当前位置:网站首页>TCP security of network security foundation
TCP security of network security foundation
2022-07-05 02:26:00 【Aploz】
One 、TCP Packet format
Source port number (16 position ): Identify the app being sent .
Target port number (16 Number ): Identify the target application .
Serial number (32 position ): Used to support data transmission and flow and error control .
Response number (32 position ): Used to support data transmission and flow and error control .
Head length (4 position ):TCP Head length .
Keep field (6 position ): Mark the packet type .
Window size (16 position ): For flow control , In terms of security , You can use the window size , Judge OS type .
The checksum (16 position ): Use part IP Head and TCP The calculated value of the header and data .
Emergency instructions (16 position ): Used to indicate that the data package contains emergency data .
optional ( Can be up to 40 byte ): optional information

URG: The data package contains emergency data
ACK: The response number is valid
PSH: Need to push data to applications
RST: Reset packet
SYN: Synchronize packets
FIN: End packet
Two 、 be based on TCP Head attack
1. classification
Head based attacks are divided into disturbance and detection
Disturbing class : Mainly disturbing TCP Layer operation .
Probe class : Send invalid header with response , As a probe OS One way , Use it to form an attack plan
2. Disrupt the attack
TCP The most frequently attacked field is the flag field , There are two types
Type 1
Create a packet with a flag combination that is not explicitly specified in the standard , for example : Set all flags to 0 and 1, Some of the past OS There is a problem in dealing with invalid flag combinations , Will exit or abandon the connection .
Type 2
Send invalid serial number in an open connection , This attack usually only breaks a single connection .
3. Detection attack
(1) Send invalid flag combination to confirm OS How to respond to , Detect attacks using a feature list , These characteristics are important for certain OS Is the only one. .
(2) Other detection attacks use the initial serial number , Some operating systems use certain initial values that determine serial numbers , By opening multiple connections ( Or at least send multiple SYN Data packets ) The attacker can determine an initial sequence number generation mode ,. The size of the startup window can also help reduce possible OS list ,TCP The standard does not specify a value for the size of the startup window , Because it's different OS Use different values
3、 ... and 、 be based on TCP Protocol attacks
1. Basic introduction
TCP The agreement is very complicated , There are a lot of attacks against it , And it's hard to eliminate , Attacks against protocols fall into two categories . The first is the attacker at the endpoint . And make incorrect communication with the attack target , The second is that attackers can sniff traffic , And insert the packet into TCP In the protocol flow .
2. Endpoint protocol attack
(1) Introduce
It usually involves sending packets out of sequence or without a complete handshake , Sending packets out of sequence usually just disturbs the current connection , Therefore, it is not very useful for attackers . Attackers can use packets outside the sequence to help confirm OS type .
(2)SYN An avalanche
SYN An avalanche (flood) Attack is a typical endpoint protocol attack .

