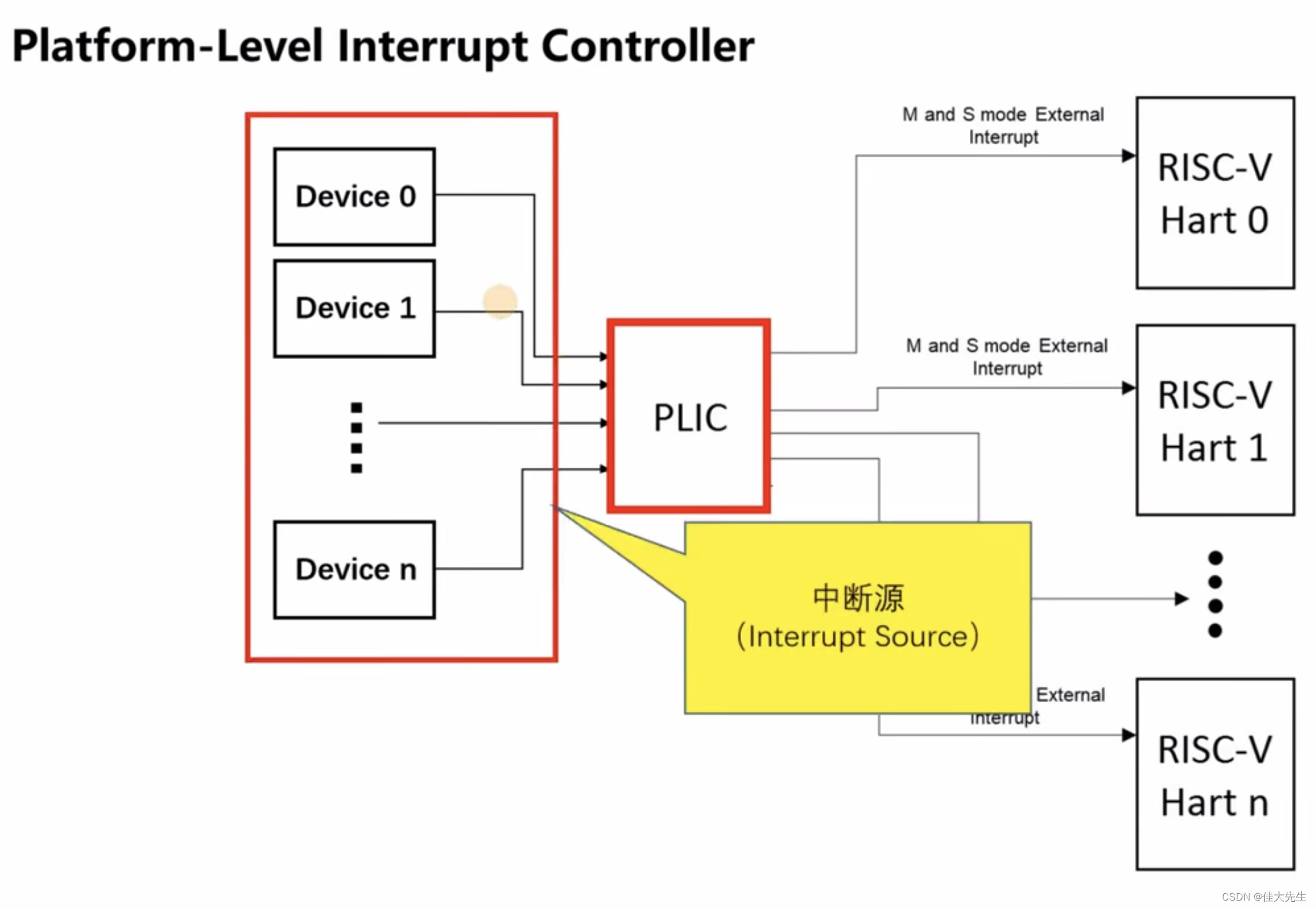
PLIC Programming interface (API) - register
- RISC-V Specifications stipulated ,PLIC Memory mapping is used in the register programming of (memory map) The way . The width of each register is 32 - bit.
- Specific register addressing adopts base + offset The format of , And base By each specific platform Define your own .
