当前位置:网站首页>Arabellacpc 2019 (supplementary question)
Arabellacpc 2019 (supplementary question)
2022-07-06 03:09:00 【WDLieqi】
D. Meeting Bahosain
The main idea of the topic
a,b Two arrays , among b The elements in the array are different , Ask us if we can a Choose an element , use b The elements inside add and subtract it infinitely , Finally let a The array elements are the same . I didn't understand the meaning of the title at all during the competition , Split .
Their thinking
Make all elements the same , that a[i] - a[j] (i, j Is an arbitrary number ) Is equal to x1 * b1 + x2 * b2 + x3 * b3 + … + xn * bn. Here we will introduce a theorem :a * x + b * y = gcd(a, b) There must be a solution . Substituting in, we can get x1 * b1 + x2 * b2 + x3 * b3 + … + xn * bn = gcd(b1, b2, b3, …, bn) There must be a solution , Here, because the multiplier is obtained by oneself , So it can be concluded that a[ i ] - a[ j ] = x * (gcd(b1, b2, …, bn)),x It's an arbitrary constant .
Finally, I came to the conclusion , As long as all a[ i ] - a[ j ] to be divisible by gcd(b1, b2, …, bn) That's all right. .
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define IOS \
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); \
cin.tie(0); \
cout.tie(0);
//#define For(i, k, n) for (int i = k; i < n; i ++)
//#define FOR(i, k, n) for (int i = k; i <= n; i ++)
#define P acos(-1);
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define PDD pair<double, double>
#define Pll pair<LL, LL>
typedef unsigned long long Uint;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const int M = 1e6 + 10, mod = 1000000007;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int dx[4] = {0, 1, -1, 0}, dy[4] = {1, 0, 0, -1};
int lowbit(int x) { return (x & -x); };
// The above can be ignored
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N], b[N];
void solve()
{
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
cin >> a[i];
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
cin >> b[i], res = (res == 0) ? b[i] : __gcd(res, b[i]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++)
{
if ((a[i] - a[i - 1]) % res != 0)
{
puts("No");
return;
}
}
puts("Yes");
}
int main()
{
IOS
int T = 1;
//cin >> T;
//scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
I. Bashar and Hamada
The main idea of the topic
k(2 <= k <= n) The number of length asks what is the maximum absolute value of the difference between each other .
Their thinking
First of all, we should understand that the order does not affect the size . Then find a rule :
Suppose a set of data {1,2,3,4,5,7}, Start ans=0;
Start :ans+= |1-7|
Insert 5: ans+=|5-1|+|5-7|=|1-7|
Insert 2: ans+=|2-1|+|2-7|+|2-5|==|1-7|+|2-5|
Insert 4: ans+=|4-1|+|4-7|+|4-5|+|4-2|==|1-7|+|2-5|
Insert 3: ans+=|3-1|+|3-7|+|3-5|+|3-2|+|3-4|==|1-7|+|2-5|+|3-4|
It's obvious to list it like this . Odd number of inserts , The number to be added remains unchanged .
You can see every insert 2 Just add a combination , As long as the combination added each time is the largest , Can guarantee the biggest answer .
Choose the one with the greatest difference in each combination , After ordering , One on the left and one on the right .