SYN Avalanche attack principle
TCP The three connection protocol of uses a SYN Data packets , This forces the server to allocate buffer space . The target of this attack is to consume all TCP resources . force TCP Reject other connection attempts . As shown in the figure , The attacker sent enough SYN Packets without sending ACK Data packets , It may cause TCP The protocol stack rejects new connections , These connection attempts often refer to half open connections . An attacker may also carry out this attack from multiple locations , It increases the difficulty of elimination . Once successful SYN An avalanche attack will drop a server and deny anyone access to it .
One way to eliminate it is at the entrance of the network Install network filters that can detect such attacks , If it is a distributed attack , Then the network filter cannot distinguish between good connection attempts and malicious connection attempts .
3. Sniff traffic attacks
(1) Introduce
These attacks are different from common packet sniffing , In common packet sniffing, attackers try to read data from the network . In this attack, the attacker inserts packets into the channel protocol , The goal is either Cut off the connection , Or steal the connection .
(2)RST Connection disconnection attack
If attacker can see traffic , Then it's easy for him to forge IP Address and send reset packets to both parties (RST) Cut off the connection .
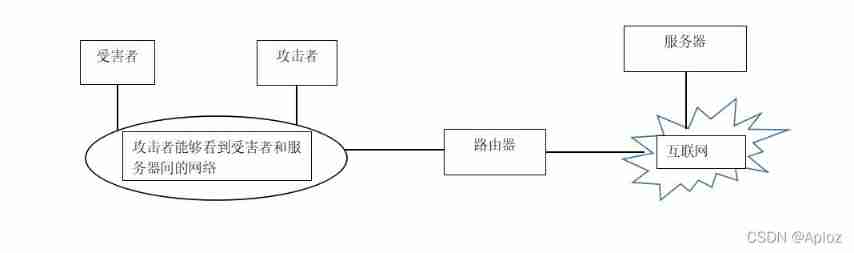
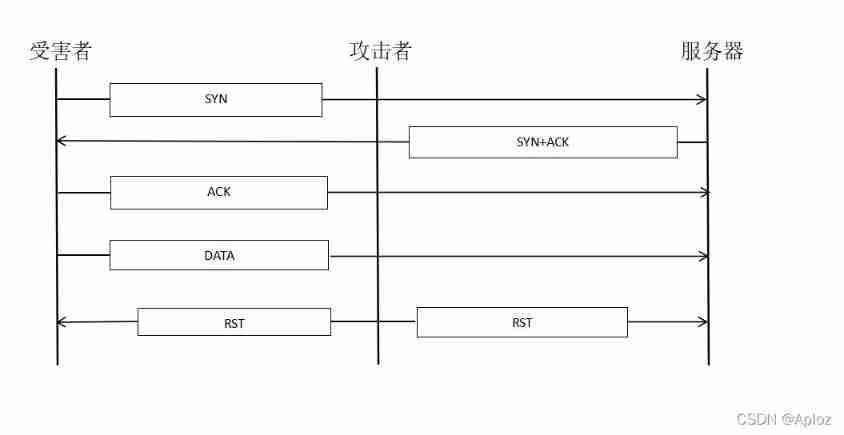
It can be seen from the figure that the attacker is connected to the network , So he can see the traffic between the victim and the server , Although the attack is on the same network as the victim , But the attacker can connect to any network where he can see this traffic . When an attacker wants to terminate a connection , He created a TCP Reset packet , And send the packet to the source IP Set the address to the victim IP Address server , The server and the victim are receiving RST Packet time , Both will terminate the connection .
The attacker needs to set the target address of the hardware to a suitable address , So that the data packet can be delivered to the appropriate device . The attacker needs to set the hardware address of the reset packet sent to the server to the router hardware address , The target hardware address of the reset packet sent to the victim needs to be set as the victim's hardware address , Attackers do not need to sniff the source hardware address , Because neither the victim nor the router will check the source hardware address .
If attacker can see network traffic and insert data into network , Then this kind of attack cannot be eliminated , If the attacker also sets the source hardware address to the victim or router hardware address , It is impossible to determine which device performs this attack . This attack can be eliminated by encryption , If in IP, But generally, the traffic in the network is not encrypted .
4. Session hijacking
(1) Introduce
Session hijacking is also an attack against protocols , This attack also requires the attacker to see the traffic between the victim and the server . The goal of session hijacking is to steal connections from one of the two parties , And forged into a party's equipment .
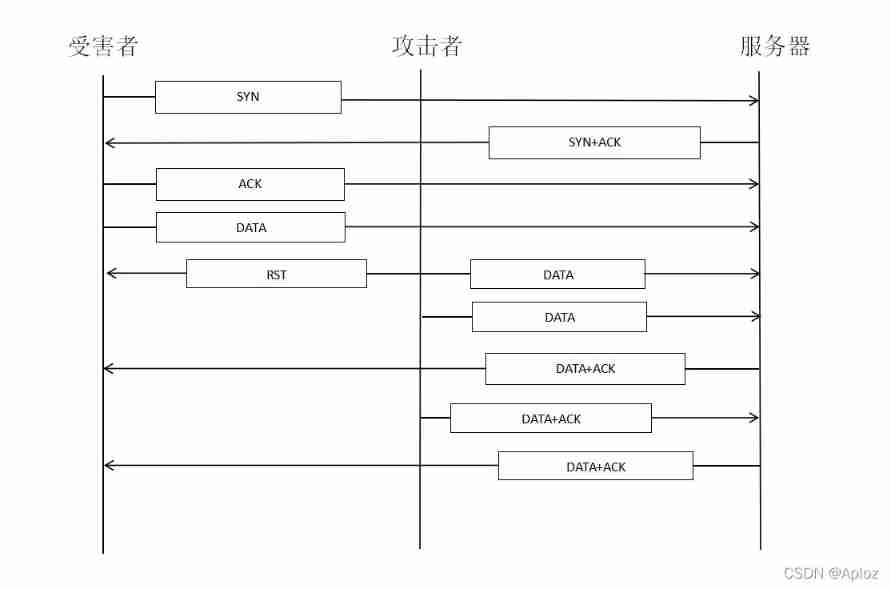
Pictured , The attacker waits until he sees the data signal , The attack begins . Send a message to the victim RST Data packets , By placing the source of the packet IP Set the address to server IP Address and set the destination address of the packet to the victim IP Address , Pretend to be a server . The serial number found in the traffic sniffer used by the attacker sends data to the server . The packets sent from the attacker to the server appear to be from the victim , The server responds to the victim with its own data . Attackers need to continuously sniff traffic , In order to obtain the data sent to the victim . The victim is still receiving traffic from the server , But because the connection has been closed , The server has no response .
The solution to this attack is encryption TCP load , An attacker cannot send data to the server , Even if you hijack this session , But in general TCP The load is encrypted by the application .
Four 、 be based on TCP Verified attack
TCP Authentication is not supported , It USES IP Layer provides all validation , Attacks using port numbers can be seen as authentication based attacks . Any application can use any port number it wants . Security devices cannot rely on ports to verify application traffic , Most of the OS It is strictly limited that some applications can only use ports with low values (1024 following ), These applications need to be run by administrator users , But this does not prevent malicious users from running applications on reserved ports .
5、 ... and 、 be based on TCP Traffic attack
The target of traffic based attacks is consumption TCP Layer resources . because TCP Resources are dense , A large amount of traffic can reduce service performance , Even avalanches are not caused by attacks , The server is overburdened by a popular application . Whether the avalanche is caused by attack or excessive traffic , There are technologies to eliminate avalanches . The most common method is to use network devices , Such as flow shaper , The most widely used term for these devices is quality of service (QOS), They divide the flow into different types according to various standards , Then allocate the loan .
边栏推荐
- Some query constructors in laravel (2)
- openresty ngx_ Lua execution phase
- 【LeetCode】98. Verify the binary search tree (2 brushes of wrong questions)
- Bumblebee: build, deliver, and run ebpf programs smoothly like silk
- The perfect car for successful people: BMW X7! Superior performance, excellent comfort and safety
- Exploration of short text analysis in the field of medical and health (I)
- [uc/os-iii] chapter 1.2.3.4 understanding RTOS
- Visual explanation of Newton iteration method
- Chinese natural language processing, medical, legal and other public data sets, sorting and sharing
- Action News
猜你喜欢
The most powerful new household god card of Bank of communications. Apply to earn 2100 yuan. Hurry up if you haven't applied!
Introduce reflow & repaint, and how to optimize it?
Matrixone 0.2.0 is released, and the fastest SQL computing engine is coming
Write a thread pool by hand, and take you to learn the implementation principle of ThreadPoolExecutor thread pool