Priority register
| Programmable register | Function description | Memory mapped address |
|---|---|---|
| Priority | Set the priority of an interrupt source | BASE + (interrupt-id) * 4 |
- Every PLIC Interrupt sources have a memory mapped address , The register pointed to by this address is used to configure the priority of the interrupt source .
- If two interrupt sources have the same priority , According to the ID Values further prioritize ,ID The smaller the value, the higher the priority
Pending register
| Programmable register | Function description | Memory mapped address |
|---|---|---|
| Pending | Used to indicate whether an interrupt source occurs | BASE + 0x1000 + ((interrupt-id/32)) |
- Every PLIC The interrupt controller contains 2 individual 32 Bit Pending register ( because 52 Interrupt sources 1 individual 32bit Cannot express completely ), every last bit Corresponding to an interrupt source , by 1 Indicates that an interrupt has occurred on the interrupt source ( Get into Pending state ), remain hart Handle , Otherwise, it means that there is currently no interrupt on the interrupt source .
- Pending Register interrupt Pending The state can pass through claim Way to clear .
- first Pending The first of the registers 0 Bit correspondence does not exist 0 Interrupt source No , Its value is always 0.
Enable register
| Programmable register | Function description | Memory mapped address |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | For something hart Turn on or off an interrupt source | BASE + 0x2000 + (hart) * 0x80 |
- Every Hart Yes 2 individual Enable register (Enable1 and Enable2) For this Hart Start or close a certain interrupt source .
- Each interrupt source corresponds to Enable One of the registers bit, among Enable1 Be responsible for controlling 131 Interrupt source No ;Enable2 Be responsible for controlling 3253 Interrupt source No . The corresponding bit Bit is set to 1 Indicates that the interrupt source is enabled , Otherwise, it means that the interrupt source is closed .
Threshold register
| Programmable register | Function description | Memory mapped address |
|---|---|---|
| Threshold | For something hart Set the threshold of interrupt source priority | BASE + 0x200000 + (hart) * 0x1000 |
- Every Hart Yes 1 individual Threshold Register is used to set the threshold of interrupt priority .
- All less than or equal to (<=) Even if the interrupt source of this threshold occurs, it will be PLIC discarded . Specially , When the threshold is 0 Interrupts that occur on all interrupt sources are allowed ; When the threshold is 7 Discard all interrupts that occur on the interrupt source .