The idea is reproduced from this blog :
https://www.cnblogs.com/studyshare777/p/12766707.html
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define IOS \
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); \
cin.tie(0); \
cout.tie(0);
//#define For(i, k, n) for (int i = k; i < n; i ++)
//#define FOR(i, k, n) for (int i = k; i <= n; i ++)
#define P acos(-1);
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define PDD pair<double, double>
#define Pll pair<LL, LL>
typedef unsigned long long Uint;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const int N = 3e5 + 10, M = 1e6 + 10, mod = 1000000007;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int dx[4] = {0, 1, -1, 0}, dy[4] = {1, 0, 0, -1};
int lowbit(int x) { return (x & -x); };
LL f[N];
void solve()
{
LL n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cin >> f[i];
sort(f + 1, f + 1 + n);
LL ans = 0, tot = 0;
ans = f[n] - f[1];
tot = ans;
cout << ans << ' ';
int r = n - 1, l = 2;
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i ++)
{
if (!(i & 1))
tot += f[r --] - f[l ++];
ans += tot;
cout << ans << ' ';
}
}
int main()
{
IOS
int T = 1;
//cin >> T;
//scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Erreur de la carte SD "erreur - 110 whilst initialisation de la carte SD
- XSS challenges bypass the protection strategy for XSS injection
- 真机无法访问虚拟机的靶场,真机无法ping通虚拟机
- 技术分享 | undo 太大了怎么办
- codeforces每日5題(均1700)-第六天
- 2.12 simulation
- 深度解析指针与数组笔试题
- NR modulation 1
- MySQL advanced notes
- How does yyds dry inventory deal with repeated messages in the consumption process?
猜你喜欢
![[network security interview question] - how to penetrate the test file directory through](/img/48/be645442c8ff4cc5417c115963b217.jpg)