【LeetCode】111. Minimum depth of binary tree (2 brushes of wrong questions)
【LeetCode】106. Construct binary tree from middle order and post order traversal sequence (wrong question 2)

Learn game model 3D characters, come out to find a job?
![Hmi-31- [motion mode] solve the problem of picture display of music module](/img/9c/0b25c0a41758652848aed2a269880f.jpg)
Hmi-31- [motion mode] solve the problem of picture display of music module

Comment mettre en place une équipe technique pour détruire l'entreprise?
![ASP. Net core 6 framework unveiling example demonstration [01]: initial programming experience](/img/3b/0ae9fbadec5dbdfc6981f1f55546a5.jpg)
ASP. Net core 6 framework unveiling example demonstration [01]: initial programming experience
随机推荐
Some query constructors in laravel (2)
Grub 2.12 will be released this year to continue to improve boot security
ASP. Net core 6 framework unveiling example demonstration [01]: initial programming experience
Advanced conditional statements of common SQL operations
A tab Sina navigation bar
Which common ports should the server open
【LeetCode】110. Balanced binary tree (2 brushes of wrong questions)
RichView TRVStyle MainRVStyle
tuple and point
A label making navigation bar
Restful Fast Request 2022.2.1发布,支持cURL导入
openresty ngx_lua变量操作
Can you really learn 3DMAX modeling by self-study?
低度酒赛道进入洗牌期,新品牌如何破局三大难题?
Asynchronous and promise
187. Repeated DNA sequence - with unordered_ Map basic content
如何搭建一支搞垮公司的技術團隊?
Go RPC call
Pytest (5) - assertion
openresty ngx_ Lua execution phase