当前位置:网站首页>Initialize your vector & initializer with a list_ List introduction
Initialize your vector & initializer with a list_ List introduction
2022-07-05 23:45:00 【Half moon and half wood Jin】
Catalog
2. use initializer_list To realize list construction vector
Initializing with a list is using "{}" To initialize your vector And other custom implementation containers . We can see STL Given in the library vector,list,map Containers can be used "{}" To initialize , for example :
vector<int> v{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
list<int> l={ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
map<int, int> m = { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 }, { 3, 3 } };So how does it come true ? In fact, its specific implementation is not as big as your phenomenon , He used a initializer_list To receive "{}" The element in is then given with initializer_list The constructor for the parameter list is then implemented through "{}" To construct containers .
1. initializer_list
Let's first introduce initializer_list:

You can see that he is C++11 There's only one of them , That means before C++98 It is not supported to construct objects with lists . It has only three ways 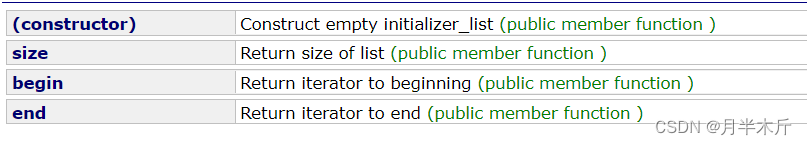
So let's test that out 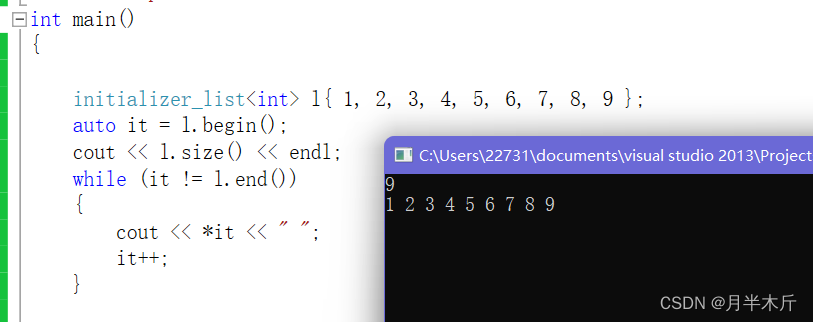
2. use initializer_list To realize list construction vector
I will be here vector All the code of the simulation implementation is given to avoid some readers' concern about vector I don't understand the specific implementation details and how to use lists vector Construction : I will also use initializer_list Part of the code is shown separately .( Here, if you're right vector If you have any questions about the simulated code, you can see my answer to vector Detailed analysis of the simulated blog :http://t.csdn.cn/vDdJ9 http://t.csdn.cn/vDdJ9)
http://t.csdn.cn/vDdJ9)
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<vector>
#include<initializer_list>
using namespace std;
namespace wbx
{
template<class T>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
/ Structure and deconstruction
vector()
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, end_of_storage(nullptr)
{}
// Construct with list vector:
vector(initializer_list<T> l)
{
_start = new T[l.size()];
_finish = _start;
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
*_finish = *it;
_finish++;
it++;
}
end_of_storage = _finish;
}
// Assign values with a list vector:
vector<T>& operator=(initializer_list<T> l)
{
reserve(l.size());
_finish = _start;
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
*_finish = *it;
_finish++;
it++;
}
return *this;
}
vector(size_t n, const T &val = T())// structure n individual T Type of val value
:_start(nullptr)// Pointer initialization is a good programming habit
,_finish(nullptr)
,end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
_start = new T[n*sizeof(T)];
_finish = _start+n;
end_of_storage = _finish;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_start[i] = val;
}
}
vector(int n,const T &val = T())// structure n individual T Type of val value , there val It must be used. const Otherwise, when parameters are passed in, they cannot be compiled
:_start(nullptr)// Pointer initialization is a good programming habit
, _finish(nullptr)
, end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
_start = new T[n*sizeof(T)];
_finish = _start + n;
end_of_storage = _finish;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_start[i] = val;
}
}
vector(const vector<T> &v)// Copy structure
:_start(nullptr),
_finish(nullptr),
end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
//vector temp(v.begin(), v.end());// You can't call the pointer of the return iterator of normal type here ,
vector<T> temp(v.cbegin(), v.cend());// because const Object can only call const Member functions of type
this->swap(temp);
}
template<class Iterator>// Here we need to define another template of iterator class , Because here we assume that vector Different types of objects stored in
// The type of iterator returned is also different , So let's reset a template class for a variety of different
// Type has universal applicability
vector(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
size_t n = last - first; // Here for frist and last The distance between should be written as distance Function to
// Get the distance between them , It's written here because a simple simulation implementation
_start = new T[n];
_finish = _start;
end_of_storage = _start + n;
while (first != last)
{
*_finish = *first;
_finish++;
first++;
}
}
~vector()
{
if (_start)
{
delete[] _start;
_start = nullptr;
_finish = nullptr;
end_of_storage = nullptr;
}
}
Operator overloading :
vector <T>operator=(vector<T> v)
{
this->swap(v);
return *this;
}
T& operator[](size_t index)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= size())
{
assert(false);
}
return *(_start + index) ;
}
/// Capacity dependent
size_t size()
{
int a = 0;
return a=_finish - _start;
}
size_t capacity()
{
return end_of_storage - _start;
}
bool empty()
{
if (_start == _finish)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void resize(size_t n, T val = T())
{
size_t oldsize = size();
if (n >capacity())
{
reserve(n - capacity());
}
for (int i = oldsize; i < n; i++)
{
_start[i] = val;
}
_finish = _start + n;// If the new size Smaller than old size There is no direct access here
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n>capacity())
{
T *temp = new T[n];
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++)
{
temp[i] = _start[i];// It must be used here = Make other copies, such as if memcpy If so, a shallow copy will occur
}
size_t oldsize = size();
if (_start)
{
delete[] _start;
}
_start = temp;
_finish = _start + oldsize;
end_of_storage = _start + n;
}
}
iterator
iterator begin()
{
return _start;
}
iterator end()
{
return _finish;
}
const_iterator cbegin()const
{
return _start;
}
const_iterator cend()const
{
return _finish;
}
/ Insert the function
void push_back(T val)
{
if (_finish == end_of_storage)
{
reserve(2 * capacity());
}
*_finish = val;
_finish++;
}
void pop_back()
{
if (empty())
{
assert(false);
}
_finish--;
}
iterator insert(iterator pos,T val)
{
if (empty()||pos==_finish)
{
push_back(val);
return pos;
}
if (_finish == end_of_storage)
{
reserve(capacity() + 1);
}
iterator temp = _finish-1;
while (temp >= pos)
{
*(temp + 1) = *temp;
temp--;
}
*pos = val;
_finish++;
return pos;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
if (pos < _start || pos >= _finish)
{
assert(false);
}
iterator ret = pos;
while (pos != _finish - 1)
{
*pos = *(pos + 1);
pos++;
}
_finish--;
return ret + 1;
}
T & front()
{
return *(_start);
}
T &back()
{
return *(_finish-1);
}
Exchange function
void swap(vector <T> &v)
{
std::swap(v._start, _start);
std:: swap(v._finish, _finish);
std::swap(v.end_of_storage, end_of_storage);
}
private:
iterator _start;
iterator _finish;
iterator end_of_storage;
};
}
using namespace std;
wbx::vector<int> static v4(5, 4);
void test1()
{
wbx::vector<int> v1{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
cout << "v1: ";
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
wbx::vector<int> v2;
v2 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
cout << "v2: ";
for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++)
{
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
wbx::vector<int> v3(11);
v3 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
cout << "v3: ";
for (int i = 0; i < v3.size(); i++)
{
cout << v3[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << v1.size() << endl;
cout << v2.size() << endl;
cout << v3.size() << endl;
cout << v1.capacity() << endl;
cout << v2.capacity() << endl;
cout << v3.capacity() << endl;
}About initializer_list Part of the code : You can see that the implementation is very simple , Just use initializer_list Internal element pairs vector Space loop assignment .
// Construct with list vector:
vector(initializer_list<T> l)
{
_start = new T[l.size()];// there start yes vector The starting address of the pointer of the underlying management array space
_finish = _start;
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
*_finish = *it;//finish yes vector The end position of the underlying array
_finish++;
it++;
}
end_of_storage = _finish;//end_of_storage yes vector The end position of the opened space
}
// Assign values with a list vector:
vector<T>& operator=(initializer_list<T> l)
{
reserve(l.size());
_finish = _start;
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
*_finish = *it;
_finish++;
it++;
}
return *this;
}边栏推荐
- 2022.6.20-6.26 AI industry weekly (issue 103): new little life
- Biased sample variance, unbiased sample variance
- TVS管和ESD管的技术指标和选型指南-嘉立创推荐
- STM32__06—单通道ADC
- The interface of grafana tool displays an error, incluxdb error
- 开关电源Buck电路CCM及DCM工作模式
- LeetCode——Add Binary
- JVM details
- Objective C message dispatch mechanism
- [EF core] mapping relationship between EF core and C data type
猜你喜欢
Breadth first search open turntable lock
PV静态创建和动态创建
CAS and synchronized knowledge
激光slam学习记录