[network security interview question] - how to penetrate the test file directory through
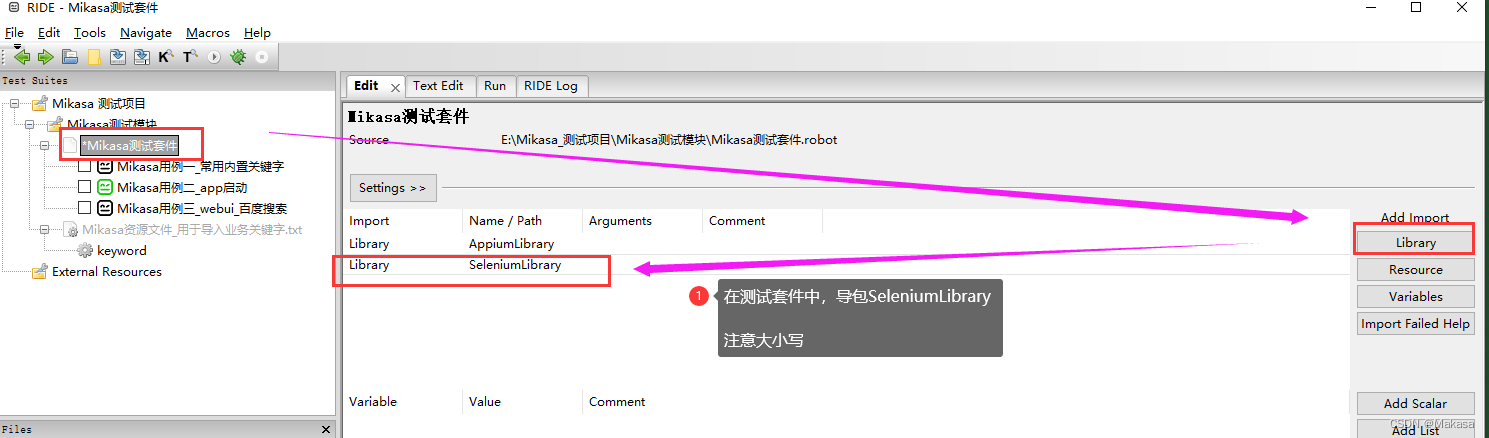
Introduction to robotframework (III) Baidu search of webui automation
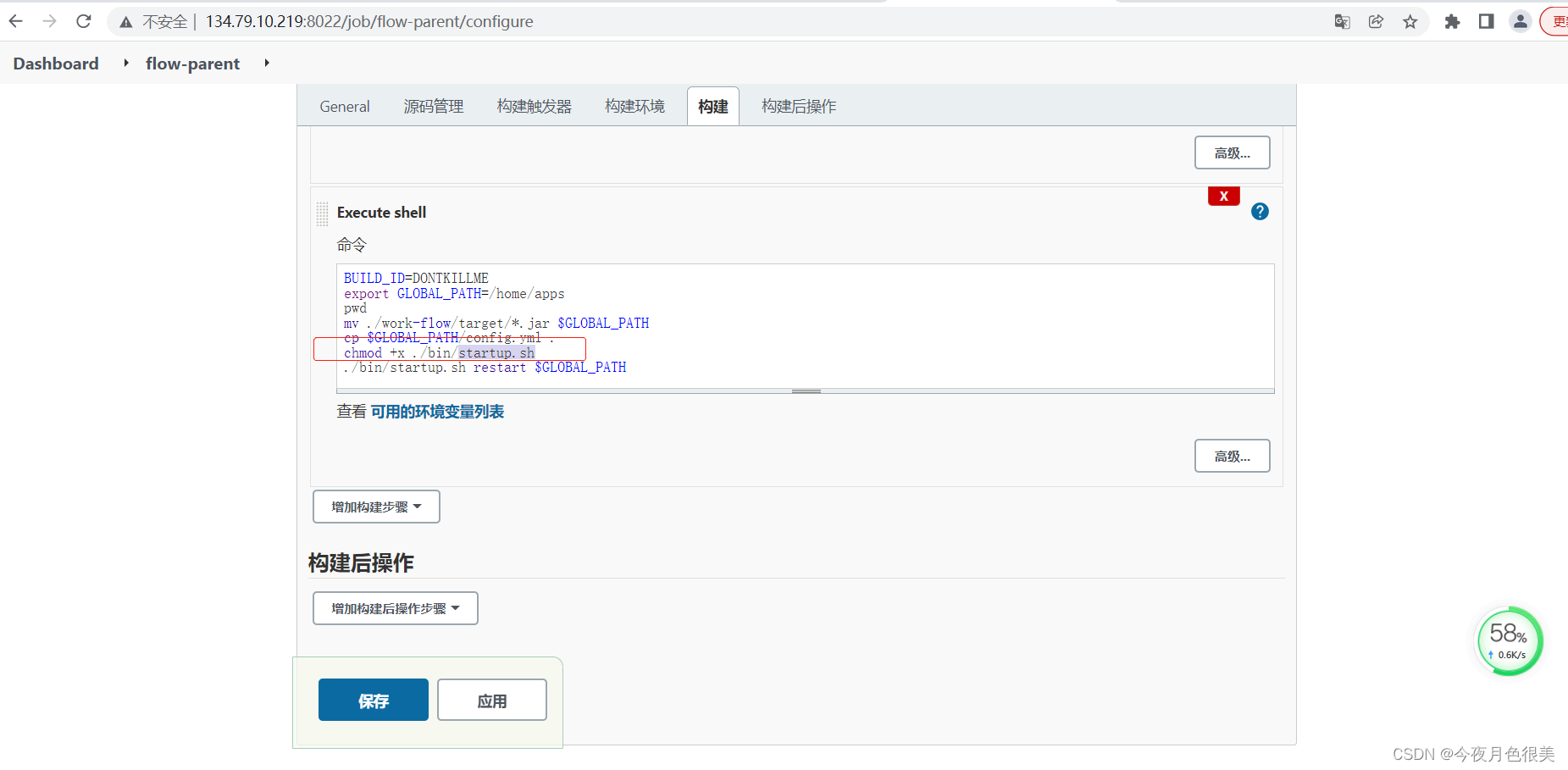
Problems encountered in 2022 work IV
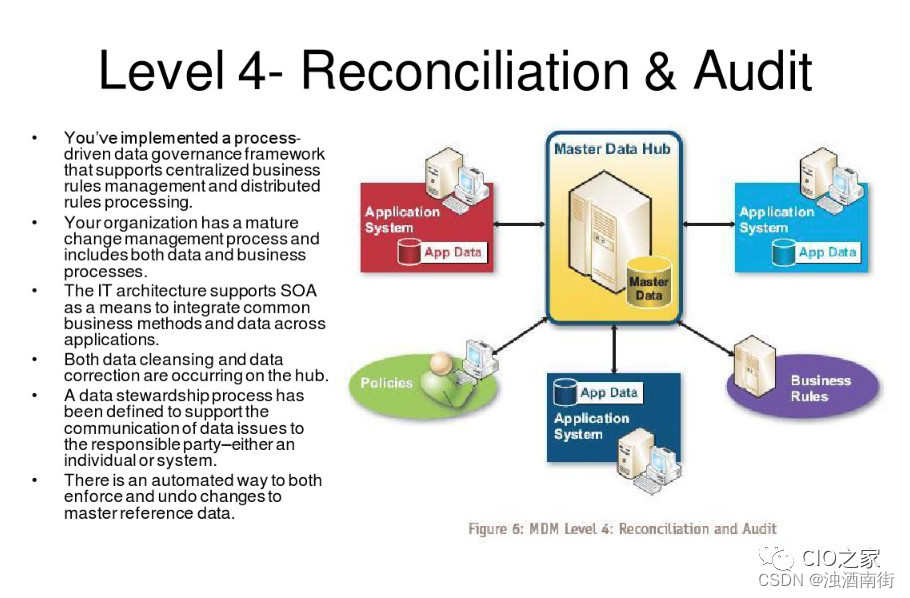
Maturity of master data management (MDM)

Era5 reanalysis data download strategy
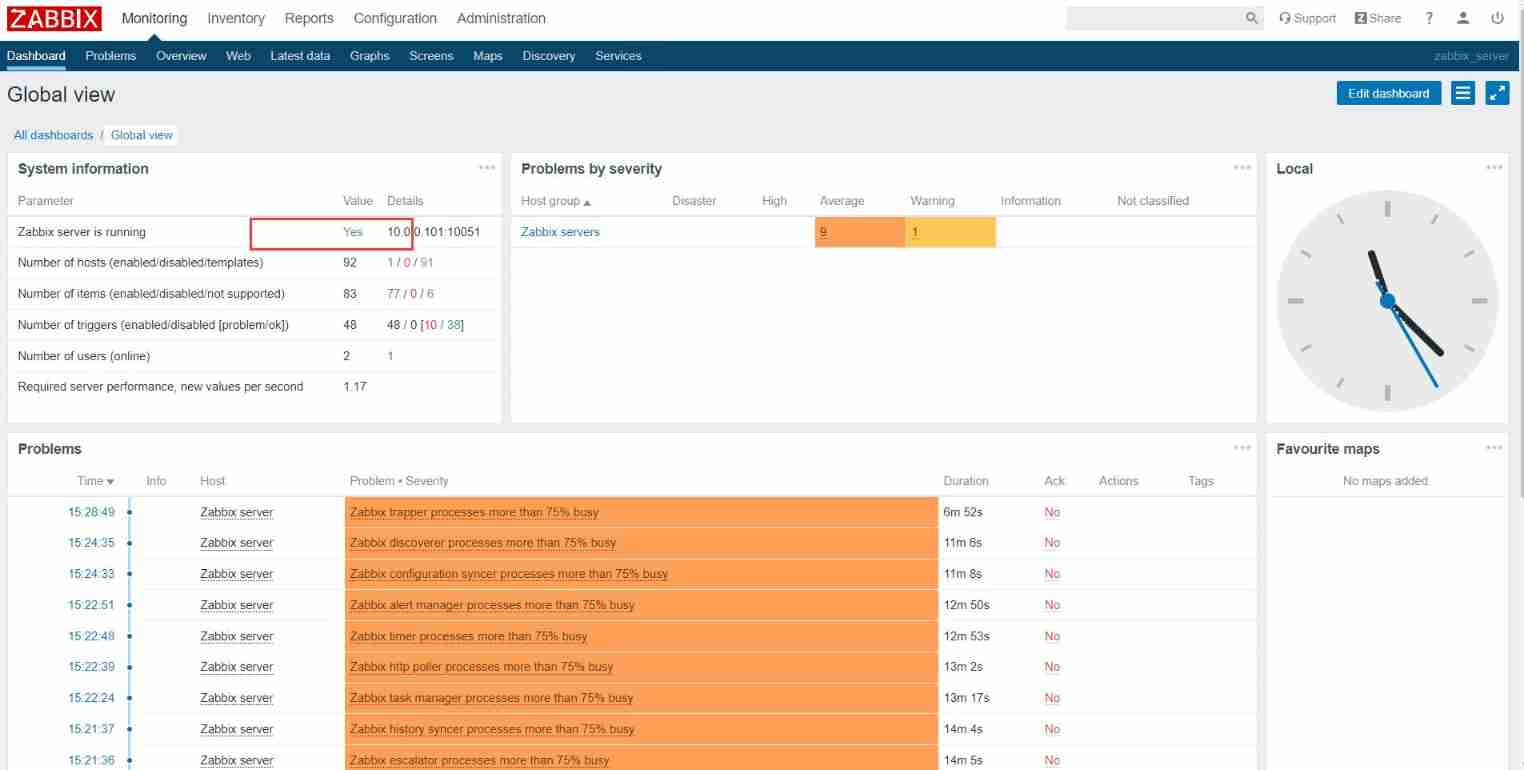
Apt installation ZABBIX

Is there a completely independent localization database technology
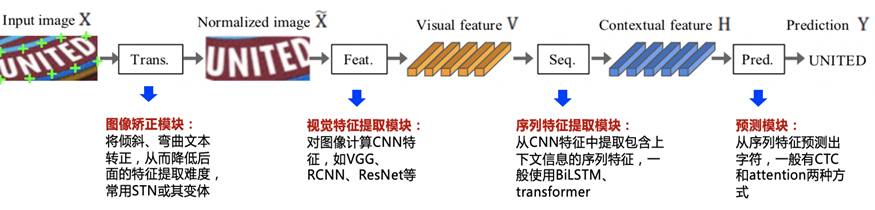
OCR文字識別方法綜述
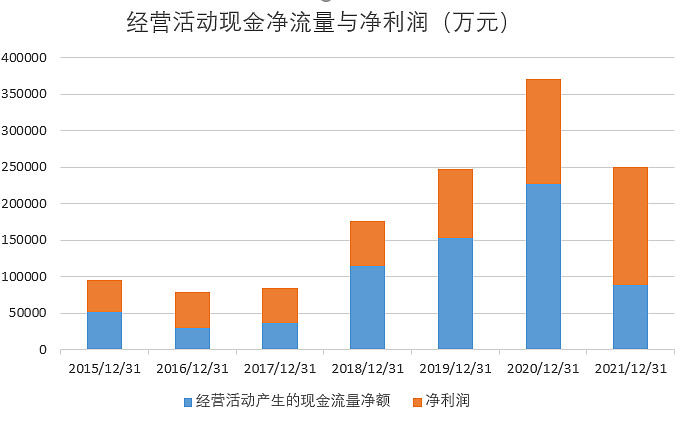
What is the investment value of iFLYTEK, which does not make money?
![Buuctf question brushing notes - [geek challenge 2019] easysql 1](/img/37/c38a933ce7fa5d2b8fa597965ffcb2.png)
Buuctf question brushing notes - [geek challenge 2019] easysql 1
随机推荐
How to accurately identify master data?
1. Dynamic parameters of function: *args, **kwargs
SD卡報錯“error -110 whilst initialising SD card
Descriptor implements ORM model
[pointer training - eight questions]
JS regular filtering and adding image prefixes in rich text
SD card reports an error "error -110 whilst initializing SD card
下一个行业风口:NFT 数字藏品,是机遇还是泡沫?
八道超经典指针面试题(三千字详解)
Derivation of anti Park transform and anti Clarke transform formulas for motor control
Atcoder beginer contest 233 (a~d) solution
3857墨卡托坐标系转换为4326 (WGS84)经纬度坐标
PMP practice once a day | don't get lost in the exam -7.5
jsscript
淘宝焦点图布局实战
BUUCTF刷题笔记——[极客大挑战 2019]EasySQL 1
resulttype和resultmap的区别和应用场景
Communication between microservices
【若依(ruoyi)】ztree 自定义图标(iconSkin 属性)
CobaltStrike-4.4-K8修改版安装使用教程