Claim/Complete register
| Programmable register | Function description | Memory mapped address |
|---|---|---|
| Claim/Complete | Get the interrupt source with the highest priority currently occurring ID/ notice PLIC The processing of the interrupt has ended | BASE + 0x200004 + (hart) * 0x1000 |
- Claim and Complete It's the same register , Every Hart One .
- Reading this register is called Claim, That is, get the interrupt source with the highest priority currently occurring ID.Claim After success, the corresponding Pending position .
- Writing to this register is called Complete. So-called Complete Means notice PLIC The processing of this route interrupt has ended .
6、 ... and 、 Interrupt processing flow
Even if the interruption occurs at the same time , It will also respond according to the filter of interrupt priority .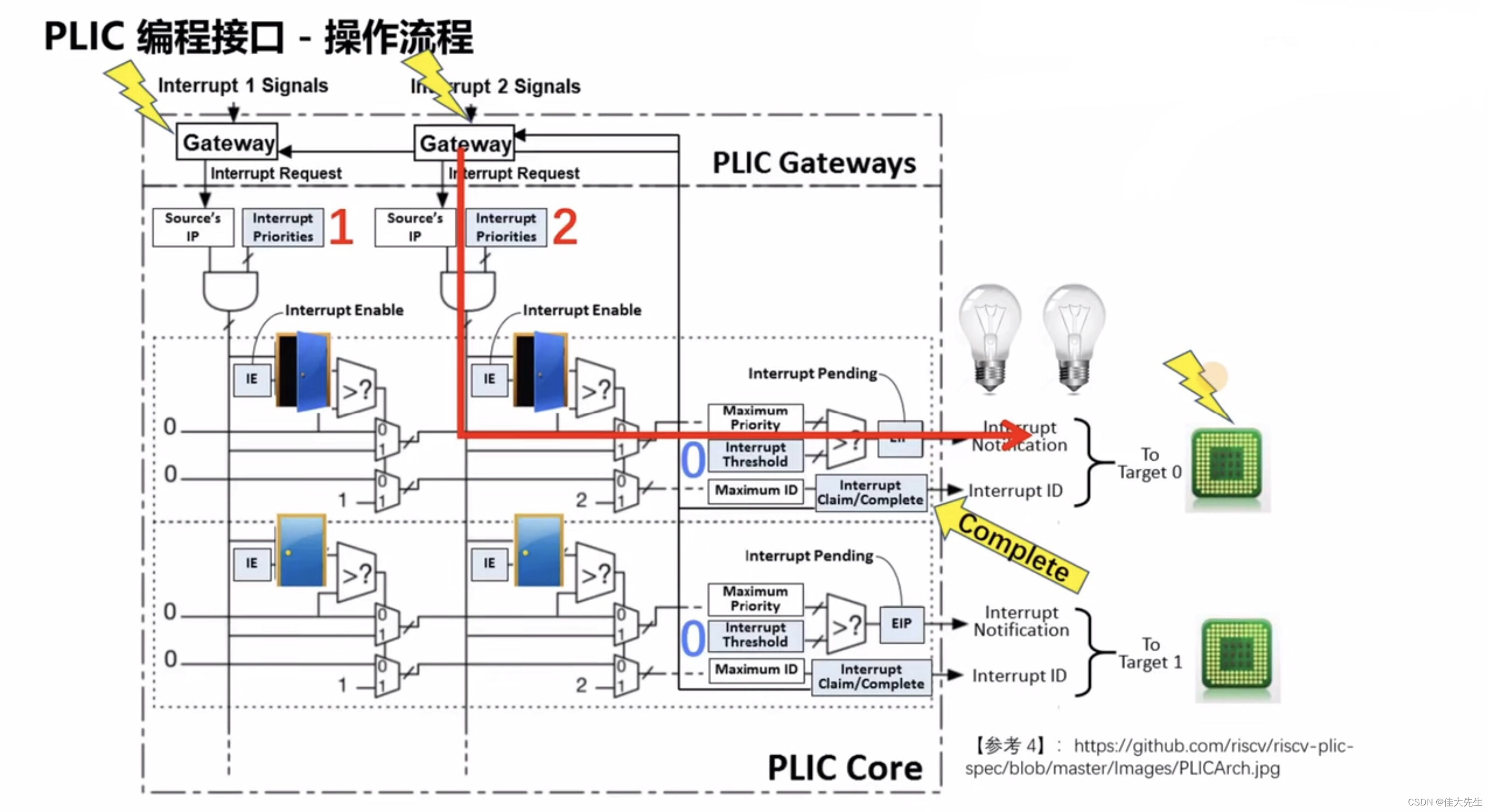
Details can be skipped
FreeRTOS The interrupt mechanism of can jump
边栏推荐
- My C language learning record (blue bridge) -- under the pointer
- 下一个行业风口:NFT 数字藏品,是机遇还是泡沫?
- Codeworks 5 questions per day (1700 average) - day 6
- tcpdump: no suitable device found
- My C language learning record (blue bridge) -- on the pointer
- Detailed use of dbutils # yyds dry goods inventory #
- 如何做好功能测试
- Reverse repackaging of wechat applet
- Precautions for single chip microcomputer anti reverse connection circuit
- These are not very good
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
JS regular filtering and adding image prefixes in rich text
ASU & OSU | model based regularized off-line meta reinforcement learning
BUUCTF刷题笔记——[极客大挑战 2019]EasySQL 1
#PAT#day10
下一个行业风口:NFT 数字藏品,是机遇还是泡沫?
Crazy, thousands of netizens are exploding the company's salary
Add one to non negative integers in the array
Some problem records of AGP gradle
Taobao focus map layout practice
The difference between sizeof and strlen in C language
[padding] an error is reported in the prediction after loading the model weight attributeerror: 'model' object has no attribute '_ place‘
[pointer training - eight questions]
银行核心业务系统性能测试方法
Linear regression and logistic regression
Microservice registration and discovery
Codeforces 5 questions par jour (1700 chacune) - jour 6
jsscript
Deep parsing pointer and array written test questions
NR modulation 1
真机无法访问虚拟机的靶场,真机无法ping通虚拟机

![[pointer training - eight questions]](/img/fd/1aa3937548a04078c4d7e08198c3a8.png)