如何让同步/刷新的图标(el-icon-refresh)旋转起来
STM32__ 06 - single channel ADC
The use of El cascader and the solution of error reporting
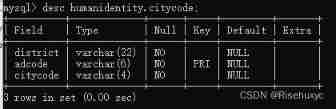
MySQL replace primary key delete primary key add primary key

5. Logistic regression
Rasa 3.x 学习系列-Rasa 3.2.1 新版本发布
随机推荐
698. 划分为k个相等的子集 ●●
UVA – 11637 garbage remembering exam (combination + possibility)
Brushless drive design -- on MOS drive circuit
Spreadjs 15.1 CN and spreadjs 15.1 en
帶外和帶內的區別
Breadth first search open turntable lock
无刷驱动设计——浅谈MOS驱动电路
Zero rhino technology joined hands with the intelligence Club: the "causal faction" forum was successfully held, and the "causal revolution" brought the next generation of trusted AI
21.PWM应用编程
多普勒效应(多普勒频移)
Qcombox (rewrite) + qcompleter (auto completion, auto loading the drop-down options of qcombox, setting the background color)
Huawei simulator ENSP - hcip - MPLS experiment
20.移植Freetype字体库
yate.conf
成为程序员的你,后悔了吗?
同事悄悄告诉我,飞书通知还能这样玩
QCombox(重写)+QCompleter(自动补全,自动加载qcombox的下拉选项,设置背景颜色)
Spire Office 7.5.4 for NET
Bao Yan notebook IV software engineering and calculation volume II (Chapter 8-12)
Difference between out of band and in band