当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)(A~D)
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)(A~D)
2022-07-07 22:48:00 【_dawn°】
A. The Third Three Number Problem

给出一个数n,找到三个数a,b,c,使得这三个数相互异或得到三个数的和等于n。
思路:其实我的思路是看到第一个样例解释来的,,
![]()
然后就想到可以是两个数相同,这样三个数的和就可以转化为两个数的和,而对于偶数,直接用n/2和0异或即可;对于奇数,样例中的1不满足,然后我就直接猜测奇数不可以满足条件,事实证明这个是可以证明的:假设二进制最后一位有k个1和3-k个0,那n的二进制最后一位的奇偶性与k*(3-k)相同,那么n的二进制最后一位应该恒为0。
AC Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int N=55;
int t,n;
int main(){
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cout.tie(0);
std::cin>>t;
while(t--){
std::cin>>n;
if(n&1){
std::cout<<-1<<'\n';
continue;
}
std::cout<<n/2<<' '<<n/2<<' '<<0<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}B. Almost Ternary Matrix
给出两个偶数,构造一个01矩阵,使得每个方块周围与它不同的方块数是2。
思路:自己画一下试试,会发现我们可以找到一个4*4的单元矩阵,根据这个单位矩阵循环输出即可,单位矩阵如下:
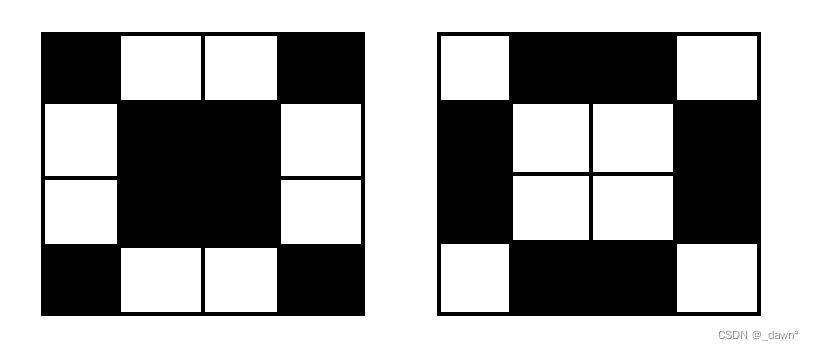
当然,01可以互换,这样代码就很简单了。
AC Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int N=55;
int t,n,m;
int ans[4][4]={1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1};
int main(){
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cout.tie(0);
std::cin>>t;
while(t--){
std::cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
std::cout<<ans[i%4][j%4]<<" \n"[j==m-1];
}
}
}
return 0;
}os:一开始因为怎么写代码想了半天hhhhh
C. The Third Problem

给出一个permutation,不过是从0~n-1,问有多少种重新排列这些数的方法,使得重新排序后的数组对于每个区间的MEX值相等。
思路:看到这个题,大概就是一个排列组合类似的题。根据观察我们可以发现,对于每一个数,只要这个数向前向后都有比该数小的元素存在,那这个数就可以在这个范围内移动,比如样例4:
1 3 7 2 5 0 6 4
比2小的只有0和1,那2就可以在第2到第五个位置移动;3也只能在这个范围内移动,因为比3小的数最向外只能到0和1的位置;而对于在比自己小的数字外围的数字,他们的位置是不能动的,比如4,比它小的0,1,2,3都在前面,很容易理解它的位置如果变化,那一定存在区间的MEX值变化了。根据这个性质,我们可以根据数字大小排序,从小到大枚举,不断更新比当前数小的数的最大范围区间,计算每个数有几种选择位置的方法,相乘即可。当然,0和1作为初始的区间范围,0和1的位置一定不能动。
AC Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int N=1e5+5;
int t,n;
int a[N];
struct node{
int id,num;
bool operator<(const node &a) const{
return num<a.num;
}
} e[N];
int main(){
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cout.tie(0);
std::cin>>t;
while(t--){
std::cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
std::cin>>a[i];
e[i].id=i;
e[i].num=a[i];
}
std::sort(e+1,e+1+n);
int r=-1,l=1e9;
ll ans=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
r=std::max(r,e[i].id);
l=std::min(l,e[i].id);
if(i>2&&e[i].id>l&&e[i].id<r){
ans*=(r-l-1-i+3);
ans%=mod;
}
}
std::cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}os:二十多分钟搞定前两个题,后面一直在想C,最后五分钟交的hhhh
D. Almost Triple Deletions

