当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of P problem, NP problem, NPC problem and NP hard problem
Detailed explanation of P problem, NP problem, NPC problem and NP hard problem
2022-07-06 06:12:00 【Zhan Miao】
1. polynomial time (Polynomial time)
Time complexity doesn't mean how long it takes a program to solve a problem , But when the scale of the problem handled by the program expands , The length of time required by the program corresponds to how fast it grows . in other words , For a program , Its efficiency in processing a specific data cannot measure the quality of the program , But we should see that when the scale of this data becomes hundreds of times , Is the running time of the program the same , Or hundreds of times slower , Or tens of thousands of times slower .
No matter how big the data is , The processing time is always so much , Let's say it's a good program , have O(1) Time complexity of , Also known as constant level complexity ; How big the data has become , How long does it take , Like looking for n The time complexity of this program is O(n), Is linear complexity , And it's like bubble sorting 、 Insert sort, etc , Data expansion 2 times , Time slows down 4 Times , The time complexity is  , The complexity is square . There are also algorithms for exhausting classes , The length of time required increases in geometric order , This is it.
, The complexity is square . There are also algorithms for exhausting classes , The length of time required increases in geometric order , This is it.  Exponential complexity of , even to the extent that
Exponential complexity of , even to the extent that  The factorial complexity of .
The factorial complexity of .
Combine the function to increase the speed and the actual operation effect of the algorithm , Polynomial time algorithm can be regarded as efficient algorithm or practical algorithm , Exponential time algorithm is not practical .
2. Deterministic algorithm and non deterministic algorithm
2.1. Deterministic algorithms
set up A Is to solve the problem B A solution algorithm of , During the whole execution of the algorithm , A definite solution can be obtained at each step , Such an algorithm is a deterministic algorithm .
2.2. Nondeterministic algorithm
set up A Is to solve the problem B A solution algorithm of , It divides the problem into two parts , They are guess stage and verification stage , among
- Guess stage : At this stage , A specific input instance of the problem x Generate an arbitrary string y, At every run of the algorithm ,y The value of may be different , therefore , Guess works in an uncertain form .
- Validation phase : At this stage , Use a deterministic algorithm ( In a limited time ) verification .① Check for y Is it a suitable form , If not , Then the algorithm stops and gets no;② If y Is the appropriate form , Then verify whether it is the solution of the problem , If it is , Then the algorithm stops and gets yes, Otherwise, the algorithm stops and gets no. It is to verify the correctness of the guessed solution .
3. Statute / reduction
problem A It can be reduced to a problem B, be called “ problem A It can be stipulated as a problem B”, It can be understood as a problem B The solution must be the problem A Solution , Therefore, it is necessary to solve the problem A It won't be difficult to solve B. This shows the problem B The time complexity must be greater than or equal to the problem A.
Now there are two questions : Solving a linear equation of one variable and solving a quadratic equation of one variable . So let's say , The former can be stipulated as the latter , That is to say, if you know how to solve a quadratic equation with one variable, you can solve it . We can write two programs corresponding to two problems , So we can find one “ The rules ”, According to this rule, change the input data of the program for solving linear equation of one variable , It is used in the program of solving quadratic equation of one variable , Two programs always get the same results . The rule is : The coefficients of the corresponding terms of the two equations remain unchanged , The coefficient of quadratic term of quadratic equation of one variable is 0.
From the definition of the statute, we can see , One problem is regulated as another problem , Time complexity has increased , The scope of application of the problem has also increased . Through constant regulation of certain issues , We can keep looking for more complex , But it's less complex to replace it with a wider range of algorithms , But it can only be used for a very small class of problems . There is such a NP problem , be-all NP The problem can be reduced to it . let me put it another way , As long as the problem is solved , So all NP All the problems have been solved . The existence of this kind of problem is unbelievable , And even more incredible , There is more than one such problem , It has a lot of , It's a kind of problem . This kind of problem is legendary NPC problem , That is to say NP- Problem completely .
4. P Class problem 、NP Class problem 、NPC problem 、NP Difficult problem
P Class problem : Problems that can be solved in polynomial time .
NP Class problem : In polynomial time “ Verifiable ” The problem of . in other words , We can't decide whether the problem is solved or not , Instead, guess a solution to prove whether the solution is correct in polynomial time . That is, the guessing process of the problem is uncertain , The verification of one of its solutions can be completed in polynomial time .P Class problems belong to NP problem , but NP Class problems do not necessarily belong to P Class problem .
NPC problem : There is such a NP problem , be-all NP The problem can be reduced to it . let me put it another way , As long as the problem is solved , So all NP All the problems have been solved . Its definition should meet 2 Conditions :
- It's a NP problem ;
- all NP Problems can be regulated to it .
NP Difficult problem :NP-Hard The problem is such a problem , It meets the NPC The second article of the definition of the problem, but it does not have to meet the first article ( That is to say ,NP-Hard The problem is better than NPC The scope of the problem is wide ,NP-Hard The problem is not limited to NP), That all the NP Problems can be reduced to it , But he is not necessarily a NP problem .NP-Hard The problem is also difficult to find the algorithm of polynomials , But it's not part of our research , Because it doesn't have to be NP problem . Even if NPC The problem found a polynomial level algorithm ,NP-Hard The problem may still not be able to get a polynomial algorithm . in fact , because NP-Hard Relaxed restrictions , It will be possible than all NPC The time complexity of the problem is higher, so it is more difficult to solve .
The relationship between the above four issues is shown in the figure below :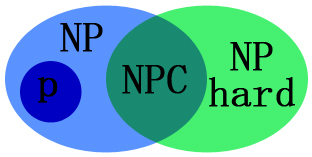
reference
Combinatorial optimization _ Zhejiang University _ University of China MOOC( MOOC )
边栏推荐
- 数字三角形模型 AcWing 1015. 摘花生
- Cognitive introspection
- 对数据安全的思考(转载)
- Testing and debugging of multithreaded applications
- Clock in during winter vacation
- Overview of three core areas of Mathematics: algebra
- C language bubble sort
- Wib3.0 leapfrogging, in leapfrogging (ง • ̀_•́) ง
- 还在为如何编写Web自动化测试用例而烦恼嘛?资深测试工程师手把手教你Selenium 测试用例编写
- LeetCode 729. 我的日程安排表 I
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
LeetCode 1200. 最小绝对差
公司視頻加速播放
在线问题与离线问题
Caused by:org. gradle. api. internal. plugins . PluginApplicationException: Failed to apply plugin
Accélération de la lecture vidéo de l'entreprise
【LeetCode】Day96-第一个唯一字符&赎金信&字母异位词
Wib3.0 leapfrogging, in leapfrogging (ง • ̀_•́) ง
数字三角形模型 AcWing 1015. 摘花生
IP day 16 VLAN MPLS configuration
全链路压测:构建三大模型
Understanding of processes and threads
Significance of unit testing
Title 1093: character reverse order
Réflexions sur la sécurité des données (réimpression)
Gtest之TEST宏的用法
LeetCode 731. 我的日程安排表 II
把el-tree选中的数组转换为数组对象
职场进阶指南:大厂人必看书籍推荐
使用Nacos管理配置
2022 software testing workflow to know


![[web security] nodejs prototype chain pollution analysis](/img/c5/256ab30e796f0859387585873cee8b.jpg)