给出一个数组,若相邻两个数不同,那可以删去这两个数。最终操作完成后数组中剩余的数都相等,问最多可以保留几个数。
思路:学习大佬的思路,太顶了
我们可以认为操作的最后结果是删除部分连续区间,而对于一个区间[l,r]来说,当且仅当满足下列条件时,可以删除:区间长是偶数;区间中出现最频繁的元素的个数最大为(r-l+1)/2。
必要性一定,证明充分性:
对于出现最频繁的数,一定可以找到一种方法,删去一个和另外一个数,那么还剩下的出现次数t<=(r-l+1)/2-1;如果删除后,这个数还是出现次数最多的,那它还是满足初始条件,依旧可以删除一个该数和另一个数;如果删除后它不是出现次数最多的数了,那一定有另外一个数满足出现次数最多的初始条件,可以删除一个该数和另外一个数,这样就是这个区间内元素之间的相互转化,最后到达平衡时就是两个元素出现次数相等,都等于l/2,这样一定是可以删去的,使得该区间长为0,证毕。
所以我们可以先处理区间可以删除的子区间,cel[l][r]=1,我们定义DP数组f[i]表示从第一个到第i个数,删去部分数达到所有数都等于a[i]后,剩余的个数最大值,f[i]到f[j]的转化方程可以表示为删除区间[j,i],使得f[i]=f[j]+1。
最后的答案不一定是f[n],因为最后剩下的数不一定都等于a[n],所以需要扫一遍取最大值。
数据范围n<=5000,O(n^2)能过。
AC Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int N=5e3+5;
int t,n;
int a[N];
int main(){
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cout.tie(0);
std::cin>>t;
while(t--){
std::cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
std::cin>>a[i];
}
int cel[n+1][n+1]={0};
for(int l=1;l<=n;l++){
int cnt[n+1]={0},max=0;
for(int r=l;r<=n;r++){
cnt[a[r]]++;
max=std::max(max,cnt[a[r]]);
if((r-l+1)%2==0&&max*2<=r-l+1)
cel[l][r]=1;
}
}
int f[n+1]={0};
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
if(cel[1][i])
f[i+1]=1;
}
f[1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<i;j++){
if((j+1>i-1||cel[j+1][i-1]==1)&&a[j]==a[i]&&f[j]>0)
f[i]=std::max(f[i],f[j]+1);
}
if(i==n||cel[i+1][n]) ans=std::max(ans,f[i]);
}
std::cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
os:怪,这个题卡memset
嘿嘿嘿,青啦青啦!
 若有错误请指教,谢谢!
若有错误请指教,谢谢!
边栏推荐
- 商品的设计等整个生命周期,都可以将其纳入到产业互联网的范畴内
- [研发人员必备]paddle 如何制作自己的数据集,并显示。
- 赞!idea 如何单窗口打开多个项目?
- "An excellent programmer is worth five ordinary programmers", and the gap lies in these seven key points
- Su embedded training - day4
- Two small problems in creating user registration interface
- 玩轉Sonar
- After going to ByteDance, I learned that there are so many test engineers with an annual salary of 40W?
- 哪个券商公司开户佣金低又安全,又靠谱
- Linkedblockingqueue source code analysis - add and delete
猜你喜欢

How does starfish OS enable the value of SFO in the fourth phase of SFO destruction?
ROS from entry to mastery (IX) initial experience of visual simulation: turtlebot3
QT adds resource files, adds icons for qaction, establishes signal slot functions, and implements
某马旅游网站开发(对servlet的优化)

Qt添加资源文件,为QAction添加图标,建立信号槽函数并实现
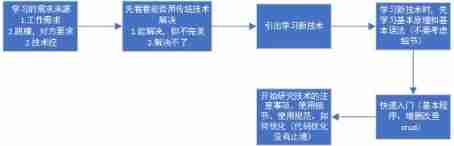
How to learn a new technology (programming language)

v-for遍历元素样式失效
接口测试要测试什么?
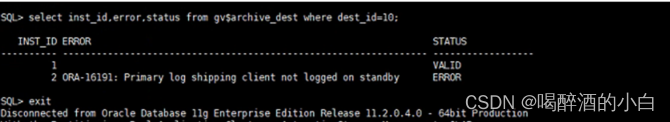
备库一直有延迟,查看mrp为wait_for_log,重启mrp后为apply_log但过一会又wait_for_log

Tapdata 的 2.0 版 ,开源的 Live Data Platform 现已发布
随机推荐
Introduction knowledge system of Web front-end engineers
[basis of recommendation system] sampling and construction of positive and negative samples
STM32F1與STM32CubeIDE編程實例-旋轉編碼器驅動
取消select的默认样式的向下箭头和设置select默认字样
Is Zhou Hongyi, 52, still young?
v-for遍历元素样式失效
Visual Studio Deployment Project - Create shortcut to deployed executable
商品的设计等整个生命周期,都可以将其纳入到产业互联网的范畴内
Is it safe to open an account on the official website of Huatai Securities?
Trust orbtk development issues 2022
Development of a horse tourism website (optimization of servlet)
The difference between get and post
《因果性Causality》教程,哥本哈根大学Jonas Peters讲授
Use filters to count URL request time
QT establish signal slots between different classes and transfer parameters
Service Mesh的基本模式
[programming problem] [scratch Level 2] draw ten squares in December 2019
[programming problem] [scratch Level 2] March 2019 draw a square spiral
第一讲:链表中环的入口结点
单机高并发模型设计
